A dual-target herbicidal inhibitor of lysine biosynthesis
Figures
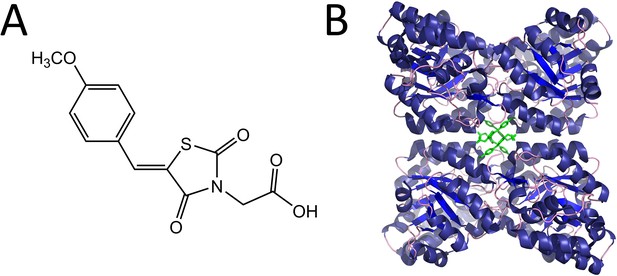
Structure and mode of binding of (Z)-2-(5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (MBDTA-2).
(A) Chemical structure of MBDTA-2. (B) The AtDHDPS1 quaternary structure with MBDTA-2 (green sticks) bound within a novel allosteric pocket (PDB ID: 7MDS) (Soares da Costa et al., 2021).
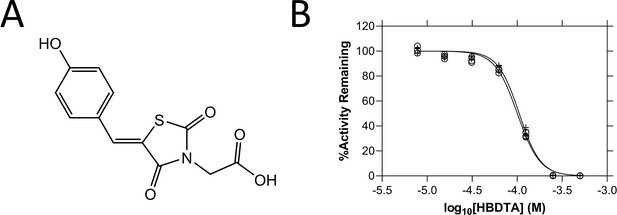
Structure and in vitro potency of (Z)-2-(5-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (HBDTA).
(A) Chemical structure of HBDTA. (B) Dose–response curves of HBDTA against recombinant AtDHDPS1 (⚬) and AtDHDPS2 (+) enzymes. Initial enzyme rate was normalised against the vehicle control to determine % activity remaining. Data were fitted to a nonlinear regression model (solid line), resulting in R2 values of 0.99.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78235/elife-78235-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
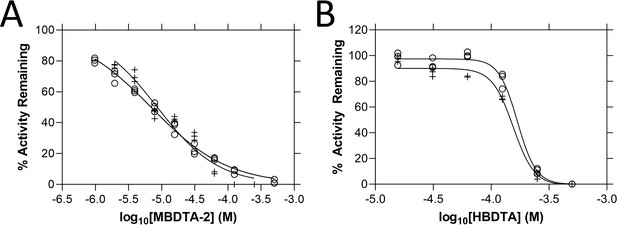
In vitro potency of (Z)-2-(5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (MBDTA-2) and (Z)-2-(5-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (HBDTA) against AtDHDPR.
Dose–response curves of (A) MBDTA-2 and (B) HBDTA against recombinant AtDHDPR1 (⚬) and AtDHDPR2 (+) enzymes. Initial enzyme rate was normalised against the vehicle control to determine % activity remaining. Data were fitted to a nonlinear regression model (solid line), resulting in R2 values of (A) 0.99 and 0.95 and (B) 0.99 and 0.99 for AtDHDPR1 and AtDHDPR2, respectively.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78235/elife-78235-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
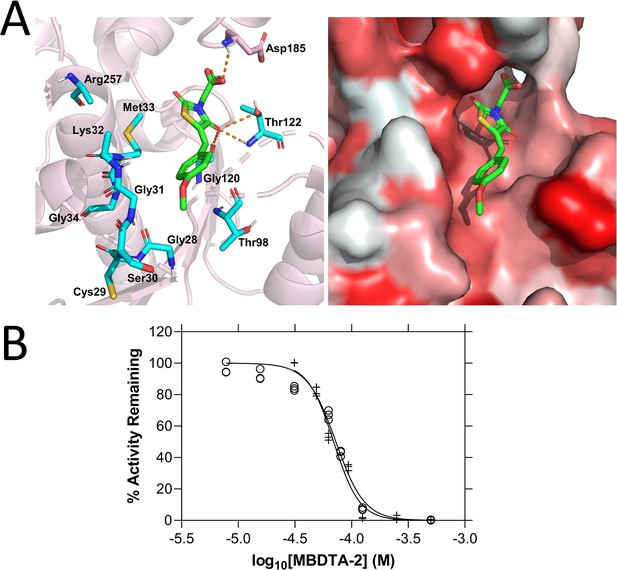
Mode of AtDHDPR2 inhibition by (Z)-2-(5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (MBDTA-2).
(A) The predicted MBDTA-2 (green)-binding site resulting from static docking with AtDHDPR2 (PDB ID: 5UA0) overlaps with the probable NADPH cofactor-binding site (cyan, left panel). Hydrophobicity of the predicted binding pocket (right panel) is represented by white-red shading indicating hydrophilic–hydrophobic residues. (B) Dose–response curves of MBDTA-2 against AtDHDPR1 (⚬) and AtDHDPR2 (+) enzymes in the presence of saturating concentrations of substrate and cofactor. Data were fitted to a nonlinear regression model (solid line), resulting in R2 values of 0.97 and 0.98 for AtDHDPR1 and AtDHDPR2, respectively.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Source data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78235/elife-78235-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
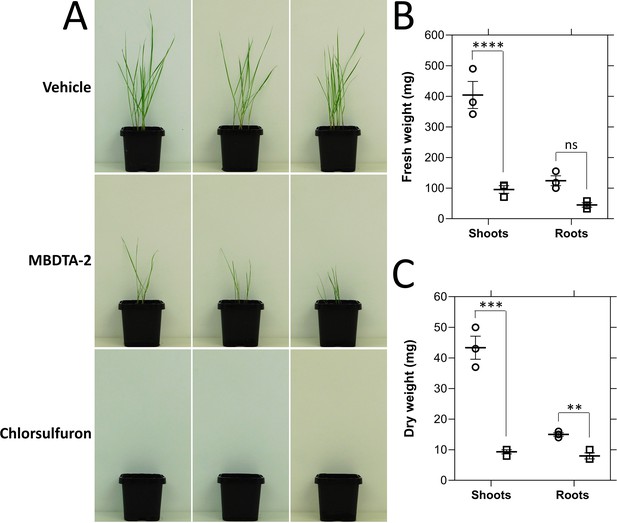
Inhibition of Lolium rigidum germination and growth by (Z)-2-(5-(4-methoxybenzylidene)-2,4-dioxothiazolidin-3-yl)acetic acid (MBDTA-2).
(A) Day growth of L. rigidum treated with three pre-emergence treatments of vehicle control (2% (vol/vol) DMSO, 0.01% Agral), or 1200 mg l−1 of MBDTA-2, or 1200 mg l−1 of chlorsulfuron. Treatments were given by pipetting 2.0 ml per pot directly onto seeds. (B) Fresh weight of L. rigidum shoots and roots following treatment of plants with vehicle control (dots) or MBDTA-2 (lines). Shoots, p = 0.00002, roots, p = 0.05233, unpaired Student’s two-tailed t-test. (C) Dry weight of L. rigidum shoots and roots following treatment of plants with vehicle control (dots) or MBDTA-2 (lines). Shoots, p = 0.00088, roots, p = 0.00374, unpaired Student’s two-tailed t-test. Data were normalised against the vehicle control. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (N = 3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Source data for Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/78235/elife-78235-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | DHDPS1 | TAIR | AtG60880 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | DHDPS2 | TAIR | AtG45440 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | DHDPR1 | TAIR | At2G44040 | |
| Gene (Arabidopsis thaliana) | DHDPR2 | TAIR | At3G59890 | |
| Software, algorithm | PyRX | Source Forge | Version 0.8 |





