ACE2 is the critical in vivo receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in a novel COVID-19 mouse model with TNF- and IFNγ-driven immunopathology
Figures
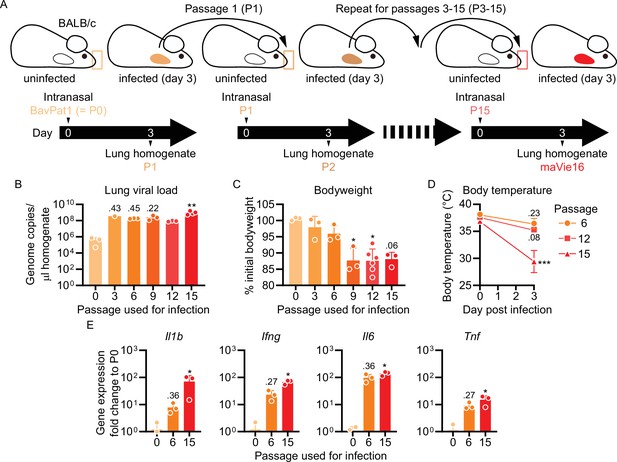
Serial pulmonary passaging of SARS-CoV-2 through BALB/c mice leads to mouse adaptation and generation of the mouse-virulent virus maVie16.
(A) Experimental strategy for generation of maVie16. BALB/c mice were intranasally inoculated with BavPat1 (passage 0/P0), followed by serial passaging of virus-containing cell-free lung homogenates of infected mice every 3 days. Passaging was repeated 15 times. (B) Lung tissue virus genome copy numbers (determined by real-time PCR) of mice 3 days after infection with virus of different passages as indicated. (C) Body weight (percentage of initial) of mice 3 days after infection. (D) Body temperature before and 3 days after infection. (E) Lung tissue expression fold change (compared to P0 mean; analyzed by real-time PCR) of indicated genes 3 days after infection. (B–E) n = 1–3; (B, C, E) symbols represent individual mice; Kruskal–Wallis test (vs. P0) with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test; (D) mean ± SD; two-way ANOVA with Sidak test (vs. the respective initial body temperature); *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001; numbers above bars show the actual p-value.
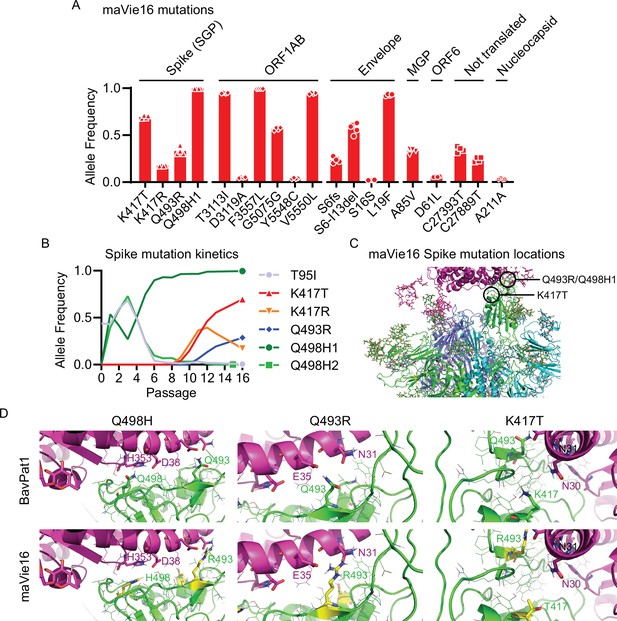
maVie16 possesses a distinct pattern of mutations and mediates in vivo pathology via angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2).
(A) Overview of allele frequencies of mutated amino acids detected in maVie16 by sequencing. Labels on top indicate the associated protein (SGP, Spike glycoprotein; ORF, open reading frame; MGP, membrane glycoprotein). (B) Spike protein mutation dynamics. (C) Modeling and location of Spike mutations. Spike trimer in cyan blue and green, mACE2 in magenta cartoon representation. Glycans in stick representations. (D) Modeling of specific BavPat1 (upper row) and maVie16 (lower row) amino acid regions in green (respective mutated positions are highlighted in yellow and labeled in green) and their interaction with mouse ACE2 (in magenta; positions of interest are labeled in magenta or black).
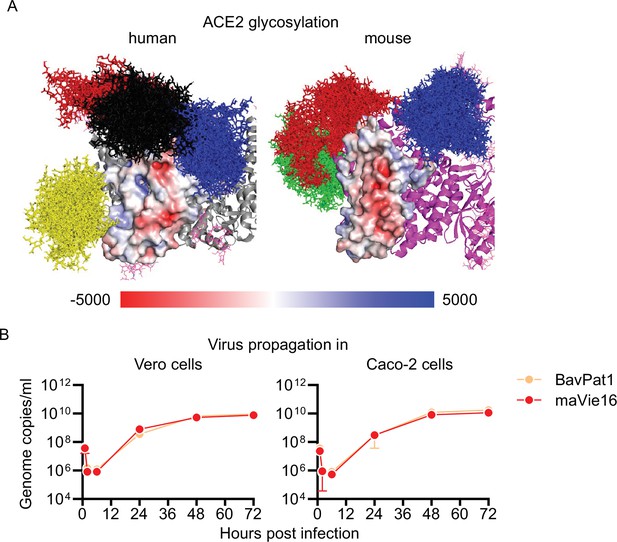
Mouse versus human angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) glycosylation and maVie16 in vitro proliferation.
(A) Surface representation of the binding interface of human (gray cartoon) and mouse (magenta cartoon) ACE2, colored according to the electrostatic potential. Red surface corresponds to a negative potential and blue surface to a positive potential. Note the more distinct pattern of negatively charged areas in the mouse ACE2 protein. A bundle of glycan conformations is shown in sticks for the glycans at N53 (blue), N90 (yellow), N322 (black), and N546 (red) in human ACE2 and at N53 (blue), N536 (green), and N546 (red) in mouse ACE2. (B) SARS-CoV-2 genome copy numbers in Vero and Caco-2 cells at indicated time points after infection with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) 0.5 of BavPat1 or maVie16.
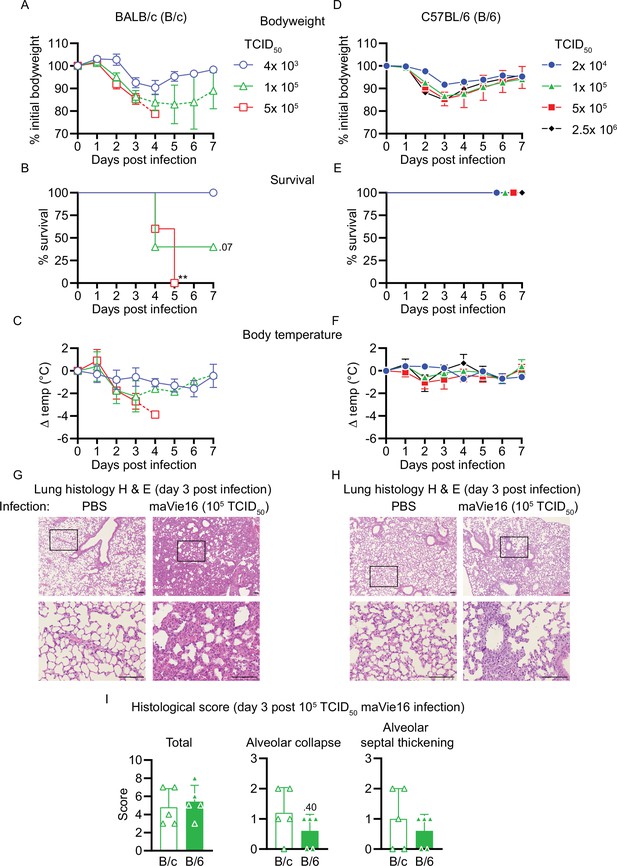
Respiratory maVie16 infection causes dose-dependent pathology in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice.
(A–C, G) BALB/c (B/c) or (D–F, H) C57BL/6 (B/6) mice were intranasally inoculated with different doses of maVie16 as indicated and monitored for (A, D) body weight, (B, E) survival and (C, F) body temperature over 7 days; dashed lines in (A) and (C) indicate trajectories of groups lacking full group size due to death of animals (see B). (G, H) Lung sections (hematoxylin and eosin stain) from mice 3 days after infection with 105 TCID50 maVie16; black rectangles in the upper pictures indicate the area magnified in the respective lower row picture; scale bars indicate 100 µm. (I) Histological score for analysis of lung sections as described in (G) and (H); symbols represent individual mice; (A, C, D, F) mean ± SD; (B) Mantel–Cox test (vs. 4 × 103 TCID50); **p≤0.01; the number next to the symbol shows the actual p-value.
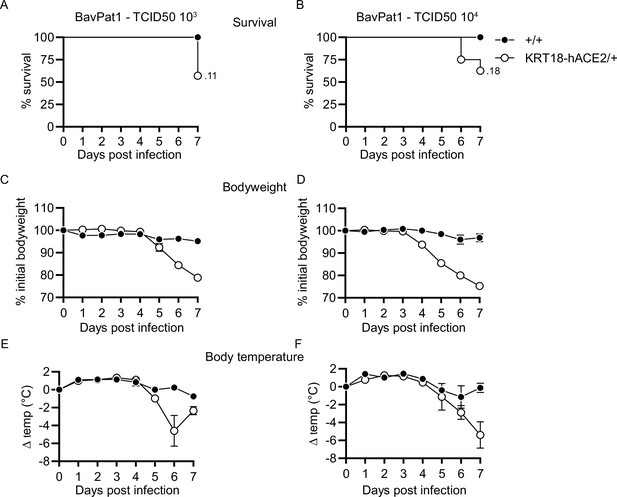
Disease kinetics of BavPat1-infected KRT18-hACE2 mice.
(A–F) Mice expressing human ACE2 under control of the human KERATIN-18 promoter (KRT18-hACE2/+) and control animals (+/+) were intranasally inoculated with (A, C, E) 103 or (B, D, F) 104 TCID50 of BavPat1 and monitored over 7 days. (A, B) Survival; (C, D) body weight; (E, F) temperature; (A–F) n = 4–7; (E, F) mean ± SD.
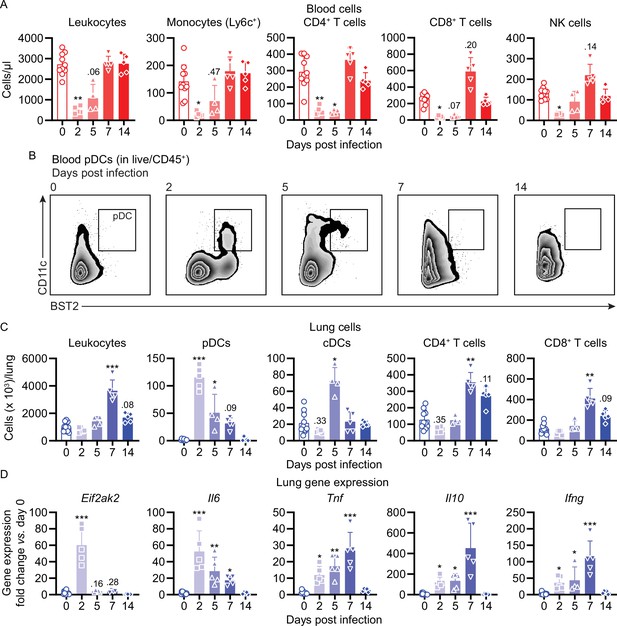
Mouse COVID-19 (mCOVID-19) is associated with transient lymphopenia, pulmonary dendritic cell, and T cell infiltration and pneumonia.
C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with PBS ( = group 0) or 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and sacrificed after 2, 5, 7, or 14 days for subsequent analysis. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of blood cell populations. (B) Density plot representation of blood plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs; identified as live/CD45+/CD11c+/BST2+) analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of whole lung cell populations (see Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for gating strategies). (D) Lung tissue expression fold change (compared to group 0 mean; analyzed by real-time PCR) of indicated genes from mice at the respective time points after infection. (A, C, D): symbols represent individual mice; Kruskal–Wallis test (vs. group 0) with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test; *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001.
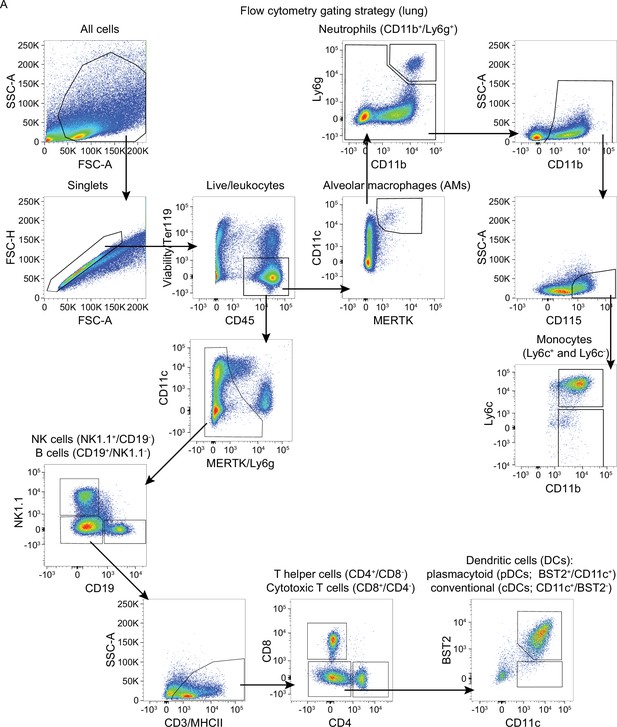
Flow cytometry gating strategy for lung cells.
C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with PBS ( = group 0) or 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and sacrificed after 2, 5, 7, or 14 days for subsequent analysis. (A) Example of the flow cytometry gating strategy for immune cell populations (shown in Figure 4C and Figure 4—figure supplement 2B). The sample is derived from an infected mouse 2 days post infection.
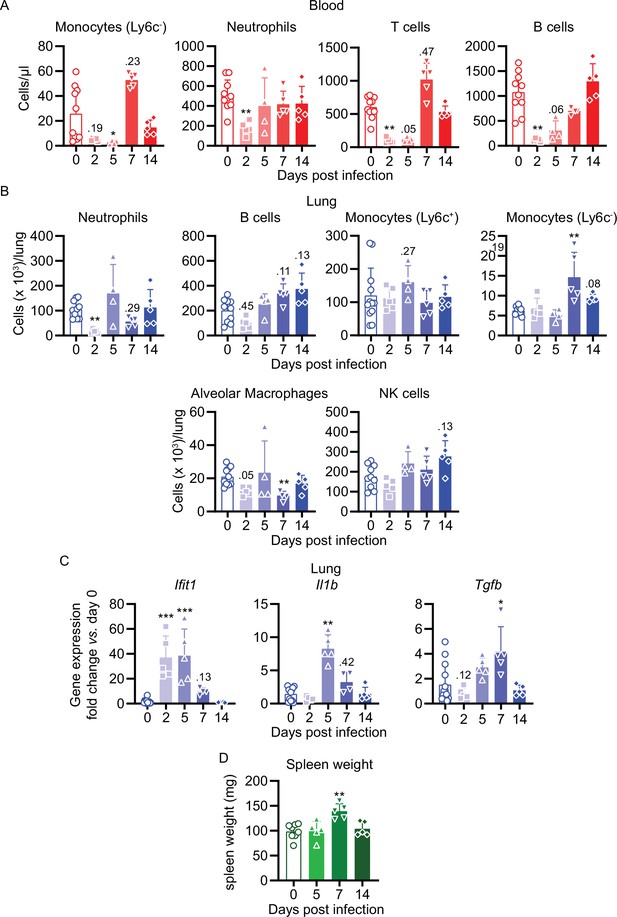
Cellular, transcriptional, and spleen weight kinetics of maVie16-infected C57BL/6 mice.
C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with PBS ( = group 0) or 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and sacrificed after 2, 5, 7, or 14 days for subsequent analysis. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of blood cell populations. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of whole lung cell populations (see Figure 4—figure supplement 1 for gating strategies). (C) Lung tissue expression fold change (compared to group 0 mean; analyzed by real-time PCR) of indicated genes from mice at the respective time points after infection. (D) Spleen weight at indicated time points after infection. (A–D) symbols represent individual mice; Kruskal–Wallis test (vs. group 0) with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test; *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001.
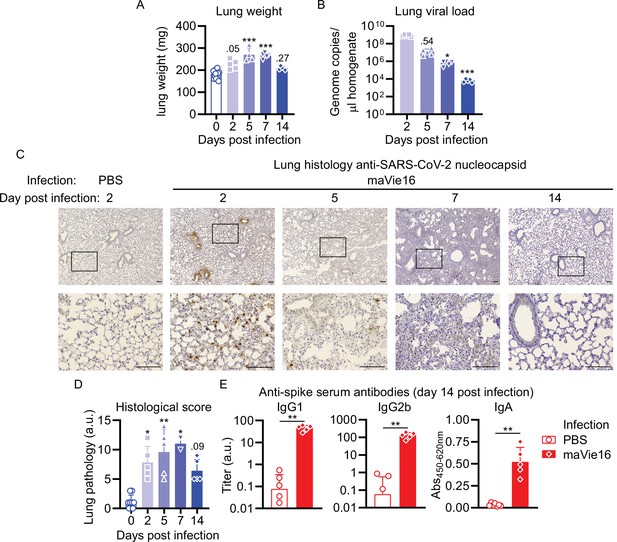
Mouse COVID-19 (mCOVID-19) is associated with transient pneumonia and antigen-specific adaptive immunity.
C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with PBS ( = group 0 or PBS) or 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and sacrificed after 2, 5, 7, or 14 days for subsequent analysis. (A) Lung tissue virus genome copy numbers (determined by real-time PCR). (B) Lung tissue weight. (C) Representative lung immunohistochemistry (anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid stain, counterstained with hematoxylin) pictures; black rectangles in the upper pictures indicate the area magnified in the respective lower row picture; scale bars represent 100 µm. (D) Lung pathology score based on histological analysis of lung tissue sections. (E) Analysis (by ELISA) of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-specific IgG1, IgG2b, and IgA plasma antibody titers 14 days after infection. (A, B, D, E) Mean + SD; symbols represent individual mice; (A, B, D): Kruskal–Wallis test (vs. [A] day 2 or [B, D] group 0) with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test; (E) Mann–Whitney test; *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001.
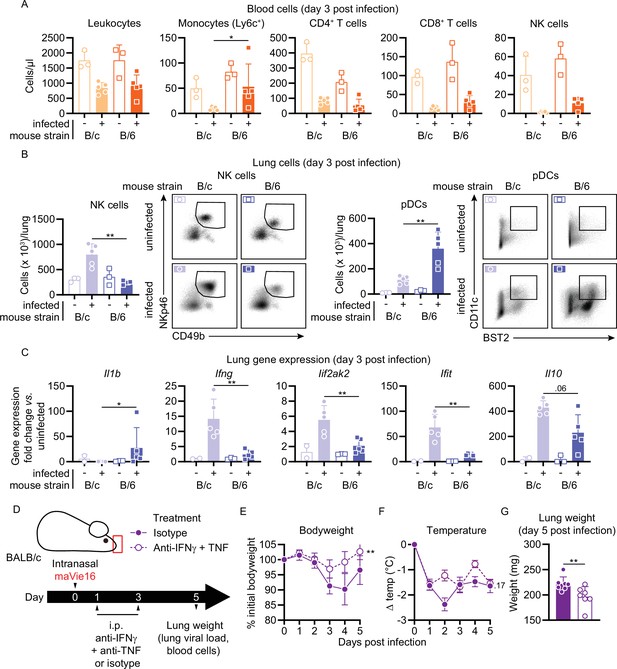
BALB/c mouse COVID-19 (mCOVID-19) is associated with an increased NK cell and interferon response and is ameliorated by IFNγ and TNF blockade.
BALB/c (B/c) and C57BL/6 (B/6) mice were intranasally inoculated with 105 TCID50 maVie16 (+) or PBS (-). Samples for analyses were collected 3 days after infection. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of blood cell populations. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of whole lung NK cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). Density plots represent examples of respective cell populations (NK cells pre-gated from live/CD45+/Ly6G-/CD3-; pDCs pre-gated from live/CD45+) (C) Lung tissue expression fold change (compared to the respective mean of uninfected samples; analyzed by real-time PCR) of indicated genes. (D) Experimental scheme for (E–G). BALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated intraperitoneally on days 1 and 3 post infection (p.i.) with a mix of 500 µg anti-IFNγ and anti-TNF or with isotype control antibody. (E) Body weight and (F) temperature kinetics over 5 days after infection. (G) Lung weight on day 5 after infection. (A–C, G) Mean + SD; symbols represent individual mice; differences between infected groups were assessed using the Mann–Whitney test; (E, F) mean ± SD; two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (vs. the respective initial body weight or temperature); in panels without respective labels, the groups were not significantly different (p<0.05); *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01.
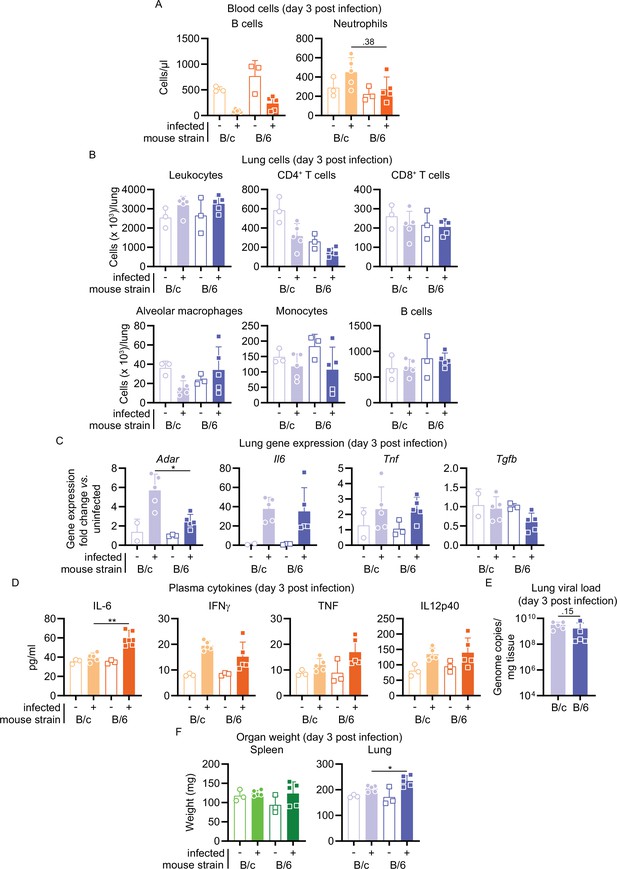
Comparison of cellular, transcriptional, and organ weight of maVie16-infected BALB/c versus C57BL/6 mice.
BALB/c (B/c) and C57BL/6 (B/6) mice were intranasally inoculated with 105 TCID50 maVie16 (+) or PBS (-). Samples for analyses were collected 3 days after infection. (A) Flow cytometry analysis of blood cell populations. (B) Flow cytometry analysis of indicated lung cell populations in whole tissue. (C) Lung tissue expression fold change (compared to the respective mean of uninfected samples; analyzed by real-time PCR) of indicated genes. (D) Plasma levels of indicated cytokines (assessed by multiplex cytokine analysis). (E) Lung tissue virus genome copy numbers (determined by real-time PCR). (F) Weight of spleen and lung. (A–F) Mean + SD; symbols represent individual mice; differences between infected groups were assessed using the Mann–Whitney test; in panels without respective labels, the groups were not significantly different (p<0.05); *p≤0.05.
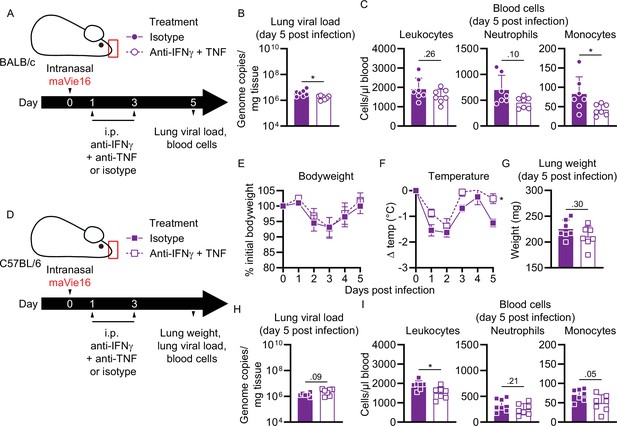
Disease parameters of maVie16-infected Ace2-deficient mice, and of infected BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice treated with anti-IFNγ and -TNF blocking antibodies.
(A) Experimental scheme for (B) and (C). BALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated intraperitoneally on days 1 and 3 post infection (p.i.) with a mix of 500 µg anti-IFNγ and anti-TNF or with isotype control antibody. (B) Lung viral load and (C) blood cell numbers 5 days p.i.; (D) experimental scheme for (E–I). C57BL/6 mice were infected with 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated intraperitoneally on days 1 and 3 p.i. with a mix of 500 µg anti-IFNγ and anti-TNF or with isotype control antibody. (E) Body weight and (F) temperature kinetics over 5 days after infection. (G) Lung weight, (H) lung viral load, and (I) blood cell numbers 5 days p.i.; (B, C, G–I) mean + SD; Mann–Whitney test; (E, F) mean ± SD; two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (vs. the respective initial body weight or temperature); *p≤0.05; ns, not significant (p>0.05).
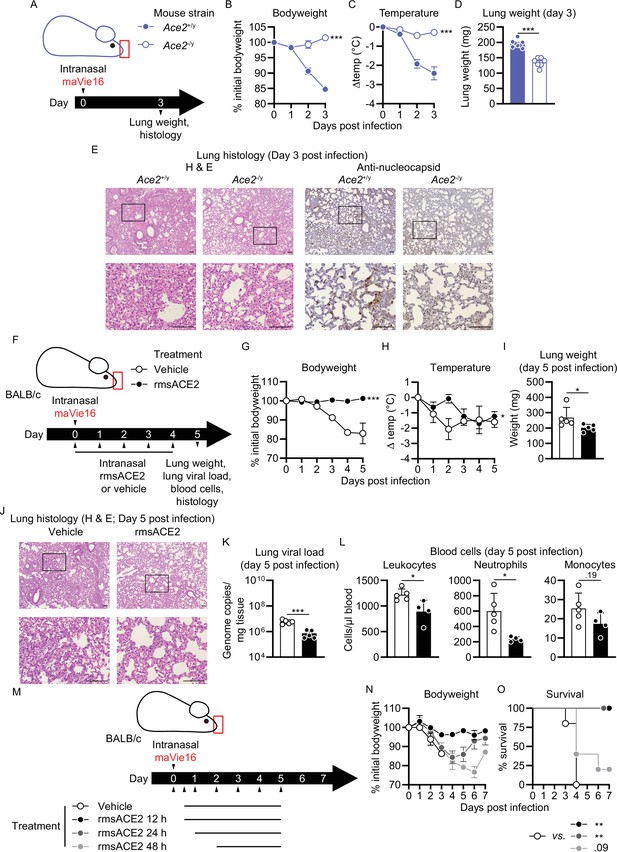
Mouse COVID-19 (mCOVID-19) pathology depends on Ace2 and is improved by recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) administration.
(A) Experimental scheme for (B–E): male Ace2-deficient (Ace2-/y) or control (Ace2+/y) mice were infected with 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16. (B) Body weight and (C) temperature kinetics over 3 days after infection. (D) Lung tissue weight 3 days post infection (p.i.). (E) Lung histology 3 days after infection (left panels: hematoxylin and eosin stain; right panels: anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid immune-stain); black rectangles in the upper pictures indicate the area magnified in the respective lower row picture; scale bars represent 100 µm. (F) Experimental scheme for (G–L). BALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated daily intranasally up to day 4 p.i. with 100 µg recombinant murine soluble (rms) ACE2 or vehicle (the first treatment was administered together with virus). (G) Body weight and (H) temperature kinetics over 5 days after infection. (I) Lung weight, (J) lung histology (hematoxylin and eosin stain), (K) lung viral load, and (L) blood cells on day 5 after infection. (M) Experimental scheme for (N) and (O). BALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated daily, intranasally up to day 5 p.i. with 100 µg rms ACE2 or vehicle. The first treatment was administered either 12 hr, 24 hr, or 48 hr p.i. (N) Body weight and (O) survival over 7 days of infection. (B, C, G, H, N, O) mean ± SD; two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (vs. the respective initial body weight or temperature); (D, I, K, L) Mann–Whitney test; * p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001; ns, not significant (p>0.05).
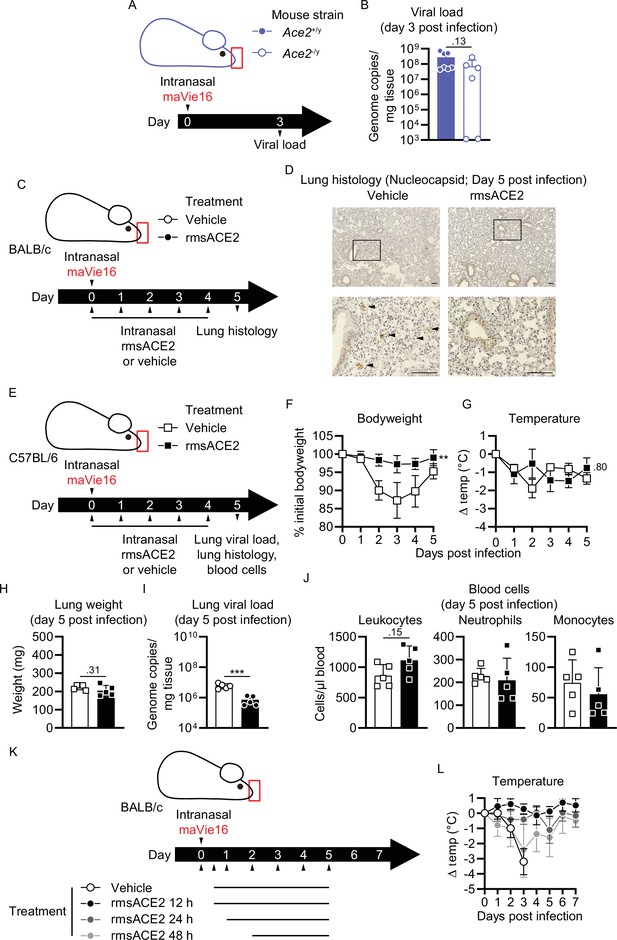
Disease parameters of maVie16-infected Ace2-deficient mice, and of infected BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice treated with recombinant mouse angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2).
(A) Experimental scheme for (B): male Ace2-deficient (Ace2-/y) or control (Ace2+/y) mice were infected with 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16. (B) Lung viral load 3 days post infection (p.i.). (C) Experimental scheme for (D). BALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated daily intranasally up to day 4 p.i. with 100 µg recombinant murine soluble (rms) ACE2 or vehicle (the first treatment was administered together with virus). (D) Lung histology (anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid immune stain) on day 5 after infection; black rectangles in the upper pictures indicate the area magnified in the respective lower row picture; arrowheads indicate infected (nucleocapsid-positive) cells; scale bars represent 100 µm. (E) Experimental scheme for (F–J). C57BL/6 mice were infected with 5 × 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated daily intranasally up to day 4 p.i. with 100 µg rms ACE2 or vehicle (the first treatment was administered together with virus). (F) Body weight and (G) temperature kinetics over 5 days after infection. (H) Lung weight, (I) lung viral load, and (J) blood cells on day 5 after infection; (K) Experimental scheme for LBALB/c mice were infected with 105 TCID50 maVie16 and treated daily, intranasally up to day 5 p.i. with 100 µg recombinant murine soluble (rms) ACE2 or vehicle. The first treatment was administered either 12h, 24h or 48h p.i. (L) Body temperature over 7 days of infection. (B, H–J) mean + SD; Mann–Whitney test; (F, G, L) mean ± SD; two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test (vs. the respective initial body weight or temperature); **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001; ns, not significant (p>0.05).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Mus musculus, male) | BALB/cJ | Own colony, Jackson Labs | JAX #000651 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus, male) | C57BL/6J | Own colony, Jackson Labs | JAX #000664 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus, male) | KRT18-hACE2 | Own colony, Jackson Labs | JAX #034860 | |
| Strain, strain background (M. musculus, male) | Ace2-/y | Own colony, Jackson Labs Crackower et al., 2002 | ||
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2) | BavPat1/2020 | Charité, Berlin, Germany | European Virology Archive# 026V-03883 | |
| Strain, strain background (SARS-CoV-2) | maVie16 | This study | This study | |
| Cell line (Chlorocebus) | Vero | ATCC | CCL-81 | |
| Cell line (Chlorocebus) | Vero TMPRSS2 (OE) | This study | This study | |
| Cell line (human) | Caco-2 | ATCC | HTB37 | |
| Antibody | Fixable Viability Dye eFluor 780 | Thermo Fisher, eBioscience | Cat# 65-0865-14 | FC (1:3000) |
| Antibody | anti-mouse CD16/32 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 101320; RRID:AB_1574975 | FC (1:50) |
| Antibody | BV510 anti-mouse CD45 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 103138; RRID:AB_2563061 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD45 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 103106; RRID:AB_312971 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE/dazzle 594 anti-mouse CD45.2 (monoclonal mouse) | BioLegend | Cat# 109845; RRID:AB_2564176 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD45R (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 103208; RRID:AB_312993 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse F4/80 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 123110; RRID:AB_893486 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 700 anti-mouse CD11b (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 101222; RRID:AB_493705 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD11b (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 101215; RRID:AB_312798 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Brilliant Violet 605 anti-mouse CD11b (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 101237; RRID:AB_11126744 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD11b (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 101208; RRID:AB_312791 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | APC anti-mouse CD11c (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | BioLegend | Cat# 117310; RRID:AB_313779 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE-Texas Red anti-mouse CD11c (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# MCD11C17;RRID:AB_10373971 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD11c (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 557401; RRID:AB_396684 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Brilliant Violet 510 anti-mouse Ly-6C (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 128033; RRID:AB_2562351 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE/Cy7 anti-mouse Ly-6G (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 127617; RRID:AB_1877262 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse Ly-6G (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 127605; RRID:AB_1236488 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | BV510 anti-mouse Ly-6G (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 127633; RRID:AB_2562937 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse Ly6G (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 127608; RRID:AB_1186099 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PerCP-Cy5.5 Siglec-F (monoclonal rat) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 565526; RRID:AB_2739281 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | eFluor 450 anti-mouse MHC Class II (I-A/I-E) (monoclonal rat) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 48-5321-82; RRID:AB_1272204 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | BV605 anti-mouse CD115 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 135517; RRID:AB_2562760 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse CD19 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 115506; RRID:AB_313641 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | BV605 anti-mouse CD19 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 115540; RRID:AB_2563067 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD19 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 115507; RRID:AB_313642 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse CD3 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100204; RRID:AB_312661 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE/Dazzle 594 anti-mouse CD3 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100245; RRID:AB_2565882 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-mouse CD3 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100217; RRID:AB_1595597 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | eFluor450 anti-mouse CD3 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100213; RRID:AB_493644 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD3 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100205; RRID:AB_312662 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse CD4 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100406; RRID:AB_312691 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | AF700 anti-mouse CD4 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100429; RRID:AB_493698 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-mouse CD4 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100433; RRID:AB_893330 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD4 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100407; RRID:AB_312692 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | AF700 anti-mouse CD8a (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100729; RRID:AB_493702 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Pacific Blue anti-mouse CD8a (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100728; RRID:AB_493426 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse CD8a (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 100707; RRID:AB_312746 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse TCRβ chain (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | BioLegend | Cat# 109207; RRID:AB_313430 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse TCRγδ (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | BioLegend | Cat# 118107; RRID:AB_313831 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-mouse NK-1.1 (monoclonal mouse) | BioLegend | Cat# 108727; RRID:AB_2132706 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | APC anti-mouse NK-1.1 (monoclonal mouse) | BioLegend | Cat# 108709; RRID:AB_313396 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse FcεRIα (monoclonal Armenian hamster) | BioLegend | Cat# 134307; RRID:AB_1626104 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PE/Cy7 anti-mouse CD117 (c-kit) (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 105813; RRID:AB_313222 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | BV421 anti-mouse CD193 (CCR3) (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 144517; RRID:AB_2565743 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | Alexa Fluor 647 anti-mouse CD49b (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 108912; RRID:AB_492880 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | AF700 anti-mouse CD49b (monoclonal rat) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 56-5971-80; RRID:AB_2574506 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PE/Dazzle 594 anti-mouse CD64 (FCγRI) (monoclonal mouse) | BioLegend | Cat# 139319; RRID:AB_2566558 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | AF700 anti-mouse CD43 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 143213; RRID:AB_2800660 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | APC anti-mouse CD44 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 103012; RRID:AB_312963 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | BV510 anti-mouse CD138 (monoclonal rat) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 563192; RRID:AB_2738059 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PerCP/Cy5.5 anti-mouse CD21/CD35 (CR2/CR1) (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 123416; RRID:AB_1595490 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | AF647 anti-mouse CD23 (monoclonal rat) | BD Biosciences | Cat# 562826; RRID:AB_2737821 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE-Cy7anti-mouse CD93 (AA4.1) (monoclonal rat) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 25-5892-82; RRID:AB_469659 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | eFluor450 anti-mouse CD90.2 (Thy1.2) (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 140305; RRID:AB_10645335 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse MERTK (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 151504; RRID:AB_2617035 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse MERTK (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 151505; RRID:AB_2617036 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | BV605 anti-mouse CD127 (IL-7α) (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 135025; RRID:AB_2562114 | FC (1:100) |
| Antibody | eFluor450 anti-mouse IgM (monoclonal rat) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 48-5890-82;RRID:AB_10671539 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | FITC anti-mouse IgD (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 405704; RRID:AB_315026 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | PE anti-mouse IgA (monoclonal rat) | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 12-4204-83; RRID:AB_465918 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | BV605 anti-mouse CD62L (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 104438; RRID:AB_2563058 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | APC/Cy7 anti-mouse TER-119 (monoclonal rat) | BioLegend | Cat# 116223; RRID:AB_2137788 | FC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Biotin anti-mouse IgG1 (monoclonal rat) | BD Pharmingen | Cat# 553441 | ELISA (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Biotin anti-mouse IgG2b (monoclonal rat) | BD Pharmingen | Cat# 553393 | ELISA (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Biotin anti-mouse IgA (polyclonal goat) | Southern Biotech | Cat# 1040-08 | ELISA (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Anti-SARS nucleocapsid (polyclonal rabbit) | Novus Biologicals | Cat# NB100-56576 | IHC (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Biotin anti-rabbit IgG (polyclonal goat) | Vector Labs | Cat# BA-1000 | IHC (1:200) |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse TNF (neutralizing) (monoclonal rat) | In house | Clone XT22 | 2 × 500 µg/200 µl/mouse i.p. |
| Antibody | Anti-mouse IFNg (neutralizing) (monoclonal rat) | In house | Clone XMG 1.2 | 2 × 500 µg/200 µl/mouse i.p. |
| Antibody | Anti-ß-galactosidase (IgG1 isotype control) (monoclonal rat) | In house | Clone GL113 | 2 × 500 µg/200 µl/mouse i.p. |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIRES2-AcGFP1 (Plasmid) | Clontech | Cat# 632435 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pIRES2-SC2quant | This study | Plasmid containing a PCR-amplified sequence of BavPat1; used as standard for quantification of virus genome copy numbers | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBluescript KS(-) | Stratagene | Cat# 212208 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBMN-I-GFP | Addgene | Plasmid 1736 | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pBMN-TMPRSS2-I-GFP | This study | Plasmid containing the PCR-amplified coding sequence of human TMPRSS2; used to transfect Vero cells to enhance in vitro virus propagation | |
| Sequence-based reagent | CoV-F3_XhoI | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CTCGAGTTTCCTGGTGATTCTTCTTCAGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | CoV-R3_BamHI | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CCTAGGTCTGAGAGAGGGTCAAGTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | CoV-F3 | Gu et al., 2020 | PCR primers, Microsynth | TCCTGGTGATTCTTCTTCAGGT |
| Sequence-based reagent | CoV-R3 | Gu et al., 2020 | PCR primers, Microsynth | TCTGAGAGAGGGTCAAGTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | CoV-P3 | Gu et al., 2020 | PCR primers, Microsynth | AGCTGCAGCACCAGCTGTCCA (FAM/TAMRA-labeled) |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Adar1_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GATGACCAGTCTGGAGGTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Adar1_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GCAGCAAAGCCATGAGATCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Eif2ak2_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | AAGTACAAGCGCTGGCAGAA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Eif2ak2_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GCACCGGGTTTTGTATCGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Ifng_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | ACTGGCAAAAGGATGGTGACA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Ifng_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | TGGACCTGTGGGTTGTTGAC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Ifit1_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CAGCAACCATGGGAGAGAATGCTGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Ifit1_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GGCACAGTTGCCCCAGGTCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il1b_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CAAAATACCTGTGGCCTTGG |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il1b_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | TACCAGTTGGGGAACTCTGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il6_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CCACGGCCTTCCCTACTTCA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il6_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | TGCAAGTGCATCGTTGTTC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il10_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | TGAGGCGCTGTCATCGATTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Il10_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | CATGGCCTTGTAGACACCTT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Tgfb_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | AGCCCGAAGCGGACTAT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Tgfb_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | TCCACATGTTGCTCCACACT |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Tnf_fwd | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GCGTGGAGCTGAGAGATAACC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Mouse Tnf_rev | This study | PCR primers, Microsynth | GATCCCAAAGTAGACCTGCCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | Human TMPRSS2_fwd | This study | PCR primers | AACCTGGGCGCCTGGGA |
| Sequence-based reagent | Human TMPRSS2_rev | This study | PCR primers | ACGTCAAGGACGAAGACCATGTG |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Collagenase I | Gibco/Thermo Fisher Scientific | 17018029 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | DNAse I | Sigma | DN25 | |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein ectodomain | Reingard Grabherr, BOKU Vienna Klausberger et al., 2021 | ||
| Peptide, recombinant protein | mrsACE2 | In house (APEIRON Biologics) Monteil et al., 2020 | ||
| Commercial assay or kit | ROTI Prep RNA Mini | Carl Roth | Cat# 8485.1 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit | QIAGEN | Cat# 52904 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | E.Z.N.A Viral RNA kit | Omega Bio-tek | Cat# R6874 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | qScript cDNA Synthesis Kit | Quantabio | Cat# 95047-500 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | PerfeCTa SYBR Green SuperMix | Quantabio | Cat# 95055 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | VectastainABC kit | Vector Labs | Cat# PK-6100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | DAB Substrate kit | Vector Labs | Cat# SK-4100 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | LEGENDplex Macrophage/Microglia Panel | BioLegend | Cat# 740846 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | LEGENDplex MU Th Cytokine Panel V02 | BioLegend | Cat# 740741 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Sodium pyruvate (100 mM) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11360070 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Penicillin streptomycin (10,000 U/ml) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 15140122 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | MEM nonessential amino acids (100×) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 11140050 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | RLT Plus | QIAGEN | Cat# 1053393 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | 2-Mercaptoethanol | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# M3148 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Antigen Unmasking Solution | Vector Labs | Cat# H3300-250 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Hematoxylin solution (Mayer’s) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# MHS16 | |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 9.1 | GraphPad Software, Inc. | https://www.graphpad.com | |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo | Becton, Dickinson and Company | https://www.flowjo.com/ | |
| Other | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 10564011 | High glucose, GlutaMAX, HEPES |
| Other | Fetal bovine serum | Sigma | Cat# F9665 | |
| Other | Goat serum | Novus Biologicals | Cat# NBP2-23475 |





