Satellite glia modulate sympathetic neuron survival, activity, and autonomic function
Figures
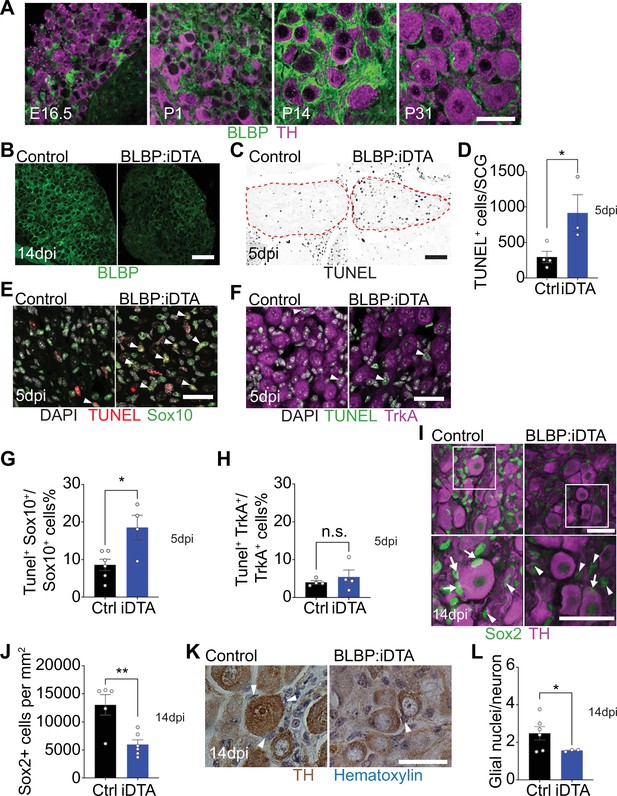
DTA-mediated ablation of satellite glia in sympathetic ganglia.
(A) Satellite glial cells, immunolabeled with brain lipid binding protein (BLBP, green), progressively ensheathe sympathetic neuron cell bodies, labeled with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH, magenta) in the superior cervical ganglia (SCG) during development. Time points shown are embryonic day 16.5 (E16.5) and postnatal days P1, P14, and P31. Scale bar: 30 μm. (B) Reduced BLBP expression in BLBP:iDTA SCG relative to control ganglia at 14 days after the last tamoxifen injection (14 dpi). Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Increased apoptosis in BLBP:iDTA SCG (outlined in red dashed line) compared to controls as detected by TUNEL labeling at 5 days post-tamoxifen injection (5 dpi). Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Quantification of apoptotic cells in SCGs at 5 dpi from n = 4 control and 3 mutant mice. Data are means ± SEM. *p<0.05, t-test. (E) Increased apoptosis of satellite glial cells assessed by Sox10 immunostaining (green) and TUNEL labeling (red) in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic ganglia compared to control at 5 dpi. DAPI channel is shown in gray. Arrowheads indicate TUNEL+;Sox10+ cells. Scale bar: 30 µm. (F) Neuronal apoptosis is similar between BLBP:iDTA and control ganglia at 5 dpi as assessed by TrkA immunostaining (magenta) and TUNEL labeling (green). DAPI channel is shown in gray. Arrowheads indicate TUNEL+;TrkA+ neurons. Scale bar: 30 µm. (G) Quantification of TUNEL+;Sox10+ cells expressed as a % of Sox10+ cells. Data are presented as means ± SEM from n = 6 control and 4 mutant mice, **p<0.05, t-test. (H) Quantification of TUNEL+;TrkA+ cells expressed as a % of TrkA+ cells. Data are presented as means ± SEM from n = 4 mice per genotype, n.s, not significant, t-test. (I) Decreased association of Sox2-labeled satellite glia (green) with TH-positive sympathetic neurons (magenta) in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic ganglia compared to controls at 14 dpi. Arrows indicate Sox2-labeled nuclei of satellite glia associated with TH-positive sympathetic neuron cell bodies, while arrowheads indicate Sox2-labeled nuclei not abutting neuronal soma. Gain in both images has been set to the same level for a better visualization of Sox2-labeled nuclei in mutant ganglia. Scale bar: 30 μm. (J) Quantification of Sox2-positive cells in control and BLBP:iDTA SCGs at 14 dpi. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals, **p<0.01, t-test. (K) TH DAB immunohistochemistry and hematoxylin staining shows fewer satellite glia nuclei (blue) associated with TH-labeled sympathetic neuron cell bodies (brown) in BLBP:iDTA ganglia at 14 dpi. Scale bar: 30 µm. (L) Quantification of glial nuclei associated with neuronal soma. Data are presented as means ± SEM from n = 6 control and 3 mutant animals, **p<0.05, t-test.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Raw data for neuronal and glia apoptosis and glia cell counts.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig1-data1-v3.xlsx
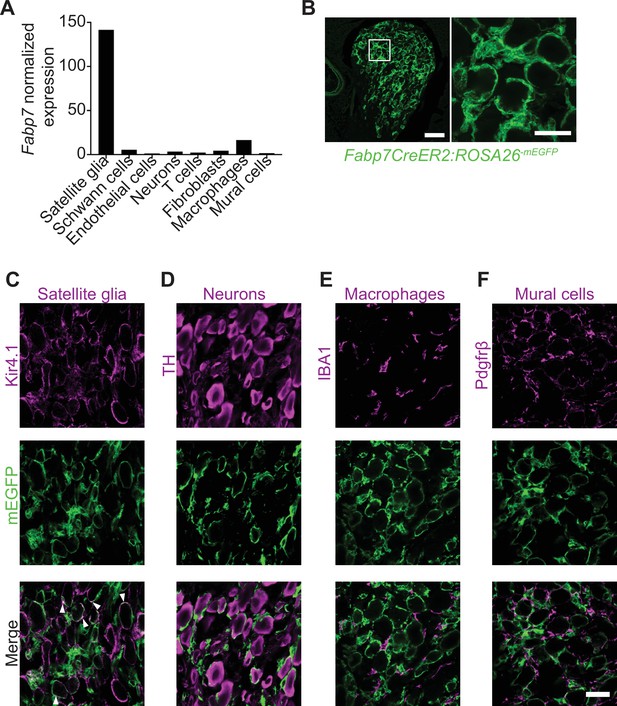
Brain lipid binding protein (BLBP) is a specific marker for adult satellite glial cells.
(A) Fabp7 mRNA is enriched in satellite glial cells compared to other ganglionic cell types based on single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis of sympathetic (superior cervical ganglia) and sensory (dorsal root ganglia) from adult mice (postnatal days 30–45) (Mapps et al., 2022). Expression is normalized to cell counts for individual ganglionic cell types. (B) Tamoxifen-induced-mEGFP reporter expression in sympathetic ganglia from Fabp7-CreER2;ROSA26mEGFP mice. Scale bar: 100 μm for left panel and 30 μm for right panel. (C–F) Co-localization of m-EGFP signal with Kir4.1 immunoreactivity (for satellite glia), but not with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH; sympathetic neurons), IBA-1 (macrophages), or Pdgfrβ (vascular mural cells) in Fabp7-CreER2;ROSA26mEGFP sympathetic ganglia. Arrowheads in (C) indicate co-localization of mEGFP and Kir4.1. Scale bar: 30 μm.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for normalized Fabp7 in sympathetic ganglia.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
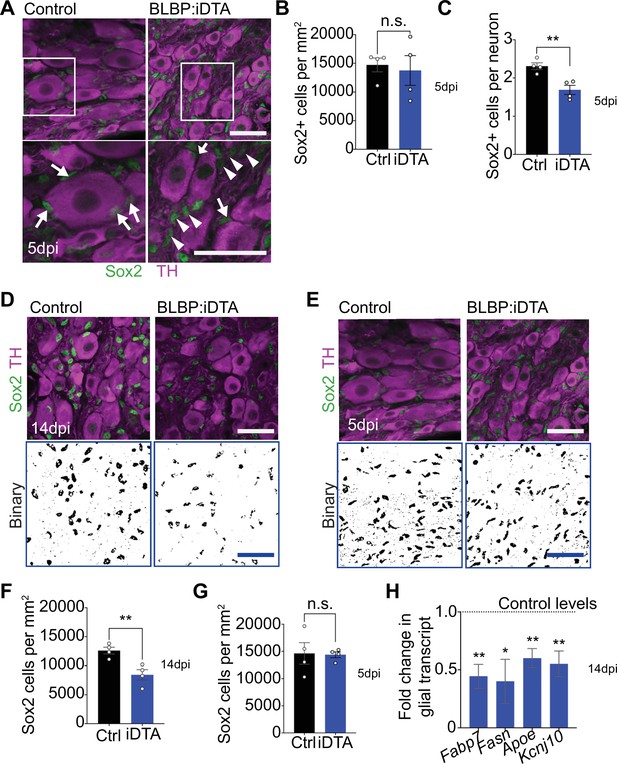
Satellite glia ablation in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic ganglia.
(A) Sox2 (green) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH; magenta) immunostaining in BLBP:iDTA and control sympathetic ganglia at 5 dpi. Arrows indicate Sox2-labeled nuclei associated with sympathetic neuron cell bodies, while arrowheads indicate Sox2-labeled nuclei that are not adjacent to neuronal soma. Scale bar: 30 μm. (B) Quantification shows similar numbers of Sox2-labeled satellite glial cells in control and mutant ganglia at 5 dpi. Data are means ± SEM from n = 4 animals per genotype, **p<0.01, n.s., not significant, t-test. (C) Fewer Sox2-positive satellite glia are found adjacent to neuron cell bodies. Data are means ± SEM from n = 4 animals per genotype, **p<0.01, t-test. (D, E) Binary images of Sox2-immunolabeled cells in BLBP:iDTA and control sympathetic ganglia at 14 dpi (D) and 5 dpi (E). Images were generated by filtering and thresholding using ImageJ. Scale bar: 30 μm. (F, G) Quantification of Sox2-labeled cells in binary images of mutant and control ganglia at 14 dpi (F) and 5 dpi (G). (F) Data are means ± SEM from n = 4 animals per genotype, **p<0.01, t-test, (G) n.s., not significant, t-test. (H) Downregulated expression of satellite glia-enriched transcripts in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic ganglia at 14 dpi as assessed by qPCR analysis. Data are means ± SEM from n = 3–5 animals per genotype, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, t-test with Bonferroni–Dunn’s correction.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data for glia cell counts and transcript changes in sympathetic ganglia.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v3.xlsx
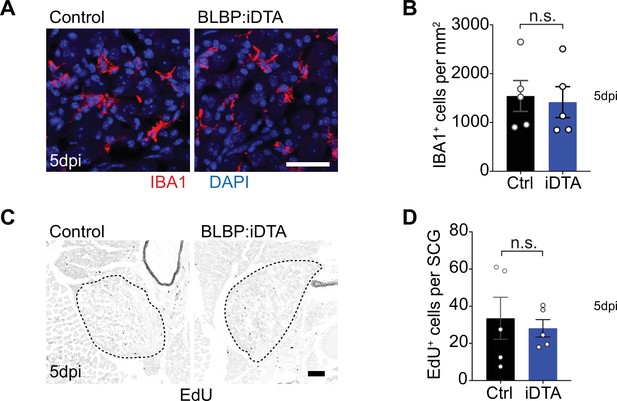
Satellite glia depletion does not induce macrophage infiltration or proliferative changes in sympathetic ganglia.
(A, B) Satellite glia depletion does not induce an increase in IBA-1-expressing macrophages in sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 30 µm. Data are means ± SEM from n = 5 animals per genotype, n.s., not significant, t-test. (C, D) Proliferation in superior cervical ganglia (SCG) (outlined by dashed line) was not altered by satellite glia depletion as assessed by EDU labeling. Scale bar: 100 µm. Data are means ± SEM from n = 5 animals per genotype, n.s., not significant, t-test.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for macrophage and cell proliferation analyses.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig1-figsupp3-data1-v3.xlsx
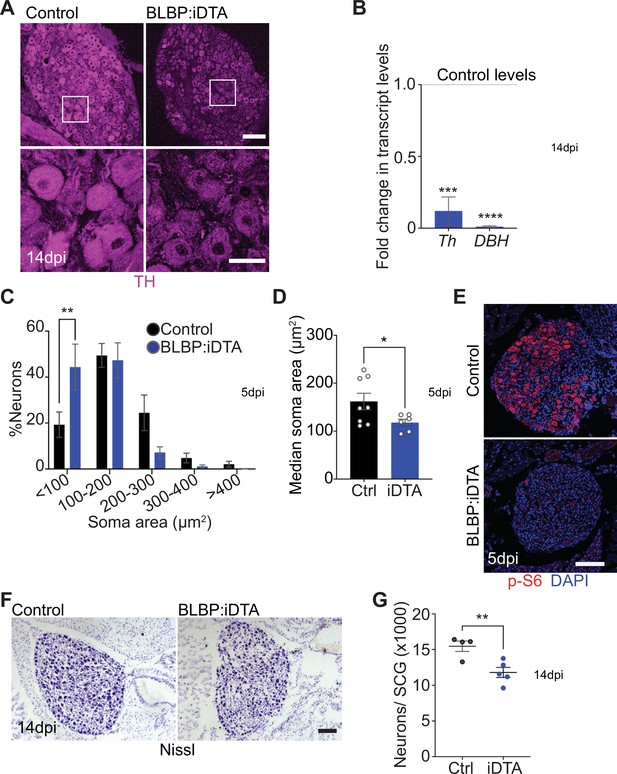
Neuronal defects in norepinephrine (NE) biosynthesis, metabolism, and survival in satellite glia-depleted mice.
(A) Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) expression is downregulated in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic neurons. Insets also show atrophied neuronal cell bodies in mutant ganglia compared to controls. Scale bar: 100 μm for upper panels and 30 μm for insets. (B) Transcripts for Th and DBH, key enzymes in norepinephrine biosynthesis, are decreased in BLBP:iDTA SCG relative to control ganglia. Data are presented as means ± SEM from superior cervical ganglia (SCG) collected from n = 3–4 animals per genotype. ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, t-test with Bonferroni–Dunn’s correction. (C) Histogram shows a greater distribution of smaller soma sizes in mutant neurons compared to controls. Results are means ± SEM from n = 6–8 animals per genotype, **p<0.01, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (D) Reduced soma sizes, represented as median values for soma areas (μm2), of sympathetic neurons from BLBP:iDTA mice compared to controls at 5 dpi. Values are means ± SEM from n = 8 control and 6 mutant animals, *p<0.05, t-test. (E) Immunostaining shows reduced p-S6 levels in BLBP:iDTA ganglia. Scale bar:100 μm. (F, G) Cell counts in Nissl-stained SCG tissue sections show reduced sympathetic neuron numbers in satellite glia-depleted mice 14 dpi. Results are means ± SEM from n = 4 control and 5 mutant animals. **p<0.01, t-test.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw data for neuronal morphology and survival.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig2-data1-v3.xlsx
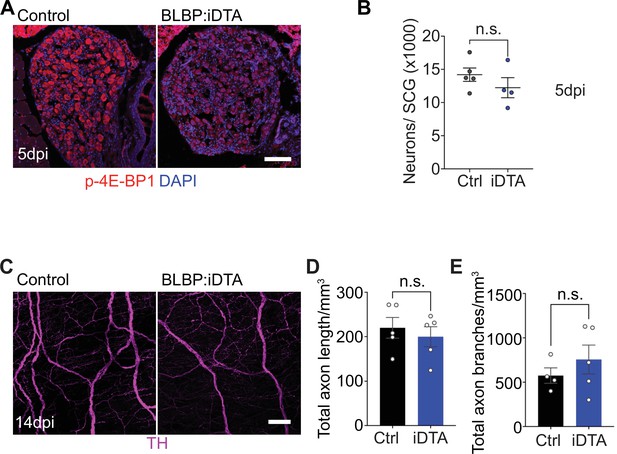
Neuronal morphology and signaling in BLBP:iDTA mice.
(A) Immunostaining shows reduced phospho-4E-BP1 expression in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic neurons compared to controls at 5 dpi. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Sympathetic neuron numbers in satellite glia-depleted mice are similar to control values at 5 dpi. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 4 mutant animals, n.s., not significant, t-test. (C) Sympathetic axon innervation of the heart is unaffected in adult BLBP:iDTA mice based on iDISCO-based tissue clearing and wholemount tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunostaining. Scale bar: 100 µm. (D, E) Quantification of axon length and branches in the heart in BLBP:iDTA and control mice. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 4 control and 5 mutant animals, n.s., not significant, t-test.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for neuronal morphology and survival.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
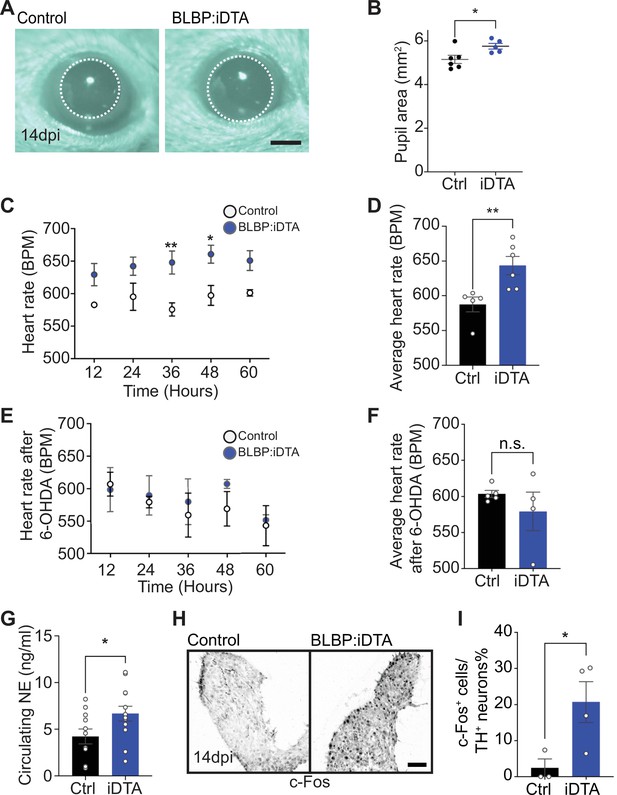
Elevated sympathetic activity in satellite glia-depleted mice.
(A, B) Dark-adapted BLBP:iDTA mice have increased basal pupil size compared to control littermates. Results are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 6 control and 5 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (C) BLBP:iDTA mice exhibit elevated heart rate, relative to controls. ECGs were recorded continuously in conscious mice for 7 days, although only data for fourth to seventh days after insertion of lead implants are included in the analysis. Results are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (D) Average heart rate over fourth to seventh days after lead implantation. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. **p<0.01, t-test. (E, F) 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) administration (150 mg/kg, i.p.) prevents elevated heart rate in BLBP:iDTA mice. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 4 mutant animals, n.s, not significant, t-test. (G) Increased circulating norepinephrine levels in BLBP:iDTA mice. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 11 control and 13 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (H, I) Increased c-Fos-positive sympathetic neurons in mutant ganglia. Quantification of c-Fos+;TH+ sympathetic neurons as a % of total number of TH+ sympathetic neurons. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 4 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data for pupil size and heart rate in mice, NE secretion, and c-Fos expression.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig3-data1-v3.xlsx
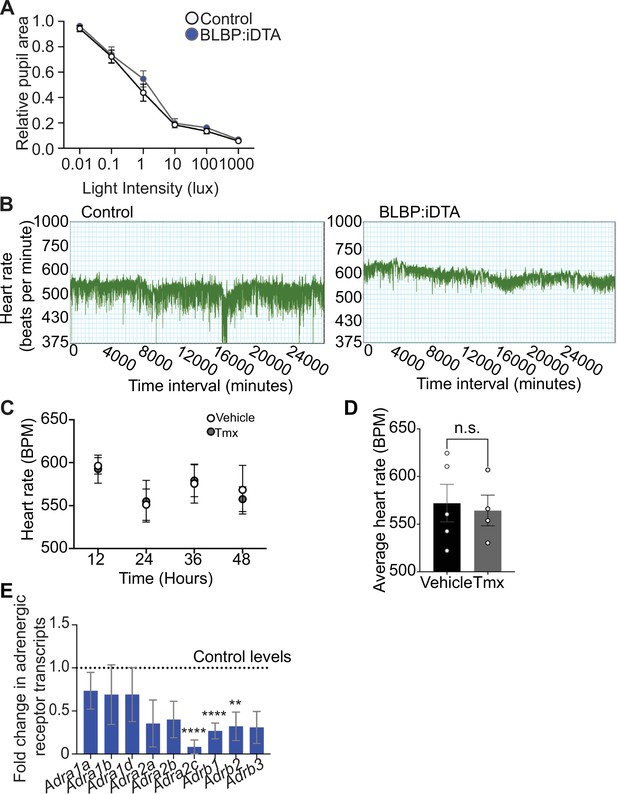
Autonomic function analyses in BLBP:iDTA mice.
(A) Parasympathetic activity is normal in satellite glia-depleted mice as assessed by measuring pupil constriction in response to increasing light intensities. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (B) Representative heart rate recordings over time show decreased heart rate variability in BLBP:iDTA mice compared to controls. (C, D) Tamoxifen treatment (180 mg/kg body weight for five consecutive days) does not alter heart rate in wild-type C57Bl/6J mice or control ROSA26eGFP-DTA mice without Cre. Values are mean ± SEM from n = 5 vehicle- and 4 tamoxifen-injected animals, n.s., not significant, t-test. (E) Downregulated adrenergic receptor expression in cardiac tissue as assessed by qPCR analysis. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 6 control and 5 mutant animals, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, t-test with Bonferroni–Dunn’s correction.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for pupil and heart rate analyses in mice and adrenergic receptor expression in heart tissue.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
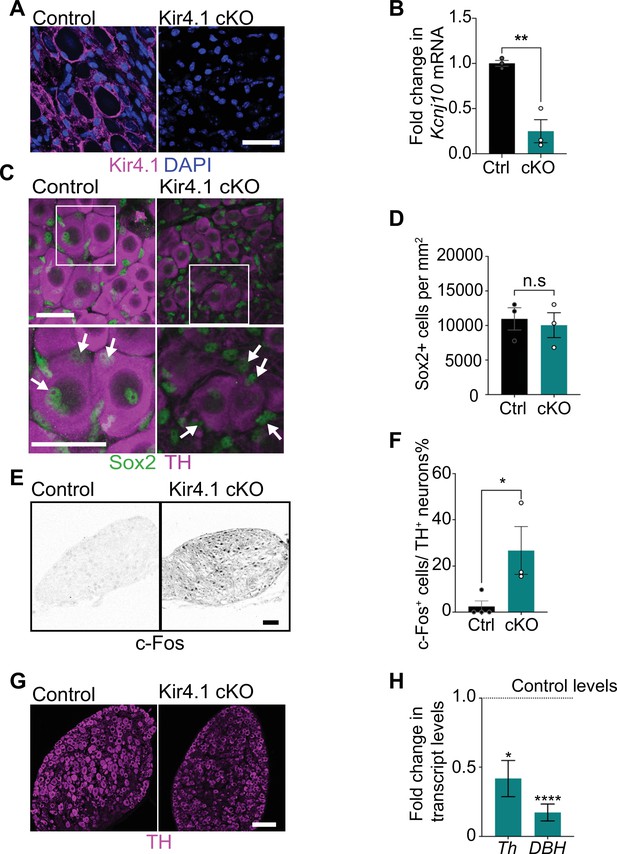
Satellite glia-specific Kir4.1 loss impairs norepinephrine (NE) enzyme expression and neuron activity.
(A, B) Reduced Kir4.1 protein and transcript (Kcnj10) in Kir4.1 cKO mice. Scale bar: 30 μm. Data in (B) are mean ± SEM from n = 3 animals per genotype, **p<0.01, t-test. (C, D) Sox2-positive satellite glial cell numbers are unaffected in Kir4.1 cKO SCG. Arrows indicate Sox2-labeled nuclei of satellite glia associated with sympathetic neuron cell bodies. Arrowheads indicate Sox2-labeled satellite glia that are not adjacent to neuronal soma. Scale bar: 30 μm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 3 animals per genotype, n.s., not significant, t-test. (E, F) Kir4.1 deletion in satellite glia results in an increase in c-Fos-positive sympathetic neurons. Quantification of c-Fos+;TH+ sympathetic neurons as a % of total number of TH+ sympathetic neurons. Scale bar: 100 μm. Quantifications are mean ± SEM from n = 3 animals per genotype, *p<0.05, t-test. (G, H) Downregulation of NE biosynthetic enzymes, TH and DBH, in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic ganglia. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3–5 animals per genotype, *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001, t-test with Bonferroni’s correction.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data for glia and neuron cell counts and gene expression changes in Kir4.1 mutant and control mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig4-data1-v3.xlsx
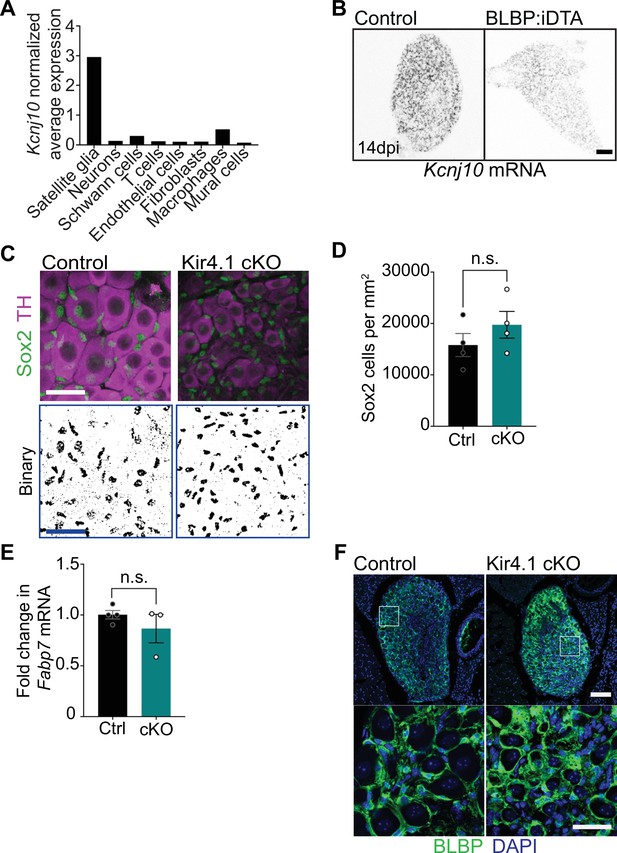
Kir4.1 expression and analyses of satellite glia in Kir4.1 cKO mice.
(A) Kcnj10 mRNA is enriched in satellite glia compared to other ganglionic cell types based on single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis of sympathetic and sensory ganglia from adult mice (postnatal days 30–45) (Mapps et al., 2022). Expression is normalized to cell counts for individual ganglionic cell types. (B) Single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH) shows decreased Kcnj10 mRNA in BLBP:iDTA sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C, D) Binary images and quantifications of Sox2-labeled cells in Kir4.1 cKO and control sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 30 µm. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 4 mutant animals, n.s., not significant, t-test. (E) Fabp7 mRNA levels are unaltered in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic ganglia as assessed by qPCR analysis. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 4 control and 3 mutant animals, n.s., not significant, t-test. (F) Brain lipid binding protein (BLBP) immunostaining shows that BLBP protein expression and satellite glial morphologies are not altered in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 30 µm.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for glia cell counts and gene expression changes in Kir4.1 mutant and control mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
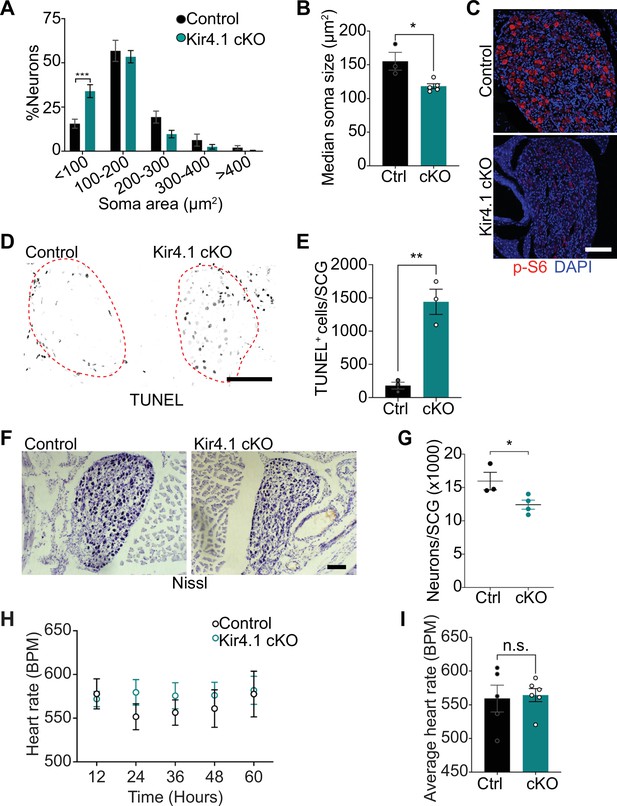
Defects in neuron viability in Kir4.1 cKO mice.
(A) Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic neurons have smaller soma sizes compared to control neurons. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 5 mutant mice, ***p<0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (B) Reduced soma size, represented as median values of soma areas (μm2) of Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic neurons compared to controls. Values are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 5 mutant animals, *p<0.05, t-test. (C) Decreased mTOR signaling based on p-S6 immunostaining in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic ganglia. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) TUNEL labeling shows increased apoptosis in Kir4.1 cKO SCG (outlined in red dashed line). Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) Quantification of apoptotic cells in control and mutant sympathetic ganglia from n = 3 mice per genotype. Data presented as mean ± SEM **p<0.01, t-test. (F, G) Decreased sympathetic neuron numbers in Kir4.1 cKO mice based on Nissl-staining and cell counts in sympathetic ganglia tissue sections. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 3 control and 4 mutant animals. *p<0.05, t-test. (H) Heart rate is unaffected by Kir4.1 deletion from satellite glia. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (I) Average heart rate over days 4–7 post-lead implantation. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals. n.s., not significant.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Raw data for neuron morphology and heart rate in Kir4.1 mutant and control mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig5-data1-v3.xlsx
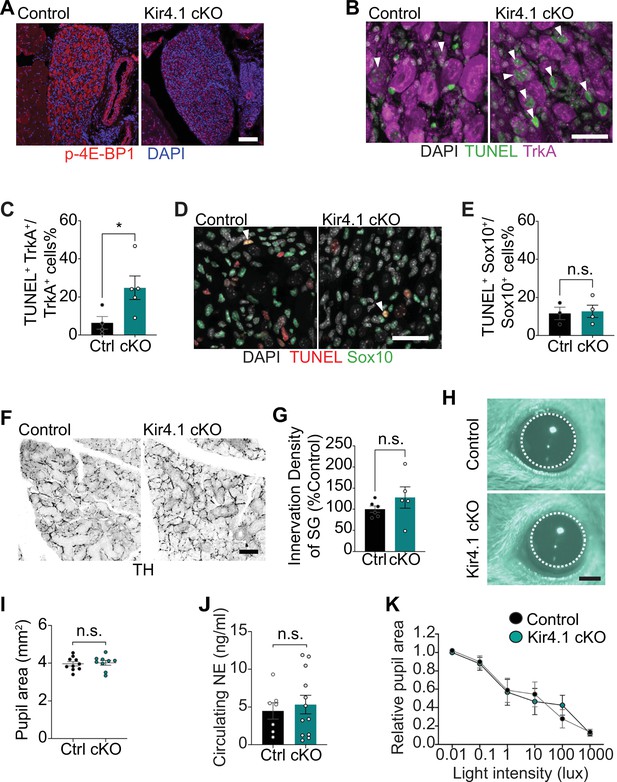
Additional morphology and functional analyses in Kir4.1 cKO mice.
(A) Reduced p-4E-BP1 levels as shown by immunostaining in Kir4.1 cKO sympathetic neurons compared to controls. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Increased neuronal apoptosis in Kir4.1 cKO ganglia as shown by TrkA immunostaining (magenta) and TUNEL labeling (green). Arrowheads indicate TUNEL+;TrkA+ sympathetic neurons. Scale bar: 30 µm. (C) Quantification of TUNEL+;TrkA+ neurons expressed as a % of total number of TrkA+ neurons. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 4 control and 5 mutant mice, *p<0.05, t-test. (D) Glial apoptosis is unaltered with Kir4.1 loss, assessed by Sox10 immunostaining (green) and TUNEL labeling (red). Arrowheads indicate TUNEL+; Sox10+ cells. Scale bar 30 µm. (E) Quantification of TUNEL+;Sox10+ glial cells expressed as a % of the total number of Sox10+ satellite glial cells. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 6 control and 4 mutant mice, n.s, not significant, t-test. (F) Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunostaining shows normal sympathetic axon innervation in Kir4.1 cKO salivary glands. Scale bar: 100 µm. (G) Quantification of sympathetic innervation density in salivary glands. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 6 control and 5 mutant mice, n.s, not significant, t-test. (H, I) Basal pupil areas are unaffected by satellite glia-specific Kir4.1 deletion. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 10 control and 9 mutant animals, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. (J) Circulating norepinephrine (NE) levels are unaltered with Kir4.1 deletion from satellite glia. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 7 control and 12 mutant animals, n.s., not significant, t-test. (K) Pupil constriction in response to light, indicative of parasympathetic activity, is normal in Kir4.1 cKO mice. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 5 control and 6 mutant animals, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for neuron and glia morphology, and pupil analyses in Kir4.1 mutant and control mice.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74295/elife-74295-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v3.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus) | Fabp7-CreER2 | Maruoka et al., 2011 | ||
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(DTA)Jpmb/J | The Jackson Laboratory | RRID:IMSR_JAX:006331 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | B6.129-Kcnj10tm1Kdmc/J | Djukic et al., 2007 | RRID:IMSR_JAX:026826 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo | Muzumdar et al., 2007 | RRID:IMSR_JAX:007576 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus) | C57Bl/6J | The Jackson Laboratory | RRID:IMSR_JAX:000664 | |
| Antibody | Anti-BLBP (mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab131137 (discontinued); RRID:AB_11157091 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-BLBP (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab32423; RRID:AB_880078 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-Sox2 (rabbit polyclonal) | Active Motif | Cat# 39823, RRID:AB_2793356 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Anti-IBA1 (rabbit polyclonal) | WAKO | Cat# 019-19741; RRID:AB_839504 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-Kir4.1 (rabbit polyclonal) | Alomone Labs | Cat# APC-035; RRID:AB_2040120 | IF (1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-pS6 (rabbit polyclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 2215S; RRID:AB_916156 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (mouse monoclonal) | Sigma | Cat# T2928; RRID:AB_477569 | IF (1:300) |
| Antibody | Anti-tyrosine hydroxylase (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Cat# ab152; RRID:AB_390204 | IF (1:300) |
| Antibody | Anti-c-Fos (rabbit polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat# ab190289; RRID:AB_2737414 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-Sox10 (goat polyclonal) | R&D Systems | Cat# AF2864; RRID:AB_442208 | IF (1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-p-4E-BP-1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Cell Signaling | Cat# 2855T; RRID:AB_560835 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-TrkA (rabbit polyclonal) | Millipore | Cat# 06-674; RRID:AB_310180 | IF (1:200) |
| Antibody | Amersham ECL Rabbit IgG, HRP-linked whole Ab from donkey (rabbit polyclonal) | Cytiva | Cat# NA934; RRID:AB_772206 | DAB (1:200) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra1a TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00442668_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra1b TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00431685_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra1d TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm01328600_m1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra2a TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00845383_s1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra2b TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00477390_s1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adra2c TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00431686_s1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adrb1 TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm00431701_s1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adrb2 TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm02524224_s1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Adrb3 TaqMan Probe | Thermo Fisher | Assay ID: Mm02601819_g1 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Eukaryotic Rn18s Endogenous Control (VIC/MGB probe, primer limited) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 4319413E | |
| Sequence-based reagent | Th_F | This paper | qPCR primers | AATCCACCACTTAGAGACCCG (‘Materials and methods’) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Th_R | This paper | qPCR primers | CTTGGTGACCAGGTGGTGAC (‘Materials and methods’) |
| Sequence-based reagent | DBH_F | This paper | qPCR primers | CATCTGGATTCCCAGCAAGACT (‘Materials and methods’) |
| Sequence-based reagent | DBH_R | This paper | qPCR primers | CAGCGACTGAAATGGCTCTTCC (‘Materials and methods’) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Rn18s_F | Ceasrine et al., 2018 | qPCR primers | CGCCGCTAGAGGTGAAATTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Rn18s _R | Ceasrine et al., 2018 | qPCR primers | TTGGCAAATGCTTTCGCTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Kcnj10_F | Harvard Primer Bank | PrimerBank ID:34328498a1 | GTCGGTCGCTAAGGTCTATTACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Kcnj10_R | Harvard Primer Bank | PrimerBank ID:34328498a1 | GGCCGTCTTTCGTGAGGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fabp7CreER2 _F | Maruoka et al., 2011 | PCR primers | TACCGGTCGACAACGAGTGATGAGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Fabp7CreER2 _R | Maruoka et al., 2011 | PCR primers | GACCGACGATGCATGTTTAGCTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(DTA)Jpmb/J _F | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | AAAGTCGCTCTGAGTTGTTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(DTA)Jpmb/J _R | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | GCGAAGAGTTTGTCCTCACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | B6.129-Kcnj10tm1Kdmc/J _F | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | TGATCTATCTCGATTGCTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | B6.129-Kcnj10tm1Kdmc/J _R | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | CCCTACTCAATGCTCTTAAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo_WT F | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | GGC TTA AAG GCT AAC CTG ATG TG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo_WT R | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | GGA GCG GGA GAA ATG GAT ATG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo_Mut F | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | CCG GAT TGA TGG TAG TGG TC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Gt(ROSA)26Sortm4(ACTB-tdTomato,-EGFP)Luo_Mut R | The Jackson Laboratory | PCR primers | AAT CCA TCT TGT TCA ATG GCC GAT C |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hydrogen peroxide solution, 30% in H2O, ACS reagent | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 216763 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | SIGMAFAST 3,3'-Diaminobenzidine tablets, tablet, to prepare 15 mL | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# D4418-50SET | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 6-Hydrodroxydopamine hydrobromide | Hello Bio | Cat# HB1889 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hematoxylin solution | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# GHS232 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Bouin’s solution | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# HT10132-1L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Glycogen | Thermo Fisher | Cat# R0551 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Maxima SYBR Green/ROX qPCR Master Mix (2×) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# K0222 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 4304437 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trizol | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 15596018 | |
| Other | DAPI | Roche | Cat# 10236276001 | (1 µg/mL) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Agarose, low EEO | Sigma | Cat# A0576-25G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant | Thermo Fisher | Cat# P36930 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Permount Mounting Media | Fisher Scientific | Cat# SP11500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Flouromount Mounting Media | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F4680-25mL | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 555 Imaging Kit | Life Technologies | Cat# 10338 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | In Situ Cell Death Detection Kit, TMR red | Roche | Cat# 12156792910 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Norepinephrine Research ELISA | Rocky Mountain Diagnostics, Inc | BA E-5200 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superscript IV First Strand Synthesis System | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 18091050 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Agilent Absolutely RNA Nanoprep Kit | Agilent | Cat# 400753 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Fluorescent Multiplex Assay | ACD | Cat# 320850 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNAscope Probe-Kcnj10-C3 | ACD | Cat# 458831-C3 | |
| Software, algorithm | LabChart 8 software (ADInstruments) | N/A | https://www.adinstruments.com/support/software | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | N/A | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ | |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN 2012 SP1 (black edition) | N/A | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/home.html | |
| Software, algorithm | ZEN 2012 (blue edition) | N/A | https://www.zeiss.com/microscopy/int/home.html |





