Protein visualization and manipulation in Drosophila through the use of epitope tags recognized by nanobodies
Figures
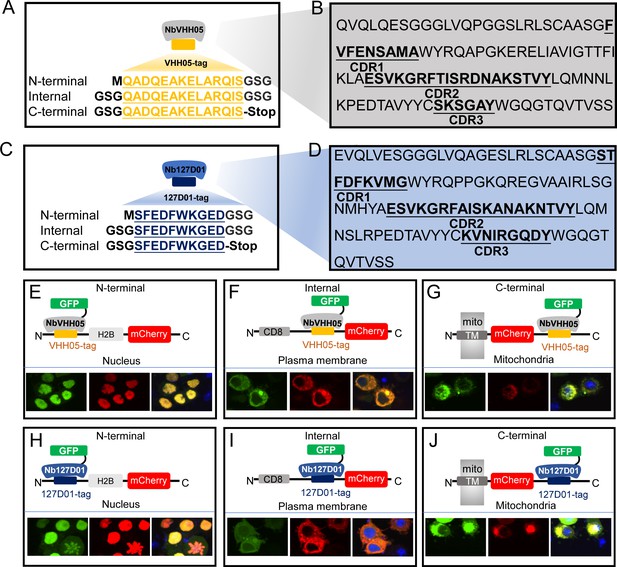
VHH05 and 127D01 NanoTag sequences and their corresponding nanobodies, and use of nanobodies as chromobodies.
(A and C) VHH05 and 127D01 were inserted at the N-terminus, internally or at the C-terminus of a protein of interest (POI). GSG denotes the linker, M is the start codon, and Stop is the stop codon. (B and D) Nanobody sequences of NbVHH05 and Nb127D01. Bolded and underlined CDR1-3 corresponds to complementarity-determining regions (CDRs). (E) Co-transfection of pAW-actin5C-NbVHH05-GFP and pAW-actin5C-VHH05-H2B-mCherry into S2R+ cells. H2B is a nuclear protein. The right most panel is GFP, the center panel is mCherry, and the rightmost is the merged image. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining shows the nuclei. (F) Co-transfection of pAW-actin5C-NbVHH05-GFP and pAW-actin5C-CD8-VHH05-mCherry into S2R+ cells. CD8 is a cell membrane protein. (G) Co-transfection of pAW-actin5C-NbVHH05-GFP and pAW-actin5C-mito-mCherry-VHH05 into S2R+ cells. Mito-mCherry-VHH05 contains a localization signal peptide for mitochondrial outer membrane targeting. (H, I, and J) Experiments are as in E, F, and G, except that pAW-actin5C-Nb127D01-GFP and pAW-actin5C-127D01-H2B-mCherry were co-transfected.
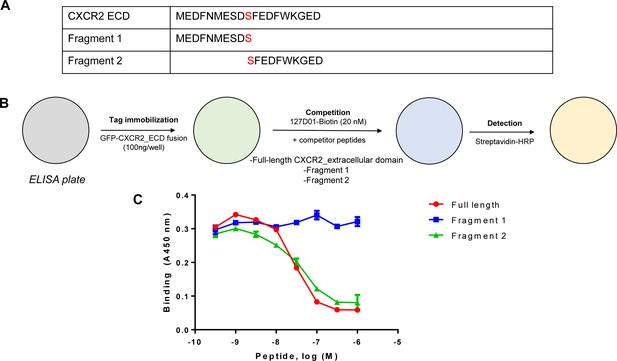
Identification of the 127D01 epitope.
(A) Synthetic peptides corresponding to the full-length extracellular domain from C-X-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CXCR2) or fragments were synthesized by solid-phase peptide synthesis using Fmoc protection of the peptide backbone and purified by reverse-phase HPLC. (B) Peptides were used in a competitive ELISA in which soluble peptides compete for binding with a conjugate consisting of GFP fused with CXCR2 ECD immobilized on the ELISA plate. (C) Representative data from a competition ELISA experiment. Data points represent mean ± SD from duplicate experiments.
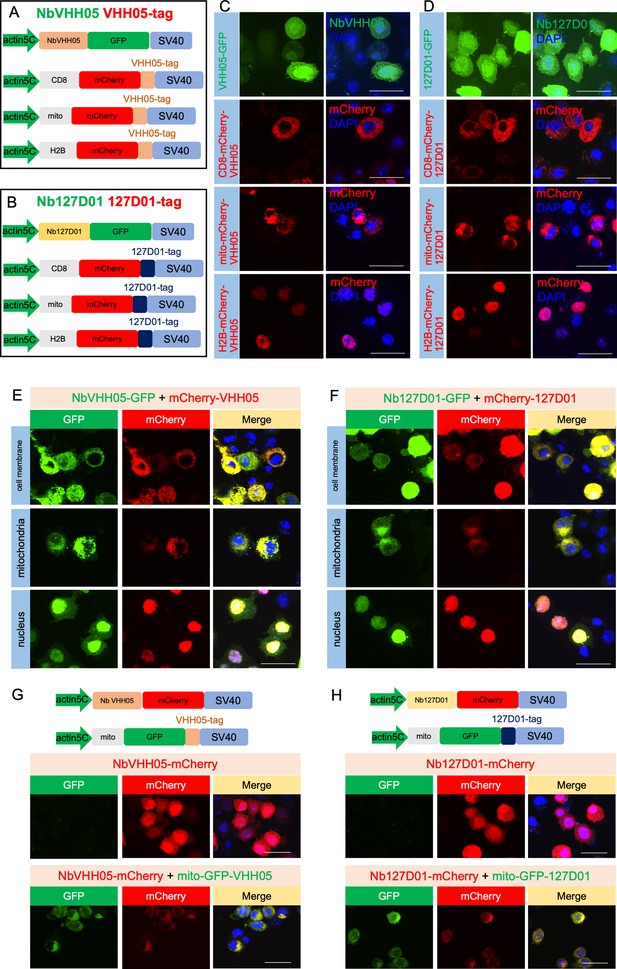
Schematic representation of the constructs and confocal images in S2R+ cells.
(A and B) Transcriptional elements promoter and SV40 of the expression vectors, the different protein coding modules are represented as colored filled boxes. (C and D) Individual transfection results of VHH05 and 127D01 vectors in S2R+ cells. Confocal images show the distribution of fluorescent proteins in the cell. DAPI staining shows the nuclei. (E) Confocal images of co-transfection of NbVHH05-GFP with different cell compartments mCherry-VHH05 vectors showed the co-localization signal of GFP and mCherry. (F) Confocal images of co-transfection of Nb127D01-GFP with different cell compartments. mCherry-127D01 vectors showed the co-localization signal of GFP and mCherry. (G) Vectors information of NbVHH05-mCherry and mito-GFP-VHH05. Confocal images of co-transfection of these two vectors showed the co-localization signal of GFP and mCherry. (H) Vector information of Nb127D01-mCherry and mito-GFP-127D01. Confocal images of co-transfection of these two vectors showed the co-localization signal of GFP and mCherry. Scale bars: 25 μm.
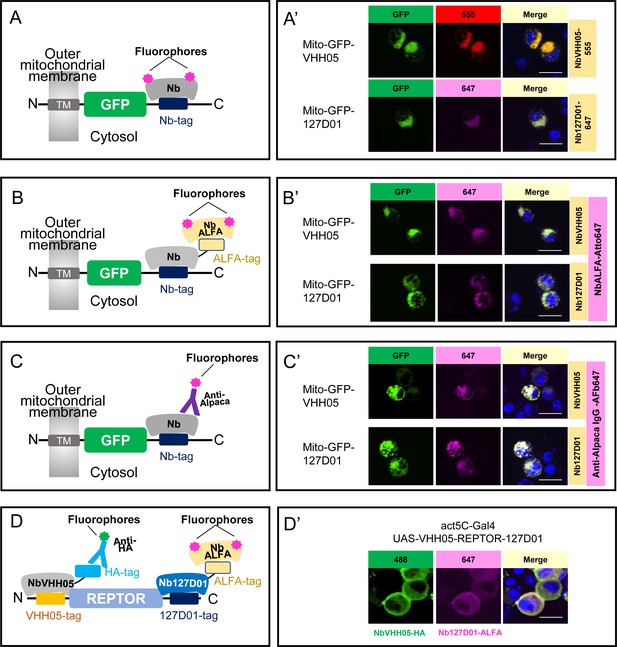
Using NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 for immunofluorescence.
(A) Fluorophore-conjugated NbVHH05 or Nb127D01 recognizes VHH05- or 127D01-tagged fluorescence proteins. (A’) VHH05- or 127D01-tagged mito-GFP can be detected by the corresponding NbVHH05-555 or Nb127D01-647 in transfected S2R+ cells. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining shows the nuclei. (B) Schematic of nanobodies containing ALFA-tag as primary antibody and NbALFA as a secondary antibody. (B’) VHH05- or 127D01-tagged mito-GFP can be detected using the corresponding nanobodies in transfected S2R+ cells. (C) Schematic of fluorophore-conjugated anti-Alpaca IgG antibodies to detect VHH05- and 127D01-tagged proteins. NbVHH05 or Nb127D01 is used as primary antibodies and anti-Alpaca IgG as secondary antibody. (C’) VHH05- or 127D01-tagged mito-GFP can be detected using the corresponding nanobodies and anti-Alpaca IgG-647 in transfected S2R+ cells. (D) Schematic of using VHH05 and 127D01 for double tagging. N-, C-terminal of REPTOR contains VHH05 and 127D01. (D’) Co-staining NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 in S2R+ cells transfected with VHH05-REPTOR-127D01. Scale bars: 10 µm.
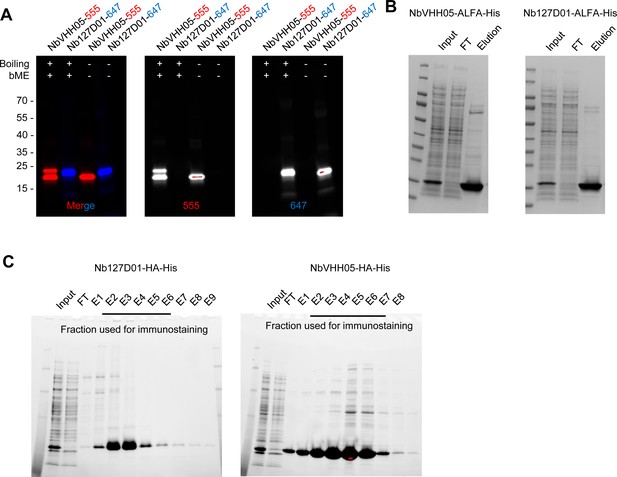
Nanobody purification and fluorophore conjugation.
(A) Fluorescence signals of NbVHH05-CF555 and Nb127D01-CF647 under 555 and 647 detection channels. (B and C) Coomassie brilliant blue staining of ALFA- and HA-tagged nanobodies purified from Escherichia coli protein expression. FT: flow-through, E1–E9: elution 1–9.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data of fluorescence signals or coomassie brilliant blue staining for Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
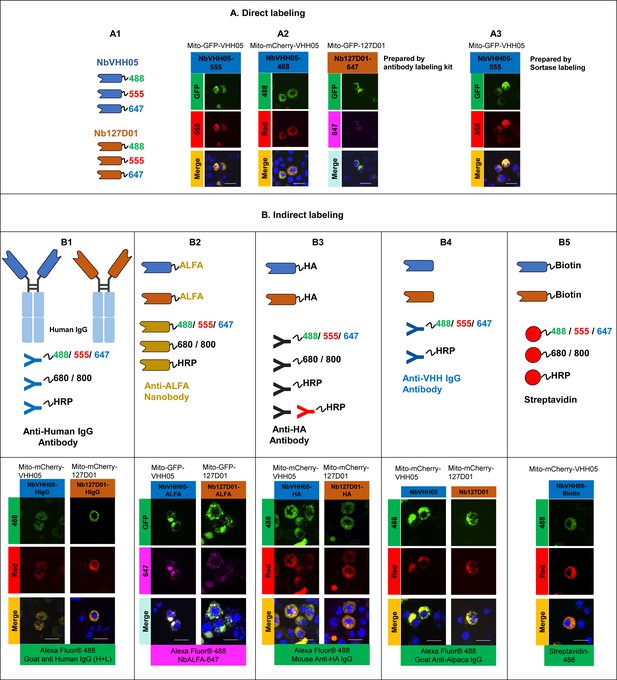
Different types of NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 and immunofluorescence examples.
(A) Direct labeling can be achieved by linking purified nanobodies with different fluorophores by antibody labeling kit or site-specifically by sortase-mediated labeling. (A1) Schematics of NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 with fluorophore-488, -555, or -647. (A2) Confocal images showing direct immunofluorescence with NbVHH05-555, NbVHH05-488, and Nb127D01-647 in S2R+ cells. (A3) Confocal images showing direct immunofluorescence with NbVHH05-555 prepared by sortase-mediated labeling. (B) Schematics of indirect labeling with nanobodies containing ALFA-tag, HA-tag, biotin, or human IgG as primary antibodies and confocal images in S2R+ cells. (B1) NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 detected with anti-VHH IgG antibody. (B2) NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 with ALFA-tag detected by NbALFA. (B3) NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 with HA-tag detected by anti-HA antibody. (B4) NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 with biotin prepared by sortase-mediated labeling detected by streptavidin. (B5) NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 with human IgG detected by anti-human IgG antibody. Scale bars: 10 µm.
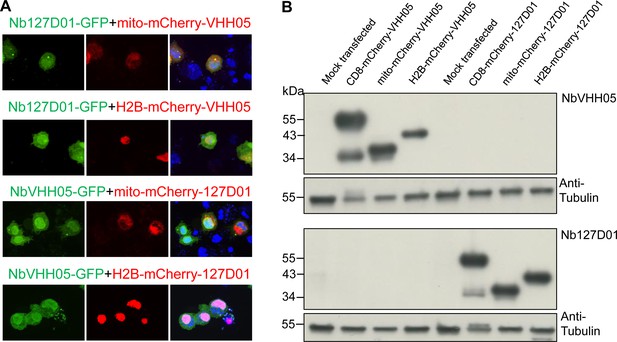
Test of potential interaction between VHH05 and 127D01.
(A) Fluorescence confocal results showed no co-localization signal. Co-transfection of Nb127D01-GFP and mito-mCherry-VHH05 or H2B-mCherry-VHH05, NbVHH05-GFP and mito-mCherry-127D01 or H2B-mCherry-127D01 in S2R+ cells. (B) Western blots indicate no cross-interaction between the two systems. Lysates from S2R+ cells transfected with different types tagged vectors (as in Figure 1) or a mock control plasmid were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. The blot was developed with NbVHH05-ALFA and Nb127D01-ALFA, followed by NbALFA-HRP or a mouse anti-tubulin primary antibody, and followed by anti-mouse IgG HRP.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 2—figure supplement 3b.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig2-figsupp3-data1-v2.zip
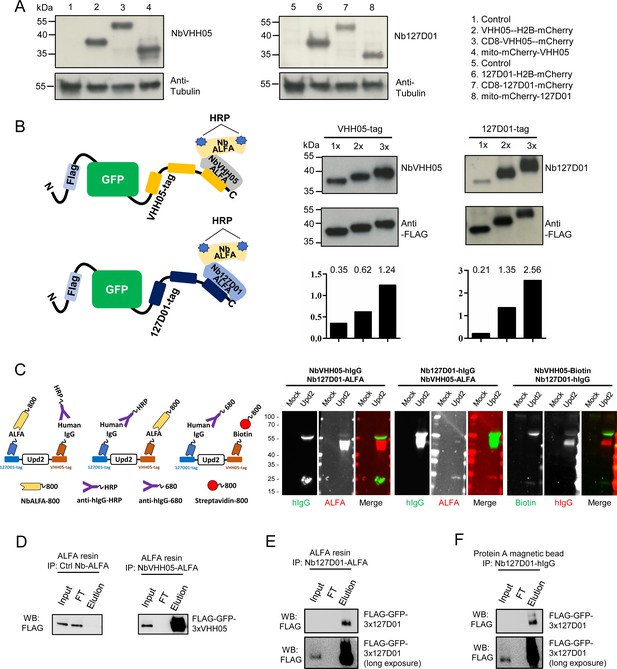
Detection of NanoTagged target proteins by western blotting and immunoprecipitation.
(A) Lysates from S2R+ cells, transfected with different tagged plasmids (as used in Figure 1) or a mock control plasmid, were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. The blot was developed with NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 followed by NbALFA-HRP or a mouse anti-tubulin primary antibody followed by anti-mouse IgG HRP. (B) Schematics depict VHH05- or 127D01-tagged secreted GFP proteins bound by NbVHH05-ALFA and Nb127D01-ALFA followed by NbALFA-HRP. Culture media from S2R+ cells transfected with secreted BiP-GFP-1xtag, BiP-GFP-2xtag, BiP-GFP-3xtag were used for the western blotting. Anti-FLAG antibody was used to show the GFP level. Histogram showing the relative gray value of anti-NbVHH05 or anti-Nb127D01 to anti-FLAG. (C) Western blots for S2R+ cell culture media containing double NanoTagged Upd2 protein: N- and C-terminus region of Upd2 contain VHH05 and 127D01, respectively, recognized by NbVHH05 or Nb127D01. The secondary antibodies were anti-hIgG-HRP, anti-ALFA-800, and Streptavidin-800. (D) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-GFP-3xVHH05 using NbVHH05-ALFA and ALFA-resin. The control nanobody failed to capture FLAG-GFP-3xVHH05. (E) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-GFP-3x127D01 using Nb127D01-ALFA and ALFA-resin. (F) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-GFP-3x127D01 using Nb127D01-hIgG and Protein A magnetic bead.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig3-data1-v2.zip
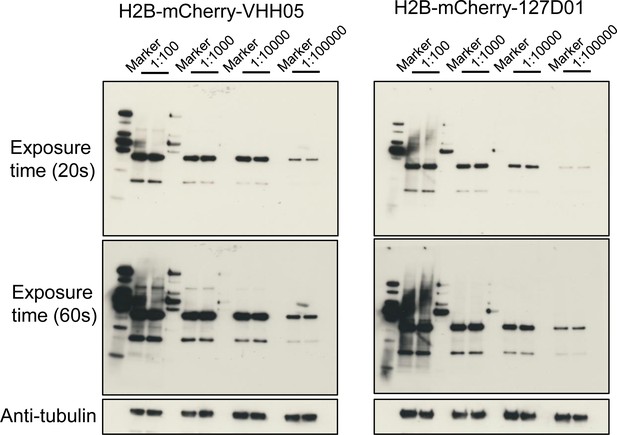
Test of nanobody concentration gradient.
Lysates from S2R+ cells transfected with H2B-mCherry-VHH05 or H2B-mCherry-127D01 were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting. The blot was developed with NbVHH05-ALFA and Nb127D01-ALFA with a concentration gradient from 1:100, 1:1000, 1:10,000, 1:100,000, followed by NbALFA-HRP or a mouse anti-tubulin primary antibody followed by anti-mouse IgG HRP. Two conditions of long-time exposure (60 s) and short-time exposure (20 s) were set for signal reading.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
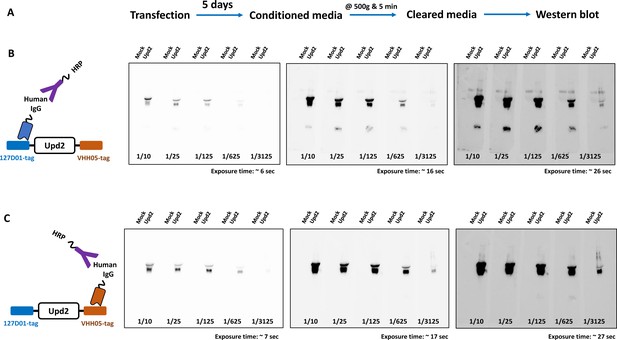
Rapid production of nanobodies in S2 cells for western blots.
(A) Production workflow of nanobodies in the fly cell line. (B) Western blot using culture media containing Nb127D01-hIgG, detected by anti-hIgG-HRP. (C) Western blot using culture media containing NbVHH05-hIgG, detected by anti-hIgG-HRP. Five different concentrations and three exposure times were used.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
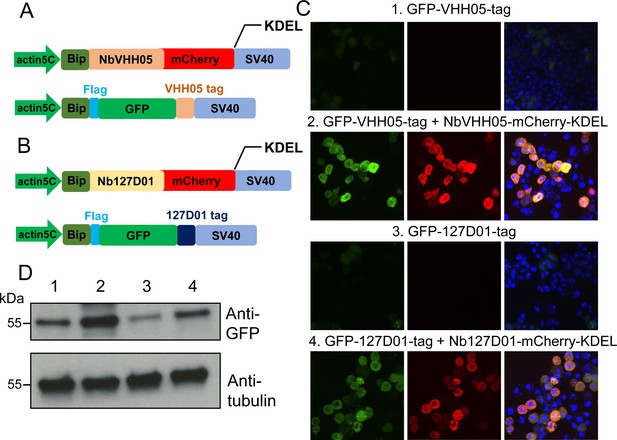
Nanobody-based system for altering localization of NanoTagged proteins.
(A and B) Diagram showing the vectors used for the secreted protein trapping method. NbVHH05/Nb127D01 fused to mCherry contain KDEL and BiP signal peptide and is driven by the actin5C promoter. (C) Four independent cell transfection experiments were performed. In 1 and 3, only GFP-VHH05 or GFP-127D01 was transfected. In 2 and 4, NbVHH05-mCherry-KDEL with GFP-VHH05, or Nb127D01-mCherry-KDEL with GFP-127D01, were co-transfected. Images show the GFP and mCherry signal 48 hr after transfection. Nuclei are stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). (D) Immunoblots of GFP and tubulin in cell lysates from transfections 1–4.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 4D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig4-data1-v2.zip
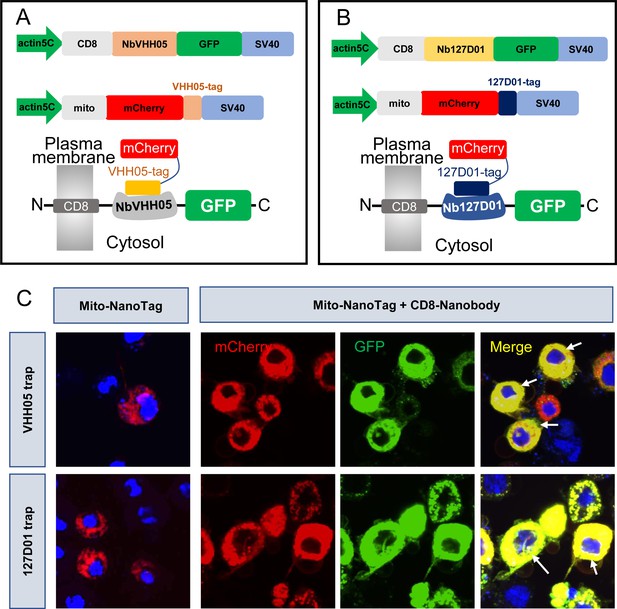
Nanobody-based system for altering localization of NanoTagged proteins.
(A and B) Diagram showing the vectors used for cytoplasmic protein trapping. NbVHH05/Nb127D01 is fused to GFP and CD8, and driven by actin5C promoter. Target proteins are mCherry containing VHH05-tag or 127D01-tag at the C-terminus and mito signal at the N-terminus. (C) Results of transfection of mito-mCherry-NanoTag or co-transfection of CD8-NbVHH05-GFP/mito-mCherry-VHH05 and CD8-Nb127D01-GFP/mito-mCherry-127D01 in S2R+ cells. GFP, mCherry, and merged channels show protein expression levels with antibody staining.
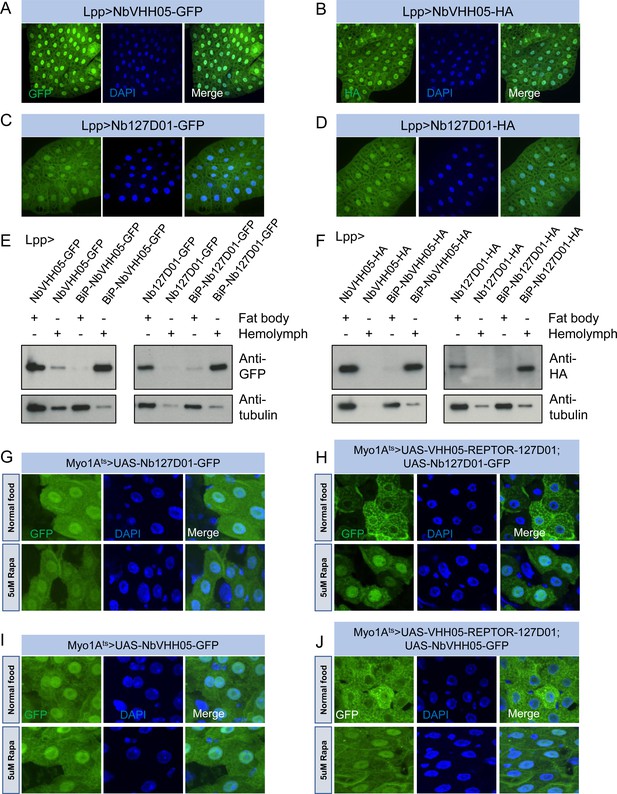
Nanobodies expression in vivo.
(A–D) Lpp-Gal4 drives fat body expression of UAS-NbVHH05-GFP, UAS-NbVHH05-HA, UAS-Nb127D01-GFP, or UAS-Nb127D01-HA, detected by GFP or anti-HA immunostaining. (E and F) Western blot detection of cytoplasmic and secreted GFP- or HA-tagged nanobodies. Lysates from fat body or hemolymph were tested by anti-GFP, anti-HA, and anti-tubulin antibodies. Cytoplasmic-expressed nanobodies: UAS-NbVHH05-GFP, UAS-Nb127D01-GFP, UAS-NbVHH05-HA, and UAS-Nb127D01-HA. Secreted-expressed nanobodies: UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-GFP, UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-GFP, UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-HA, and UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-HA. (G–J) Confocal images of Drosophila adult guts expressing 127D01-EGFP/VHH05-GFP and VHH05-REPTOR-127D01 with or without rapamycin (Rapa) treatment for 15 hr. REPTOR shuttles into the nucleus upon Rapa treatment. (G and I) as controls only express 127D01-EGFP or VHH05-GFP in the ECs. (H) combines 127D01-EGFP with VHH05-REPTOR-127D01 and (J) combines VHH05-EGFP with VHH05-REPTOR-127D01.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 5E and F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig5-data1-v2.zip
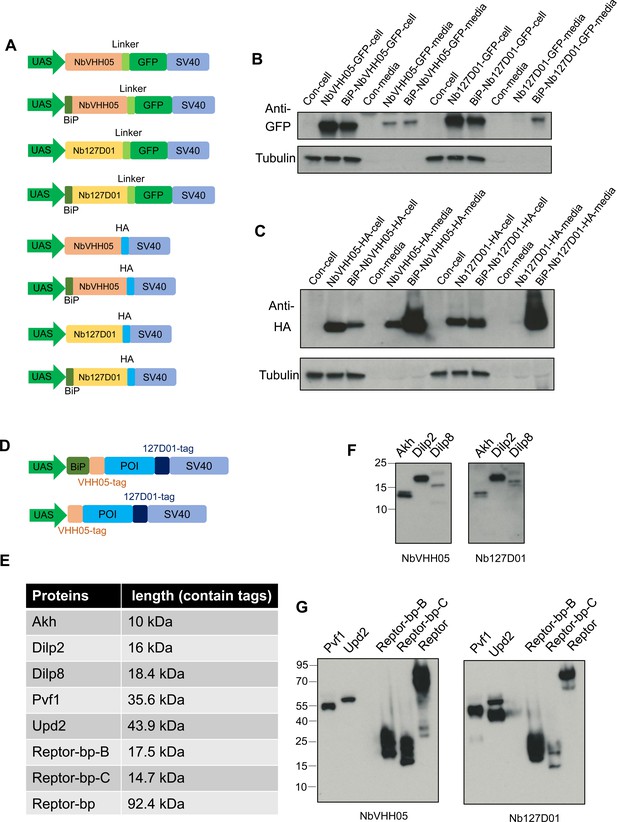
Transgenic vector information and test in S2R+ cells.
(A) Series of UAS vectors expressing NbVHH05 and Nb127D01 fused to GFP and HA or containing BiP signal. Transcriptional elements such as the promoter and SV40 of the expression vectors, and the different protein coding modules are represented as colored filled boxes. (B) Lysates or culture media from S2R+ cells transfected with GFP vectors were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and by western blot. The blot was developed with anti-GFP antibody or anti-tubulin antibody. (C) Lysates or culture media from S2R+ cells transfected with HA vectors were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and by western blot. The blot was developed with anti-HA antibody or anti-tubulin antibody. (D) Two types of UAS vectors for overexpressing NanoTag-labeled genes. N-, C-terminal of protein of interest (POI) contains VHH05 and 127D01. BiP is the signal for labeling secreted proteins. (E) Five secreted proteins and three cytoplasm proteins were labeled, and their sizes are indicated. (F) Western blot results of three small size secreted proteins, Akh and Dilp8 showed multiple bands, and Dilp2 only showed a single band. (G) Western blot results of Pvf1, Upd2, REPTOR-bp-B, REPTOR-bp-C, REPTOR-bp-B. The blot was developed with NbVHH05-ALFA and Nb127D01-ALFA followed by NbALFA-HRP in F and G.
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data of Western blot for Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
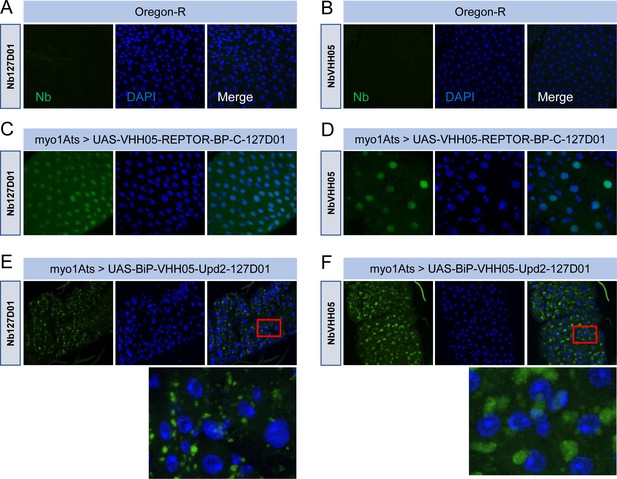
Immunostaining of double NanoTag-labeled proteins.
(A and B) are control Oregon-R flies stained with NbVHH05 and Nb127D01. (C and D) UAS-VHH05-REPTOR-bp-C-127D01 driven by Myo1Ats-Gal4 adult fly guts stained with NbVHH05 and Nb127D01. (E and F) UAS-BiP-VHH05-Upd2-127D01 driven by Myo1Ats-Gal4 adult fly guts stained with NbVHH05 and Nb127D01. Red box indicates an enlarged area of the gut.
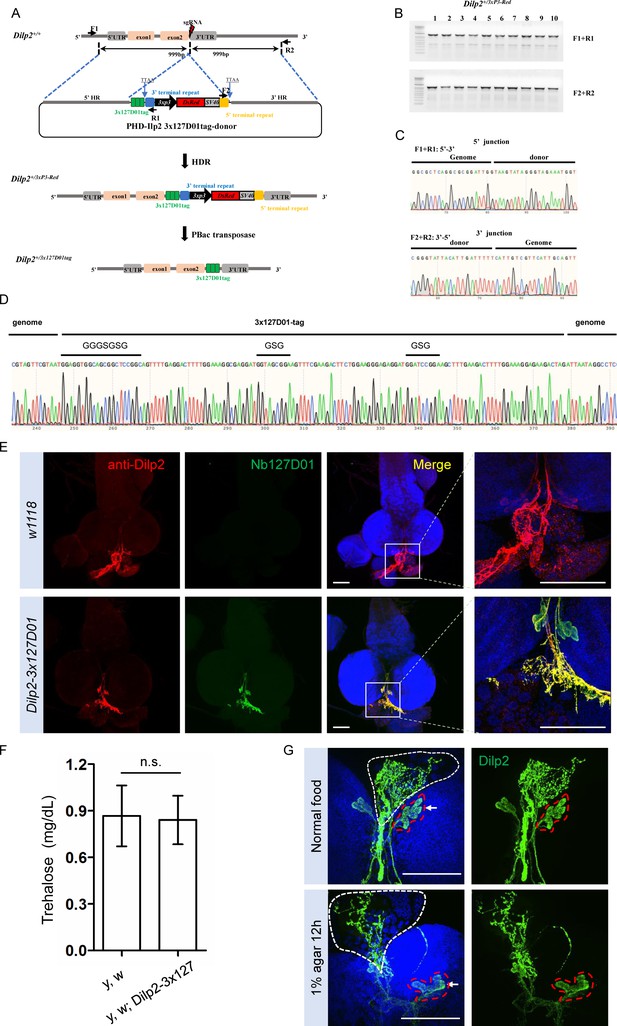
Integration of 3x127D01 into Dilp2 shows a robust expression pattern in the brain.
(A) Workflow and schematic representation of the Dilp2 gene and the sgRNA targeting site. (B) PCR amplification was used to confirm the insertion. (C) Representative sequencing chromatogram of PCR products from the junction PCR. (D) Sequencing results of the DNA fragments showing 3x127D01-tag genome–donor integration. (E) Larval brains of w1118 and Dilp2−3x127D01 co-stained with anti-Dilp2 antibody and Nb127D01. Box demarcates Dilp2-expressing cells and Dilp2-positive neuronal projections. (F) Measurement of whole body trehalose concentration in y,w and y,w; Dilp2−3x127D01 flies. Data are represented as mean ± SD and two-tailed t-tests were used to generate p values, n.s. indicates statistically non-significant. (G) Nanobody immunostaining showing different Dilp2 expression after starvation. Red outline demarcates Dilp2-expressing cells and white outline demarcates Dilp2-positive neuronal projections. Scale bars: 100 µm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data of agarose gel electrophoresis diagram for Figure 6B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig6-data1-v2.zip
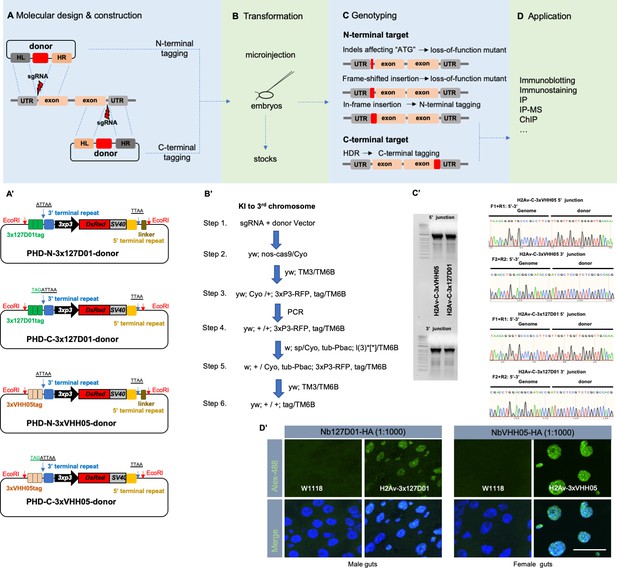
Endogenous VHH05- or 127D01-tagging using CRISPR/Cas9.
Workflow (A), fly embryos transformation (B), genotyping (C), and applications (D). (A’) Common scarless vectors used for constructing donors. N-terminal vectors (PHD-N-3x127D01-donor or PHD-N-3xVHH05-donor) and C-terminal vectors (PHD-C-3x127D01-donor or PHD-C-3xVHH05-donor) contain EcoRI restriction enzyme sites that introduce the homologous arm sequences into donors. (B’) Workflow example for introducing knock-in (KI) tags into the third chromosome. (C’) Genotyping example of KI 3xVHH05-tag and 3x127D01-tag into the C-terminus of H2A variant (H2Av). Gel results showing the 5’ and 3’ PCR junctions. Representative sequencing chromatogram of PCR products from the junction PCR. (D’) Immunostaining of H2Av-3x127D01 and H2Av-3xVHH05. Adult male or female guts were dissected and stained with Nb127D01-HA or NbVHH05-HA. Scale bars: 20 µm.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data of agarose gel electrophoresis diagram for Figure 6—figure supplement 1C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
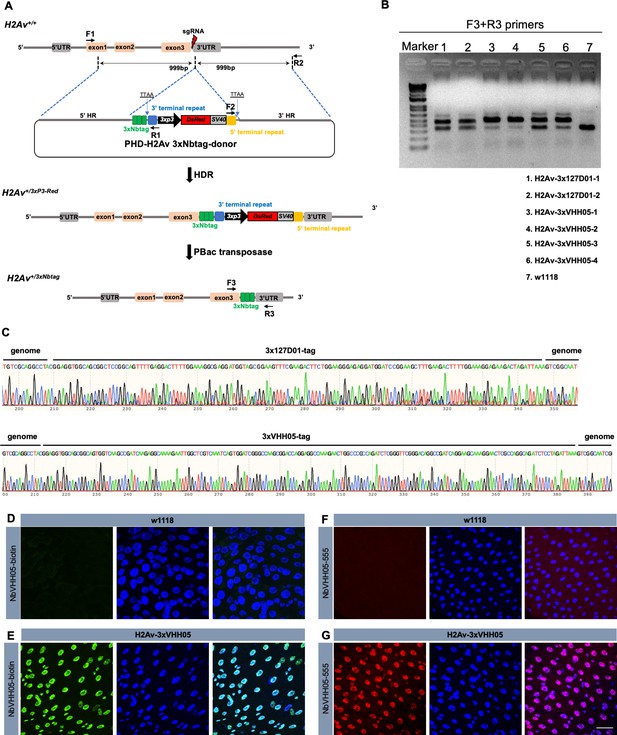
Schematic representation of the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knock-in approach and the targeted integration of transgene constructs.
(A) Schematic representation of the H2A variant (H2Av) gene and the sgRNA targeting site. The thin gray line represents the H2Av genomic locus, with open boxes indicating the promoter, exons, and poly(A) signal. A 164 bp fragment (gray box) located at the 5′ end represents the 5' UTR. The two 79, 119, and 233 bp fragments (pink boxes) are exon 1, exon 2, and exon 3, respectively. A 322 bp fragment (gray box) located at the 3′ end is the poly(A) signal. The red lightning icon indicates the sgRNA site. In the PHD donor construct, the DsRed2 marker expression cassette is driven by the eye-specific 3xP3 promoter. DNA fragments of 999 and 999 bp at the 5′ and 3′ ends were PCR-amplified, subcloned into vectors, and used as homology arms (5' HR and 3' HR, respectively). The 3xNanoTag sequence is shown in the green box. 3’ terminal repeat and 5’ terminal repeats are the piggyBac transposase recognition sequences. Primer positions for amplification analysis of the integrated insertions in transformed flies are shown by arrows. Primer pairs of F1/R1 and F2/R2 were used to amplify the 5′- and 3′-end insertion junctions, respectively. The donor plasmid and sgRNA were injected into the embryos and the donors integrated into the genome. Positive individuals were screened for red fluorescence of the eye. The selection marker was removed by crossing with flies expressing the transposase. Primer pairs of F3/R3 were used to amplify the final insertion. (B) PCR amplification was used to confirm the insertions. Two H2Av-3x127D01, four H2Av-3xVHH05 heterozygous, and w1118 genomic DNA were used as template and the thick gel bands showed the corrected insertion. (C) Sequencing results of the integrated diagnostic DNA fragments showing 3xtag genome–donor integration. (D and E) Indirect immunostaining of H2Av-3xVHH05 flies. Adult female guts were dissected and stained with NbVHH05-biotin and visualized by Streptavidin-488. (F and G) Direct immunostaining of H2Av-3xVHH05 flies. Adult female guts were dissected and stained with NbVHH05-555. (A and C) were w1118, (B and D) are H2Av-3xVHH05. Scale bars: 20 µm.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data of agarose gel electrophoresis diagram for Figure 6—figure supplement 2B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-a-Tubulin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# T5168; RRID: AB_477579 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-GFP | Invitrogen | Cat# A11120; RRID: AB_221568 | IF (1:300) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-GFP | Molecular Probes | Cat# A-6455 RRID:AB_221570 | WB (1:10,000) |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-HA | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 3 F10; RRID: AB_2314622 | WB (1:10,000) IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-FLAG M1 | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# F3040; RRID: AB_439712 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Dilp2 | Park et al., 2014 | N/A | IF (0.5 µg/ml) |
| Other | NbALFA-HRP | NanoTag Biotechnologies | Cat# N1502-HRP | WB (1:5000) |
| Other | NbALFA-Atto647 | NanoTag Biotechnologies | Cat# N1502-At647N-L | IF (1:500) |
| Other | NbALFA-800CW | NanoTag Biotechnologies | Cat# N1502-Li800-L | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-alpaca IgG-647 | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 128-605-230 RRID: AB_2810930 | IF (1:500) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-HA-Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A-21287 RRID: AB_2535829 | IF (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Goat anti-human IgG Fc-HRP | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# A18829 RRID: AB_2535606 | WB (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Donkey anti-human IgG-DyLight 680 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# SA5-10130 RRID: AB_2556710 | WB (1:5000) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Streptavidin-DyLight 800 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 21851 | WB (1:5000) |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 488 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# S32354 RRID: AB_2315383 | IF (1:500) |
| Other | NbVHH05-HA | This paper | N/A | WB (1:5000) IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | NbVHH05-ALFA | This paper | N/A | WB (1:5000) IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | NbVHH05-hIgG | This paper | N/A | WB (1:100) IF (1:20) See *Note |
| Other | NbVHH05-555 | This paper | N/A | IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | NbVHH05-biotin (sortagging) | This paper | N/A | IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | NbVHH05 –555 (sortagging) | This paper | N/A | IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | Nb127D01-HA | This paper | N/A | WB (1:5000) IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | Nb127D01-ALFA | This paper | N/A | WB (1:5000) IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Other | Nb127D01-hIgG | This paper | N/A | WB (1:100) IF (1:20) See *Note |
| Other | Nb127D01-647 | This paper | N/A | IF (1:500) See *Note |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Phusion polymerase | New England Biolabs | Cat# M0530 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Q5 polymerase | New England Biolabs | Cat# M0494 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Taq polymerase | Clontech | Cat# TAKR001 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | EcoRI | New England Biolabs | Cat# R0101 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | XbaI | New England Biolabs | Cat# R0145 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | BglII | New England Biolabs | Cat# R0144 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | NheI | New England Biolabs | Cat# R3131 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | NsiI-HF | New England Biolabs | Cat# R3127 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | NcoI-HF | New England Biolabs | Cat# R3193 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | XhoI | New England Biolabs | Cat# R0146 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | BbsI | New England Biolabs | Cat# R0539 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | AarI | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# ER1581 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | T4PNK | New England Biolabs | Cat# M0201 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | T4 DNA ligase | New England Biolabs | Cat# M0202 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Fetal bovine serum | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# A3912 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Schneider’s media | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 21720–024 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin-streptomycin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15070–063 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ESF921 media | Expression Systems | Cat# 96–001 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Proteinase K | Roche | Cat# 3115879001 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | RNase A | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# EN0531 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail | Pierce | Cat# 78440 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trypsin inhibitor benzamidine | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 434760 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Rapamycin | LC Laboratories | Cat# R-5000 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | HRP-Conjugated Streptavidin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# N100 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Trehalase (prokaryote) | Megazyme | Cat# E-TREH | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Gibson assembly | New England Biolabs | Cat# E2611 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEBuilder HiFi assembly | New England Biolabs | Cat# E2621 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Golden Gate Assembly | New England Biolabs | Cat# E1601 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | pJET-1.2 vector kit | Fermentas | Cat# K1231 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | QIAquick Gel Extraction Kit | Qiagen | Cat# 28706 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | QIAquick Spin Columns | Qiagen | Cat# 28115 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Effectene | Qiagen | Cat# 301427 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | B-PER II Bacterial Protein Extraction Reagent | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 78260 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Mix-n-Stain CF 555 Antibody Labeling Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# MX555S100 RRID: AB_10960067 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Mix-n-Stain CF 647 Antibody Labeling Kit | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# MX647S100 RRID: AB_10961766 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Ni-NTA resin | EMD Millipore | Cat# 70691–3 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PD-10 column | GE Healthcare | Cat# GE17-0851-01 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Lysis buffer | Pierce | Cat# 87788 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SDS sample buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 39001 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | 4–20% polyacrylamide gel | Bio-Rad | Cat# 4561096 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagents | Amersham | Cat# RPN2209 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagents | Pierce | Cat# 34095 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | ALFA Selector ST resin | Nanotag Biotechnologies | Cat# N1511 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Pierce IP lysis buffer | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 87787 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Protein A magnetic beads | Bio-Rad | Cat# 1614013 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tetramethylbenzidine-containing solution | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# N301 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Glucose Hexokinase Reagents | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# TR15421 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pWalium10 | DGRC | Cat# 1470 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMK-33GW | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-26b | Novagen | Cat# 69862 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pQUASp-mCD8mCherry | Addgene | Cat# 46164 RRID: Addgene_46164 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBac (3xP3-gTc’v; pUb:lox-mYFP-lox-H2BmCherry) | Addgene | Cat# 119064 RRID: Addgene_119064 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pcDNA4TO-mito-mCherry-10xGCN4_v4 | Addgene | Cat# 60914 RRID: Addgene_60914 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | PXL-IE1-EGFP-nos-Cas9 | Xu et al., 2020 | N/A | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-2xHA-DsRed | Addgene | Cat# 80822 RRID: Addgene_80822 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCFD3 | Addgene | Cat# 49410 RRID: Addgene_49410 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-NbVHH05-GFP | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171570 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-Nb127D01-GFP | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171571 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-NbVHH05-mCherry | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171572 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-Nb127D01-mCherry | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171573 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-H2B-mCherry-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-mito-mCherry-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-mCherry-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-H2B-mCherry-127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-mito-mCherry-127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-mCherry-127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-VHH05-H2B-mCherry | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-VHH05-mCherry | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-127D01-H2B-mCherry | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-127D01-mCherry | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-BiP-NbVHH05-mCherry-KDEL | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171574 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-BiP-Nb127D01-mCherry-KDEL | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171575 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-NbVHH05-GFP | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171576 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-CD8-Nb127D01-GFP | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171577 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-2xVHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-3xVHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-2x127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAW-HGP-BiP-FLAG-GFP-3x127D01 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Akh-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Dilp2-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Dilp8-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Pvf1-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-127D01-REPTOR-bp-B-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-127D01-REPTOR-bp-C-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMT-HGP-v3-Nb127D01-hIgG | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171564 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pMT-HGP-v3-NbVHH05-hIgG | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171565 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-26b-Nb127D01-HA-His | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171566 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-26b-NbVHH05-HA-His | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171567 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-26b-Nb127D01-ALFA-His | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171568 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pET-26b-NbVHH05-ALFA-His | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171569 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-NbVHH05-HA | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-HA | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-Nb127D01-HA | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-HA | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-NbVHH05-GFP | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-GFP | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-Nb127D01-GFP | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-GFP | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-127D01-REPTOR-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Upd2-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pW10-UAS-BiP-127D01-Akh-VHH05 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pCFD3-H2Av-sgRNA | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-C-3x127D01-H2Av-DsRed | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-C-3xVHH05-H2Av-DsRed | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-C-3x127D01-DsRed | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171578 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-C-3xVHH05-DsRed | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171580 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-N-3x127D01-DsRed | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171579 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pScarlessHD-N-3xVHH05-DsRed | This paper Addgene | Cat# 171581 | |
| Cell line (Drosophila melanogaster) | S2R+ | DGRC | Cat# 150 RRID: CVCL_Z831 | FlyBase Report: FBtc0000150 |
| Cell line (Drosophila melanogaster) | ESF921-adapted S2 cells | Expression Systems | Cat# 94–005S | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w1118 | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | y,v; P{nos- phiC31\int.NLS}X; P{CaryP}attP40 | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | y,w; P{nos- phiC31\int.NLS}X; P{CaryP}attP2 | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | y,w; nos-Cas9/CyO | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | y,w; TM3, Sb/TM6,Tb | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; Gla/CyO | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; If/CyO; MKRS/TM6, Tb | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Myo1A-Gal4, tub-Gal80ts | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Lpp-Gal4 | Perrimon lab | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-NbVHH05-HA, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-NbVHH05-HA, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-Nb127D01-HA, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-Nb127D01-HA, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-NbVHH05-GFP, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-NbVHH05-GFP, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-Nb127D01-GFP, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-Nb127D01-GFP, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-HA, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-HA, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-HA, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-HA, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-GFP, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-NbVHH05-GFP, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-GFP, w + attp2 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-Nb127D01-GFP, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-BiP-VHH05-Upd2-127D01, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-VHH05-REPTOR-127D01, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | yw; UAS-VHH05-REPTOR-BP-C127D01, w + attp40 | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w; H2Av-3xVHH05/TM3, Sb | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w; H2Av-3x127D01/TM3, Sb | This paper | N/A | See *Note |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | TOP10 Escherichia coli | Invitrogen | Cat# C404010 | |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | BL21 (DE3) Escherichia coli | New England Biolabs | Cat# C25271 | |
| Sequence-based reagent | All oligos | This paper | See Supplementary file 1 | |
| Software, algorithm | Photoshop | Adobe | RRID:SCR_014199 | |
| Software, algorithm | ImageJ | NIH | RRID:SCR_003070 | |
| Software, algorithm | Excel | Microsoft | RRID:SCR_016137 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism6 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 | |
| Other | Joystick Micromanipulator | NARISHIGE | Cat# MN-151 | |
| Other | FemtoJet Microinjector | Eppendorf | Cat# LV41365120 | |
| Other | Garfunkel Nikon Ti2 Spinning Disk | Nikon | N/A | |
| Other | Kimble Kontes pellet pestles | Millipore | Cat# Z359947 | |
| Other | Immobilon-P polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane | Millipore | Cat# IPVH00010 | |
| Other | ChemiDoc MP imaging system | Bio-Rad | Cat# 17001402 | |
| Other | Kodak M35 X-OMAT Automatic Processors | KODAK | Cat# RT-KP-M35A | |
| Other | Hyperfilm ECL | Amersham | Cat# GE28-9068-35 | |
| Other | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# D1306 RRID: AB_2629482 | (1 µg/ml) |
-
*Note: Further information and requests for resources and reagents used in this paper should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the Lead Contact, Norbert Perrimon (perrimon@genetics.med.harvard.edu.). Transgenic flies used to express these two nanobodies and plasmids used to express and prepare nanobodies, which have been submitted to public reagent resource centers, Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center, Drosophila Genomics Resource Center and Addgene.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Primers used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-supp1-v2.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74326/elife-74326-transrepform1-v2.docx





