A Tad-like apparatus is required for contact-dependent prey killing in predatory social bacteria
Figures
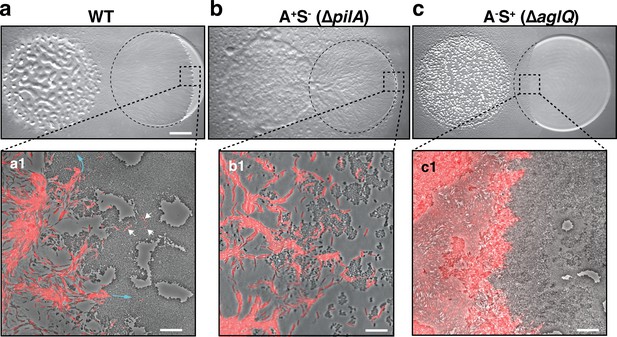
A-motility is required for invasion of prey colonies.
Colony plate assays showing invasion of an E. coli prey colony (dotted line) 48 hr after plating by WT (a, Video 1), A+S- (b) and A-S+ (c, Video 2) strains. Scale bar = 2 mm. (a1) Zoom of the invasion front. Myxococcus single cells are labeled with mCherry. Blue arrows show the movement of ‘arrowhead’ cell groups as they invade prey colonies. White arrows point to A-motile single cells that penetrated the prey colony. Scale bar = 10 µm. See associated Video 1 for the full time lapse. (b1) Zoom of the invasion front formed by A+S- cells. The A-motile Myxococcus cells can infiltrate the prey colony and kill prey cells. Scale bar = 10 µm. (c1) Zoom of the invasion front formed by A-S+ cells. Note that the S-motile Myxococcus cells come in contact with the prey colony, but in absence of A-motility, the predatory cells fail to infiltrate the colony and remain stuck at the border. Scale bar = 10 µm. See associated Video 2 for the full time lapse.
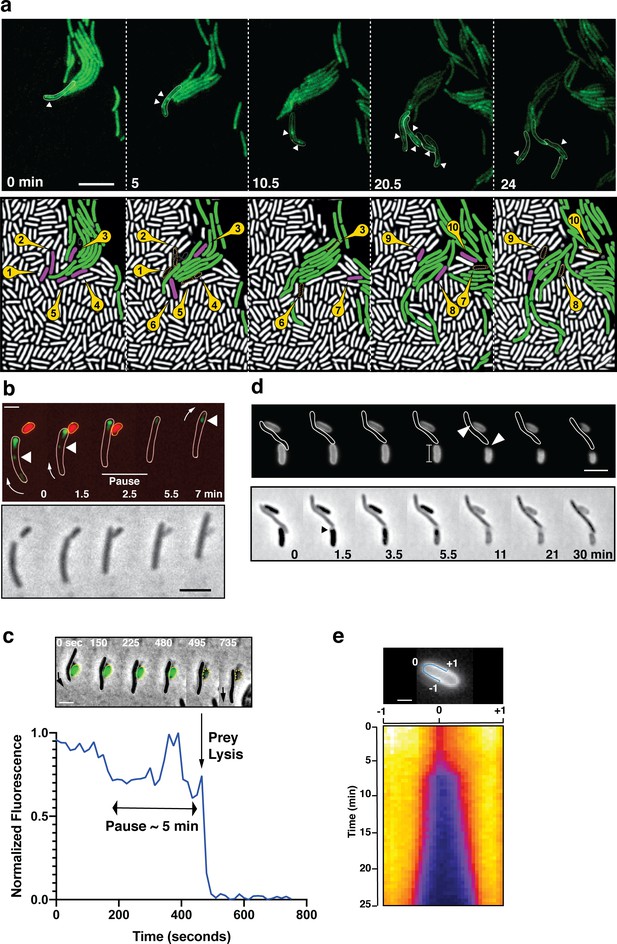
A-motile cells kill prey cells by contact.
(a) Prey (E. coli) colony invasion by an ‘arrowhead formation’. Activity of the A-motility complex is followed by monitoring Myxococcus cells expressing the bFA-localized AglZ-YFP protein. Upper panel: Cells within the arrowhead (outlined in white) assemble bFAs (white arrowheads). Lower panel: Semantic segmentation (see methods) of the total cell population, E. coli (white) and Myxococcus (green). The numbered and colored E. coli cells (magenta) are the ones that are observed to lyse as the Myxococcus cells penetrate the colony. See associated Video 3 for the full time lapse. Scale bar = 10 µm. (b) bFAs are disassembled when Myxococcus establishes lytic contacts with prey cells. Shown is an AglZ-YFP expressing Myxococcus cell establishing contact with an mCherry-expressing E. coli cell (overlay and phase contrast image). Note that the Myxococcus cell resumes movement and thus re-initiates bFA (white arrowheads) formation immediately after E. coli cell lysis. See associated Video 4 for the full time lapse. Scale bar = 2 µm. (c) Myxococcus (outlined in white) provokes E. coli plasmolysis. Top: shown is a GFP-expressing E. coli cell lysing in contact with a Myxococcus cell. GFP fluorescence remains stable for 5 min after contact and becomes undetectable instantaneously, suggesting plasmolysis of the E. coli cell. Scale bar = 2 µm. Bottom: graphic representation of fluorescence intensity loss upon prey lysis. (d,e) Myxococcus contact provokes local degradation of the E. coli peptidoglycan. (d) E. coli PG was labeled covalently with the fluorescent D-amino acid TADA. Two E. coli cells lyse upon contact. Holes in the PG-labelling are observed at the contact sites (white arrows). Note that evidence for plasmolysis and local IM membrane contraction is visible by phase contrast for the lower E. coli cell (dark arrow). Scale bar = 2 µm. (e) Kymograph of TADA-labeling corresponding to the upper E. coli cell. At time 0, which corresponds to the detection of cell lysis, a hole is detected at the contact site and propagates bi-directionally from the initial site showing that the prey cell wall is degraded in time after cell death. Scale bar = 1 µm.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
E. coil loss of fluorescence during contact-dependent lysis (Figure 2c).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig2-data1-v2.xlsx
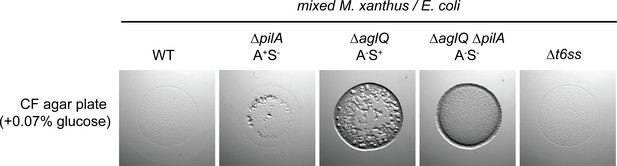
A-motility appears to be essential for predation.
WT M. xanthus and the different motility mutant strains were mixed with E. coli and spotted on CF 1.5% agar plates (+0.07% glucose). After 24 hr of incubations pictures were taken, showing that WT and ∆t6ss had similar predation efficiencies. A A+S- (∆pilA) strain presented a predation efficiency slightly reduced. However, the A-S+ strain (∆aglQ) was greatly impaired at predating. No predation was observed for the A-S- strain (∆aglQ ∆pilA). Therefore, A-motility appears to be essential for predation.
Contact-dependent killing by an A-S- motility mutant (∆aglQ ∆pilA).
Growth of E. coli cells leads to contact with non-motile Myxococcus cells and rapid lysis. Example cell reflects events observed for n=20 events. Scale bar = 2 µm.
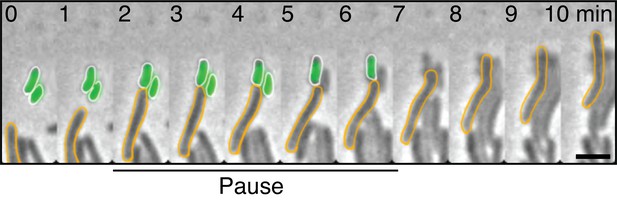
Contact-dependent killing by a ∆t6ss mutant.
E. coli prey cells are labeled with GFP to monitor contact-dependent lysis. Example cell reflects events observed for n=20 events. Scale bar = 2 µm.
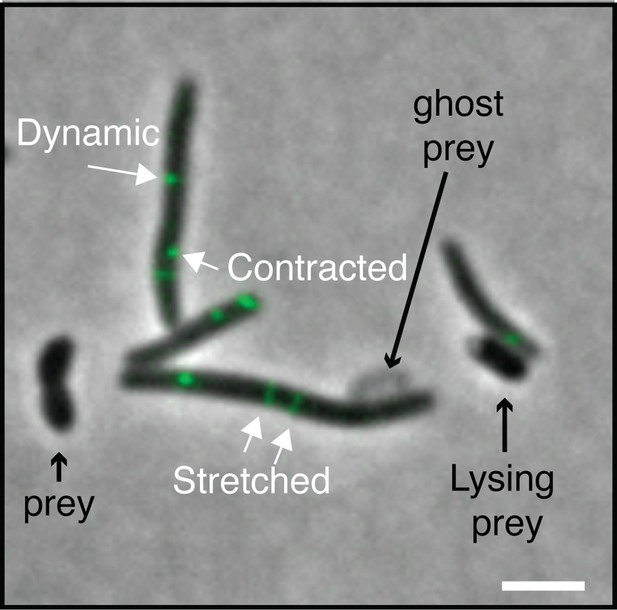
T6SS VipA sheath assembly in Myxococcus cells during predation.
Several assembly patterns are observed as described in other bacteria. Stretched: extended T6SS sheaths. Contracted: retracted T6SS sheath. Scale bars = 2 µm.
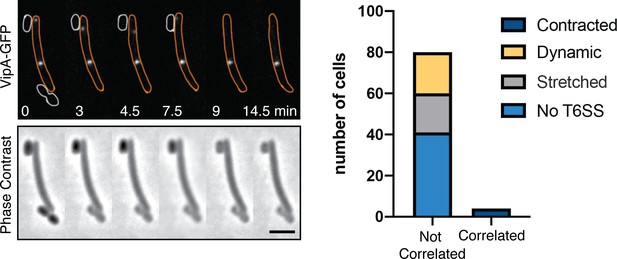
Prey contact-dependent lysis is not correlated to T6SS sheath contraction.
Contact-dependent lysis and VipA-GFP dynamics were observed simultaneously. Contraction and lysis at the contacted site were only marginally observed (correlated) suggesting that T6SS intoxication plays a minor role at best in contact-dependent killing.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 5—source data 1
Contact-dependent lysis and VipA-GFP dynamics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig2-figsupp5-data1-v2.xlsx
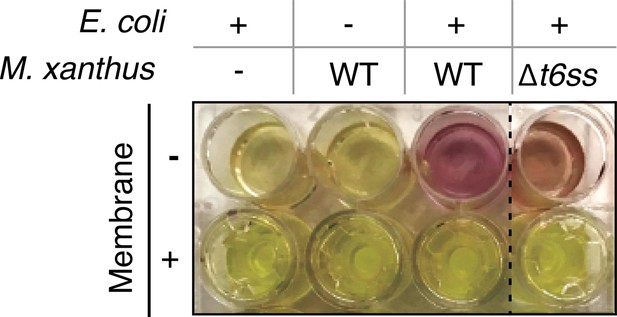
Contact-dependent lysis in liquid cultures.
E. coli lysis is detected as extracellular release of the β-galactosidase allows hydrolysis of CPRG which becomes colored after 24 hr. Lysis is not observed when Myxococcus (WT or ∆t6ss) and E. coli are separated by a membrane, showing that it is contact-dependent.
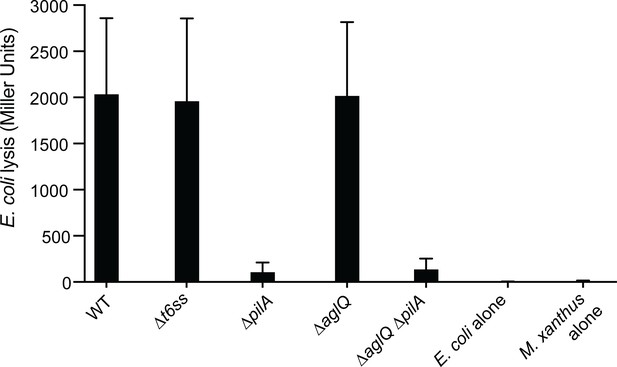
CPRG colorimetric assay performed on motility and T6SS mutant strains.
β-galactosidase activities of the cell lysates (n=4, expressed in Miller Units) were measured for each strain. After 24 hr incubation, only WT, ∆t6ss and A-S+ strains had the ability to lyse E. coli in liquid. PilA appears to be essential for cell-cell contact with E. coli and cell lysis in liquid. This experiment was independently performed four times. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 7—source data 1
CPRG assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig2-figsupp7-data1-v2.xlsx
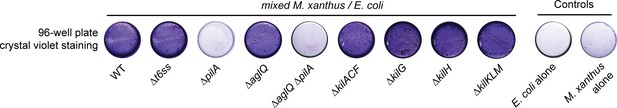
Crystal violet assay.
After 24 hr incubation, wells containing the different M. xanthus strains mixed with E. coli were stained with a crystal violet solution to revealed biofilm formation. The ∆pilA strains appeared to be deficient at forming a biofilm in the presence of a prey.
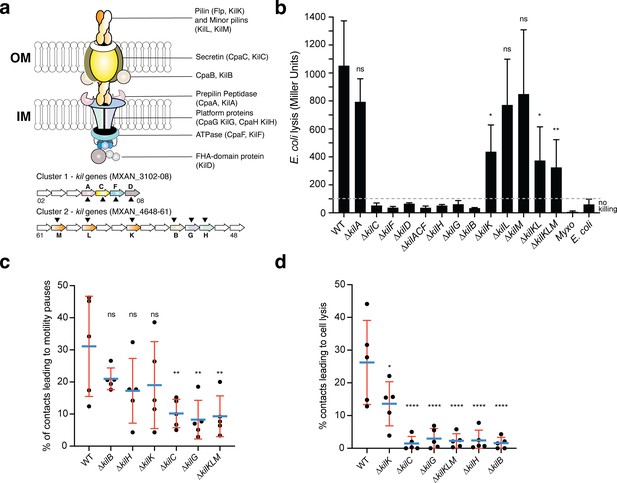
A Tad-like apparatus is required for prey recognition and contact-dependent killing.
(a) Model structure of the Kil system following bioinformatics predictions. Annotated cluster 1 and cluster 2 genes are shown together with the possible localization of their protein products. Dark triangles indicate the genes that were deleted in this study. (b) kil mutants are impaired in E. coli lysis in liquid. Kinetics of CPRG-hydrolysis by the β-Galactosidase (expressed as Miller Units) observed after co-incubation of Myxococcus wild-type (WT) or the kil mutants with E. coli for 24 hr. M. xanthus and E. coli alone were used as negative controls. This experiment was performed independently four times. (c) The percentage of contacts with E. coli leading to a pause in motility was calculated for M. xanthus wild-type (from five independent predation movies, number of contacts observed n=807) and the kil mutants (number of contacts observed for ∆kilC: n=1780; ∆kilH: n=1219; ∆kilG: n=1141; ∆kilB: n=842; ∆kilK: n=710; ∆kilKLM: n=1446) (d) The percentage of contacts with E. coli leading to cell lysis was also estimated. In panels (b), (c), and (d), error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. One-way ANOVA statistical analysis followed by Dunnett’s posttest was performed to evaluate if the differences observed, relative to wild-type, were significant (*: p≤0.05, **: p≤0.01, ****: p≤0.0001) or not (ns: p>0.05).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
CPRG assay (Figure 3b).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Counting percentage of contacts with a prey leading to motility pauses and prey cell lysis (Figure 3c and d).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig3-data2-v2.xlsx
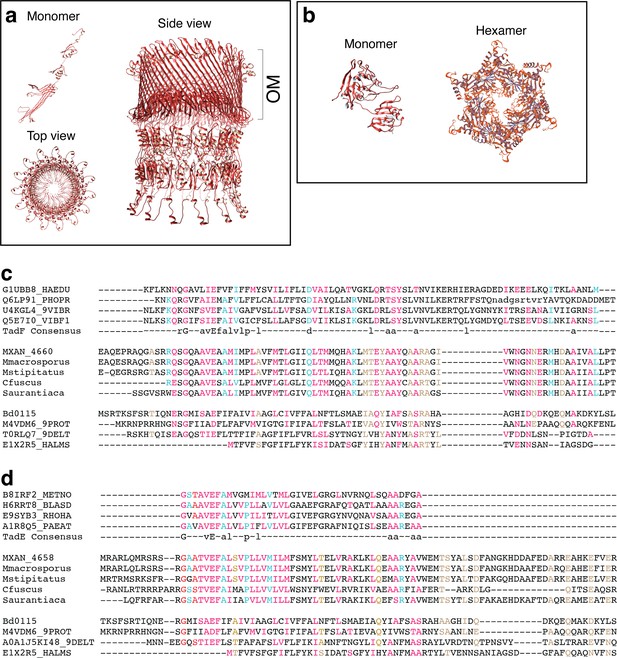
Bioinformatics analyses of Kil proteins.
(a, b) Structural models of the putative KilC secretin (a) and KilF hexameric ATPase (b). KilC Secretin: tertiary and quaternary structural models were based on the structure of E. coli type II secretion system GspD protein D (PDB identifier 5WQ7) and generated with SWISS-MODEL (Materials and methods). KilF ATPase: modeled with Phyre2 and SWISS-MODEL based on the structure of the Sulfolobus acidocaldarius FlaI ATPase (PDB identifier 4II7). (c, d) Analysis of putative pseudo-pilin proteins. For clarity, the multiple alignment is separated in three blocks representing the three different groups, the alpha-proteobacteria, the Myxococcales and the Bdellovibrionales. All sequences, except the one from C. fuscus, were taken from HHPRED matrix alignments. Residues conserved between the pfam domains TadF and the MXAN_4660 family (c), as well as between the TadE and the MXAN_4658 family (d) are highlighted in cyan; residues conserved between the Bd0115 family and the MXAN_4660 family (c), as well as the residues conserved between the Bd0115 family and the MXAN_4658 family (d) are highlighted in brown; residues conserved in all families (TadF, MXAN_4660, Bd0115, TadE, MXAN_4658) are highlighted in red. (c) HHPRED-based multiple sequence alignment of MXAN_4660 (KilM) with the TadF domain and pilus assembly protein Bd0115 from B. bacteriovorus. Myxobacterial sequences correspond to the following NCBI RefSeq IDs: Myxococcus xanthus: WP_011554652; Myxococcus stipitatus: WP_015350653; Myxococcus macrosporus: WP_043711698; Stigmatella aurantiaca: WP_013376800; Cystobacter fuscus: WP_002624349. (d) HHPRED-based multiple sequence alignment of MXAN_4658 with the TadE domain and pilus assembly protein Bd0115 from B. bacteriovorus. Myxobacterial sequences correspond to the following NCBI RefSeq IDs: M. xantus: WP_011554650; M. stipitatus: WP_015350651; M. macrosporus: WP_043711696; S. aurantiaca: WP_013376798; C. fuscus: WP_002624796.
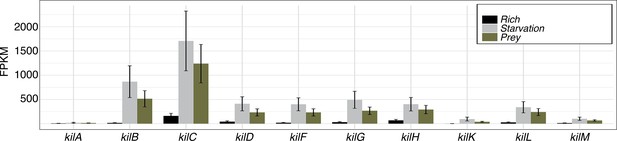
The kil genes are expressed during starvation.
RNA-seq analysis of kil gene expression in rich medium, starvation medium and starvation medium with live prey cells extracted and computed from data by Livingstone et al., 2018. For each gene and condition, the data is compiled from three independent biological replicates. Note addition of prey does not change the expression profile which is significantly induced by starvation alone.
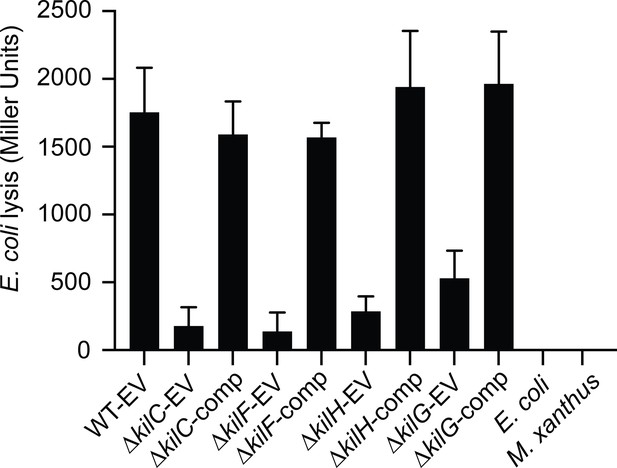
CPRG colorimetric assay.
In a 96-well plate, the different kil strains transformed with pSWU19-EV (Empty Vector) or complemented (comp) with a pSWU19 carrying the different kil genes were incubated with E. coli in liquid. After 24 hr incubation, β-galactosidase activities (expressed as Miller Units) of the different cell lysates were measured. The kil mutants ectopically expressing the different kil genes under the control of the pilA promoter presented a restored predation phenotype similar to WT-EV control. E. coli and M. xanthus alone were used as negative controls. This experiment was independently performed twice with at least two experimental replicates per strain each time. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
CPRG assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
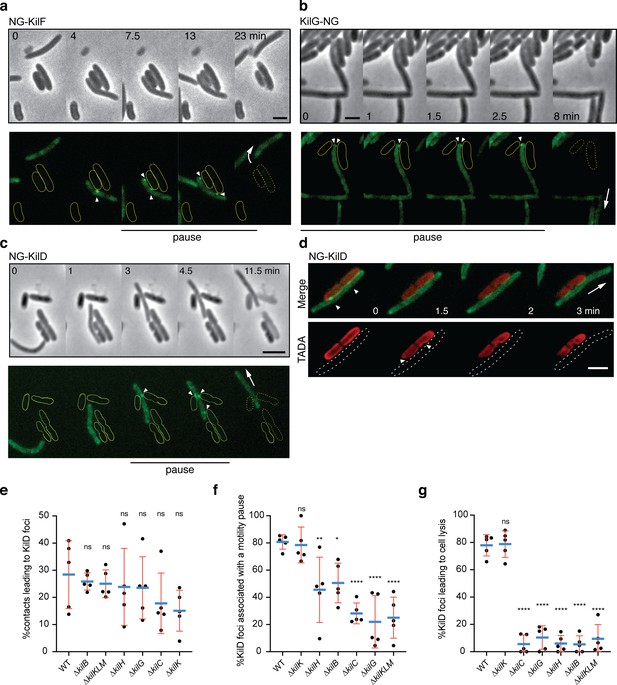
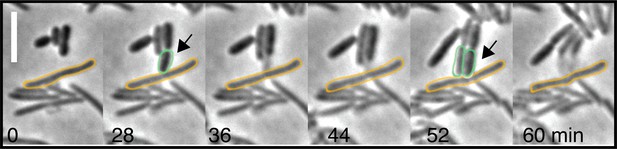
The Kil Tad-like system assembles upon contact and causes prey cell lysis.
(a) NG-KilF clusters form in contact with the prey and their formation precedes cell lysis. Scale bar = 2 µm. See associated Video 5 for the full time lapse. (b) KilG-NG forms clusters at the contact site with the prey and their formation is followed by the prey cell lysis. Scale bar = 2 µm. See associated Video 6 for the full time lapse. (c) NG-KilD clusters only form in contact with the prey and their formation precedes cell lysis. Scale bar = 2 µm. See associated Video 7 for the full time lapse. (d) PG-holes are formed at the cluster-assembly sites. Representative picture of TADA-labeled E. coli cells in the presence of NG-KilD expressing Myxococcus xanthus cells. PG holes and clusters are indicated with white arrows. Scale bar = 2 µm. (e) The percentage of contacts with E. coli leading to NG-KilD foci formation was calculated for M. xanthus wild-type (from five independent predation movies, number of contacts observed n=807) and the kil mutants (number of contacts observed for ∆kilC: n=1780; ∆kilH: n=1219; ∆kilG: n=1141; ∆kilB: n=842; ∆kilK: n=710; ∆kilKLM: n=1446). (f) The percentage of NG-KilD foci associated with a motility pause was also estimated for M. xanthus WT (from five independent predation movies, number of NG-KilD foci observed n=198) and the kil mutants (number of NG-KilD foci observed for ∆kilC: n=320; ∆kilH: n=270; ∆kilG: n=251; ∆kilB: n=215; ∆kilK: n=94; ∆kilKLM: n=355). (g) The percentage of NG-KilD foci leading to E. coli lysis was estimated as well. In panels (d), (e), and (f), error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean. One-way ANOVA statistical analysis followed by Dunnett’s posttest was performed to evaluate if the differences observed, relative to wild-type, were significant (*: p≤0.05, **: p≤0.01, ****: p≤0.0001) or not (ns: p>0.05).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Counting percentage of contacts with a prey leading to NG-KilD foci formation and counting percentage of NG-KilD foci associated with motility pause and prey cell lysis (Figure 4e, f and g).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
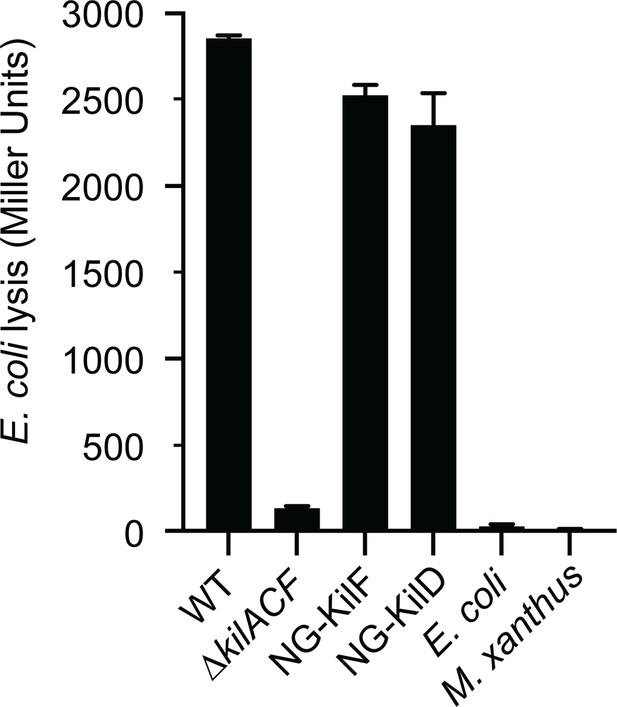
The strains expressing Neon Green (NG) fusions of KilD or KilF have predation phenotypes similar to wild-type in a CPRG colorimetric assay.
This experiment was independently performed twice. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
CPRG assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
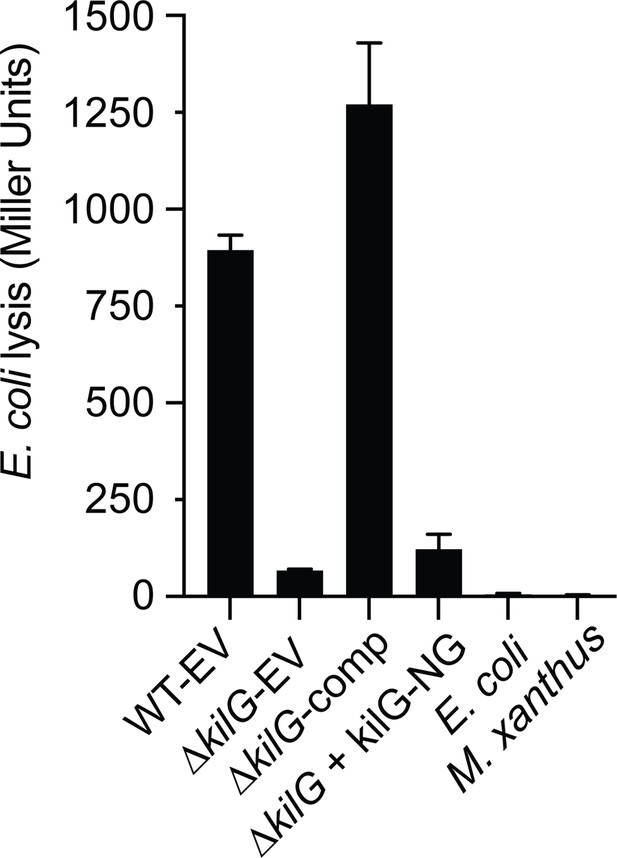
The ∆kilG strain expressing KilG-NG is defective in predation.
In a 96-well plate, ∆kilG transformed with pSWU19-EV (Empty Vector), pSWU19-PpilA-kilG (comp) or pSWU19-PpilA-kilG-NG was incubated with E. coli in liquid. After 24 hr incubation, a CPRG colorimetric assay was performed: β-galactosidase activities (expressed as Miller Units) of the different cell lysates were measured. Only ∆kilG pSWU19-PpilA-kilG complemented strain presented a restored predation phenotype similar to the WT-EV control. E. coli and M. xanthus alone were used as negative controls. This experiment was performed once with four experimental replicates per strain. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
CPRG assay.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
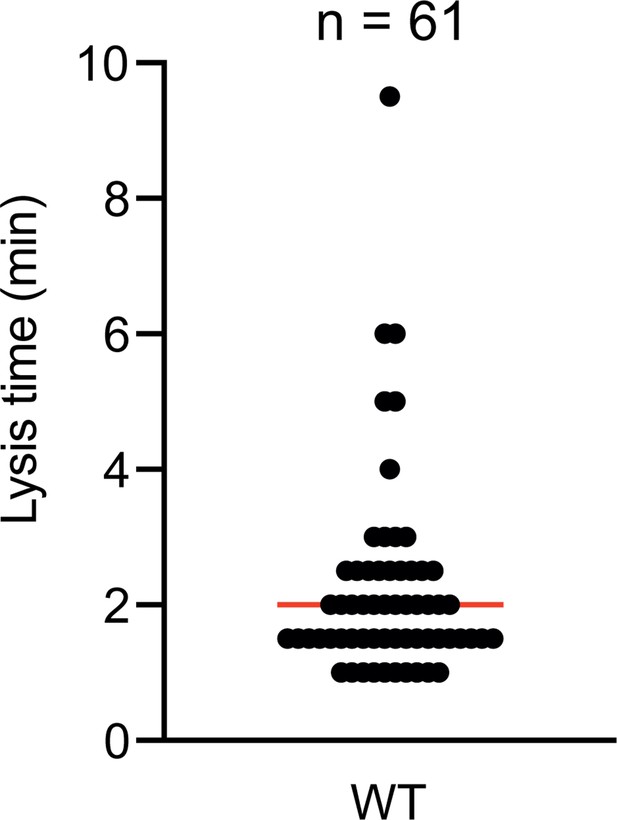
Time to lysis after cluster formation.
Time to lysis was determined by first monitoring cluster formation and then loss of contrast by the prey cell. The measurements were performed over two biological replicates (n=61). The median is shown as a red bar.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Lysis time.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig4-figsupp3-data1-v2.xlsx
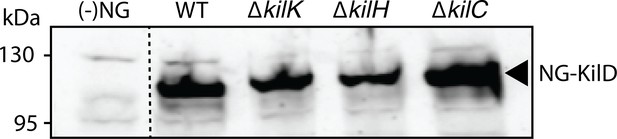
Stable expression of NG-KilD in different mutant backgrounds.
NG-KilD is detected at the expected molecular weight by the anti-neon Green antibody. (-) NG: DZ2 Myxococcus cell extracts that do not express neon Green. Dotted line indicates gel splicing.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 4—source data 1
Western Blot.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig4-figsupp4-data1-v2.zip
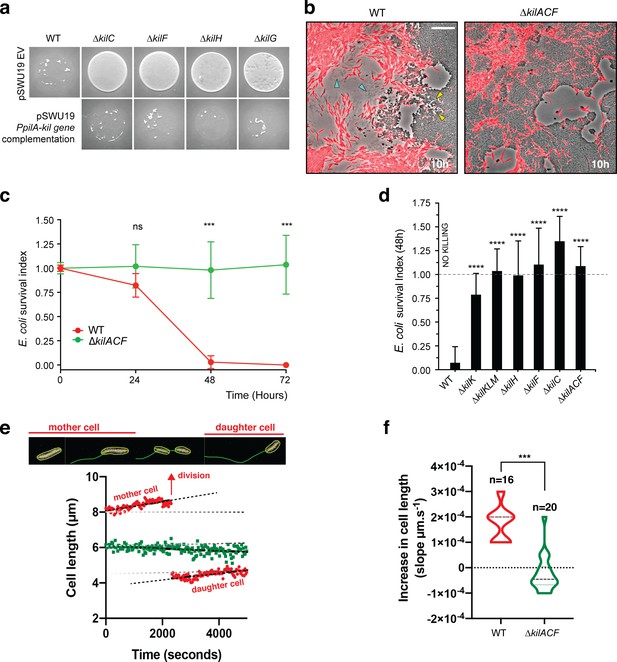
The kil genes are required for M.xanthus nutrition over prey cells.
(a) The Kil system is essential for predation. Core deletion mutants in Tad-like genes, ∆kilC (Secretin), ∆kilF (ATPase), ∆kilH (IM platform), and ∆kilG (IM platform) were mixed with E. coli and spotted on CF agar plates (+ 0.07% glucose). After 24 hr of incubation, the mutants carrying the empty vector (EV) pSWU19 were strongly deficient in predation. The same kil mutants ectopically expressing the different kil genes under the control of the pilA promoter presented a restored predation phenotype similar to the WT-EV control. (b) A kil mutant can invade but cannot lyse E. coli prey colonies. mCherry-labeled WT and triple kilACF mutant are shown for comparison. Note that invading WT cells form corridors (yellow arrowheads) in the prey colony and ghost E. coli cells as well as cell debris (blue arrowheads) are left behind the infiltrating Myxococcus cells. In contrast, while the ∆kilACF penetrates the prey colony, corridors and prey ghost cells are not observed. Scale bar = 10 µm. See corresponding Video 9 for the full time lapse. (c) The kil genes are essential for prey killing. E. coli mCherry cells were measured by flow cytometry at time 0, 24, 48, and 72 hr after the onset of predation. The E. coli survival index was calculated by dividing the percentage of ‘E. coli events’ at t=24, 48, or 72 hr by the percentage of ‘E. coli events’ at the beginning of the experiment (t=0). This experiment was independently performed three times (n=6 per strain and time point). For each sample, 500,000 events were analyzed. Each data point indicates the mean ± the standard deviation. For each time point, unpaired t-test (with Welch’s correction) statistical analysis was performed to evaluate if the differences observed, relative to wild-type, were significant (***: p≤0.001) or not (ns: p>0.05). (d) E. coli survival in presence of the different kil mutant strains at 48 hr. E. coli mCherry cells were measured by flow cytometry at time 0 and 48 hr after predation. This experiment was independently performed three times (n=9 per strain and time point). Events were counted as in (c) and each data point indicates the mean ± the standard deviation. One-way ANOVA statistical analysis followed by Dunnett’s posttest was performed to evaluate if the differences observed, relative to wild-type, were significant (****: p≤0.0001). (e, f) The kil genes are essential for Myxococcus growth on prey. (e) Cell growth during invasion. Cell length is a function of cell age during invasion and can be monitored over time in WT cells (in red). In contrast, cell length tends to decrease in a ∆kilACF mutant (in green) showing that they are not growing in presence of prey. See associated Video 10 for the full time lapse. (f) Quantification of cell growth in WT and in ∆kilACF mutant backgrounds. Each individual cell was tracked for 5 hr in two biological replicates for each strain. Violin plot of the growth distributions (shown as the cell size increase slopes) are shown. Statistics: Student t-test, ***: p<0.001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Flow cytometry (Figure 5c and d).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 2
M. xanthus growth during prey colony invasion (Figure 5e).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig5-data2-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 5—source data 3
Increase in M. xanthus cell length during predation (Figure 5f).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig5-data3-v2.xlsx
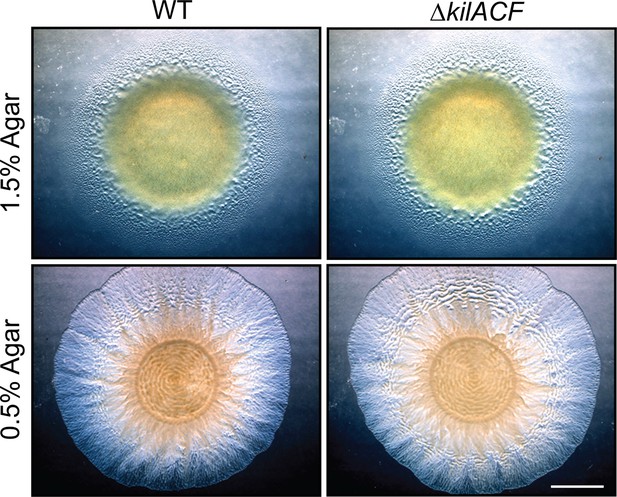
Growth and motility of WT and ∆kilACF strains on agar supporting both A- and S-motility (1.5%) and S-motility only (0.5%).
Scale bar = 2 mm.
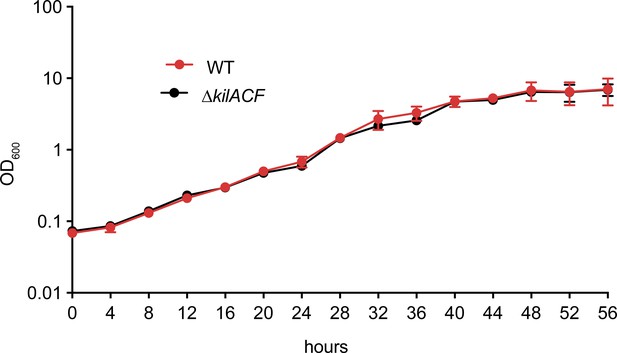
Growth curves of WT and ∆kilACF in CYE-rich medium.
The measurements were performed over three biological replicates. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Growth curves.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig5-figsupp2-data1-v2.xlsx
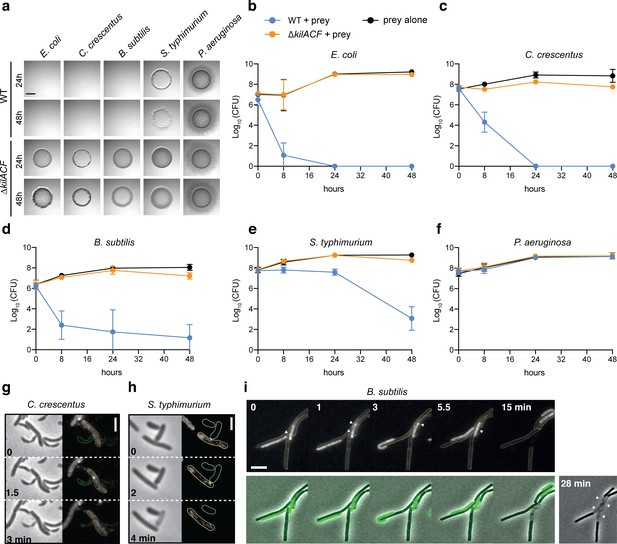
The Kil system mediates killing against diverse bacterial species.
(a) The kil genes are predation determinants against various species. To evaluate if M. xanthus kil mutant had lost the ability to lyse by direct contact different preys, prey-cell suspensions were directly mixed with M. xanthus WT or ∆kilACF and spotted on CF agar (+ 0.07% glucose). After 24 and 48 hr of incubation, pictures of the spots corresponding to the different predator/prey couples were taken. Note that Pseudomonas aeruginosa is resistant in this assay. Scale bar = 3.5 mm. (b, c, d, e, f) Prey cell survival upon predation was evaluated by CFU counting. The different preys (KanR) were mixed with M. xanthus WT (blue circles) or ∆kilACF (orange circles) strains and spotted on CF agar (+ 0.07% glucose). Spots were harvested after 0, 8, 24, and 48 hr of predation, serially diluted and platted on agar plates with kanamycin for CFU counting. The prey alone (black circles) was used as a control. Two experimental replicates were used per time point. This experiment was independently performed three times. Error bars represent the standard deviation to the mean. (g) NG-KilD cluster formation and subsequent contact-dependent killing of Caulobacter crescentus. Scale bar = 2 µm. See corresponding Video 11 for the full time lapse. (h) NG-KilD cluster formation and subsequent contact-dependent killing of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium. Scale bar = 2 µm. See corresponding Video 12 for the full time lapse. (i) NG-KilD cluster formation and subsequent contact-dependent killing of B. subtilis. See corresponding Video 13 for the full time lapse. Scale bar = 2 µm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Prey CFU counts during predation (Figure 6b,c,d,e,f).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
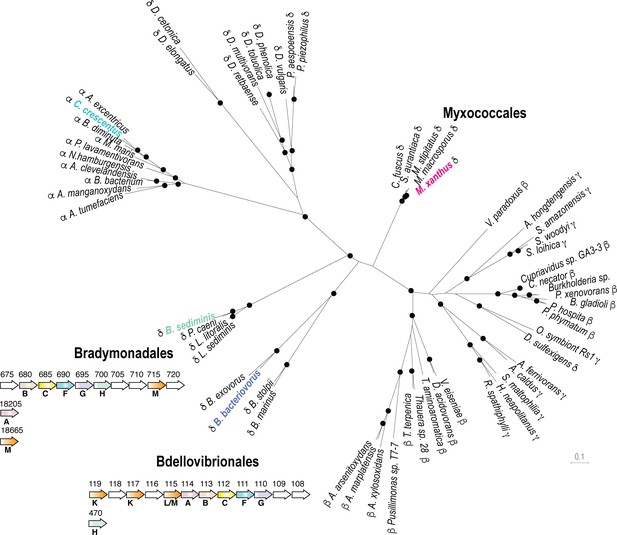
The Kil system is conserved in predatory delta-proteobacteria.
Phylogenetic tree of the Type-IV filamentous system that gave rise to the M. xanthus Kil system. Only the four well-conserved Kil system components were used for constructing the phylogenetic tree. Dots indicate stable bootstrap values (> 75), classes are indicated next to species names. The M. xanthus Kil system is also found in other Myxococcales and closely related systems are also present in Bradymonadales and Bdellovibrionales, suggesting a functional specialization related to predation. The genetic organization of kil-like genes is shown for example members of each orders, Bradymonas sediminis and Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus (see also Supplementary file 2). The nomenclature and color code for Kil homologs are the same as in Figure 3. Gene accession numbers (KEGG) are shown above gene symbols.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Supermatrix alignment.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-fig7-data1-v2.docx
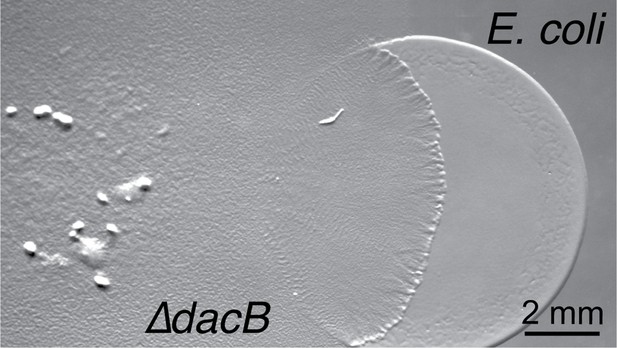
Predation phenotype of a Myxococcus D,D-decarboxylase mutant (Zhang et al., 2020a).
Colony plate assays showing invasion of an E. coli prey colony 48 hr after plating by a dacB mutant. Scale bar = 2 mm.
Videos
Invasion of an E. coli colony by WT Myxococcus cells.
This movie was taken at the interface between the two colonies during invasion. The movie is an 8x compression of an original movie that was shot for 10 hr with a frame taken every 30 s at ×40 magnification. To facilitate Myxococcus cells tracking, the wild-type strain was labeled with the mCherry fluorescent protein.
A-motility is required for prey invasion.
This movie was taken at the interface between the two colonies during invasion. The movie is an 8x compression of an original movie that was shot for 10 hr with a frame taken every 30 s at ×40 magnification. To facilitate Myxococcus cells tracking, the A-S+ (ΔaglQ) strain was labeled with the mCherry fluorescent protein.
Prey invasion by A-motile cells in ‘arrowhead’ formations.
Focal adhesions and thus active A-motility complexes were detected with an AglZ-Neon green fusion. The movie contains 51 frames taken every 30 s at ×100 magnification. Shown side-by-side are fluorescence images, fluorescence overlaid with phase contrast and MiSiC segmentation (lysing E. coli cells are colored magenta and blue).
A Myxococcus cell kills an E. coli cell by contact.
The Myxococcus cell expresses AglZ-NG and the E. coli cell expresses mCherry. Shown side-by-side are fluorescence images and MiSiC segmentation (Myxococcus: green, E. coli: magenta). The movie contains 20 frames taken every 30 s at ×100 magnification.
NG-KilF cluster formation in contact with E. coli prey cells.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with E. coli cells. The movie was shot at x100 magnification objective for 30 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
KilG-NG cluster formation in contact with E. coli prey cells.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with E. coli cells. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 9 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
NG-KilD cluster formation in contact with E. coli prey cells.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with E. coli cells. The movie was shot at x100 magnification objective for 15 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
NG-KilD clusters form in a ∆kilC mutant but no motility pauses and prey cell lysis can be observed.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact E. coli cells. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 5.5 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
A ∆kilACF still invades but does not kill E. coli prey cells.
This movie was taken at the interface between the two colonies during invasion. The movie is a 4x compression of an original movie that was shot for 4.5 hr with a frame taken every 30 s at ×40 magnification. To facilitate tracking of Myxococcus ∆kilACF, cells are labeled with the mCherry fluorescent protein.
Predatory cells division and tracking during invasion of prey colony.
To follow cell growth and division at the single cell level during prey invasion, WT cells were mixed with a WT strain expressing the mCherry at a 50:1 ratio and imaged every 30 s at ×40 magnification for up to 10 hr within non-labeled prey colonies. Cell growth was measured by fitting cell contours to medial axis model followed by tracking under Microbe-J. Real time of the track for the example cell: 95 min.
NG-KilD cluster formation in contact with Caulobacter crescentus.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with a C. crescentus cell. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 7 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
NG-KilD cluster formation in contact with Salmonella typhimurium.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with an S. enterica Typhimurium cell. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 20 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
NG-KilD cluster formation in contact with Bacillus subtilis.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cell in predatory contact with a B. subtilis cell. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 30 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is not lysed by Myxococcus and does not induce NG-KilD cluster formation.
Shown is an overlay of the fluorescence and phase contrast images of a motile Myxococcus cells mixed with Pseudomonas cells. The movie was shot at ×100 magnification objective for 30 min. Pictures were taken every 30 s.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Table 1: Characteristics of Myxococcus xanthus proteins.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Table 2: M. xanthus proteins with homologs identified in B. bacteriovorus HD100, C. crescentus CB15 and B. sediminis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Table 3: Strains.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Table 4: Plasmids.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-supp4-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 5
Table 5: Primers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-supp5-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72409/elife-72409-transrepform-v2.docx





