Compartmentalization and persistence of dominant (regulatory) T cell clones indicates antigen skewing in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Figures
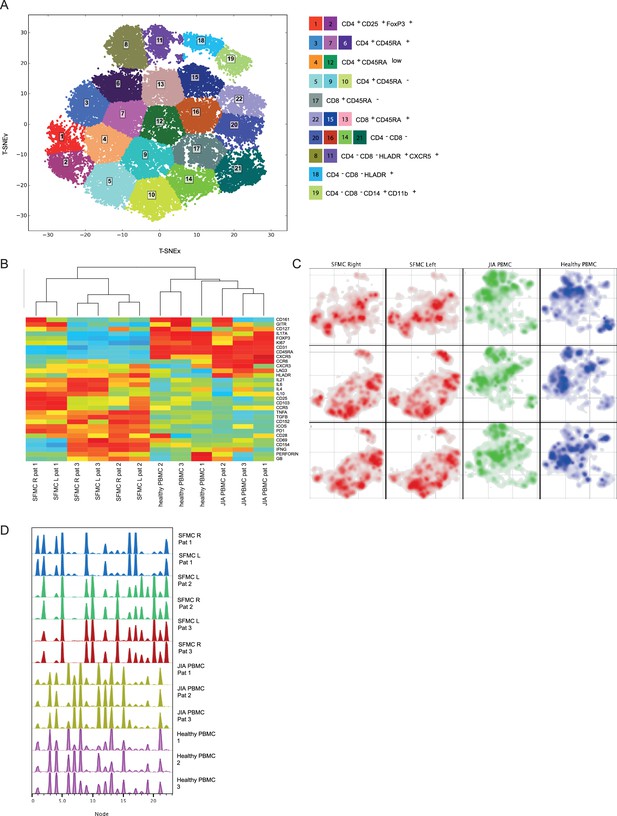
Overall immune architecture in left and right affected joints is very similar but distinct from peripheral blood.
(A) Density maps based on t-SNE dimensional reduction and k-means clustering analysis on SF and PB samples, resulting in 22 cellular nodes. (B) Preliminary hierarchal clustering on the median expression of all markers, excluding lineage markers. (C) Density maps of immune cellular populations within the t-SNE maps. (D) Node frequency fingerprints showing the distribution across the nodes of SFMCs and PBMCs. PB, peripheral blood; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; SF, synovial fluid; SFMC, synovial fluid mononuclear cell; t-SNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.
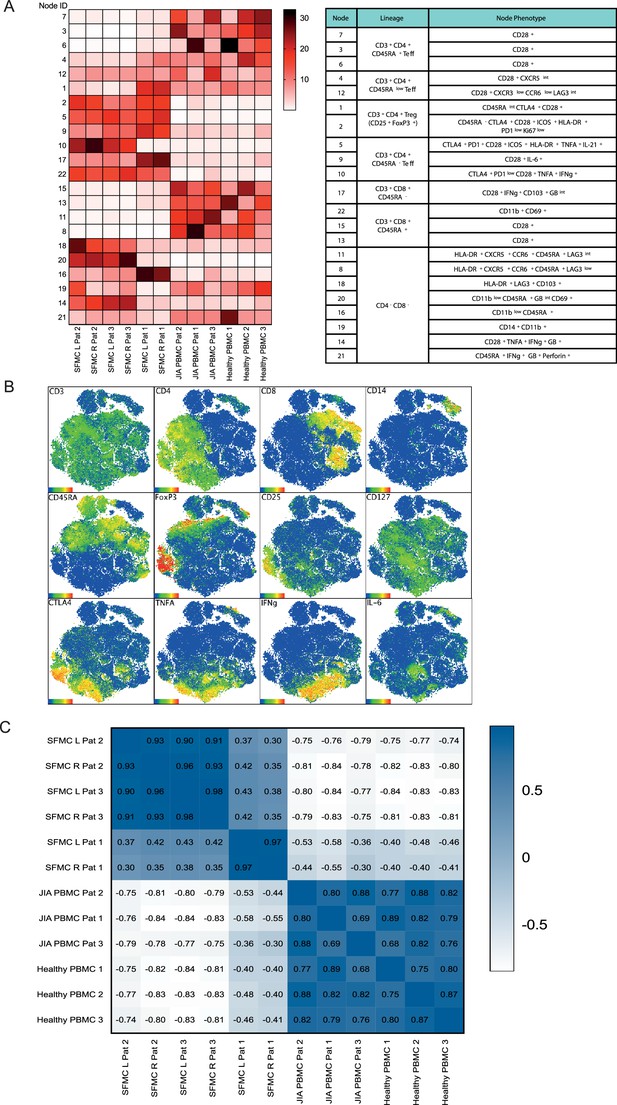
Preliminary analysis reveals correlation between SFMC from distinct joints.
(A) Node frequency showing the distribution of T cell markers across the nodes of SFMCs an PBMCs in the CyTOF analysis. (B) Marker expression of t-SNE dimensional reduction and k-means clustering analysis on SFMC and PBMC samples (C) Correlation matrix using spearman correlation of the entire spectrum of node frequency given in (A). PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; SF, synovial fluid; SFMC, synovial fluid mononuclear cell; t-SNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.
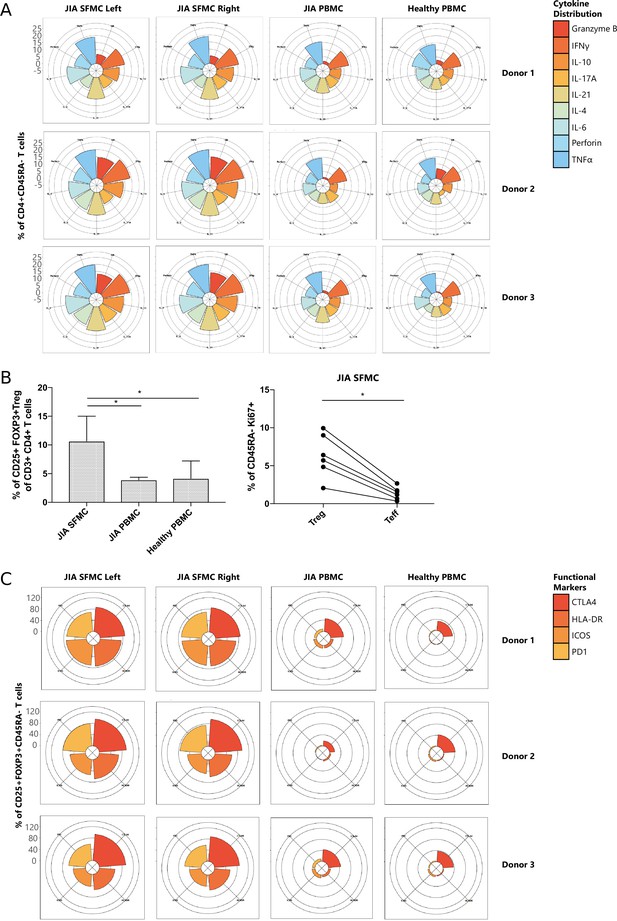
T cells display similar phenotypical and functional profiles at distinct inflamed locations.
(A) Cytokine production of CD4+CD45RA− memory T cells depicted in radar plots. Axis indicates the proportion of positive cells for individual cytokines (indicated by coloring) within the memory T cell fraction. (B) Percentage CD25+FOXP3+ Treg of CD3+CD4+ cells in SFMC and PBMC of JIA patients and healthy children, and percentage of Ki67+ cells within CD45RA− cells in Treg and non-Treg in SFMC (nonparametric Mann-Whitney, *=p<0.05). For SFMCs, data from the right and left knee joints for all patients is shown. (C) Expression of functional markers by CD25+FOXP3+CD45RA− cells. JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; SFMC, synovial fluid mononuclear cell.
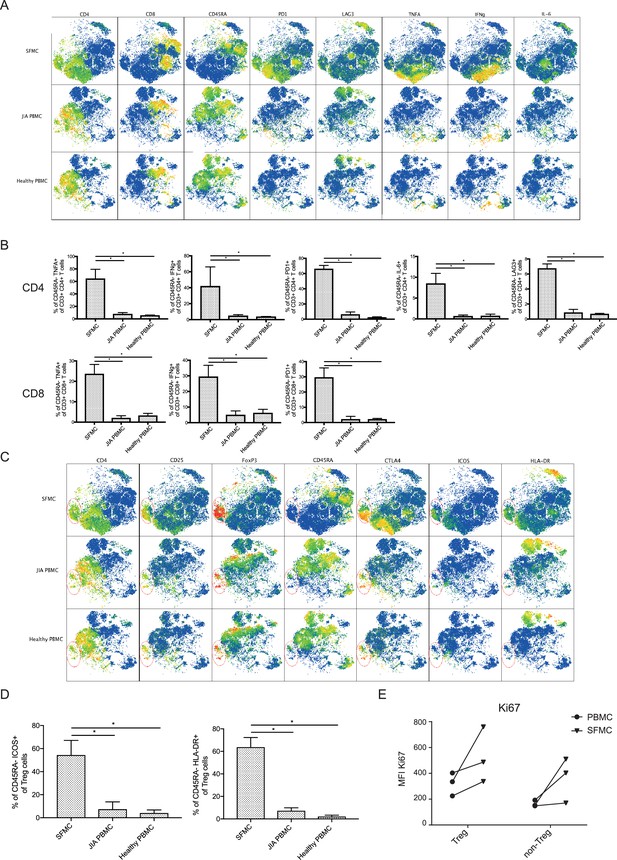
JIA SFMCs display an activated expression profile.
(A) t-SNE plots showing the expression profile of phenotypical and functional markers in SFMC and PBMC from JIA patients and PBMC from healthy children. (B) Bar charts showing the percentage of specific cell populations within CD4+CD45RA− and CD8+CD45RA− cells (nonparametric Mann-Whitney, *=p<0.05). (C) TtSNE plots showing the expression profile of phenotypical and functional Treg markers in SFMC, PBMC from JIA patients and PBMC from healthy children. (D) Quantification of CD45RA−ICOS+ and CD45RA−HLA−DR+ expression on CD25+FOXP3+ Treg (nonparametric Mann-Whitney, *=p<0.05). (E) MFI of Ki67 protein expression in Treg and non-Treg as determined by flow cytometry. JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; SFMC, synovial fluid mononuclear cell; t-SNE, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding.
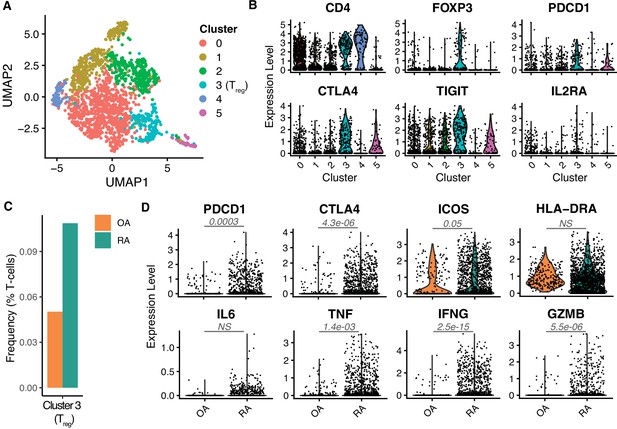
Tregs are increased in autoimmune rheumatic disease and express markers of enhanced activation.
(A) UMAP of scRNA-seq data of T cells obtained from RA and OA patients. Colors indicate different clusters, with cluster 3 being classified as Tregs. (B) Expression of prototypical Treg markers across different clusters identified in (A). (C) Frequency of Tregs as a percentage of the total number of T cells (y-axis) in OA (orange) and RA (green) patients. (D) Expression of markers associated with chronic TCR activation (PDCD1, CTLA4, and ICOS), and cytokines (TNF, IFNG, and GZMB) across OA (orange) and RA (green) patients. Numbers indicate p values (Wilcoxon rank-sum test) of the comparison between OA and RA. OA, osteoarthritis; NS, not significant; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
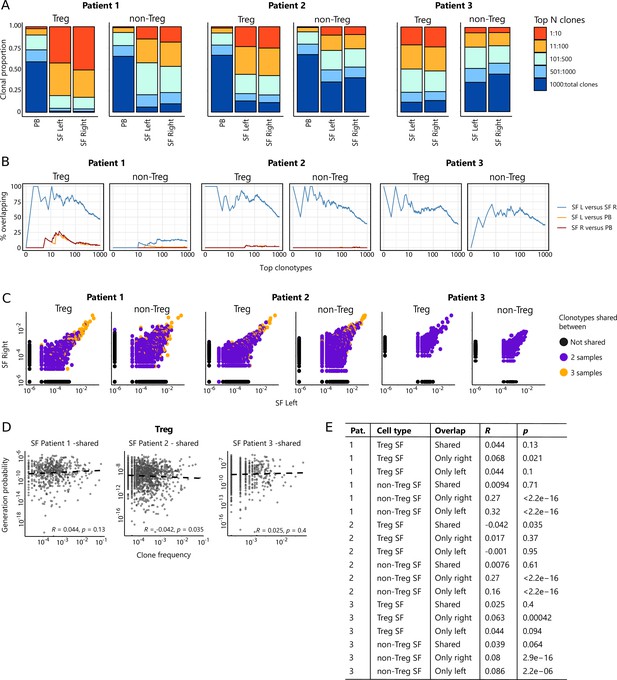
Highly dominant T cell clones are shared in synovial fluid (SF) from left and right joints and peripheral blood (PB).
(A) Clonal proportions of the TCRβ clones as detected in Treg and non-Treg sorted from PBMC, SF left joint, SF right joint of two different JIA patients. (B) Sequential intersection of abundant TCRβ clonotypes (based on amino acid sequence) across samples. Top clonotypes (ranging from 1 to 1000) are given on the x-axis, with the percentage of sequences overlapping between two given samples on the y-axis. For patient 3, no PB sample was available. (C) Frequency plots showing the overlapping Treg and non-Treg clones between left joint derived SF (x-axis) and right joint derived SF (y-axis), with color coding highlighting the clones that are shared with none of the other samples (black circle), shared in two samples (purple) and all three samples (PB, SF left, SF right; yellow). (D) Correlation (linear regression, dashed line) between frequency (x-axis) and generation probability (y-axis) of TCR clones shared across SF two samples. (E) Results of correlation between frequency and generation probability across all samples. p, p value; Pat., patient; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; R, Spearman’s Rho; SF, synovial fluid.
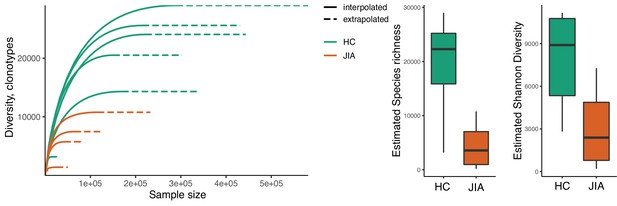
The JIA peripheral Treg repertoire is less diverse than healthy.
Sample-based rarefaction and extrapolation curves. Solid lines depict observed data, dashed lines depict extrapolated data. Calculated for all healthy samples (green), and JIA samples (orange). Every line represents one individual sample. Boxplots show median of estimated species richness (left) and estimated Shannon diversity (right) calculated from the rarefied and extrapolated data shown in (A). JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; HC, healthy control.
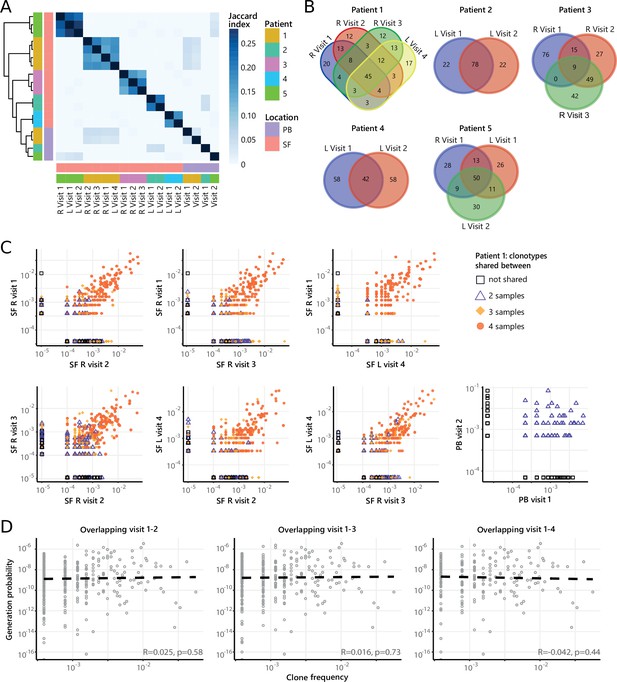
Persistence of Treg clones over the course of relapse remitting disease.
(A) Heatmap showing overlap (Jaccard index, light blue = limited overlap, darkblue = high overlap) of Treg derived TCRβ sequences obtained from SF or PB from JIA patients over time. L=left knee, R=right knee. (B) Venn diagrams displaying the 100 most abundant unique TCRβ clones, defined by amino acid sequence, for longitudinal SF samples from all patients. (C) Frequency plots showing the overlapping Treg clones between visits for SF and PB, with color coding and shapes highlighting the number of samples in which unique clones are found. L=left; R=right. (D) Correlation (linear regression, dashed line) between frequency (x-axis) and generation probability (y-axis) of TCR clones shared across two visits for SF samples. PB, peripheral blood; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
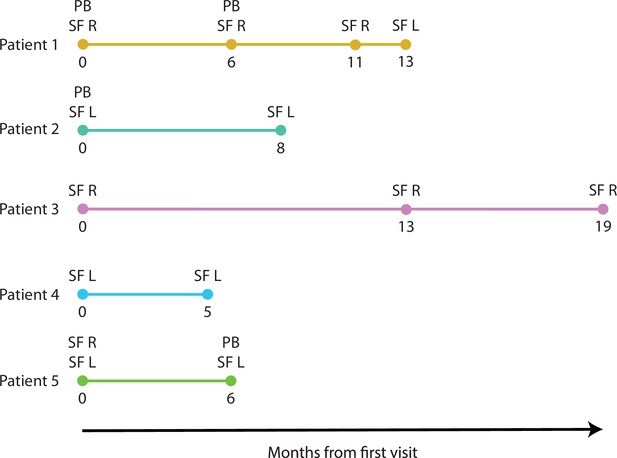
Longitudinal sampling timelines of JIA patients.
JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; L, left; PB, peripheral blood; R, right; SF, synovial fluid.
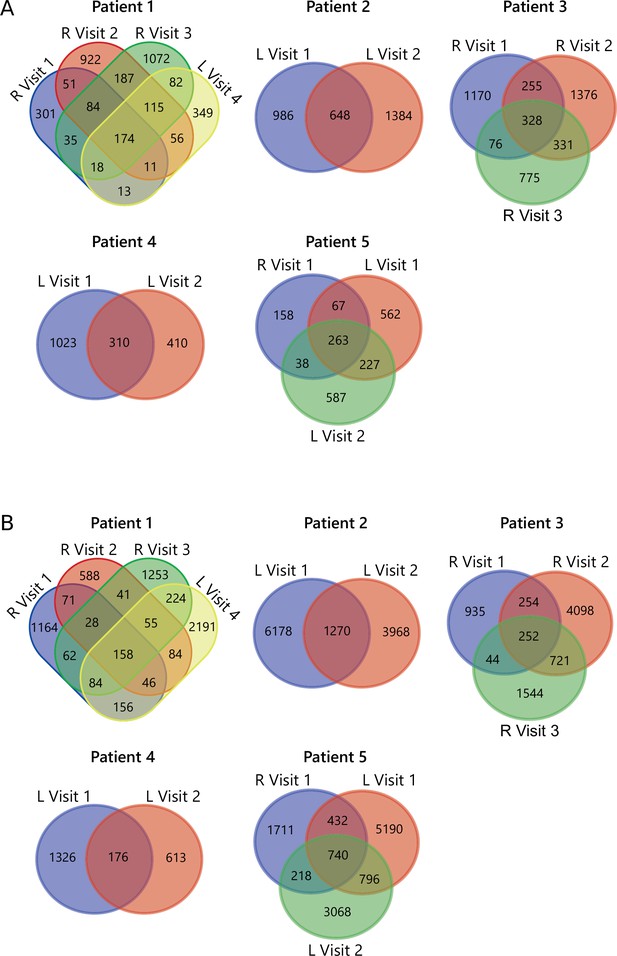
TCR overlap analysis.
(A) Venn diagrams displaying the overlap of all unique TCRβ clones, defined by amino acid sequence, for longitudinal SF samples from all patients for Tregs and (B) non-Tregs. SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
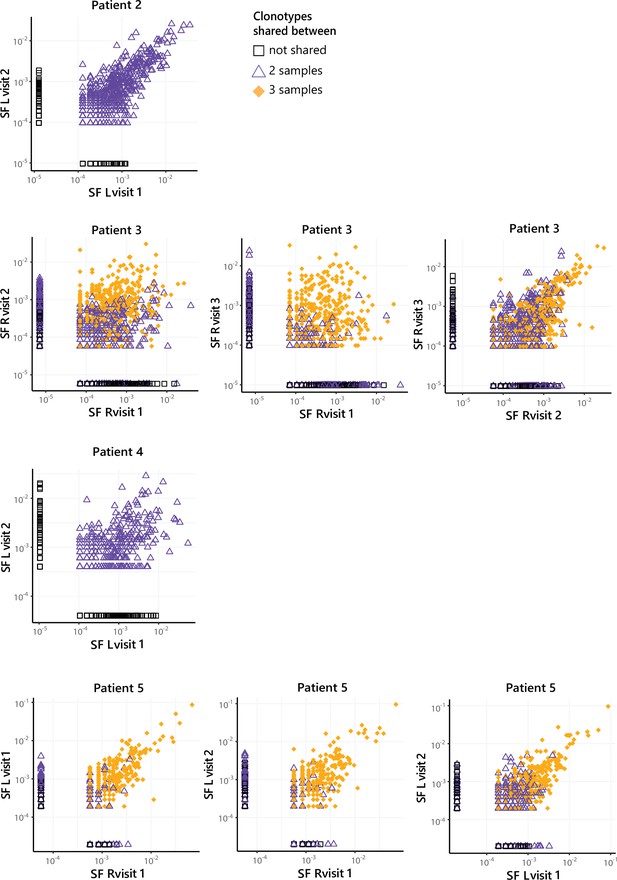
JIA Treg TCR frequencies over time in the remaining four patients.
Frequency plots showing the overlapping Treg clones between visits for SF and PB, with color coding and shapes highlighting the number of samples in which unique clones are found. JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; L, left; PB, peripheral blood; R, right; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
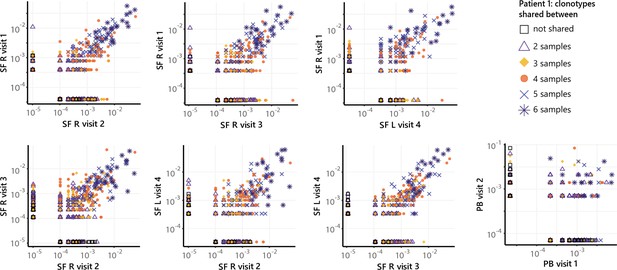
Frequencies of TCRs from persistent Tregs shared across SF and PB samples.
Frequency plots showing the overlapping Treg clones between visits for SF and PB for patient 1, with color coding and shapes highlighting the number of samples in which unique clones are found. PB, peripheral blood; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
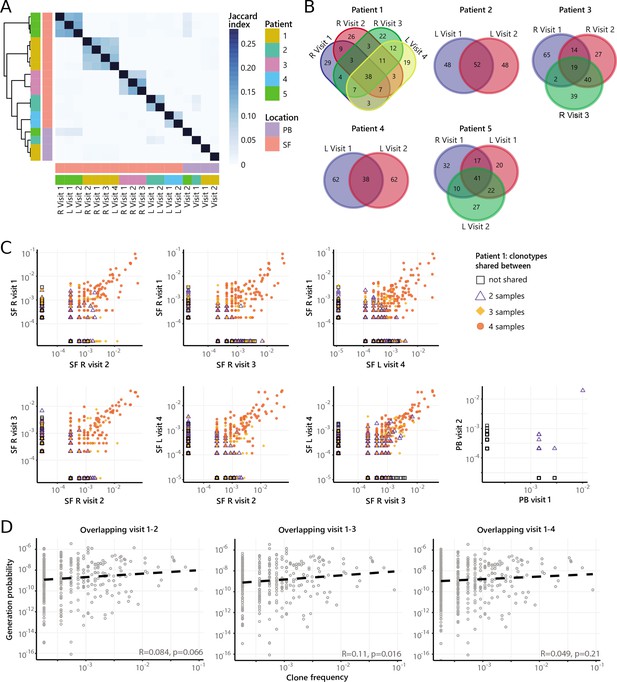
Persistence of non-Treg clones over the course of relapse remitting disease.
(A) Heatmap showing overlap (Jaccard index, light blue = limited overlap, darkblue = high overlap) of non-Treg derived TCRβ sequences obtained from SF or PB from JIA patients over time. L, left knee, R, right knee. (B) Venn diagrams displaying the 100 most abundant unique TCRβ clones, defined by amino acid sequence, for longitudinal SF samples from all patients. (C) Frequency plots showing the overlapping non-Treg clones between visits for SF and PB, with color coding and shapes highlighting the number of samples in which unique clones are found. L, left; R, right. (D) Correlation (linear regression, dashed line) between frequency (x-axis) and generation probability (y-axis) of TCR clones shared across two visits for SF samples. JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; PB, peripheral blood; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
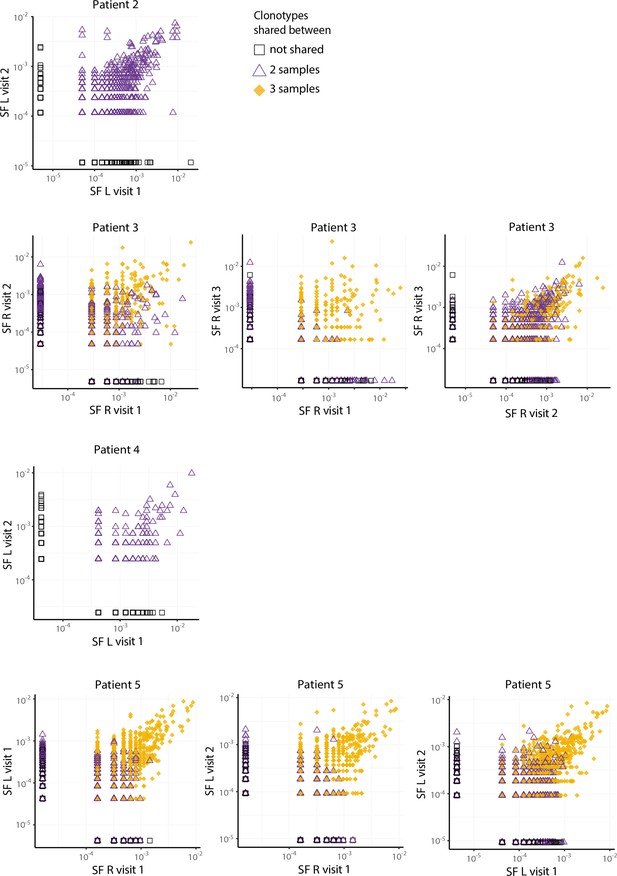
JIA non-Treg TCRβ frequencies over time in the remaining four patients.
Frequency plots showing the overlapping non-Treg clones between visits for SF and PB, with color coding and shapes highlighting the number of samples in which unique clones are found. JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; L, left; PB, peripheral blood; R, right; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
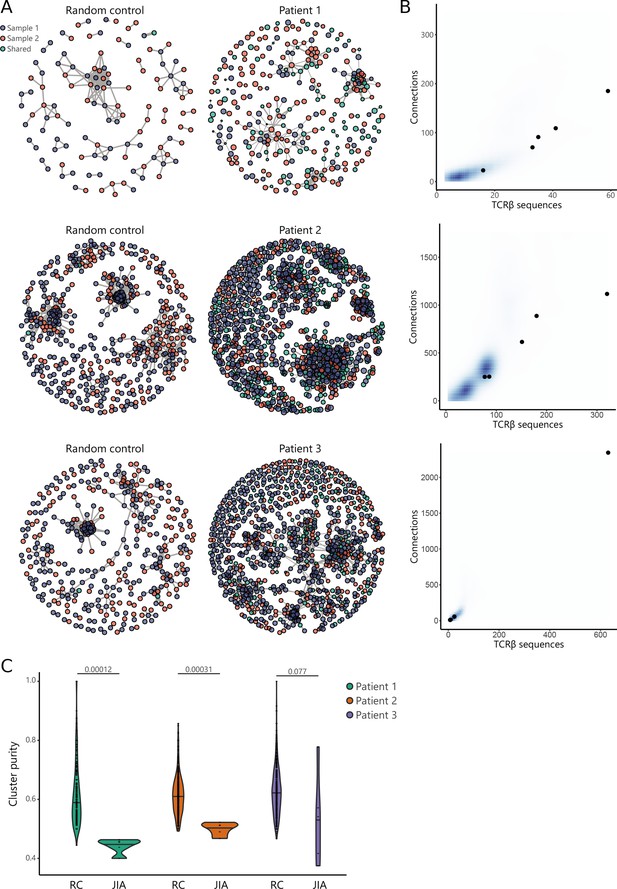
TCR similarity analysis of sequences found across distinct JIA patient knees.
(A) TCR similarity networks based on amino acid k-mer sharing (k=3) between TCR sequences. Every node represents one TCRβ sequence, with sequences present in one sample (SF from left or right knees) highlighted in blue and orange, and sequences shared across two samples highlighted in green. Nodes are connected if TCRs share at least eight k-mers. Networks from JIA patient repertoires (right) are compared to random repertoires (left), with the same repertoire size. (B) Number of TCR sequences (x-axis) and their connections (y-axis) to other TCR sequences of the top five similarity clusters identified in (A). Blue density maps depict clusters identified in random repertoires (N=100), while black circles depict clusters identified in JIA patients. (C) Cluster purity (y-axis, %) for the top five clusters identified in random repertoires (RC), and JIA patient TCR similarity networks. Numbers indicate p-value of difference between RC and JIA (Mann-Whitney). JIA, juvenile idiopathic arthritis; RC, random repertoires; SF, synovial fluid; TCR, T cell receptor.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological sample (human) | Peripheral blood | University Medical Center Utrecht | Healthy donors and JIA patients | |
| Biological sample (human) | Synovial fluid | University Medical Center Utrecht | JIA patients | |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD3 (UCHT1) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 300402 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD4 (SK3) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 344625 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD8 (SK1) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 344727 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD11b (ICRF44) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 301302 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD16 (3G8) (Mouse monoclonal) | Fluidigm | Cat#: 3209002B | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD14 (M5E2) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 301843 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IL-4 (8D4-8) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 500707 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IFN-g (B27) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 506513 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IL-17A (BL168) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 512302 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IL-21 (3A4-N2) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 513009 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD161 (HP-3G10) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 339902 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD45RA (HI100) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 304102 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD69 (FN50) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 310902 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD28 (CD28.2) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 302923 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD152 (BNI3) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 555851 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD154 (24-31) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 310835 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human HLA-DR (L243) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 307612 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human LAG3 (17B4) (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab40466 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human PD1 (EH12.2H7) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 329941 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human Ki67 (20Raj1) (Mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific/eBioscience | Cat#: 14-5699-82 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human ICOS (C398.4A) (Armenian Hamster monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 313512 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD31 (WM59) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 303102 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD103 (B-Ly7) (Mouse monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific/eBioscience | Cat#: 14-1038-82 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CXCR3 (G025H7) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 353718 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CXCR5 (RF8B2) (Rat monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 552032 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CCR5 (NP-6G4) (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab115738 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CCR6 (G034E3) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 353402 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD25 (M-A251) (Mouse monoclonal) | BD Biosciences | Cat#: 555429 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD127 (A019D5) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 351302 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human FOXP3 (PCH101) (Rat monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific/eBioscience | Cat#: 14-4776-82 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human GITR (621) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 311602 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human TGF-B (TW4-2F8) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 349602 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IL-10 (JES3-9D7) (Rat monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 501402 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human TNF-alpha (Mab11) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 502902 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human IL-6 (MQ2-13A5) (Rat monoclonal) | Thermo Fisher Scientific/eBioscience | Cat#: 16-7069-85 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human Granzyme B (CLB-GB11) (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab103159 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human Perforin (B-D48) (Mouse monoclonal) | Abcam | Cat#: ab47225 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD45-A (HI30) (Mouse monoclonal) | Fluidigm | Cat#: 3089003B | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD45-B, C or D (HI30) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 304002 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | DNA (singlets) Cell-ID Intercalator-Ir | Fluidigm | Cat#: 201192 | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Cisplatin (Live/Dead) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: 479306-1G | CyTOF (5μg/ml) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD3-BV510 (UCHT1) (Mouse monoclonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 300448 | FACS (dilution 1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD4-FITC (SK3) (Mouse monoclonal) | eBioscience | Cat#: 11-0047-42 | FACS (dilution 1:100) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD25-PE/Cy7 (2A3) (Mouse monoclonal) | BD | Cat#: 335789 | FACS (dilution 1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-human CD127-AF647 (A019D5) (Mouse monolonal) | BioLegend | Cat#: 351318 | FACS (dilution 1:50) |
| Antibody | Anti-human FOXP3-eF450 (PCH101) (Rat monoclonal) | eBioscience | Cat#: 48-4776-42 | FACS (dilution 1:50) |
| Chemical compound, drug | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: P1585 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Ionomycin | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat#: I9657 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Brefeldin A | eBioscience | Cat#: 00-4506-51 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Monensin | BioLegend | Cat#: 420701 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set | eBioscience | Cat#: 88-8824-00 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | EQ Four Element Calibration beads | Fluidigm | Cat#: NC1307119 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy mini kit | Qiagen | Cat#: 74104 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | RNeasy Micro Kit | Qiagen | Cat#: 74004 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | SMARTer RACE cDNA Amplification kit | Clontech | Cat#: 634923 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NGSgo-LibrX | GenDx | Cat#: 2342605 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NGSgo-IndX | GenDx | Cat#: 2342153 | |
| Software, algorithm | FlowJo (v.10.2) | TreeStar | ||
| Software, algorithm | MarVis | https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-92 | ||
| Software, algorithm | Seurat (v.4.1.1) | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | ||
| Software, algorithm | iNEXT (v.3.0.0) | https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12613 | ||
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism (v.7.0) | GraphPad | ||
| Software, algorithm | RTCR | https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw339 | ||
| Software, algorithm | OLGA | https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz035 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Clinical characteristics of JIA patients and healthy controls included in the study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79016/elife-79016-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Overview of the CyTOF T cell panel with 37 markers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79016/elife-79016-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/79016/elife-79016-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





