Repair of noise-induced damage to stereocilia F-actin cores is facilitated by XIRP2 and its novel mechanosensor domain
Figures
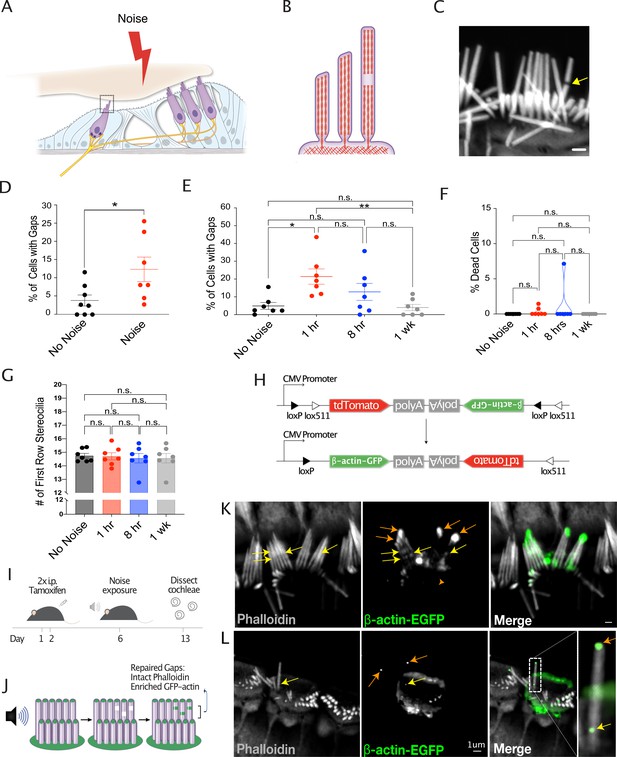
Noise-induced lesions in the F-actin cores of stereocilia is repaired by actin remodeling.
(A) Cartoon showing cross section of the organ of Corti. (B) Cartoon depicting side view of an inner hair cell (IHC), with a gap in stereocilia F-actin. (C) Representative image of an IHC with a gap in stereocilia F-actin, indicated by arrow. Scale bar: 1 μm. (D) Increased percentage of cells with phalloidin-negative gaps in IHC stereocilia F-actin following 1 hr noise exposure (*, p=0.0306). No Noise: n=8 organs of Corti, 4 mice; Noise: n=7 organs of Corti, 4 mice. (E) Percentage of cells with gaps initially increases 1 hr following 2 hr noise exposure (p=0.004) but then decreases (p=0.003) to levels not significantly different than in unexposed mice (p=0.74). n=7 organs of Corti, 4 mice per group. (F) Percentage of dead IHCs per cochlea does not significantly change within 1 week of noise exposure. No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p=0.974, No Noise vs 8hr - n.s., p=0.521, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p>0.999. n=7 organs of Corti, 4 mice per group. (G) Number of tallest row stereocilia per hair cell does not significantly change at any measured point within 1 week of noise exposure. No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p>0.999, No Noise vs 8 hr - n.s., p=0.969, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.969. (H) Diagram of Cre-mediated inversion in FLEx-β-actin-EGFP mice following tamoxifen injection. Expression of tdTomato is turned off and EGFP-β-actin expression is turned on. (I) Experimental schematic for the observation of the localization of newly synthesized EGFP-tagged β-actin. Mice are injected on days 1 and 2 with tamoxifen and exposed to noise on day 6. Cochleae were dissected and processed on day 13. (J) Cartoon demonstrating the expected localization of EGFP-tagged β-actin in repaired gaps. (K, L) Representative examples from >8 experiments of likely repaired gaps. Yellow arrows point to sites of enriched EGFP-tagged β-actin along stereocilia length with intact phalloidin staining in a Cre-recombined cell following 1 week of recovery from noise exposure. Orange arrows indicate EGFP-labeled stereocilia tips. Due to low recombination rates, the surrounding cells do not express EGFP-β-actin. All error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Quantification of stereocilia gap frequency, hair cell death, and number of stereocilia in control and noise-exposed mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig1-data1-v2.xlsx
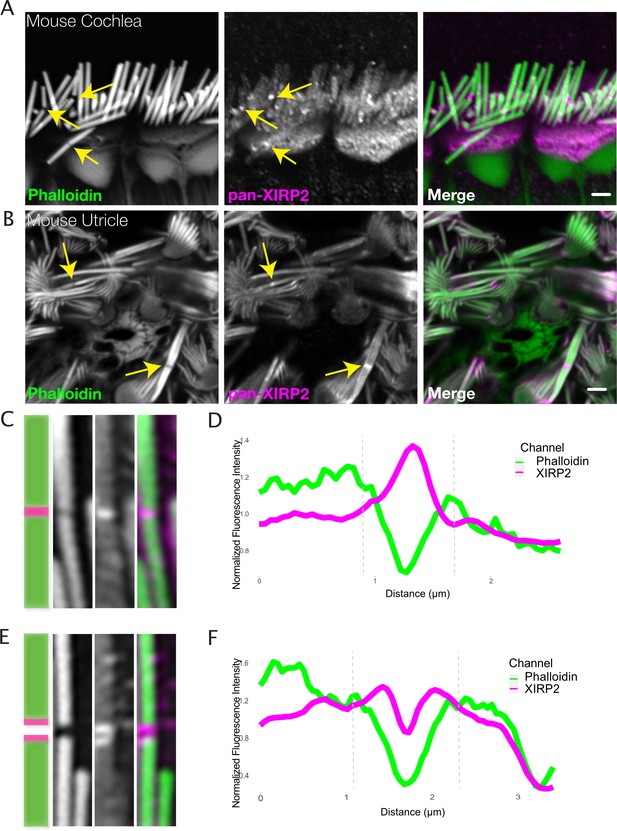
Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is enriched at gaps in stereocilia F-actin cores.
(A) XIRP2 immunostaining is enriched at noise-induced gaps in phalloidin staining in inner hair cells (IHCs) (yellow arrows). (B) XIRP2 immunostaining is enriched at naturally occurring phalloidin-negative gaps in utricle hair cells (yellow arrows). (C) Cartoon and representative image (1×5 μm) of XIRP2 enrichment throughout length of gap in phalloidin signal. (D) Line scan of fluorescence intensity in phalloidin (green) and XIRP2 (magenta) channels along the length of a gap in which XIRP2 is enriched throughout the gap. (E) Cartoon and representative image (1×5 μm) of XIRP2 enrichment at the edges of a gap. (F) Line scan of fluorescence intensity in phalloidin (green) and XIRP2 (magenta) channels in which XIRP2 is only enriched at the edges of the gap. Images are representative of >10 experiments.
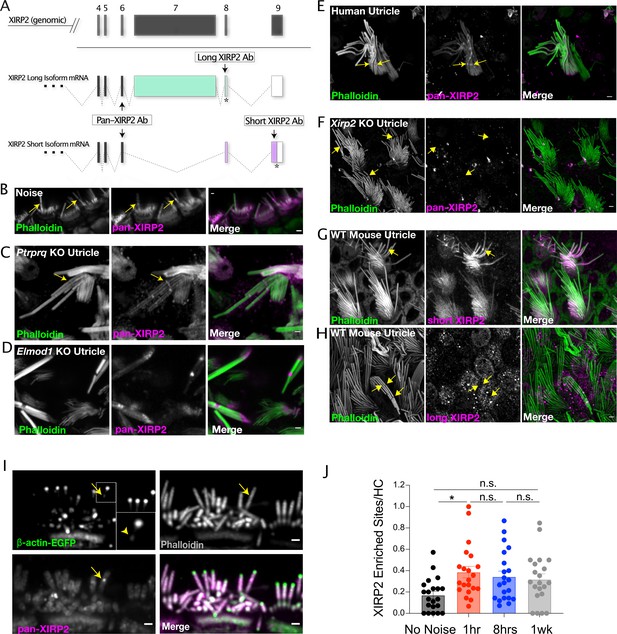
The short isoform of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is enriched at gaps and remains there after repair.
(A) Diagram of Xirp2 gene structure and isoforms indicating the positions encoding the epitopes recognized by antibodies used in the figure. (B) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps (yellow arrows) in inner hair cells (IHCs) induced by overexposure to noise (120 dB broadband [1–22 kHz] for 2 hr). (C) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps in a utricle hair cell in a P25 Ptrpq knockout mouse. (D) XIRP2 enrichment in gaps (yellow arrows) in IHCs in a P20 Elmod1 knockout mouse. (E) XIRP2 enrichment at gaps (yellow arrows) in a human utricle hair cell. (F) XIRP2 staining is absent in Xirp2 knockout utricle hair cells. (G) Short XIRP2 is enriched at gaps (yellow arrows). (H) Long XIRP2 is excluded from the hair bundle and not present in gaps (yellow arrows). (I) XIRP2 enrichment is colocalized with sites of enriched synthesized β-actin synthesized after noise exposure that likely represent repaired gaps (yellow arrow). (J) The number of XIRP2 enriched sites in stereocilia increases following noise exposure (No Noise vs 1 hr, *, p=0.039, 1 hr vs 8 hr - n.s., p=0.956, 8 hr vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.979, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.227). n=7 organs of Corti; 4 mice per group. All scale bars are 1 μm. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Images are representative of >3 experiments.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Quantification of number of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2)-enriched sites in stereocilia in control and noise-exposed mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
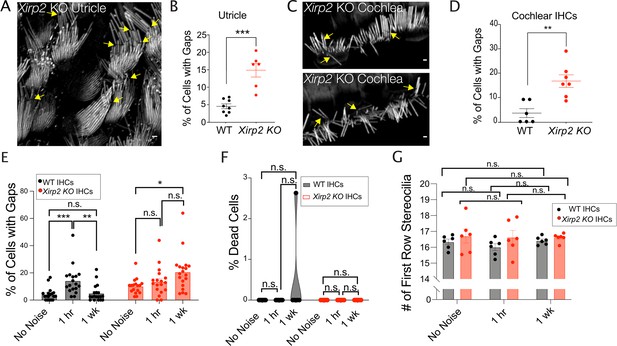
Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is required for the repair of gaps.
(A) Gaps (yellow arrows) in stereocilia F-actin in utricle hair cells from P6 Xirp2 knockout mice. (B) There is a significantly larger percentage of utricle hair cells with gaps in P20 Xirp2 knockout mice than in age-matched wild-type (WT) mice (***, p=0.001). WT: n=8 utricles, 4 mice; Xirp2 knockout: n=6 utricles, 3 mice. (C) Gaps (yellow arrows) in stereocilia F-actin in cochlear inner hair cells (IHCs) from P20 Xirp2 knockout mice. (D) There is a significantly larger percentage of IHCs with gaps in P20 Xirp2 knockout mice than in age-matched WT mice (**, p=0.002). WT: n=6 organs of Corti; Xirp2 knockout: n=7 utricles, 4 mice. (E) Percentage of cells with gaps decreases to before noise levels within 1 week after initial increase in WT mice, but in Xirp2 knockout mice, the percentage of cells with gaps further increases during this time period. WT: No Noise vs 1 hr - ***, p<0.001, 1 hr vs 1 week - **, p=0.0013, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.9502; Xirp2 knockout (KO): No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p=0.6166, 1 hr vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.1226, No Noise vs 1 week - *, p=0.014. n=18 organs of Corti, 9 mice per group. (F) Percentage of dead IHCs per cochlea does not significantly change within 1 week of noise exposure in WT or Xirp2 knockout mice. WT: No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p>0.9999, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.3765; Xirp2 KO: No Noise vs 1 hr - all values 0, No Noise vs 1 week - all values 0. n=6 organs of Corti, 3 mice per group. (G) Number of tallest row stereocilia per hair cell does not significantly change within 1 week of noise exposure in WT or Xirp2 knockout mice. WT: No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p=0.3846, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.9469; Xirp2 KO: No Noise vs 1 hr - n.s., p=0.9870, No Noise vs 1 week - n.s., p=0.9769. n=6 organs of Corti, 3 mice per group. All scale bars are 1 μm. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Images are representative of >3 experiments.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Quantification of stereocilia gap frequency, hair cell death, and number of stereocilia in wild-type (WT) and Xirp2 knockout (KO) hair cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
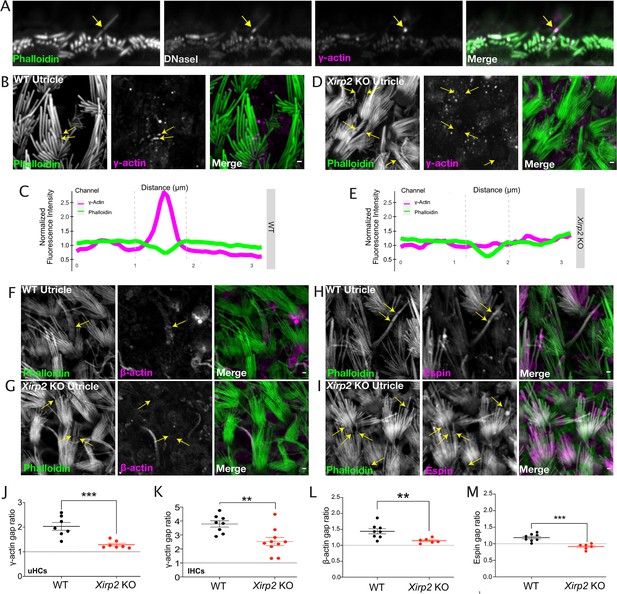
Monomeric γ-actin is no longer recruited to gaps in the absence of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2).
(A) Representative image of co-labeling of γ-actin and DNAseI enrichment in a noise-induced gap in inner hair cell (IHC) stereocilia F-actin cores. Yellow arrow indicates the site of the gap. (B) γ-Actin immunostaining is enriched in gaps (yellow arrows) in utricle hair cells. (C) Line scan of fluorescence intensity in phalloidin (green) and γ-actin (magenta) channels along the length of a gap in a wild-type (WT) mouse where γ-actin immunostaining is enriched. (D) γ-Actin gap enrichment is decreased in Xirp2 knockout mice (yellow arrows). (E) Line scan of fluorescence intensity in phalloidin (green) and γ-actin (magenta) channels along the length of a gap in a Xirp2 knockout mouse where γ-actin immunostaining is enriched. (F) Representative image of β-actin enrichment at a gap in a WT utricle hair cell. Yellow arrow indicates a gap. (G) β-Actin gap enrichment is decreased in gaps in Xirp2 knockout utricles. Yellow arrow indicates representative gap. (H) Representative image of espin enrichment at a gap in a WT utricle hair cell. Yellow arrows indicate gaps. (I) Espin gap enrichment in utricle hair cells is reduced in Xirp2 knockout mice. Yellow arrows indicate gaps. (J) The enrichment of γ-actin at gaps, defined as the ratio of the fluorescence intensity at the center of the phalloidin-negative gap to the intensity at the edge of the gap, is decreased in Xirp2 knockout mice (***, p<0.001). (K) The enrichment of γ-actin at noise-induced IHC gaps is decreased in Xirp2 knockout mice (***, p<0.001). (L) The enrichment of β-actin at gaps is decreased in Xirp2 knockout mice (**, p=0.0098). (M) The enrichment of espin at gaps is decreased in Xirp2 knockout mice (***, p<0.001). All scale bars are 1 μm. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Images are representative of >3 experiments.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Quantification of immunofluorescence of γ-actin, β-actin, and espin at stereocilia gaps.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
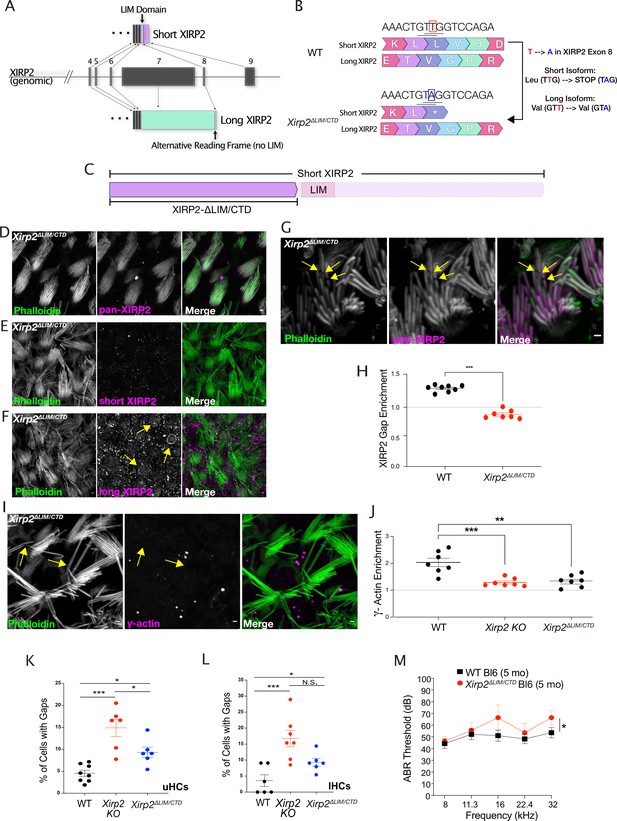
The C-terminal domain of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is required for its recruitment to gaps, and its deletion in the Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice causes an accumulation of gaps and mild hearing loss.
(A) Diagram of Xirp2 gene structure and isoforms indicating the position of the LIM domain and the region of alternative reading frame targeted in the generation of the Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice. (B) Diagram indicating the position of the 1 bp substitution in exon 8 of Xirp2 to generate the Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice. The T→A mutation introduced a stop codon in the short isoform but did not alter the amino acid sequence of the long isoform. (C) The LIM domain of short XIRP2 and the rest of the C-terminus is removed from short XIRP2 in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice. (D) XIRP2-ΔLIM/C-terminal domain (CTD) (recognized by an antibody against the N-terminus) is still expressed and localizes to the hair bundle. (E) Immunostaining with an antibody targeting the CTD of XIRP2 is absent in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice, indicating the successful truncation of short XIRP2. (F) The bundle signal in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice is not due to compensatory localization of long XIRP2. (G) Unlike full-length XIRP2, XIRP2-ΔLIM/CTD immunostaining is not enriched at gaps (yellow arrows). (H) Line scan of fluorescence intensity in phalloidin (green) and XIRP2 (magenta) channels along the length of a gap in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice in which XIRP2 is not enriched. (H) The enrichment of XIRP2 immunostaining at gaps is decreased from 1.27-fold in wild-type (WT) mice to 0.85-fold in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice (***, p<0.0.001). n=8 utricles, 4 mice per group. (I) γ-Actin immunostaining enrichment is decreased in gaps (yellow arrows) in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice. (J) γ-Actin gap enrichment is decreased from ~2-fold in WT to 1.3-fold in Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice (***, p<0.001). n=7 utricles, 4 mice per group. Values for Xirp2 knockout mice is same as in Figure 5J. (K) There is a significantly larger percentage of utricle hair cells with gaps in P20 Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice than in age-matched WT mice type (*, p=0.0255). WT: n=8 utricles, 4 mice; Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice: n=6 utricles, 3 mice. (L) There is a significantly larger percentage of inner hair cells (IHCs) with gaps in P20 Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice than in age-matched WT mice (**, p=0.007). WT: n=6 organs of Corti, 3 mice; Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice: n=7 organs of Corti, 4 mice. (M) Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD C57Bl/6J mice have elevated hearing thresholds compared to WT mice at 5 months of age, as measured by auditory brainstem response (ABR) (*, p=0.031). n=14 WT mice, 8 Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD C57Bl/6J mice. All scale bars are 1 μm. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM). Images are representative of >3 experiments.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Quantification of immunofluorescence of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2), γ-actin at stereocilia gaps, and hair cell numbers and gap frequency in wild-type (WT), Xirp2 knockout (KO), and Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
-
Figure 6—source data 2
Auditory brainstem response (ABR) data of wild-type (WT) and Xirp2ΔLIM/CTD mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig6-data2-v2.xlsx
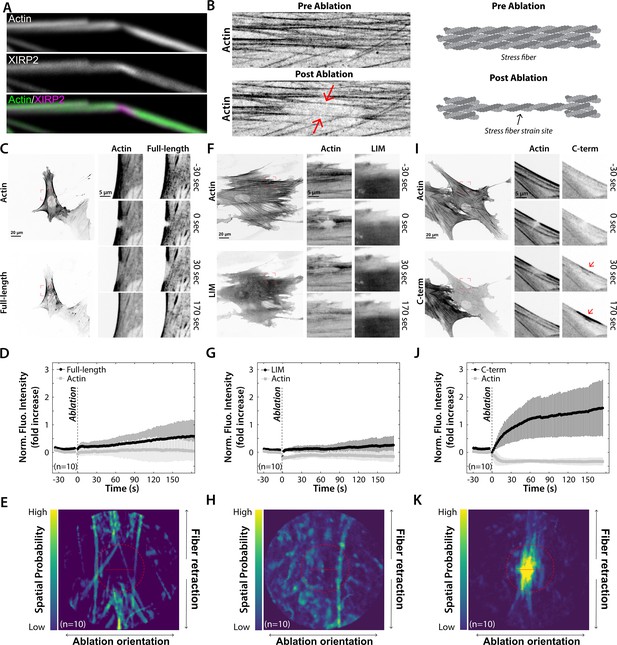
The C-terminal domain (CTD) of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) recognizes stress fiber strain sites.
(A) Representative image of a bent stereocilium, characterized by local F-actin depolymerization (reduced phalloidin signal) and enrichment of XIRP2. (B) Representative images and cartoon of actin before and after an induced stress fiber strain site. The red arrows indicate thinning actin stress fibers. (C, F, I) Human foreskin fibroblasts (HFFs) co-expressing mApple-actin and EGFP-coupled versions of either full length (C), the LIM domain (F) or CTD (I) of XIRP2. The magnified inset images (red boxed regions) show the localization of the actin and XIRP2 constructs during formation of a laser-induced strain site (the ablation timepoint is indicated by ‘0 s’). The red arrows indicate relocation of the CTD of XIRP2 to stress fiber strain sites (I, Video 3) which is not observed for the full-length (C, Video 1) or LIM (F, Video 2) constructs. (D, G, J) Average fluorescence intensity traces and standard deviations of the actin and XIRP2 signals in the region of strain. Following stress fiber strain induction, a large and rapid increase of the fluorescence intensity of the CTD XIRP2 construct is observed (J) which is not the case for the full-length (D) and LIM domain (G) constructs. The slight increase in intensity of full-length XIRP2 during the last minute of the experiment (D) is due to the recognition of unstrained actin following stress fiber repair. (E, H, K) Spatial probability of XIRP2 recruitment to stress fiber strain sites. The brightest signal of the CTD of XIRP2 is located inside the region of strain (red dashed circle). The brightest LIM domain signal is distributed randomly (H) whereas full-length XIRP2 is primarily recruited outside the region of strain indicating it recognizes unstrained actin filaments (E). The red line represents the 5 μm ablation line.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Normalized fluorescence intensity fold changes, of FL (full-length), LIM_only, and C-terminal domain (CTD) (C-term domain) of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) tagged with EGFP, after laser ablation.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig7-data1-v2.xlsx
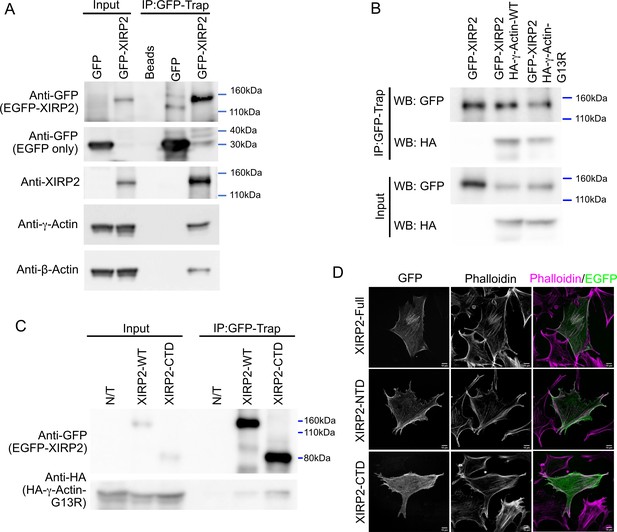
Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) interacts with monomeric and filamentous actin through distinct domains.
(A) Endogenous β- and γ-actin co-immunoprecipitate with heterologously expressed short XIRP2. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with the EGFP or EGFP-XIRP2 construct as indicated on the top of each lane. Total cell extract was loaded in input lanes. Immunoprecipitates (IP) were pulled down with GFP-Trap agarose beads followed by western blotting for the indicated antibodies (left). GFP-Trap beads (Beads) were incubated with non-transfected cell extracts as a negative control. (B) XIRP2 interacts with monomeric γ-actin. EGFP-XIRP2 WT plasmid was co-transfected with HA-γ-actin wild-type (WT) or the polymerization-incompetent HA-γ-actin G13R mutant. GFP-Trap beads were used for pulldown. Cells transfected with only EGFP-XIRP2 were used as negative control. EGFP-XIRP2 pulls down both the WT and the G13R mutant γ-actin. (C) The C-terminal domain (CTD) of XIRP2 is sufficient to pull down monomeric γ-actin. EGFP-XIRP2 WT or the CTD-encoding construct was co-transfected with HA-γ-actin-G13R plasmid. GFP-Trap beads were used for pulldown, and cells transfected with only HA-γ-actin-G13R (N/T) were used as negative control. Both the full-length and the CTD pulldown HA-γ-actin-G13R. (D) Full-length XIRP2 and the N-terminal domain (NTD) colocalize with F-actin, while the CTD is predominantly cytosolic and colocalizes only with a select subset of stress fibers. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with plasmid constructs encoding EGFP-XIRP2 WT, NTD (including the LIM domain) or the CTD, fixed and counterstained with phalloidin.
-
Figure 8—source data 1
Western blots showing co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of EGFP-Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) with β- and γ-actin, Co-IP of EGFP-XIRP2 with wild-type (WT) and polymerization-incompetent γ-actin, and Co-IP of EGFP-tagged full-length and C-terminal domain (CTD) of XIRP2 with polymerization-incompetent γ-actin.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig8-data1-v2.zip
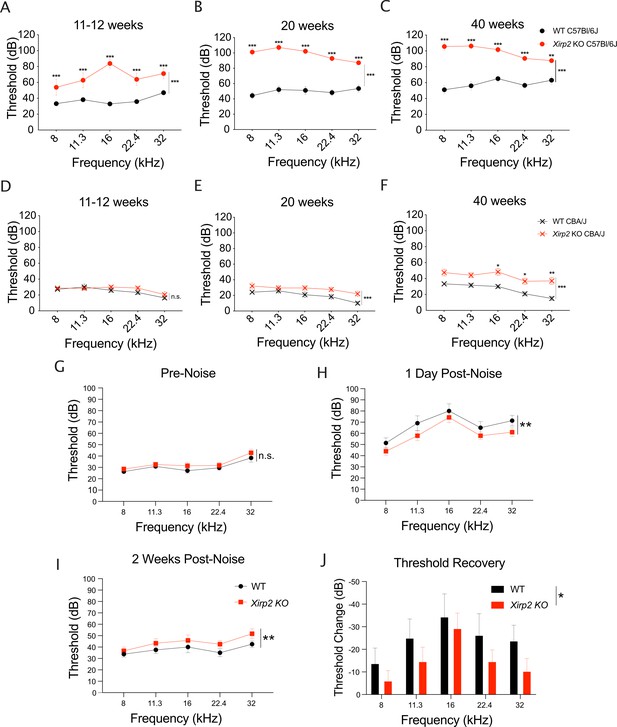
Xirp2 knockout mice are more susceptible to age-related and noise-induced hearing loss.
(A) Auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds are significantly elevated in Xirp2 knockout (KO) mice on the C57Bl/6J background at 11–12 weeks of age (***, p<0.001). n=17 wild-type (WT), 9 Xirp2 KO. (B) ABR thresholds are further elevated in C57Bl/6J XIrp2 KO mice at 18 weeks (***, p<0.001). n=14 WT, 9 Xirp2 KO. (C) ABR thresholds are progressively increased in C57Bl/6J Xirp2 KO mice at 40 weeks (***, p<0.001). n=10 WT, 9 Xirp2 KO. (D) ABR thresholds are not significantly elevated in Xirp2 KO mice on the CBA/J background at 11–12 weeks of age (n.s, p=0.090). n=11 WT, 12 Xirp2 KO. (E) By 18 weeks, ABR thresholds are significantly elevated in CBA/J Xirp2 KO mice (***, p=<0.001). n=6 WT, 12 Xirp2 KO. (F) ABR thresholds are further increased in CBA/J Xirp2 KO mice by 40 weeks of age (***, p=<0.001). n=6 WT, 12 Xirp2 KO. (G) Prior to noise exposure, Xirp2 knockout mice backcrossed to the CBA/J background do not have significantly different ABR hearing thresholds than WT CBA/J mice (n.s., p=0.058). n=12 WT mice, 14 Xirp2 KO mice. (H) Following a noise-induced temporary hearing threshold shift (1 day following noise exposure (105 dB octave band, 1 hr)), WT CBA/J mice have elevated ABR hearing thresholds compared to XIRP2 KO CBA/J mice (**, p=0.007). n=12 WT mice, 14 Xirp2 KO mice. (I) Following 2 weeks recovery, Xirp2 KO CBA/J mice have elevated ABR hearing thresholds compared to WT CBA/J mice (**, p=0.009). n=8 WT mice, 14 Xirp2 KO mice. (J) Xirp2 KO CBA/J mice have decreased ABR hearing threshold recovery during the 2 weeks following exposure to noise. (**, p=0.005). n=8 WT mice, 14 Xirp2 KO mice. All error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).
-
Figure 9—source data 1
Auditory brainstem response thresholds of aged and noise-exposed Xirp2 knockout (KO) mice on C57Bl/6J or CBA/J background.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/72681/elife-72681-fig9-data1-v2.xlsx
Videos
EGFP-tagged full-length Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is not recruited to stress fiber strain sites.
A focused laser beam was used to induce strain sites in stress fibers of fibroblasts transfected with mApple-actin and EGFP-tagged full-length XIRP2. Cells were imaged for 3 min and 30 s, alternating between the actin and XIRP2 channel, with images taken approximately every 2 s. After 30 s of imaging the steady state, 5 μm region was illuminated with the 405 laser to induce a strain site via photoablation. The remainder of the time lapse was then imaged. EGFP-tagged full-length XIRP2 showed no recruitment to ablation sites.
EGFP-tagged LIM domain of Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2) is not recruited to stress fiber strain sites.
A focused laser beam was used to induce strain sites in stress fibers of fibroblasts transfected with mApple-actin and EGFP-tagged XIRP2-LIM domain. Cells were imaged for 3 min and 30 s, alternating between the actin and XIRP2-LIM channel, with images taken approximately every 2 s. After 30 s of imaging the steady state, 5 μm region was illuminated with the 405 laser to induce a strain site via photoablation. The remainder of the time lapse was then imaged. EGFP-tagged XIRP2-LIM showed no recruitment to ablation sites.
EGFP-tagged Xin actin binding repeat containing 2 (XIRP2)-C-terminal domain (CTD) shows rapid recruitment to stress fiber strain sites.
A focused laser beam was used to induce strain sites in stress fibers of fibroblasts transfected with mApple-actin and EGFP-tagged XIRP2-CTD. Cells were imaged for 3 min and 30 s, alternating between the actin and the XIRP2-CTD channel, with images taken approximately every 2 s. After 30 s of imaging the steady state, 5 μm region was illuminated with the 405 laser to induce a strain site via photoablation. The remainder of the time lapse was then imaged. EGFP-tagged XIRP2-CTD displayed strong recruitment to the ablation site.





