Heritability and cross-species comparisons of human cortical functional organization asymmetry
Figures
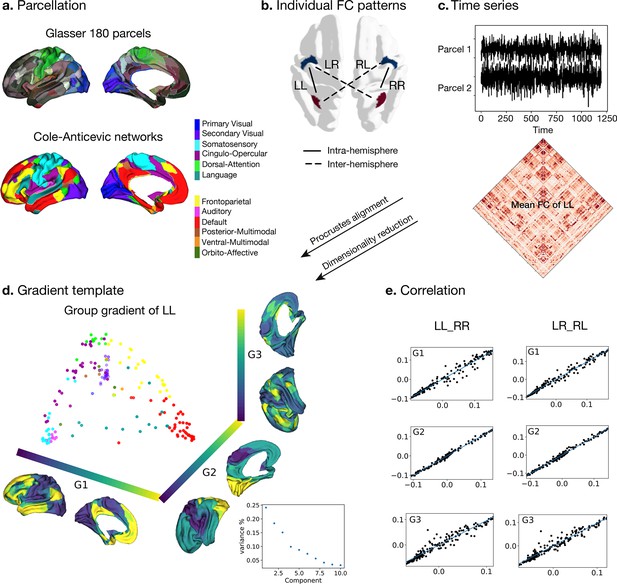
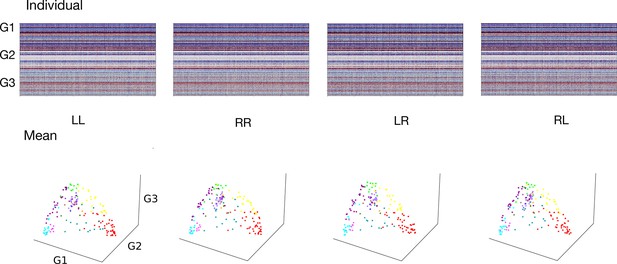
Processing of functional gradients in humans.
(a) Parcellation using Glasser atlas (Glasser et al., 2016) in each hemisphere and Cole-Anticevic (CA) networks (Ji et al., 2019) for humans. (b) Individual FC in each hemispheric pattern, that is left-left (LL, intra-hemisphere), right-right (RR, intra-hemisphere), left-right (LR, inter-hemisphere), and right-left (RL, inter-hemisphere). (c) Time series of two parcels and the mean functional connectivity (FC) matrix between left and left hemisphere (LL). (d) Gradient template using the group-level gradient of LL. Dots represent parcels and are colored according to CA networks. The decomposition scatter on the right below depicts x-axis (number of eigenvectors) and y-axis (the contribution of each eigenvector to the total). (e) Correlation between left and right mean gradients across subjects of intra- and inter-hemispheric patterns. Left panel is the correlation between gradients of FC LL and FC RR (intra-hemispheric pattern). Right panel is the correlation between gradients of FC LR and FC RL (inter-hemispheric pattern). All correlation coefficients along G1, G2, and G3 are greater than 0.9.
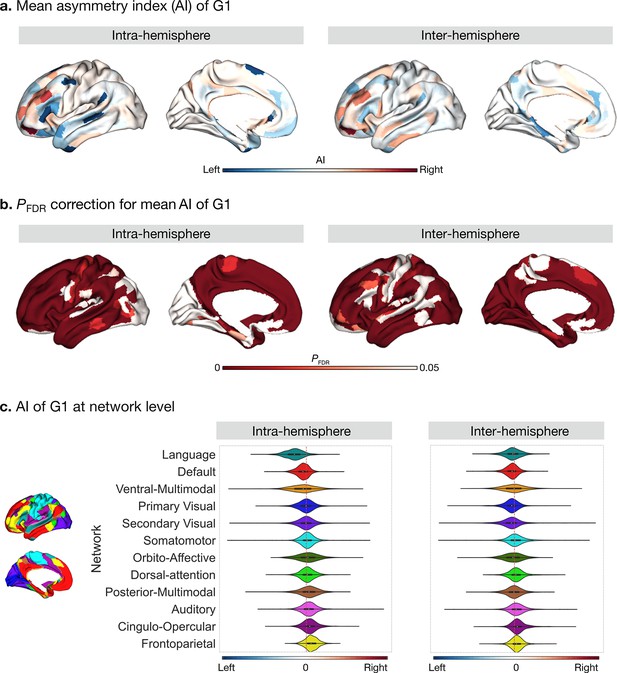
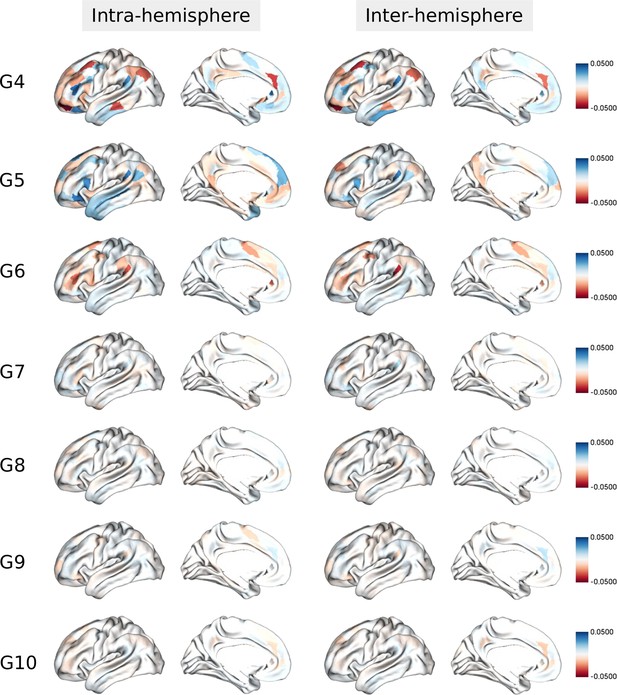
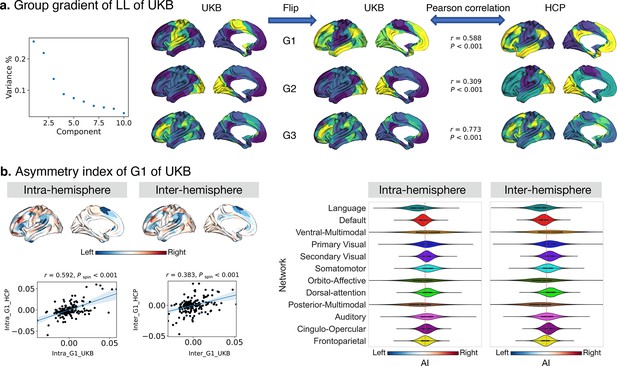
Asymmetry of functional gradients in humans and its heritability.
(a) Mean asymmetry index (AI) of intra- and inter-hemispheric patterns in humans. Red and blue indicate rightward and leftward asymmetry respectively. (b) FDR correction for the P values of AI shown in A; (c) Violin plots of mean AI network loading across individuals (n=1014), with median, 25%-75%, and distribution at 25/75% -/+1.5 interquartile range. Networks are ranked from leftward (language) to rightward asymmetry (frontoparietal) along the intra-hemispheric principal gradient.
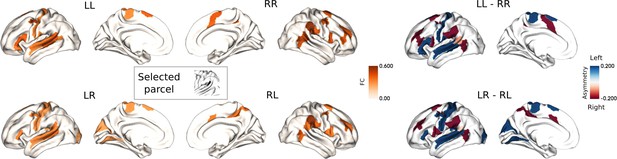
FC profiles of the most asymmetric parcel (No.25: Peri-Sylvian language area).
The upper panel is LL versus RR, and the lower panel is LR versus RL as well as their difference in connectivity (right panel), blue and red reflect leftward and rightward FC.
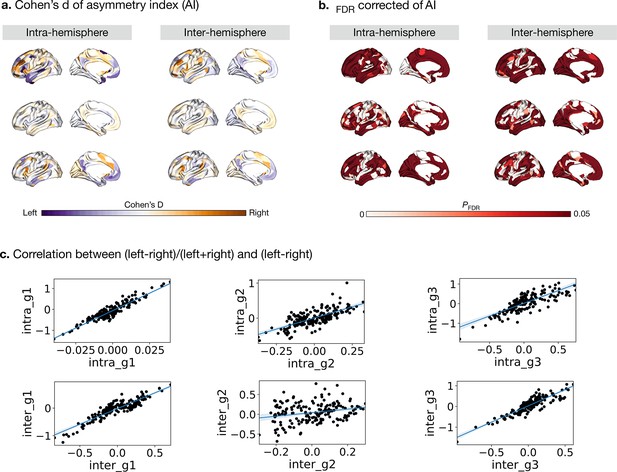
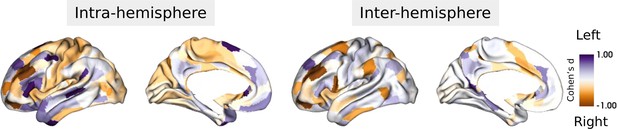
Cohen’s d (yellow-purple) and PFDR (red) of asymmetry index with (left-right)/(left +right).
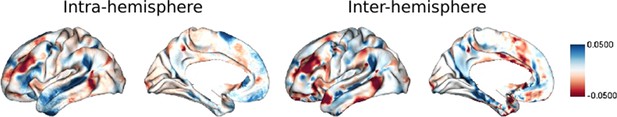
Vertex-wise asymmetry along G1.
To test the vertex-wise asymmetry, we randomly chose 100 subjects and used the vertex-wise FC gradients to calculate the asymmetry.
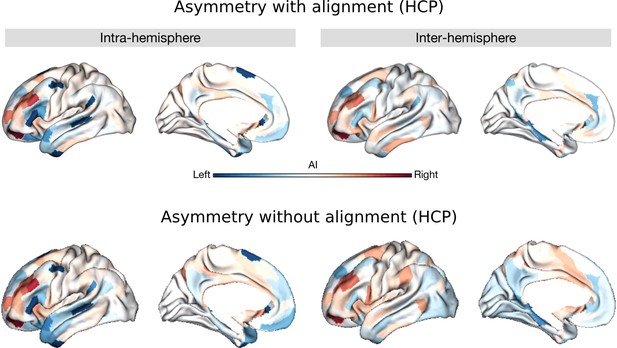
Asymmetry of functional gradients using HCP.
Upper panel is the map with Procrustes alignment (main findings). Lower panel is the map without alignment. Blue color indicates the leftward asymmetry and red color indicates the rightward asymmetry.
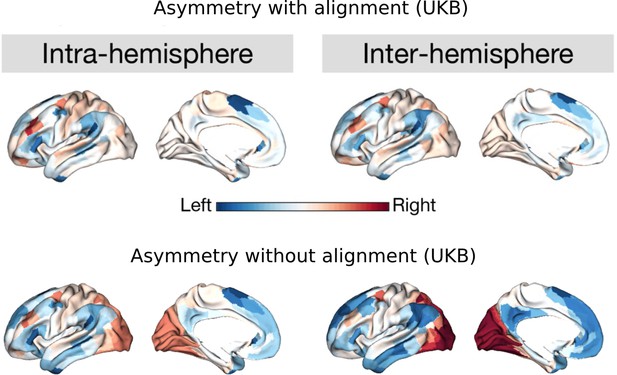
Asymmetry of functional gradients using UKB.
Upper panel is the map with Procrustes alignment (main findings). Lower panel is the map without alignment. Blue color indicates the leftward asymmetry and red color indicates the rightward asymmetry.
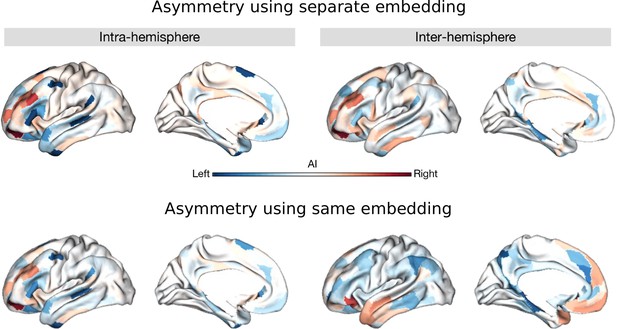
Asymmetry using LL_RR and LR_RL patterns in the same models instead of separate models.
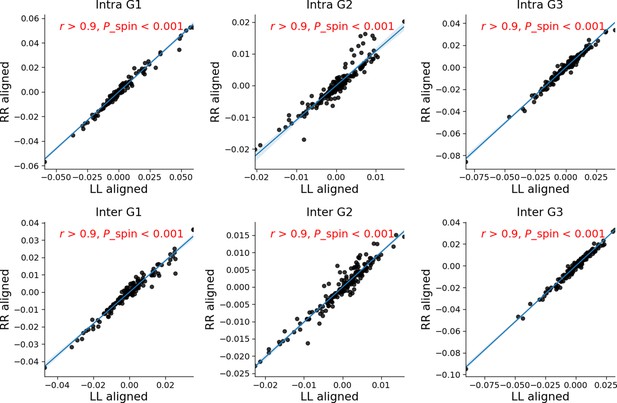
Correlations between LL aligned gradients asymmetry and RR aligned gradients asymmetry.
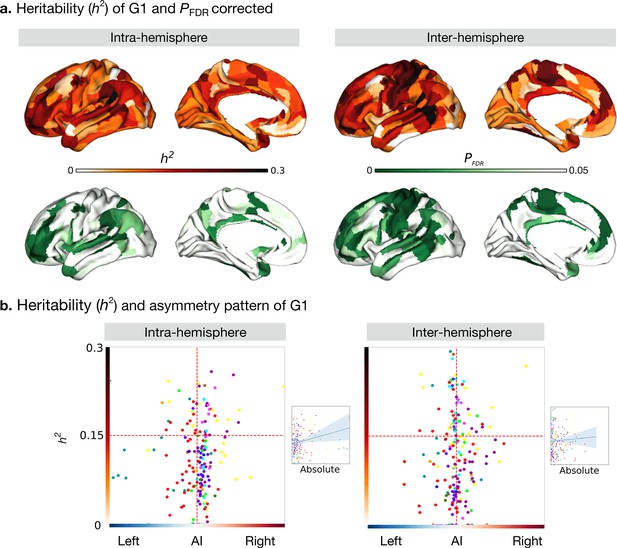
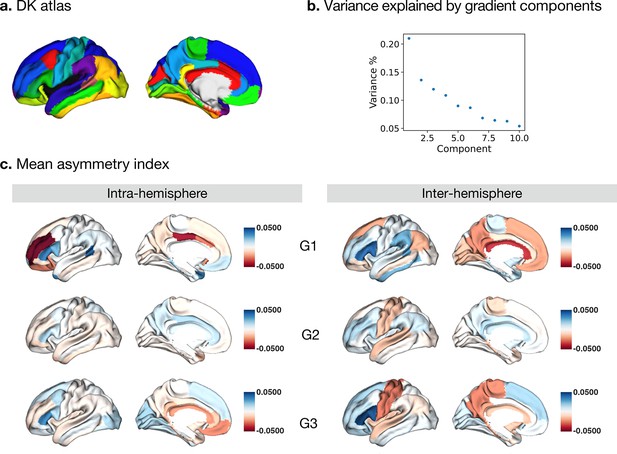
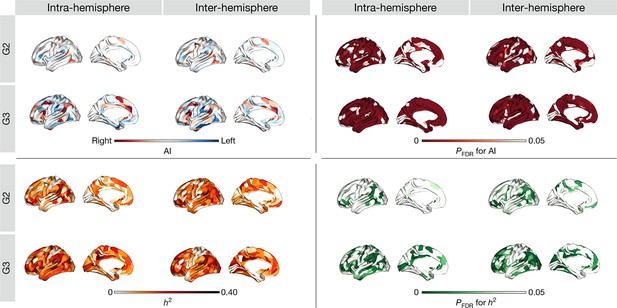
Heritability of asymmetry of functional G1.
(a) Heritability (orange colorbar) and p values after FDR correction (green colorbar). (b) Scatter plot of heritability and AI scores. The x- and y-axes are the mean asymmetry index and heritability, respectively. Dots represent parcels and are colored according to CA networks. The small scatter plots with a regression line are the corresponding absolute mean asymmetry index (x-axis) and heritability (y-axis).
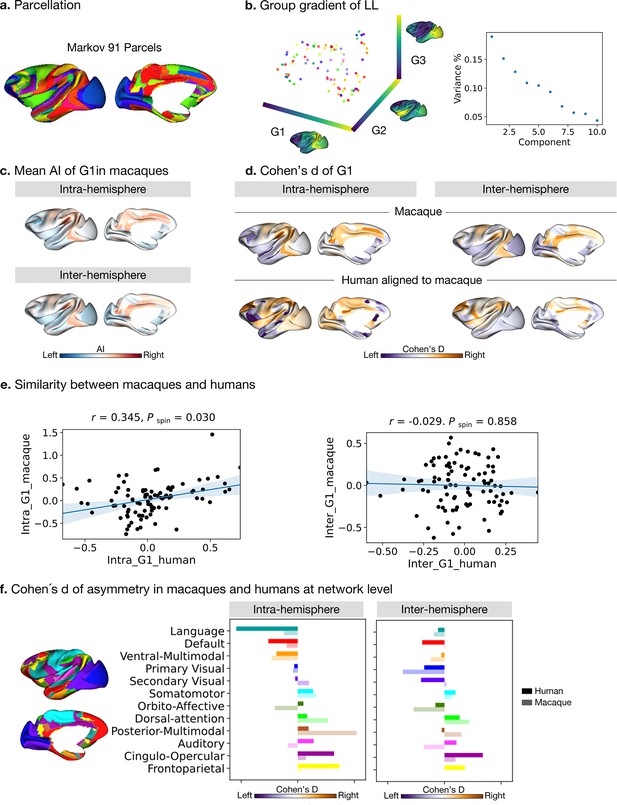
Asymmetry of functional gradients in macaques.
(a) Parcellation used Markov atlas in macaques Markov et al., 2014. (b) Template gradients of group level connectivity of LL. (c) Mean asymmetry index of G1 in macaques. (d) Normalized (Cohen’s d) asymmetry of G1 in macaques and humans aligned to macaque’s surface. Purple indicates leftward asymmetry, whereas yellow indicates rightward asymmetry. (e) Similarity of normalized asymmetry of G1 between humans and macaques. (f) The details of how the human Cole-Anticevic network atlas is projected to the macaque surface can be seen in the Methods. Bold colors indicate human mean cohen's D values in a given network and pastel colors indicate macaque mean cohen's D values in a given network. Networks are ranked from leftward (language) to rightward asymmetry (frontoparietal) along the intra-hemispheric principal gradient in humans for comparison.
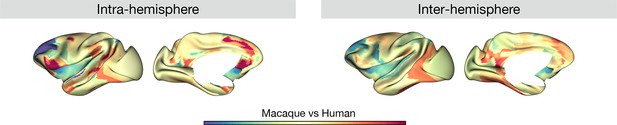
Macaque versus human region-wise difference maps based on the normalized (Cohen’s d) asymmetry of G1.
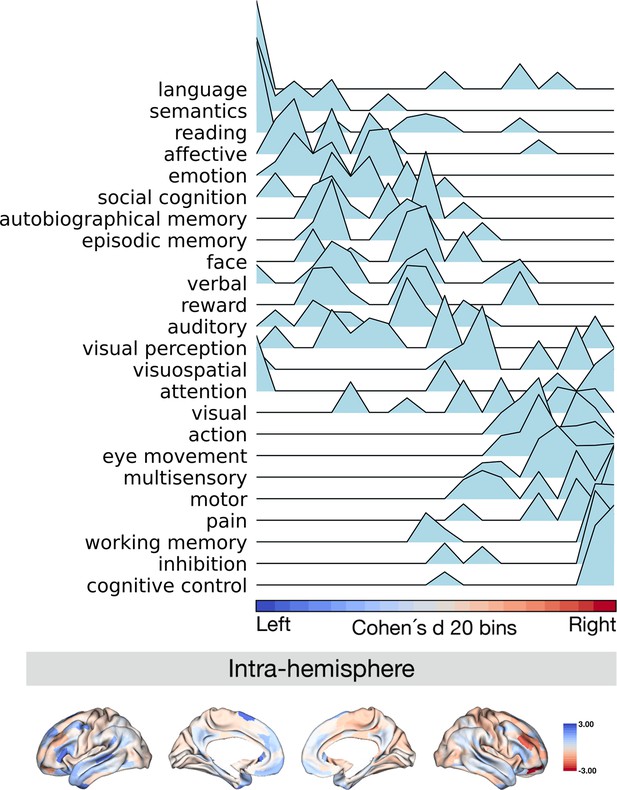
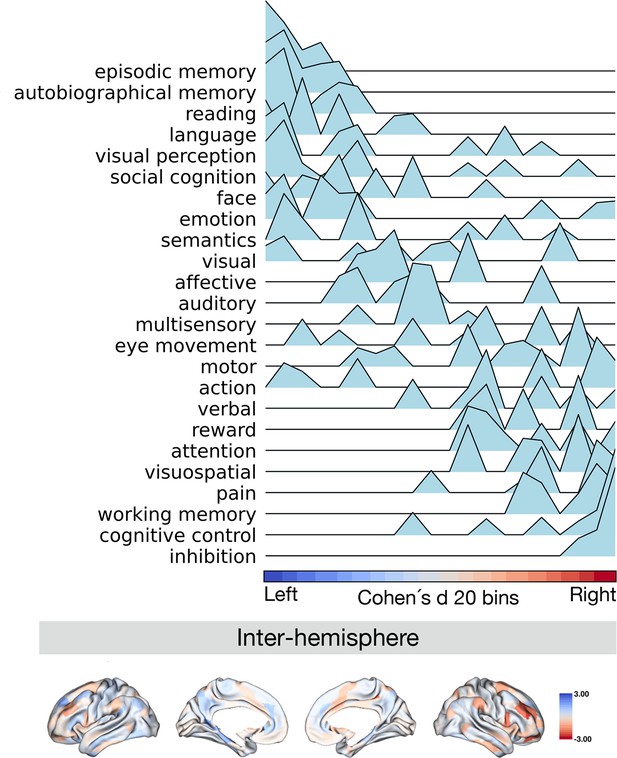
Projection of meta-analytical task-based function along normalized asymmetry of G1 (intra-hemisphere).
The 20 bins were generated by normalized (Cohen’s d) asymmetry of G1 in humans. Cool color indicates regions showing leftward dominance and warm color indicates regions showing rightward dominance. The order of the terms of the y-axis was generated by the weighted score of activation (z-score >0.5) * normalized asymmetry.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Summary of asymmetry index and heritability of G1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77215/elife-77215-supp1-v3.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/77215/elife-77215-mdarchecklist1-v3.pdf