Intact Drosophila central nervous system cellular quantitation reveals sexual dimorphism
Figures
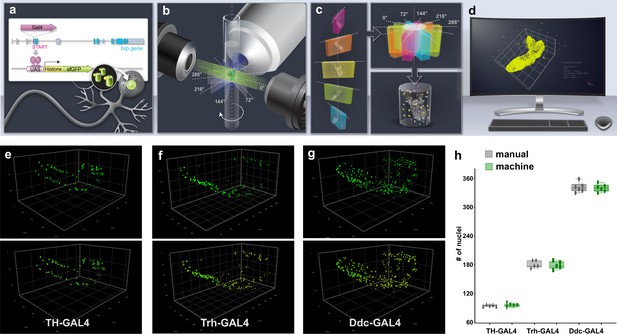
Intact whole CNS quantitation pipeline schematic and validation.
(a–d) Illustration of an intact whole central nervous system (CNS) genetic, imaging and computational pipeline. (a) Genetic reagents: GAL4 is introduced into the exons of genes encoding synaptic proteins (e.g. bruchpilot [brp]) to capture their expression pattern with high fidelity. GAL4 expression regulates the production of UAS fluorescent-histone reporters, which target to the nucleus of cells, producing a punctate signal. (b) Imaging: the intact CNS is imaged at high resolution using light-sheet microscopy. Images are captured at five different angles at 72° intervals. (c) Assembly: multiview light sheet images are registered, fused, and deconvolved. (d) Quantitation: the volume is segmented, and the nucleus number and relative position are measured. Three-dimensional coordinates of the geometric centre of every nucleus can be calculated to produce a point cloud of nuclei positions.(e–h) Pipeline validation. Three-dimensional images before segmentation (above) and subsequent to segmentation (below) of (e) dopaminergic (TH-GAL4) neurons, (f) serotonergic neurons (Trh-GAL4) and (g) dopa decarboxylase expressing (Ddc-GAL4) neurons. (h) Manual or automated quantification of nuclei numbers in these volumes are similar. Scale squares in (e) and (g) are 100 μm and in (f) is 50 μm. (h) Bars indicate minimum and maximum values.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
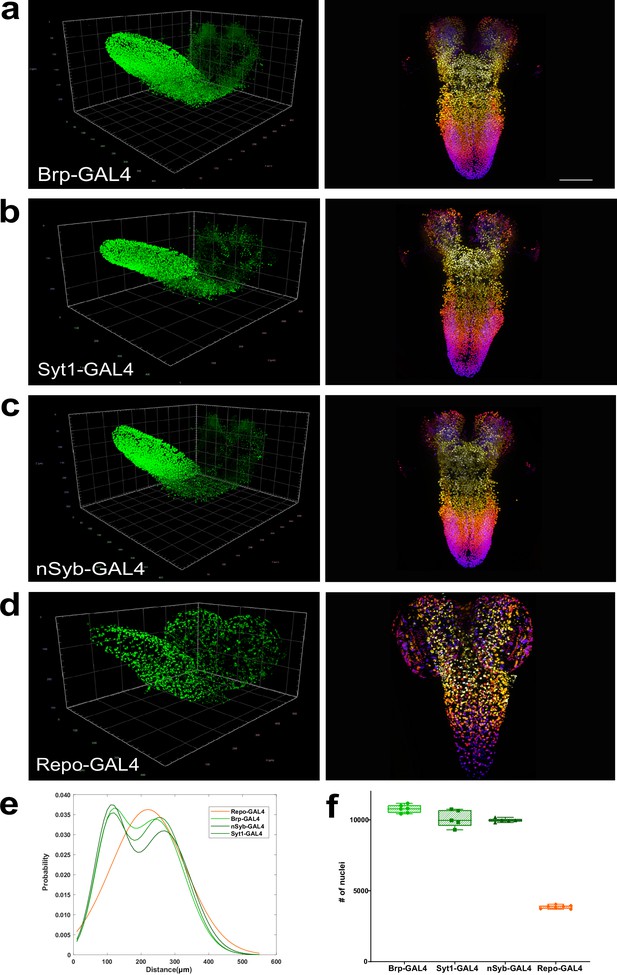
Quantitation of neurons and glia in the whole female larval CNS.
(a–d) Multiview deconvolved images (left) and z-stack projections (right) (colours represent z position) of the central nervous system (CNS) of (a) brp-GAL4, (b) Syt1-GAL4, (c)nSyb-GAL4, and (d) repo-GAL4. (e) Distribution of inter-nuclei distances for each line. (f) Quantification of the number of labelled nuclei in each line. (a–d) left; scale squares (a) and (c) = 50 μm, (b) and (d) = 100 μm; right images identical magnification, scale bar = 100 μm. (f) Bars indicate minimum and maximum values.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
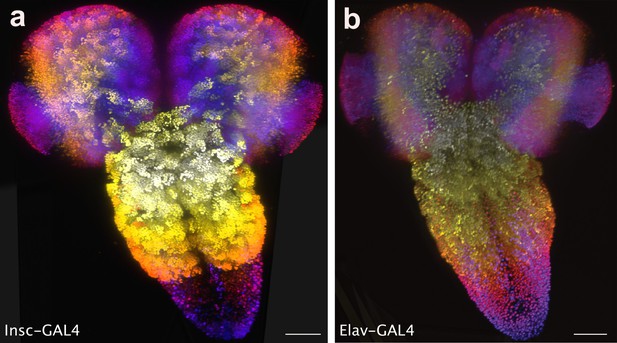
Larval CNS stem cells.
Central nervous system (CNS) projections labelled with (a) insc-GAL4 and (b) elav-GAL4. insc-GAL4 labels neuronal stem cells. elav-GAL4 also labels a fraction of stem cells in addition to potentially glial cells. Colours represent z position. Scale bar: 50 μm.
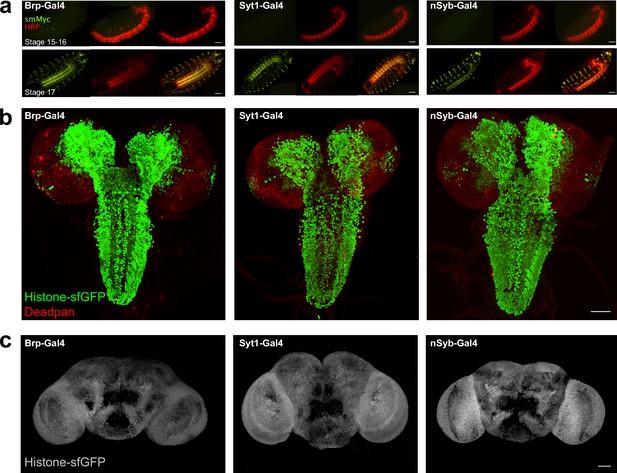
Developmental expression of neuronal GAL4 lines.
(a) Expression UAS_smFP(myc) (green) under control of brp-GAL4, Syt1-GAL4, and nSyb-GAL4 at embryonic stages 15–16 (upper) and stage 17 (lower). Neuronal membranes are labelled with anti Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) (red) (b) Labelling of L3 larval central nervous system (CNS) with Deadpan (red) and UAS_histone-sfGFP (green) under control of brp-GAL4, Syt1-GAL4, or nSyb-GAL4 (c) histone-sfGFP expression in the adult brain under control of brp-GAL4, Syt1-GAL4, or nSyb-GAL4. Scale bar = 50 μm in (a), (b), and (c).
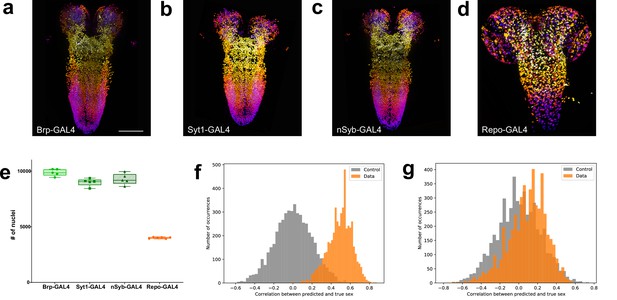
Quantitation of neurons and glia in the male larval CNS and topological comparison of sex differences.
(a–d) Example z-stack projections (colours represent z position) of male larval central nervous system (CNS) of (a) brp-GAL4, (b) Syt1-GAL4, (c) nSyb-GAL4, and (d) repo-GAL4. (e) Quantification of the number of labelled nuclei in each line. (f) The distribution of correlations between the ground truth and the prediction made by the support vector machine (SVM) using topological features is indicative of sexual dimorphism of the higher order structure of neuron point clouds (g) Simpler point cloud features such as properties of the distributions of inter-nuclei distances are not indicative of this. (a–d): identical magnification, scale bar = 100 μm. (e) Bars indicate minimum and maximum values.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
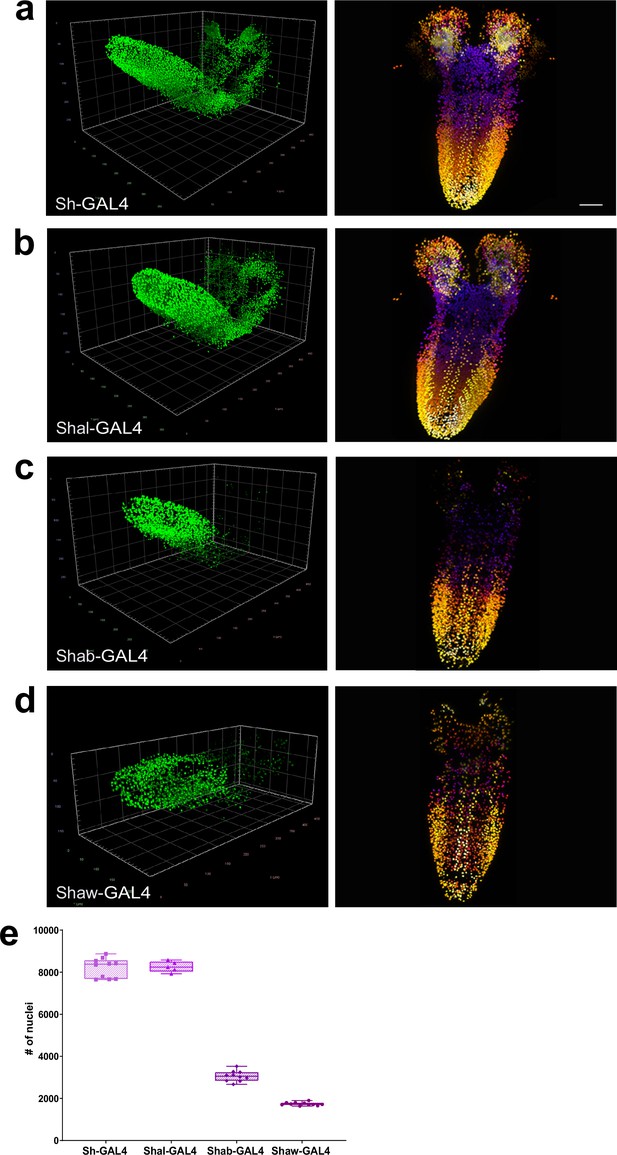
Quantitation of the number of neurons expressing voltage-gated potassium channel genes.
(a–d) Multiview deconvolved images (left) and z-stack projections (right) (colours represent z position) of potassium channel family members: (a) Sh-GAL4, (b) Shal-GAL4, (c) Shab-GAL4, and (d) Shaw-GAL4. (e) Quantification of the number of labelled nuclei in each line. (a–d) left, scale squares = 50 μm, right, identical magnification, scale bar = 50 μm. (e) Bars indicate minimum and maximum values.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source Data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
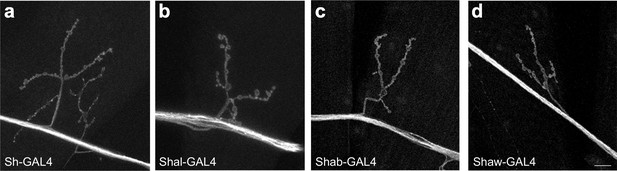
Expression of voltage gated K+ channel GAL4 lines in motor neurons.
Expression in example motor neurons and neuromuscular junction terminals of UAS_mKO-CAAX by (a) Sh-GAL4, (b) Shal-GAL4, (c) Shab-GAL4, and (d) Shaw-GAL4. All four lines express in motor neurons as predicted from mutant analysis. All images identical magnification, scale bar = 10 μm.
Videos
Larval CNS labelled with TH-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Trh-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Ddc-GAL4.
Female CNS labelled with brp-GAL4.
Female CNS labelled with Syt1-GAL4.
Female CNS labelled with nSyb-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with brp-GAL4 and repo-QF2.
Larval CNS labelled with Syt1-GAL4 and repo-QF2.
Larval CNS labelled with nSyb-GAL4 and repo-QF2.
Female CNS labelled with repo-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Sh-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Shal-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Shab-GAL4.
Larval CNS labelled with Shaw-GAL4.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| strain, strain background (Escherichia Coli) | One shot top10 | Invitrogen | Cat#: C404010 | |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | y[1] w[*]; Mi{y[+mDint2]= MIC}Syt1[MI02197] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 21985007 | BDSC:35973FLYB: FBal0314405 RRID:BDSC_35973 | FlyBase symbol: Mi{y[+mDint2]= MIC}Syt1[MI02197] |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | y[1] w[*] Mi{y[+mDint2]= MIC}Sh[MI10885] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 21985007 | BDSC:56260FLYB: FBal0297530 RRID:BDSC_56260 | FlyBase symbol: Mi{MIC}ShMI10885 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | y[1] w[*];Mi{y[+mDint2]= MIC}Shal[MI10881] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 21985007 | BDSC:56089FLYB: FBal0295200 RRID:BDSC_56089 | FlyBase symbol: Mi{MIC}ShalMI10881 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | y[1] w[*]; Mi{y[+mDint2]=MIC} Shab[MI00848] | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 21985007 | BDSC:34115FLYB: FBal0249123 RRID:BDSC_34115 | FlyBase symbol: Mi{MIC}ShabMI00848 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | nSyb-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 18621688 | BDSC: 39171FBgn0013342 RRID:BDSC_39171 | Flybase symbol: P{GMR57C10-GAL4} |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | repo-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center PMID: 7926782 | BDSC:7415FLYB: FBal0127275 RRID:BDSC_7415 | FlyBase symbol: P{GAL4}repo |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | repo-QF2 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Centerdoi:10.1534/ genetics.116.191783 | BDSC:66477FLYB: FBal0322908 RRID:BDSC_66477 | FlyBase symbol: P{ET-QF2.GU}repo |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Shaw-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 21985007 | BDSC:60325FLYB: FBal0304243 RRID:BDSC_60325 | FlyBase symbol: GAL4Shaw- MI01735-TG4.1 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Ddc-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center doi:10.1006/ dbio.1994.1261 | BDSC:7009FLYB: FBtp0012451 RRID:BDSC_7009 | FlyBase symbol: P{Ddc-GAL4.L} |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | TH-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock CenterPMID: 12555273 | BDSC:8848FLYB: FBtp0114847 RRID:BDSC_8848 | FlyBase symbol: P{ple-GAL4.F}3 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Trh-GAL4 | Bloomington Drosophila Stock Centerdoi:10.1371/journal. pone.0010806 | BDSC:38389FLYB: FBtp0055412 RRID:BDSC_38389 | FlyBase symbol: P{Trh-GAL4.long} |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS_H2A-GFP | Steve Stowers (Montana SU)doi:10.1371/journal. pgen.1008609 | FLYB: FBgn0001196 | |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | QUAS_H2A-mCherry | Steve Stowers(Montana SU)doi:10.1371/journal. pgen.1008609 | FLYB: FBgn0001196 | |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | brp-GAL4 | This paper, available upon request, https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB:FBgn0259246 | See Materials and Methods, Section 2 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Syt1-Gal4 | This paper, available upon request, https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB: FBal0314405 | See Materials and Methods, Section 4 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Sh-Gal4 | This paper, available upon request,https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB: FBal0297530 | See Materials and Methods, Section 4 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Shal-Gal4 | This paper, available upon request,https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB: FBal0249123 | See Materials and Methods, Section 4 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | Shab-Gal4 | This paper, available upon request,https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB: FBal0249123 | See Materials and Methods, Section 4 |
| genetic reagent (D. melanogaster) | UAS_H2A::GFP- T2A-mKok::Caax | This paper, available upon request,https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | FLYB: FBgn0001196 | See Materials and Methods, Section 3 |
| antibody | anti-myc9EH10(Mouse monoclonal) | DSHB | DSHB Cat# 9E 10, RRID:AB_2266850 | IF(1:100) |
| antibody | anti-GFP(Chicken polyclonal) | Abcam | Cat#ab13970 | IF(1:500) |
| antibody | anti-Deadpan(Rat monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#ab195173 | IF(1:50) |
| antibody | Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L), Alexa Fluor 488 (Goat polyclonal Secondary Antibody) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat#115-545-166 | IF(1:400) |
| antibody | Goat Anti-Horseradish Peroxidase,Alexa Fluor 647 (Goat polyclonal) | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat#123-605-021 | IF(1:200) |
| antibody | Goat anti-Chicken IgY (H+L), Alexa Fluor 488 (Goat polyclonal Secondary Antibody) | ThermoFisher | Cat#A-11039 | IF(1:500) |
| antibody | Goat anti-Rat IgG (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed, Alexa Fluor 594 (Goat polyclonal Secondary Antibody) | ThermoFisher | Cat#A-11007 | IF(1:500) |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pBID_DSCP-G-Gal4 (plasmid) | McCabe Lab,Available upon request.https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | Cat# #35,200 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pJFRC81-10XUAS-IVS- Syn21-GFP-p10 (plasmid) | Addgene | Cat#: 36,432 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pHD-sfGFP Scareless dsRed (plasmid) | Addgene | Cat#: 80,811 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pCFD3 (plasmid) | Addgene | Cat#: 49,410 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pCR4 brp-Gal4 | This paper, available upon request, https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | CRISPR construct inserted in D. Melanogaster | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pBID LexO_H2A-mCherry | Gift from Steve Stowers (Montana SU), DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008609 | ||
| recombinant DNA reagent | pCS2+ChMermaid S188 | Addgene | Cat#: 53,617 | |
| recombinant DNA reagent | pBID-UAS_H2A::GFP-T2A-mKok::Caax | This paper, available upon request, https://www.epfl.ch/labs/mccabelab/resources/ | construct inserted in D. Melanogaster | |
| sequence-based reagent | pCFD3 gRNA brp-5’ | This paper | Guide RNA for Brp CRISPR knock in | GGTGAACCGA CCGGGACAAC |
| sequence-based reagent | pCFD3 gRNA brp-3’ | This paper | Guide RNA for Brp CRISPR knock in | GGGAGCCCCGC GACCGCTCC |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Ha1 Fo | This paper | PCR primer | GAGAGAGCATCT CGATTGTGCCGTGTG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Pam7 Re | This paper | PCR primer | AATGTTGTCCCG GTCGGTTCACCG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Pam7_In1 Re | This paper | PCR primer | TTCTAGCGTCCAA CGGCTCAGCTGTG GGCCATTTTCTAGT AATGTTGTCCCGG TCGGTTCACCG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp HA_In1 Fo | This paper | PCR primer | ACTAGAAAATGGCC CACAGCTGAGCC |
| sequence-based reagent | brp V5_In1 Re | This paper | PCR primer | TAGAATCGAGACCG AGGAGAGGGTTAGGG ATAGGCTTACCCATT GCTGAAATTCACACA CACACAGAATTCATGAG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp V5_ Fo | This paper | PCR primer | GGTAAGCCTATCCC TAACCCTCTCCTC |
| sequence-based reagent | brp PB5’ Re | This paper | PCR primer | TTAAGGGATCTTTCTA TTAGTATAACACTGCATGC |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Ex2 fo | This paper | PCR primer | AAATTGCATGCAGTGTT ATACTAATAGAAAGATCC CTTAATCGGCAGTCCAT ACTACCGCGACATGGATG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Pam2_Re | This paper | PCR primer | TCTGGAGCGGT CGCGGGGC |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Pam2_Brp Ha2 Re | This paper | PCR primer | GCTCGTCCTCTAGGTAC AGGCCCCGTTCGAGGGA TCTGTCTCTGGAGC GGTCGCGGGG |
| sequence-based reagent | brp Ha2 Fo | This paper | PCR primer | GACAGATCCCTC GAACGGGGCC |
| sequence-based reagent | Syn21 H2A Fo | This paper | PCR primer | AACTTAAAAAAAAAA ATCAAAATGTCTGGA CGTGGAAAAGGTGGC |
| sequence-based reagent | H2A Re | This paper | PCR primer | CCCAAGAAGACC GAGAAGAAGGCC |
| sequence-based reagent | H2A-GFP Fo | This paper | PCR primer | ACAGGCTGTTCTGT TGCCCAAGAAGACC GAGAAGAAGGCCAT GGTGTCCAAGGG CGAGGAG |
| sequence-based reagent | GFP-T2A Re | This paper | PCR primer | GGGTTCTCCTCCAC ATCGCCGCAGGTCAG CAGGCTGCCGCGGC CCTCCTTGTACAGCT CATCCATGCCCAGG |
| sequence-based reagent | T2A-mKok Fo | This paper | PCR primer | GCGGCAGCCTGCT GACCTGCGGCGATG TGGAGGAGAACCCC GGGCCCATGGTGAGT GTGATTAAACCAG AGATGAAGATG |
| sequence-based reagent | mKok-Caax Re | This paper | PCR primer | TTACATAATTACACA CTTTGTCTTTGACTT CTTTTTCTTCTTTTTA CCATCTTTGCTCATGG AATGAGCTACTGCAT CTTCTACCTGC |
| chemical compound, drug | Formaldehyde 37% | Sigma | Cat#: 252,549 | |
| chemical compound, drug | Low melt agarose | Peq gold | Cat#: 35–2010 | |
| chemical compound, drug | VECTASHIELD Antifade Mounting Media | VECTOR Laboratories | Cat#: H-1000 | |
| chemical compound, drug | FluoSpheres, 0.2 µm, red fluorescent (580/605) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat#: F8810 | |
| commercial assay or kit | Zero Blunt TOPO PCR Cloning Kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: 450,245 | |
| commercial assay or kit | pCR8/GW/TOPO TA Cloning Kit | Invitrogen | Cat#: K250020 | |
| commercial assay or kit | Gateway LR Clonase II Enzyme mix | Invitrogen | Cat#:11791020 | |
| commercial assay or kit | NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix | New England Biolabs | Cat#: E2621S | |
| commercial assay or kit | KLD enzyme mix | New England Biolabs | Cat#:M0554S | |
| commercial assay or kit | Platinium Superfi polymerase | Invitrogen | Cat#:12359010 | |
| software, algorithm | CNS nuclei distance (code for Matlab) | https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo | This manuscript | |
| software, algorithm | Fiji | https://fiji.sc/ | RRID:SCR_002285 | |
| software, algorithm | Arivis Vision4D 3.0.0 | Arivis | RRID:SCR_018000 | |
| software, algorithm | MATLAB (R2018a) | MathWorks | RRID:SCR_001622 | |
| software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism 9.0 | GraphPad | RRID:SCR_002798 |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
CNS nuclei center of geometry coordinates.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/74968/elife-74968-supp1-v1.xlsx







