Genomic landscape of lymphatic malformations: a case series and response to the PI3Kα inhibitor alpelisib in an N-of-1 clinical trial
Figures
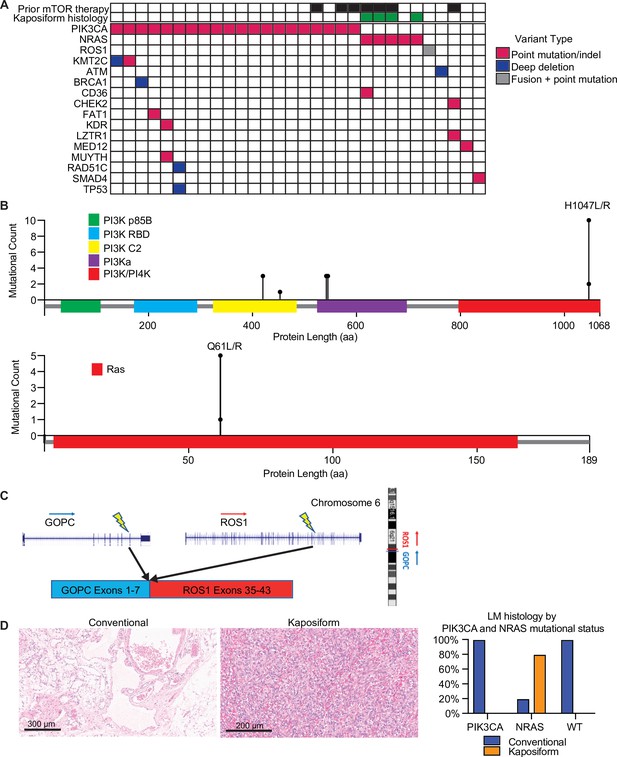
Mutational landscape and histopathology of lymphatic malformations (LMs).
(A) Oncoprint showing mutational landscape of 30 LM samples sequenced. (B) Lollipop plot showing spectrum of PIK3CA and NRAS mutations in this cohort. (C) Schema showing details of GOPC–ROS1 fusion identified in an NRAS and PIK3CA wild-type LM. (D) Representative histologic images for LMs with conventional and kaposiform histology. The relative frequencies of PIK3CA and NRAS mutations in the two histologic variants are plotted.
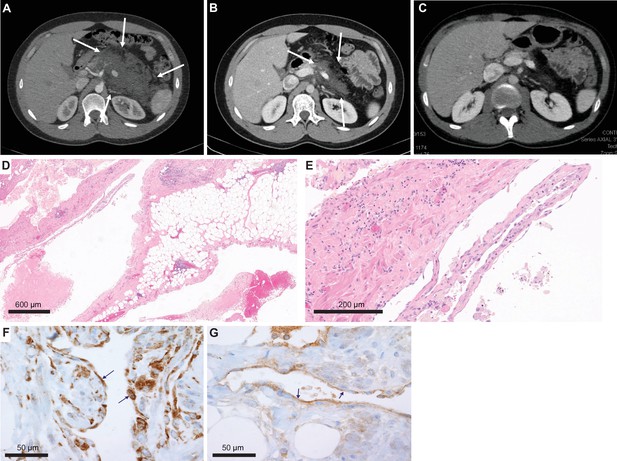
Imaging and histological analysis of lymphatic malformation (LM) patient.
(A) Baseline CT abdomen scan at the time of presentation demonstrating a large retroperitoneal/pancreatic LM. (B) CT abdomen scan 6 weeks after the initiation of alpelisib. (C) CT abdomen scan 1 year into the trial. (D, E) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained photomicrographs of the LM showing dilated lymphatic channels percolating through visceral fat and associated patchy lymphocytic inflammation (×4 and ×20, respectively). (F) Immunohistochemistry utilizing an anti-P-6S antibody demonstrates PI3Ka pathway activation within the channels’ lining cells. (G) Anti-P-AKT positivity in the lining endothelium of lymphatic channels as well.
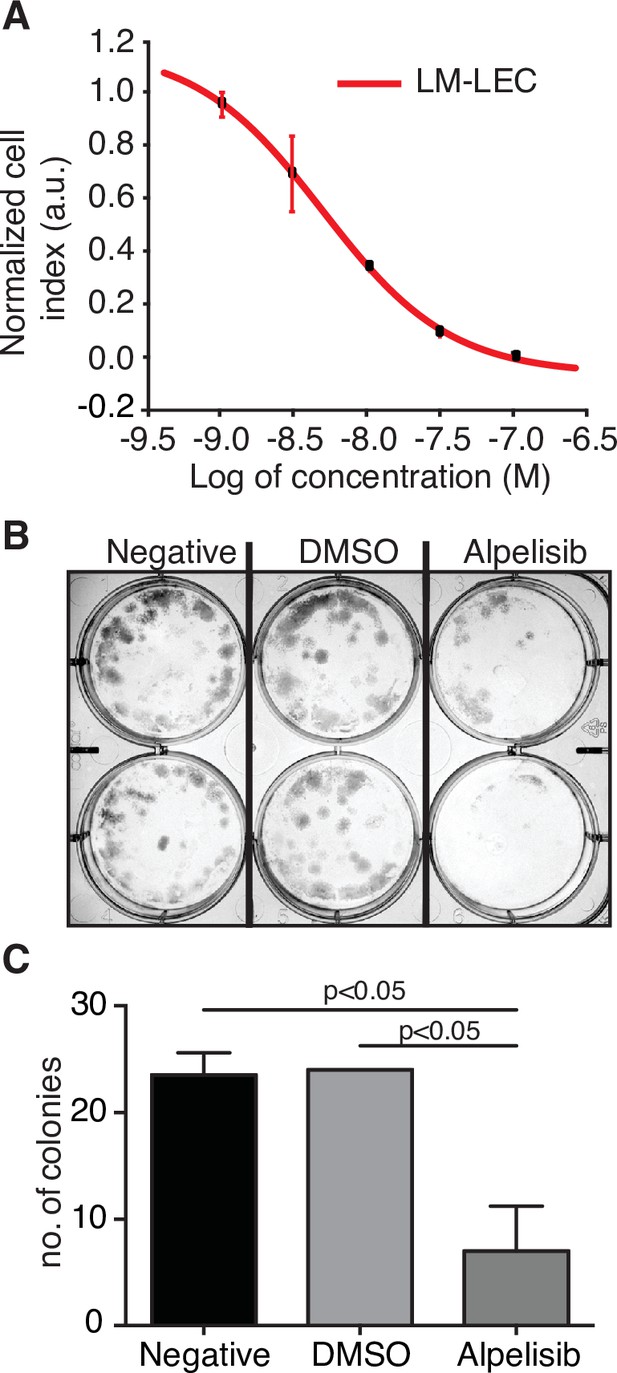
Alpelisib reduces lymphatic malformation-lymphatic endothelial cell (LM-LEC) viability.
(A) Logarithmic dose–response curve of alpelisib was performed using the xCELLigence RTCA system. 1, 3, 10, 30, and 100 nM (n = 5 replicates) of alpelisib were used to determine the concentration–response curve. The alpelisib half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated for LM-LEC at 24 hr after treatment as 4.72 × 10−9 M. Error bars are shown as mean +/- standard deviation (SD), which was automatically calculated for each data point by the xCELLigence RTCA system software (Version 2.0) based on five replicates per drug concentration. (B) Illustrative picture of LM-LEC clonogenic plaques at 24 hr after alpelisib treatment (4.72 × 10−9 M). Negative, no treatment; dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), vehicle control. Experiments were performed two times with similar results. LM-LEC colonies were stained with crystal violet (0.3%). (C) Colony count 24 hr after alpelisib treatment (4.72 × 10−9 M; n = 2 wells/condition). Error bars are shown as mean +/- SD calculated by GraphPad Prism by determining the square root of variance for each data point deviation relative to the mean.
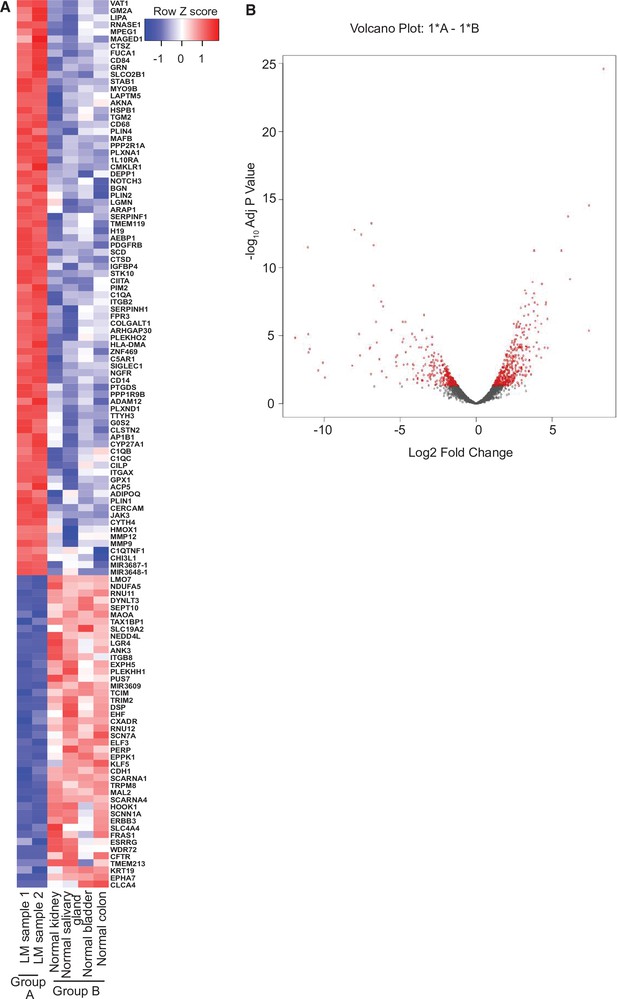
RNA-seq analysis of lymphatic malformation (LM) samples from index patient (#9).
(A) The heatmap summarizes the results of the differential gene expression analysis. Up- and downregulated genes are shaded red and blue, respectively. (B) The volcano plot summarizes the distribution of genes that were differentially expressed. The vertical axis shows the p value and the horizontal shows the fold-change. The genes that were more than twofold changed and had an adjusted p value less than 0.05 are shaded red. Similar numbers of genes were up- or downregulated.
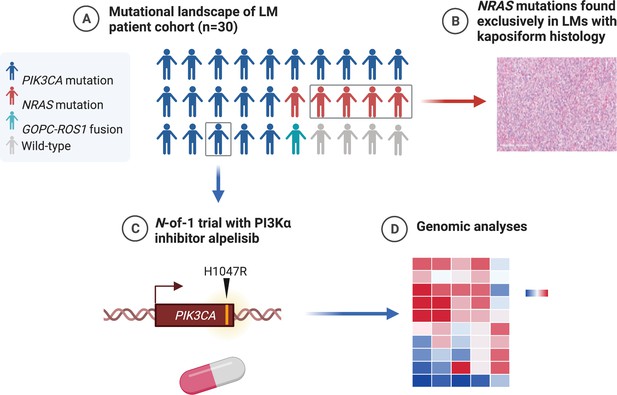
Graphical summary of the mutations found in genomic analysis of lymphatic malformation (LM) patient cohort (created with BioRender.com).
(A) The majority of LMs have driver mutations that are potentially targetable. (B) LMs with NRAS mutations had kaposiform histopathology. (C) An N-of-1 clinical trial is reported in a patient with a targetable PIK3CA mutation. (D) Comprehensive genomic analyses may reveal further actionable molecular insights.
Tables
Clinical and histological features of lymphatic malformation cohort.
| Patient | Age(years) | Sex | Submitted clinical syndrome | Localized vs. multifocal | Location of LM(s) | Specimen type | LM histology | PIK3CA or NRAS alteration | % VAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | M | CLOVES | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E542K | 14 |
| 2 | 4 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E542K | 7 | |
| 3 | 1 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 11 | |
| 4 | 17 | M | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 4 | |
| 5 | 18 | M | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047L | 4 | |
| 6 | 8 | F | Klippel–Trenaunay | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 9 |
| 7 | 9 | M | Localized | Visceral | Core biopsy | Conventional | PIK3CA E545K | 7 | |
| 8 | 3 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA C420R | 5 | |
| 9 | 23 | M | Localized | Visceral | Incisional biopsy | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 4 | |
| 10 | 16 | F | PTEN-like hamartoma | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 3 |
| 11 | 3 | F | CLOVES | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E545K | 12 |
| 12 | 1 | M | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 2 | |
| 13 | 4 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E542K | 6 | |
| 14 | 5 | M | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 5 | |
| 15 | 1 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E545K | 1 | |
| 16 | 14 | F | Multifocal | Visceral | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA C420R | 14 | |
| 17 | 2 | F | CLOVES | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA C420R | 38 |
| 18 | 16 | F | CLOVES | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA E453K | 32 |
| 19 | 10 | F | CLOVES | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047L | 15 |
| 20 | 9 | M | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | PIK3CA H1047R | 5 | |
| 21 | 9 | F | Multifocal | Visceral | Excision | Kaposiform | NRAS Q61R | 5 | |
| 22 | 8 | M | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Kaposiform | NRAS Q61R | 5 | |
| 23 | 9 | F | Multifocal | Visceral | Excision | Kaposiform | NRAS Q61R | 1 | |
| 24 | 45 | M | Multifocal | Visceral | Core biopsy | Conventional | NRAS Q61R | 6 | |
| 25 | 10 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Core biopsy | Kaposiform | NRAS Q61R | 14 | |
| 26 | 17 | M | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | WT | NA | |
| 27 | 24 | M | Localized | Bone | Core biopsy | Conventional | WT | NA | |
| 28 | 3 | M | Multifocal | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | WT | NA | |
| 29 | 11 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues | Excision | Conventional | WT | NA | |
| 30 | 9 | F | Localized | Superficial soft tissues, bone | Biopsy | Conventional | WT | NA |
-
CLOVES – congenital lipomatous overgrowth, vascular anomalies, epidermal nevi, and skeletal anomalies; NA – not applicable; VAF – variant allele frequency of PIK3CA or NRAS.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Somatic coding mutations identified from whole-genome sequencing.
The genetic coding variants that exist in lymphatic malformation (LM) but do not exist in germline DNA. These pass MuTect2 quality filters (designed to call somatic variants only) and have three or more alternate reads. VAF, variant allele frequency; COSMIC, Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74510/elife-74510-supp1-v1.docx
-
Transparent reporting form
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74510/elife-74510-transrepform1-v1.pdf





