A method for low-coverage single-gamete sequence analysis demonstrates adherence to Mendel’s first law across a large sample of human sperm
Figures
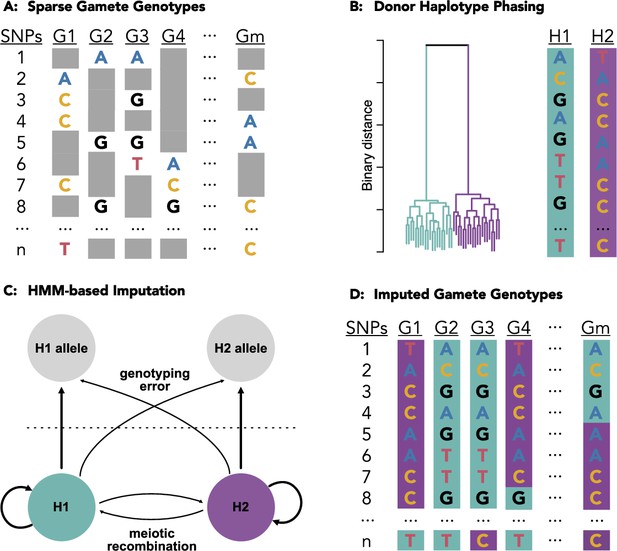
Schematic of the methods underlying rhapsodi (R haploid sperm/oocyte data imputation).
Low coverage data from individual gametes (A) is clustered to phase the diploid donor haplotypes (B). A Hidden Markov Model, with tunable rates of genotyping error and meiotic crossover, is applied to trace the most likely path along the phased haplotypes for each gamete (C) thereby imputing the missing gamete genotypes (D) which can be used to discover meiotic recombination events as transitions from one donor haplotype to the other (e.g., purple [H2] to teal [H1] in gamete G4 between SNPs 7 and 8).
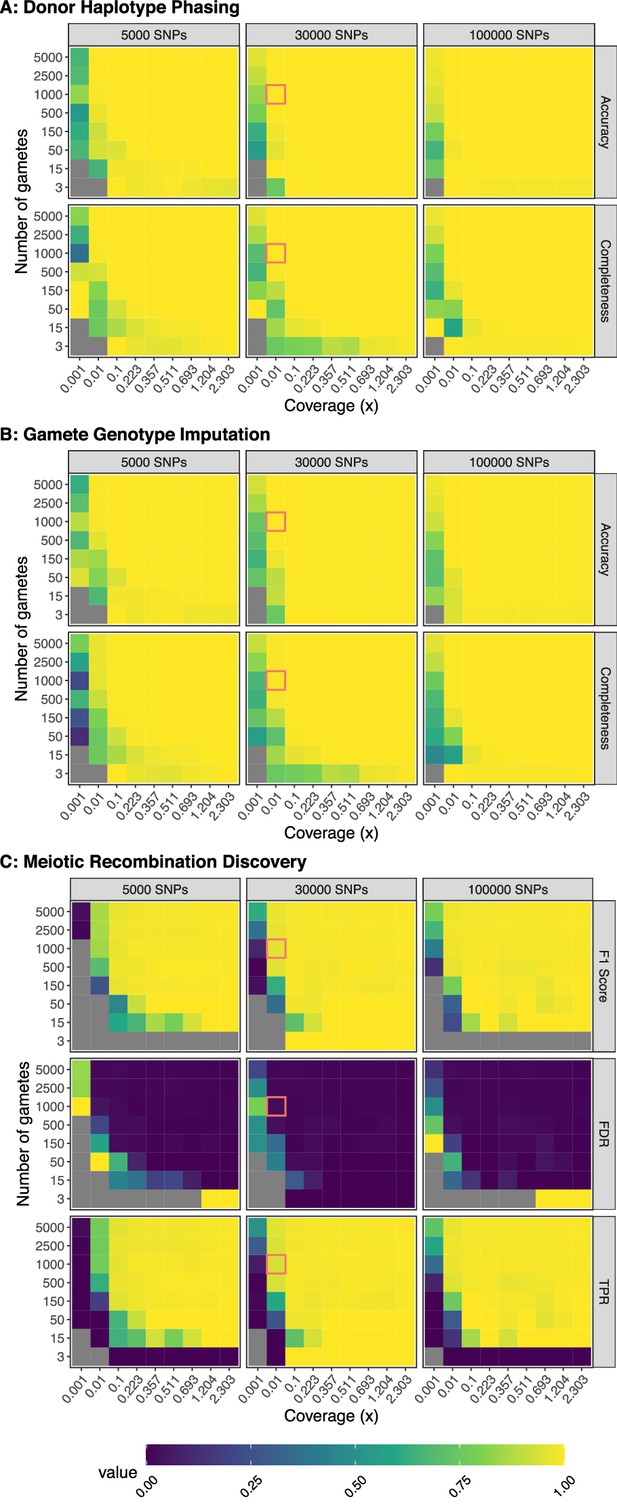
Benchmarking performance across a range of study designs.
Values represent the average of three independent trials. FDR: False Discovery Rate; TPR: True Positive Rate. For phasing and imputation, gray indicates that no hetSNPs remained after downsampling. For meiotic recombination discovery, gray indicates the absence of a prediction class (e.g., zero FNs, FPs, TNs, or TPs). Simulations roughly matching the characteristics of the Sperm-seq data are outlined in red.
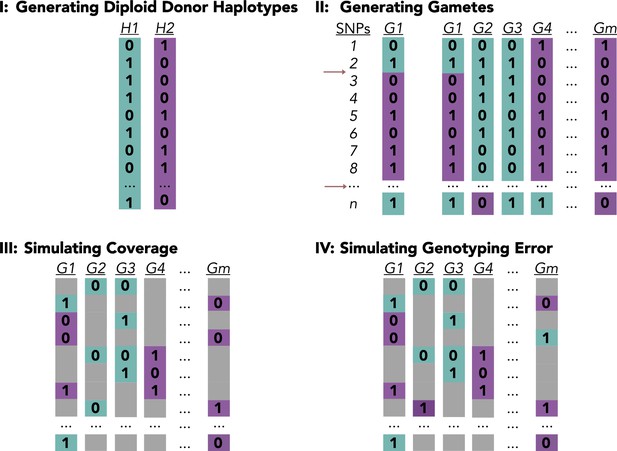
Generative model.
(I) The first step of the generative model builds the phased haplotypes of the diploid donor, with n hetSNPs. (II) In the second step, gamete genotypes are derived from the diploid donor haplotypes by simulating meiotic recombination events, repeating the process for all gametes, {1, …, m}. (III) In the third step, low-coverage sequencing data is generated by removing genotypes from a copy of the gamete genotype matrix. (IV) In the final step, genotyping error is simulated by randomly replacing a small fraction of genotypes with the opposite allele.
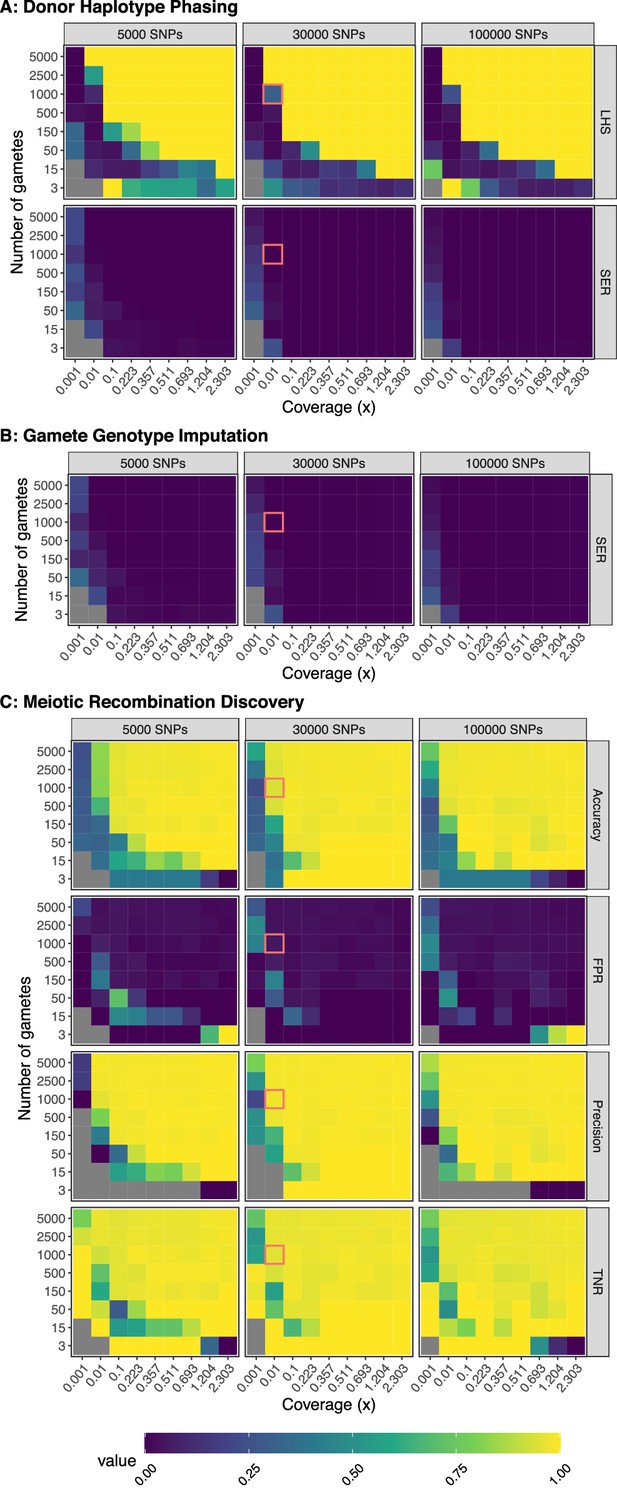
Benchmarking performance across a range of study designs - Additional Metrics.
Input data were created from the generative model and analyzed with rhapsodi. For all data in this figure, the genotyping error and recombination rates were matched between models. Each value is the average of three independent trials. LHS: Largest Haplotype Segment (as ratio of segment length / total hetSNPs); SER: Switch Error Rate; FPR: False Positive Rate; TNR: True Negative Rate.

Illustration of switch error rate (SER) and accuracy.
The top row shows the true haplotypes of a given chromosome and the bottom row shows the inferred haplotypes. Purple denotes alleles assigned to one haplotype and teal alleles to the other. The example chromosome is 60 hetSNPs long. Switch errors occur at two positions, demarcated by the red boxes. The switch error rate is calculated as the number of first mismatches (i.e., number of red boxes) divided by the total length of the chromosome. Therefore, the SER for this gamete would be 2/60 or 3.3%. In contrast, the accuracy considers all matching positions (i.e., one minus the length of the red boxes) in the numerator: 1 - (15/60) or 75%.
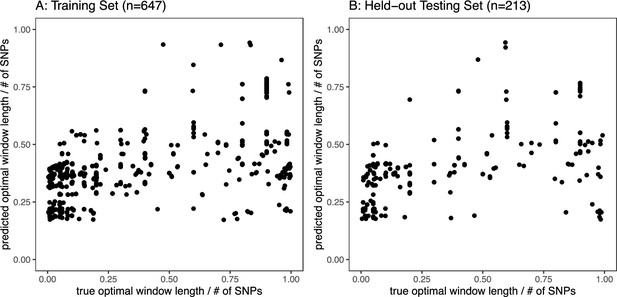
Automatic phasing window size calculation.
A beta regression model relating optimal phasing window size (represented as window size / of SNPs) to number of gametes, coverage, genotyping error rate, and recombination rate was fit on the training data and applied to the held-out test set. The number of gametes, coverage, and recombination rate were significantly associated with optimal window size. The model performed well with both the training and test sets, with no obvious loss when generalizing to new data. This model is implemented as an optional feature for automatic phasing window size calculation, given the input data parameters, within the rhapsodi software package.
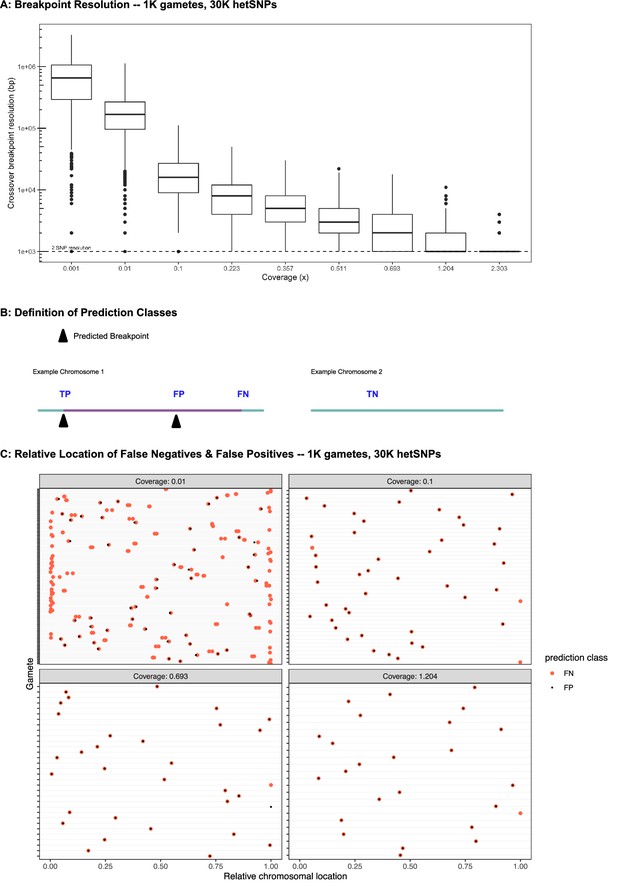
Discovery of meiotic recombination events in simulated data reflecting characteristics of the Sperm-seq data.
(A) Breakpoint resolution stratified by depth of coverage. Resolution is scaled to base pairs assuming pairwise nucleotide diversity of 0.001 (i.e., one hetSNP per 1000 bp). The minimum possible resolution of 2 hetSNPs is denoted with a dashed line. (B) Definition of prediction classes. True positive (TP); True negative (TN); False positive (FP); & False negative (FN). Colors reflect the donor haplotypes, and transitions between these colors indicate recombination events. (C) Relative locations of FN & FP breakpoints within gametes from selected, simulated coverages. Each row in each panel represents an individual gamete with at least one FN or FP. Pairs of FPs and FNs is owed to slight displacement of the inferred crossover breakpoint, which may arise by consequence of premature or delayed switching behaviors of the HMM.
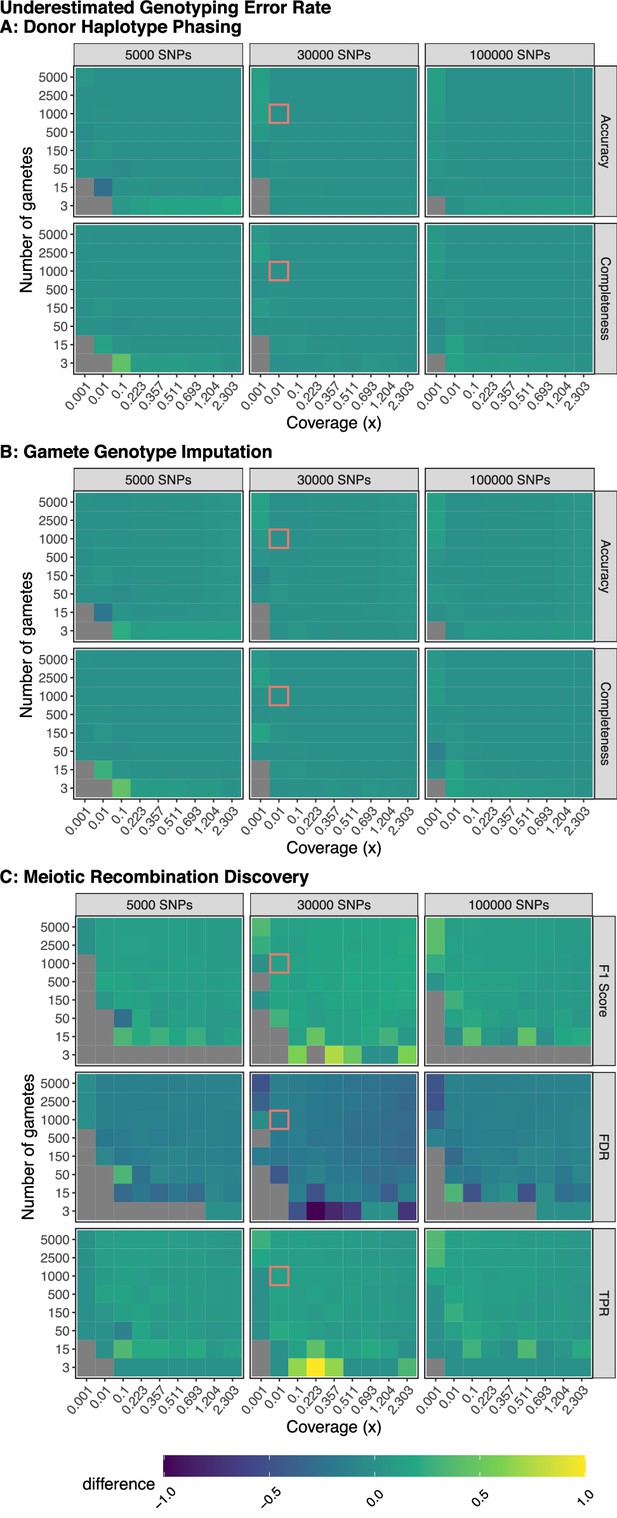
Model robustness when genotyping error is underestimated.
Plotted values are the difference between the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the generative model and rhapsodi use the same parameters (Figure 2) and the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the rhapsodi genotyping error (0.005) is underestimated compared to the rate used by the generative model (0.05). The average recombination rate is 1 per chromosome in both models.
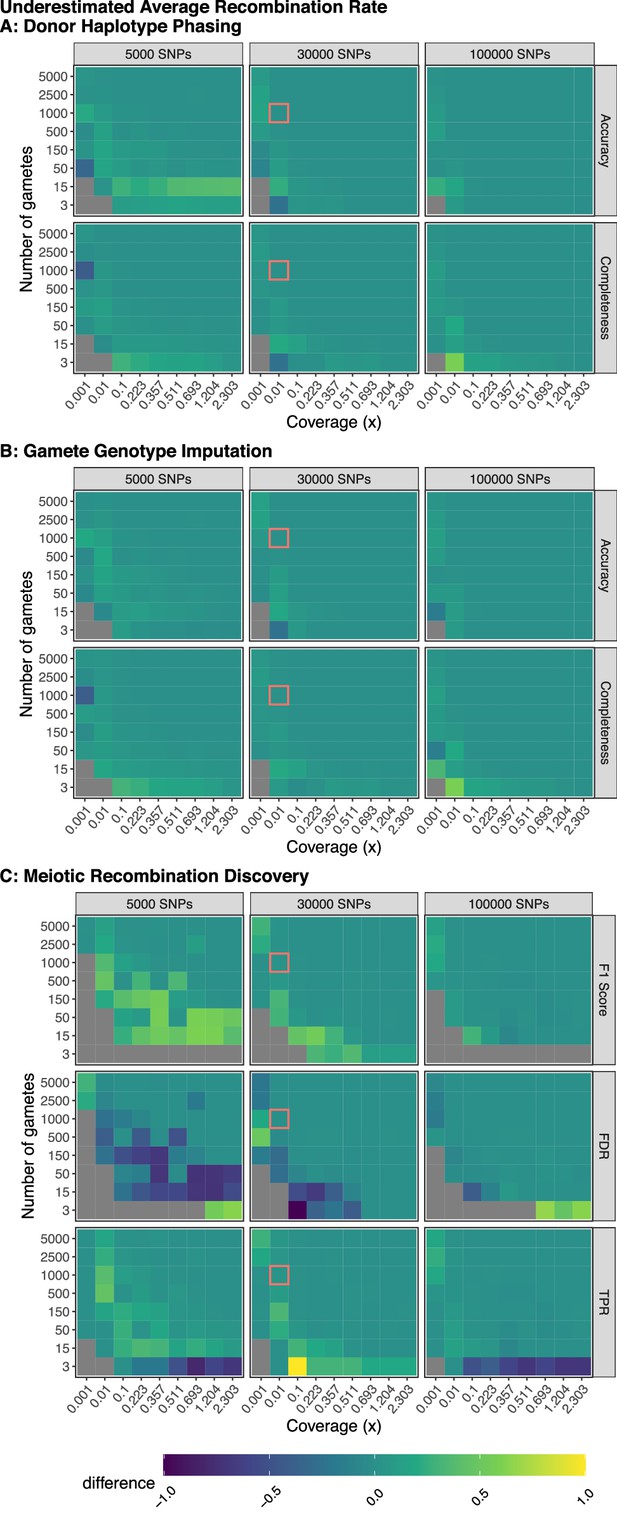
Model robustness when recombination rate is underestimated.
Plotted values are the difference between the mean performance (across 3 independent trials) when the generative model and rhapsodi use the same parameters (Figure 2) and the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the rhapsodi recombination rate (1) is underestimated compared to the rate used by the generative model (3). The genotyping error rate is 0.005 in both models.
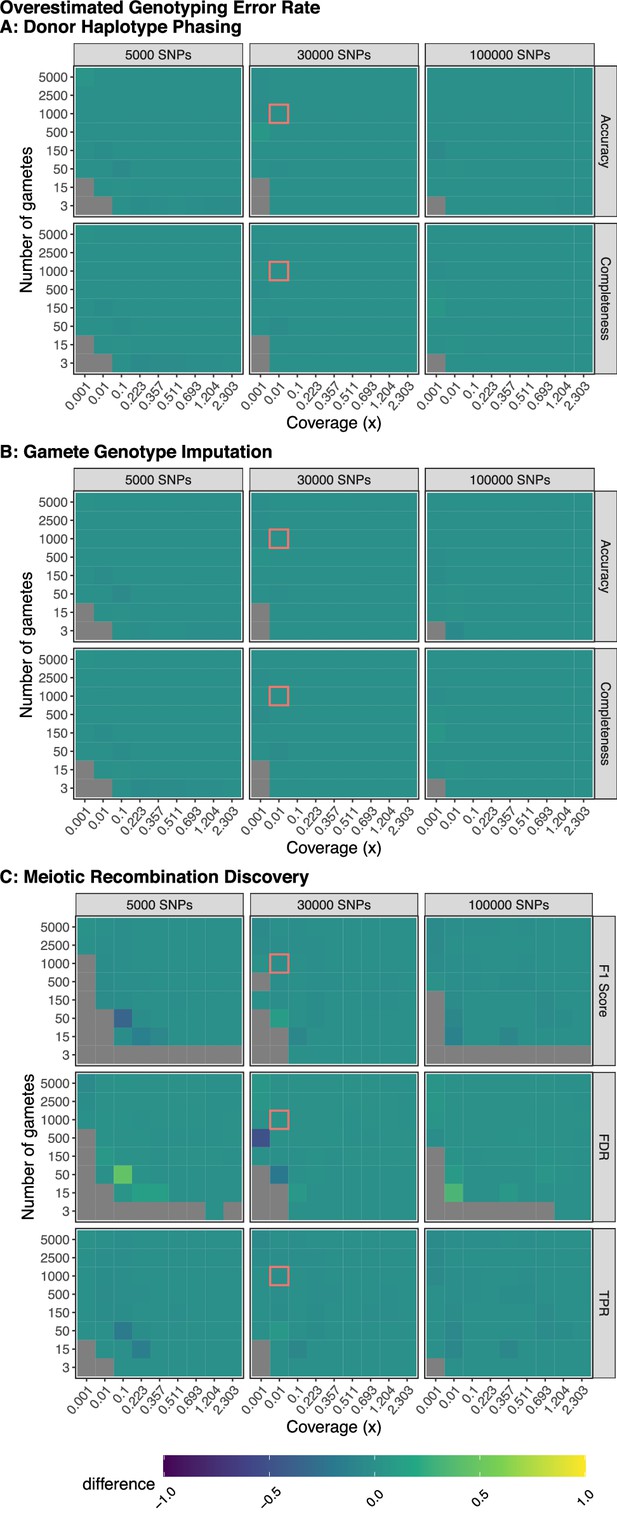
Model robustness when genotyping error is overestimated.
Plotted values are the difference between the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the generative model and rhapsodi use the same parameters (Figure 2) and the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the rhapsodi genotyping error rate (0.005) is overestimated compared to the rate used by the generative model (0.001). The average recombination rate is 1 per chromosome in both models.
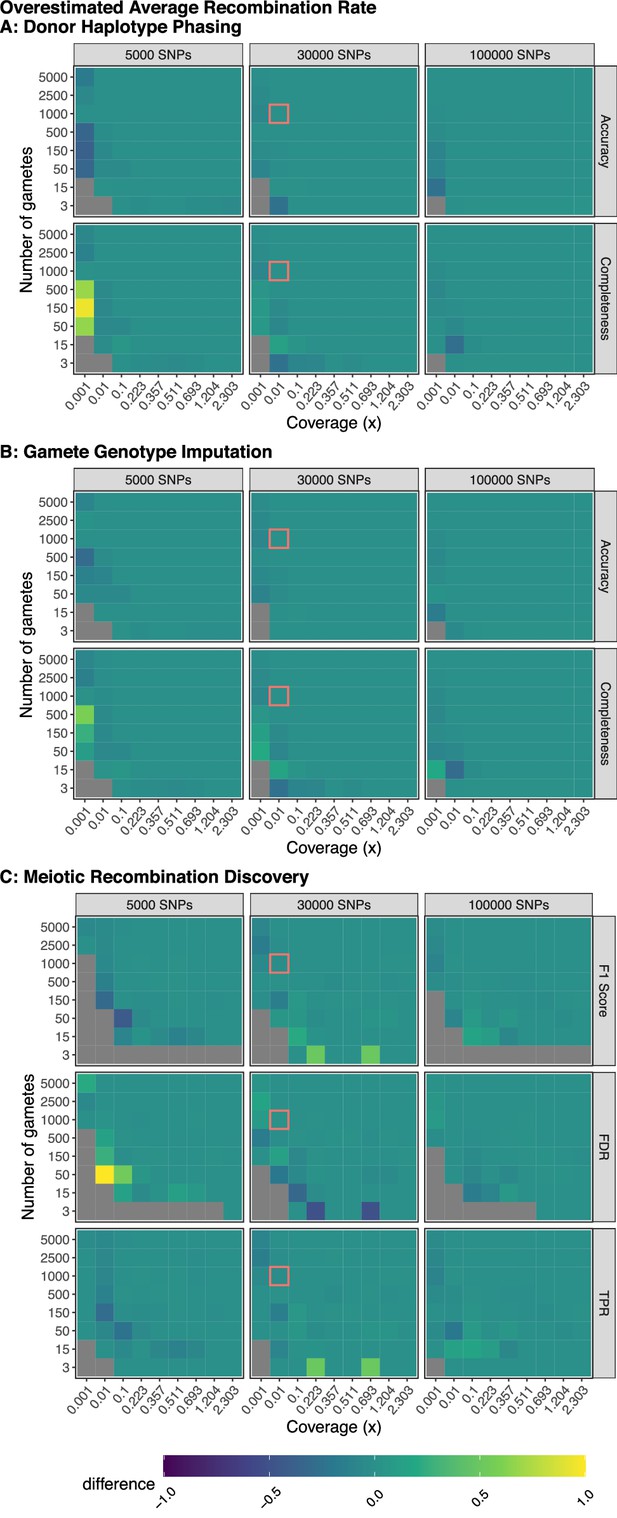
Model robustness when recombination rate is overestimated.
Plotted values are the difference between the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the generative model and rhapsodi use the same parameters (Figure 2) and the mean performance (across three independent trials) when the rhapsodi recombination rate (1) is overestimated compared to the rate used by the generative model (0.6). The genotyping error rate is 0.005 in both models.
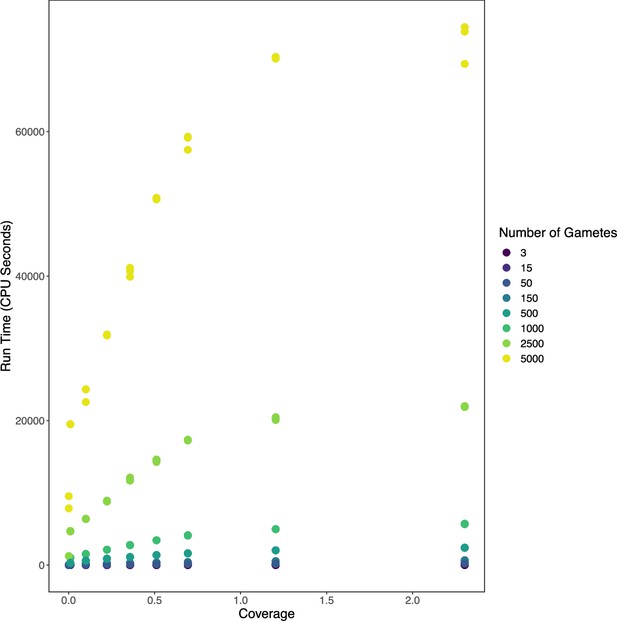
Benchmarking rhapsodi runtime across a range of simulated data profiles.
We generated sperm-seq datasets with 100,000 SNPs and varied coverages and numbers of gametes. We measured runtime of rhapsodi analysis using the rhapsodi_autorun function. Reported time is in CPU seconds, or the combined runtime of all CPUs involved in computation.
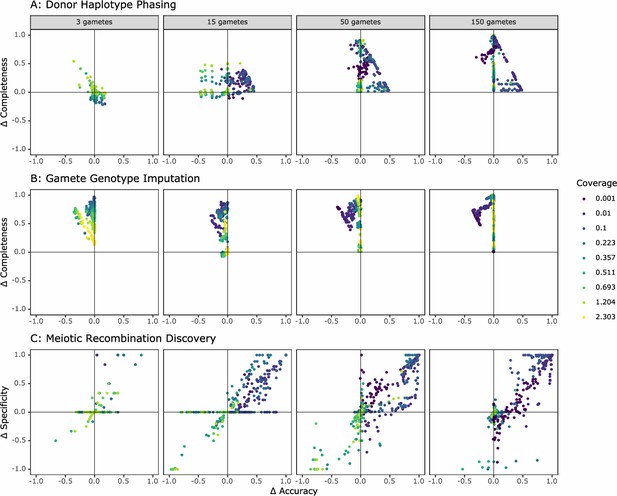
Comparison of the performance of rhapsodi to Hapi, an existing gamete genotype imputation tool.
For each panel, we depict the difference in performance between the tools (rhapsodi minus Hapi). Each point represents a simulated dataset, and only datasets successfully analyzed by both tools are displayed.
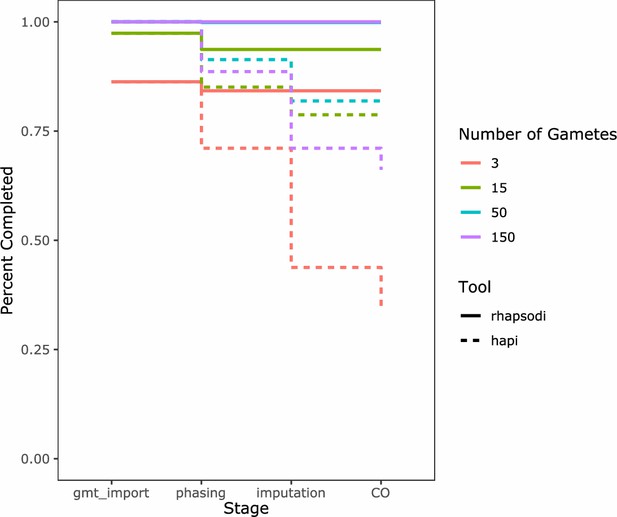
Comparison of the percentage of simulated datasets successfully analyzed by rhapsodi and Hapi across: (1) data import (gmt_import), (2) donor haplotype phasing (phasing), (3) gamete genotype imputation (imputation), and (4) meiotic recombination discovery (CO) stages.
The datasets were stratified into groups according to the number of gametes used in construction, signified by color. The run completion trend for each tool is signified by line-type.
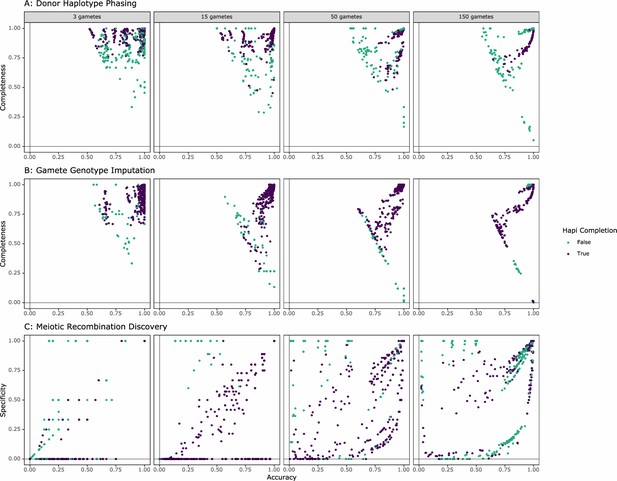
Performance of rhapsodi on each simulated dataset, colored based on Hapi’s ability to successfully analyze each given data set.
False = Not successful; True = Successful. Each column is defined by the number of gametes used in data construction. (A) The relationship between phasing accuracy and completeness. (B) The relationship between mean gamete imputation accuracy and mean completeness. (C) The relationship between meiotic recombination discovery accuracy and specificity.
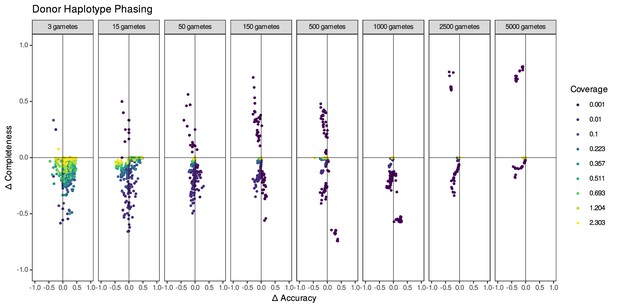
Comparison of accuracy and completeness for rhapsodi phasing methods windowWardD2 and linkedSNPHapCUT2.
Datasets have varied coverages and gamete numbers, and all have 100,000 SNPs. Each panel shows the difference in performance between phasing methods (windowWardD2 minus linkedSNPHapCUT2) at a given number of gametes. Each point represents a simulated dataset; only datasets successfully phased by both methods are displayed; of 5713 simulations, 1241 simulations that could not be phased using linkedSNPHapCUT2 and 48 simulations that could not be phased using either method are not pictured.
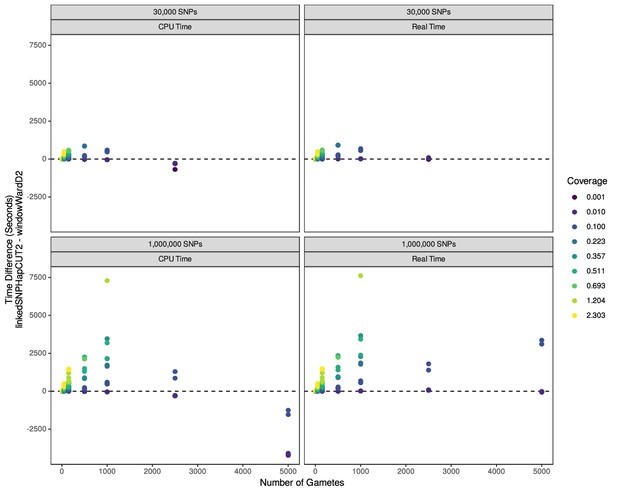
Difference in runtime between windowWardD2 and linkedSNPHapCUT2 algorithms for phasing across a range of simulated data.
Datasets have varied coverages, gamete numbers, and numbers of SNPs. Figure shows both CPU time and wall time. Points above the y=0 line represent datasets for which the windowWardD2 method performs faster. Evaluation of linkedSNPHapCUT2 does not include the time necessary to convert the files for use with HapCUT2. Panel (A) shows total user and system time. Panel (B) shows real time. Each point shows the difference in total time (in seconds) required for each phasing method (linkedSNPHapCUT2 minus windowWardD2). Number of gametes in each simulation is shown on the x axis. Only simulations for which both phasing methods were successful are shown (of the 432 datasets, 365 were successfully phased using windowWardD2 and 266 were successfully phased using linkedSNPHapCUT2); the file conversion together with calling HapCUT2 were allowed to time out after 3 days.
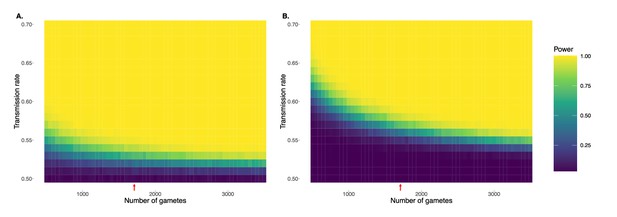
Simulation demonstrating power to detect deviations from binomial expectations across sample sizes of sperm, without (A) and with (B) multiple hypothesis testing correction.
For each combination of transmission rate and number of gametes, power was calculated based on 1000 independent simulations and assuming full knowledge of gamete genotypes. Panel A uses the standard α = 0.05, while panel B uses an adjusted p-value threshold of 1.78 x 10-7 as employed in our study. Note that this correction is conservative in that it adjusts for multiple testing across the genome as well as across donor individuals. Red arrows indicate gamete sample sizes roughly matching the Sperm-seq data (average n = 1711 sperm cells per donor).
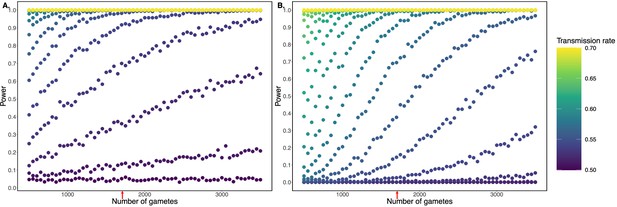
Simulation demonstrating power to detect deviations from binomial expectations across sample sizes of sperm cells, without (A) and with (B) multiple hypothesis testing correction.
For each combination of transmission rate and number of gametes, power was calculated based on 1000 independent simulations and assuming full knowledge of gamete genotypes. Panel A uses the standard alpha = 0.05, while panel B uses an adjusted p-value threshold of 1.78 x 10-7 as employed in our study. Note that this correction is conservative in that it adjusts for multiple testing across the genome as well as across donor individuals. Red arrows indicate gamete sample sizes roughly matching the Sperm-seq data (average n = 1711 sperm cells per donor).
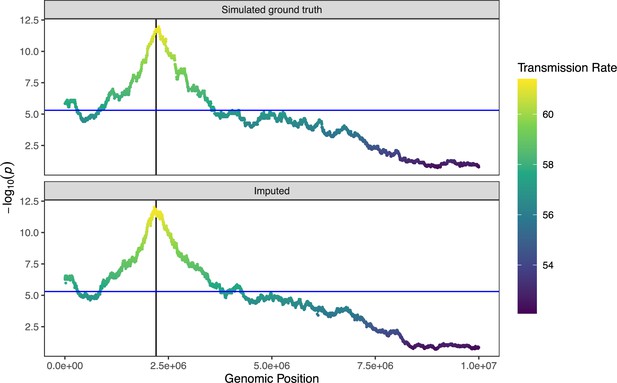
Simulated signature of transmission distortion.
We simulated 1000 gametes with 10,000 SNPs. We generated TD by choosing an allele at random and removing 30% of gametes which carried that allele. We simulated coverage of 0.01× and genotyping error rate of 0.005 and then imputed gamete genotypes using rhapsodi. Top and bottom panels show results of testing for transmission distortion on simulated ground truth and imputed data, respectively.
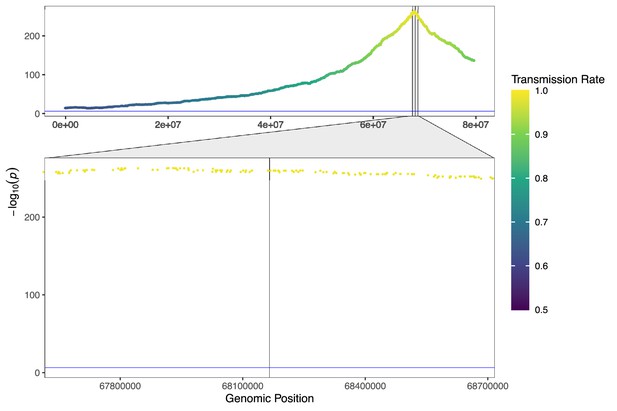
Simulated signature of strong (k=0.99) transmission distortion.
We simulated data with 974 gametes, 79,630 SNPs, and 0.0075× coverage, corresponding to the data profile of donor NC26 chromosome 8. Zooming in to region surrounding the causal SNP (denoted with the black, vertical line), we observe that the causal SNP and several flanking SNPs were filtered out due to apparent homozygosity across the sample of sperm cells. However, the imputed gamete genotypes still exhibit signal of the strong TD on either side of this region, far below the p-value threshold of genome-wide significance.
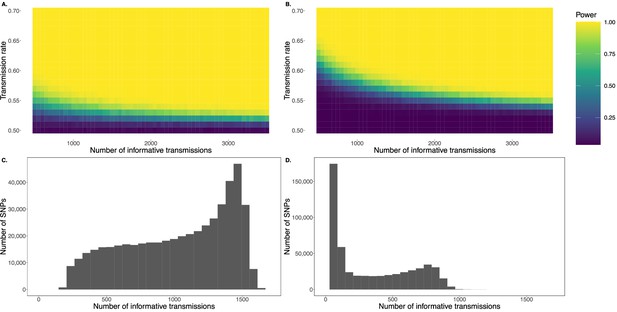
Simulation demonstrating power to detect deviations from expectations using the transmission disequilibrium test (TDT), as applied to human pedigree studies, without (A) and with (B) multiple testing correction (alpha = 0.05 and 10-7, respectively).
The latter threshold is the standard for genome-wide significance (10-7) used in past studies (Meyer et al., 2012). The sample size refers to the number of informative transmissions, where each trio with a parent heterozygous for the SNP of interest has one informative transmission of the given SNP. Power was calculated based on 1000 independent simulations. Panels C and D show the distributions of the number of informative transmissions per SNP from the two pedigrees in Meyer et al., 2012 for which data were publicly available: AGRE (C) and HUTT (D). Meyer et al., 2012 removed SNPs with fewer than 200 informative transmissions in AGRE and fewer than 50 informative transmissions in HUTT prior to their analysis. Note that the number of informative transmissions is typically substantially less than the total number of offspring in each pedigree (after quality control and sample size cutoffs, 1518 for AGRE and 848 for HUTT).
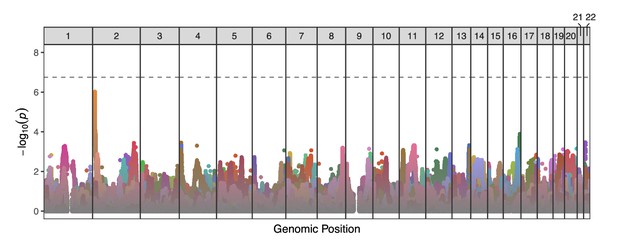
Manhattan plot displaying genome-wide TD scan results for all 25 sperm donors across the 22 autosomes.
P-values are correlated across large genomic intervals due to the high degree of linkage disequilibrium among sperm cells from a single donor. Colors distinguish results from different donors. No individual test was significant after multiple testing correction (p-value threshold = 1.78 × 10-7).
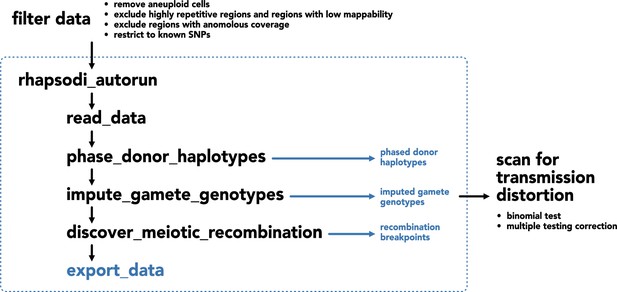
Workflow for application of rhapsodi to data from human sperm and downstream investigation of transmission distortion.
Raw data containing hetSNPs from each chromosome are filtered to limit spurious signal caused by sequencing error. The autorun function from rhapsodi is applied, which generates and exports data from phased donor haplotypes, imputed gamete genotypes, and meiotic recombination breakpoints. Using the imputed gamete genotypes (generated with the unsmoothed option in rhapsodi), we conduct a binomial test for transmission distortion. We compare our results with our genome-wide threshold for statistical significance, which takes into account multiple hypothesis testing and the extreme linkage disequilibrium in these data.
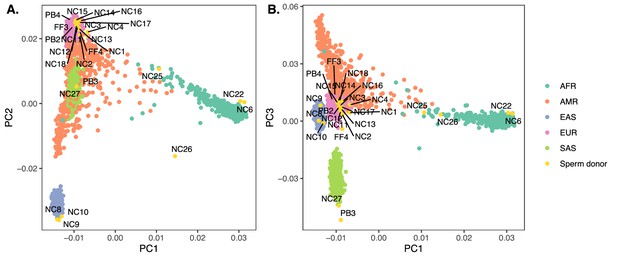
Inference of genetic similarity to reference samples from the 1000 Genomes Project.
We use a principal component analysis approach to investigate the genetic similarity of each donor with individuals from the 1000 Genomes Project (Ma and Amos, 2012). Donor individuals are shown in yellow, each labeled with its Donor ID (FF3, NC1, etc.), following the conventions from the papers in which they were initially published (Bell et al., 2020; Leung et al., 2021) and throughout our manuscript. Panel (A) contrasts PC1 with PC2, while panel (B) contrasts PC1 with PC3. The points representing the individuals from the 1000 Genomes Project are color-coded based on their reported superpopulation: Africa (AFR), Americas (AMR), East-Asia (EAS), Europe (EUR), South-Asia (SAS). Results are broadly consistent with self-reported ancestries, including for individuals of recent admixed ancestry (Bell et al., 2020).
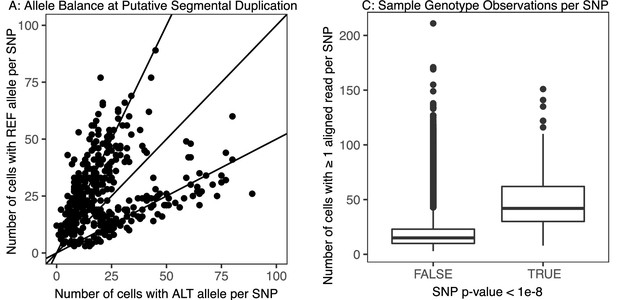
Example of evidence for a segmental duplication in donor NC17, chromosome 6.
(A) For a segment of the chromosome enriched for low uncorrected p-values (p-value < 1 × 10-8), we plot each hetSNP based on the number of sperm in which it was observed as the reference allele or alternative allele. Points cluster on lines with slope = 0.5 and slope = 2, deviating from the null expectation of clustering on slope = 1 (equal representation of the alternative and reference alleles across the pool of sperm). (B) To compare, we consider SNPs across the rest of the chromosome, outside of this region. Points cluster to the line slope = 1. (C) Across the whole chromosome, we consider the number of sperm cells in which each SNP is observed, based on whether their uncorrected p-value was greater or less than 1 × 10-8.
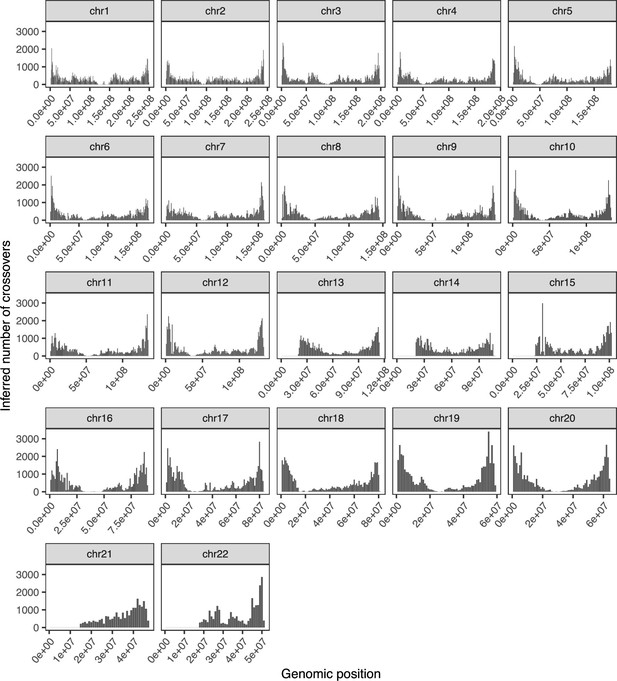
Recombination map of inferred crossovers in the Sperm-seq data.
This map displays counts of the inferred number of crossovers within each 1 Mbp bin for each chromosome, pooling inference across the 25 donors. We used the midpoint of each crossover’s predicted breakpoints to localize the event to a specific bin.
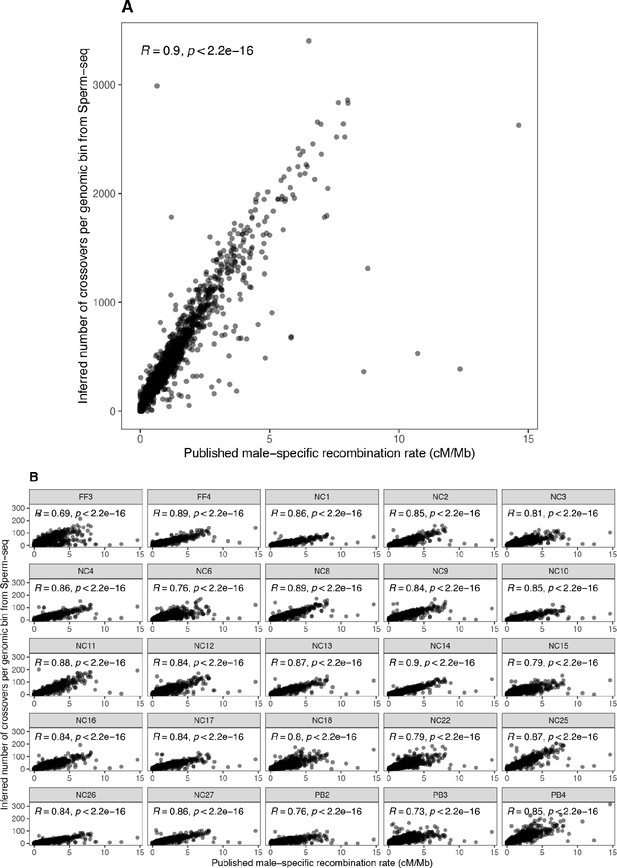
Comparison of inferred crossover recombination map to published deCODE male-specific recombination map.
By binning the deCODE recombination map within each 1 Mbp bin for each chromosome, a weighted average recombination rate was calculated and compared to the number of Sperm-seq inferred crossovers for each corresponding bin. (A) A high correlation of 0.9 was observed overall. (B) Sample specific correlations ranged from 0.69 to 0.9. Information from each sample is shown with its Donor ID (FF3, NC1, etc.), following the conventions from the papers in which they were initially published (Bell et al., 2020; Leung et al., 2021) and throughout our manuscript.
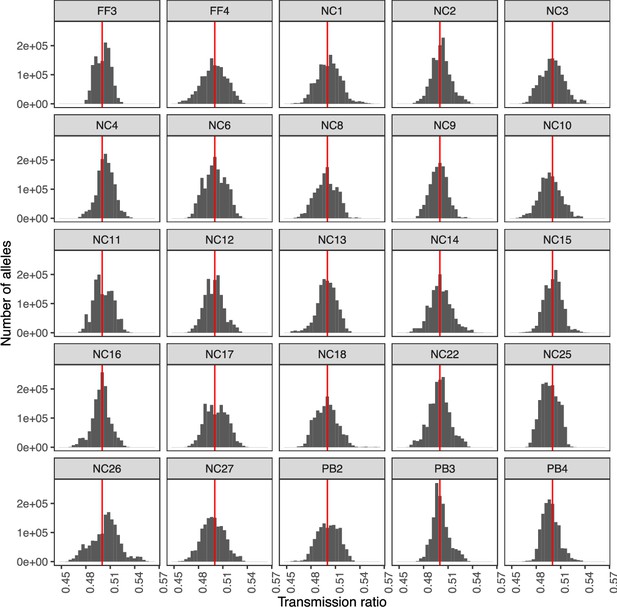
Visualization of transmission rate of each allele within the pool of sperm, by donor.
Points are distributed around a transmission rate of 0.5 (shown as red line).
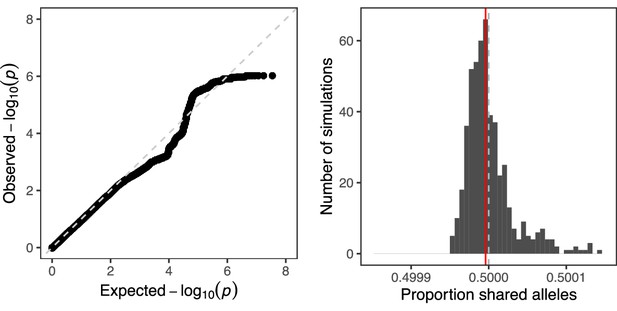
Quantifying global evidence of TD.
(A) Quantile-quantile plot comparing the distribution of p-values from our genome-wide scan for TD to that expected under the null hypothesis. The dashed line corresponds to x = y. (B) Mean allele sharing across all pairs of sperm from null simulations (n=500) is depicted with grey bars. The same mean computed on the observed data (0.499996) is depicted with a red line, while the null proportion of 0.5 is depicted with a gray dashed line.





