Epidermal threads reveal the origin of hagfish slime
Figures
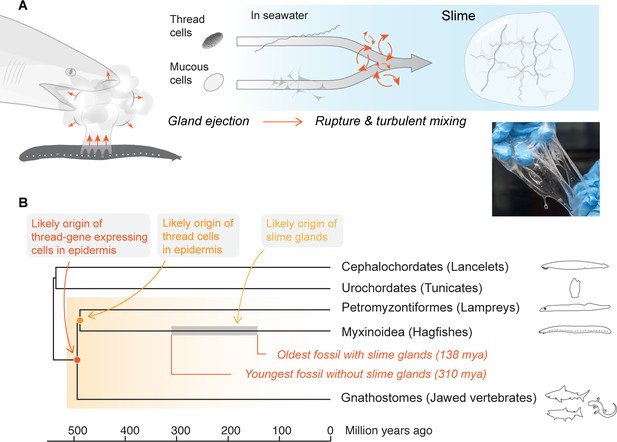
Mechanism and evolutionary history of hagfish slime.
(A) Hagfish defensive slime is produced by rapid ejection and rupture of mucous cells and thread cells into seawater by slime glands. Top shows a schematic sequence of slime formation. Threads and mucus are released from ruptured cells and mix with seawater to form large volumes of dilute, soft, viscoelastic slime (lower right). (B) A consensus tree of chordates highlighting the origins of epidermal thread cells and hagfish slime glands. Orthologs of intermediate filament thread genes are expressed in the skin of lampreys, hagfishes, teleost fishes, and amphibians (orange shade), and thus likely have an origin that dates back to the common ancestor of vertebrates. Epidermal cells producing large threads are only known in hagfishes and lampreys (see also Figure 1—figure supplement 1), and thus epidermal thread cells likely originated in their common ancestor. The gray segment highlights a wide window of time between 138 and 310 million years ago when the hagfish slime glands evolved (Miyashita, 2020).
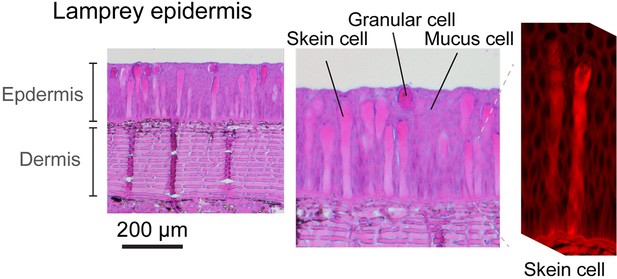
Cross-section of lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) epidermis based on hematoxylin-eosin (H&E)-stained cross-sectional slides.
Right shows a lamprey skein cell imaged with confocal laser scanning microscopy. The large fiber in lamprey skein cell ranges 80–120 and 30–60 μm in length and width, respectively (see also Lane and Whitear, 1980).
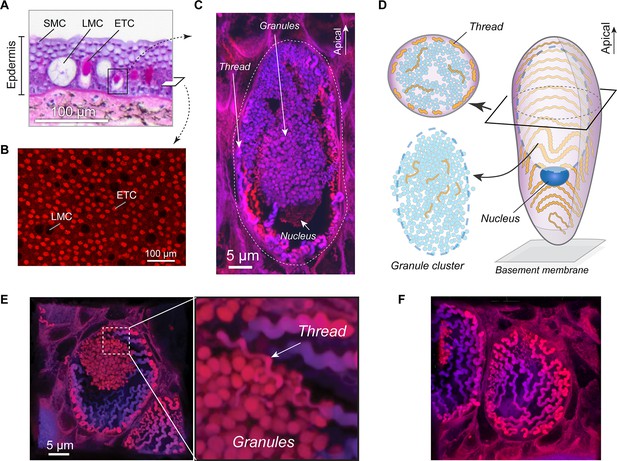
Morphology of the hagfish epidermal thread cell.
(A) Cross-section of dorsal epidermis from a Pacific hagfish (Eptatretus stoutii; hematoxylin-eosin-stained; bright-field microscopy). SMC, small mucous cell; LMC, large mucous cell; ETC, epidermal thread cell. (B) The basal layer of epidermis containing epidermal thread cells and large mucous cells, as captured in en face view. ETCs are characterized by granules and threads stained with the fluorescent stain eosin; LMCs appear as circular voids. (C) Longitudinal cross-section of an ETC, showing a cluster of granules, the nucleus located at the basal region of the granules, and a helical thread located mainly along the inner surface of the plasma membrane. (D) Schematic of major cellular components of an ETC. (E) Oblique cross-section of an ETC, showing the relative positions of the granule cluster and threads. Enlarged area shows a region where the thread is intimately associated with the granule cluster. (F) A close-up of the inner plasma membrane, showing the thread packed in a single layer in a switchback pattern. All images were captured with confocal microscopy unless otherwise noted.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Density of epidermal cells.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
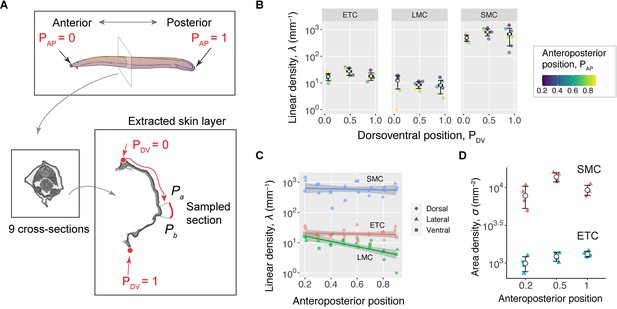
Abundance of hagfish epidermal cells.
(A) Schematic showing anteroposterior position (PAP), with 0 representing the snout and 1 the tip of the tail. (Bottom left) Schematic showing dorsoventral positions (PDV) in a hagfish in cross-section (see Materials and methods). (B) Linear density (λ) of each cell type for dorsal, lateral, and ventral regions along the hagfish (N=1 hagfish). Values are means ± SD. Dots represent data for each cross-section, with color representing PAP. The linear density of epidermal thread cells (ETCs) was relatively consistent as a function of circumferential position, with the mean value ranging between 17 and 27 mm–1. The other two cell types, small mucous cells and large mucous cells, had similarly uniform distributions. The small mucous cells exhibited the highest density (126–434 mm–1), and the large mucous cells had the lowest among the three (2–6 mm–1). (C) Among all three types of epidermal cells, only the large mucous cells exhibited a change in density with respect to the anteroposterior position. Based on linear regression models, we found no significant effect of anteroposterior position on the densities of ETCs and small mucous cells (p>0.1). However, in large mucous cells, we found a significant effect, with slope = –1.47 ± 0.30, p<0.001. (D) Area density () of small mucous cells and ETCs sampled from laser confocal images taken in en face view from two hagfishes at three different anteroposterior positions (N=2 samples per location). Values are means ± SD. Colored dots represent data for each sampled area. Data available in Figure 2—source data 1.
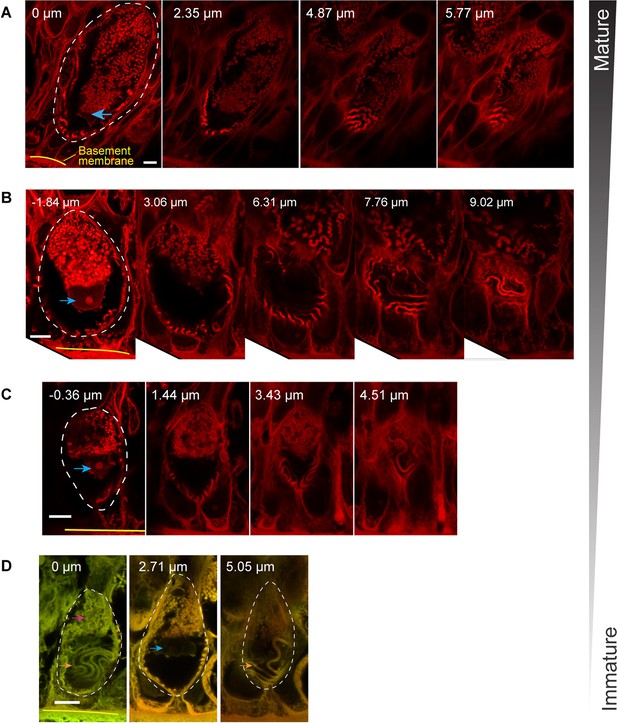
Morphology of epidermal thread cell (ETC) at different developmental stages.
(A–D) Developmental sequence of ETCs represented by cells of different sizes, with smaller cells at the bottom. Each cell is shown with images stacks at different z-distance, as annotated on the top. Note the variations in thread shape. Scale bars, 5 μm. All images were acquired from hematoxylin-eosin (H&E)-stained slides using confocal microscopy (Zeiss LSM980). The mature ETCs are 54.1±2.8 μm in length (in apical-basal direction) and 22.8±0.6 μm in width (means ± SD; N=5 cells).
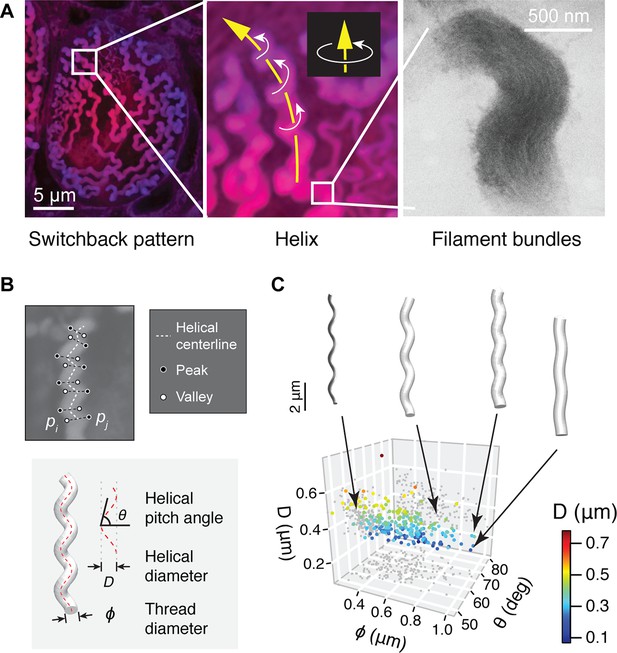
Geometry of hagfish epidermal threads.
(A) Three levels of epidermal thread structure. (Left-middle) At the micro-scale, the thread traces a right-handed helix, the centerline of which is arranged in a switchback pattern on the inner surface of the cell membrane. Yellow arrow denotes the direction of increase; white arrows denote direction of helical rotation. (Right) At the nano-scale, a thread consists of a dense bundle of intermediate filament proteins, shown here in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (see also Figure 3—figure supplement 1). (B) The peaks and valleys of the projected thread sections were used as landmarks for morphometric analysis. Blue dots, peaks; white dots, valleys; white dashed line, centerline. , thread diameter; , helical pitch angle; , helical diameter. (C) Variations in thread geometry with respect to a morpho-space defined by thread diameter , helical pitch angle , and helical diameter . With increasing pitch angle , thread diameter increases (p<0.05; linear regression model) and helical diameter decreases (p<0.001), illustrated with idealized threads.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Geometry of epidermal threads sampled using laser confocal microscopy.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
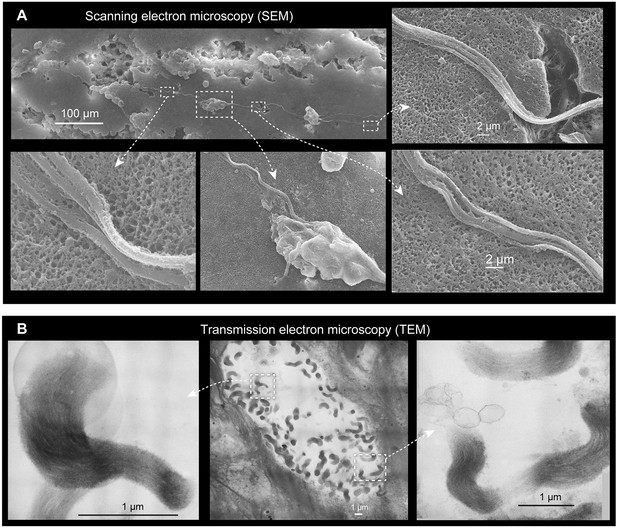
Morphology of epidermal threads.
(A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images showing details of a single epidermal thread cell (ETC) thread on the epidermal surface abraded with sandpaper, showing subfilament structure. (B) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of an ETC in cross-section, showing sub-micron structures of threads as parallelly aligned filament bundles, which is consistent with the thread structure observed in the Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa) (Blackstad, 1963).
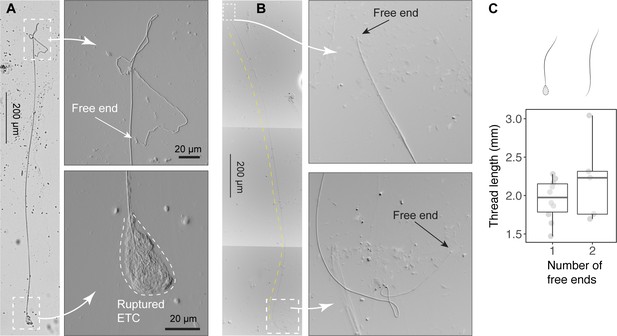
Size of released epidermal threads.
(A) A partially released thread (~2 mm long) from a ruptured epidermal thread cell (ETC), as viewed under light microscopy (see also Figure 4—figure supplement 1). (B) A thread with two free ends. (C) Boxplots of thread length () measurements based on threads with one free end (N=10) and two free ends (N=5). Values are length from individual threads. For threads with one free end, = 1.95 ± 0.27 mm (mean ± SD); for threads with two free ends, = 2.2 ± 0.54 mm, with this mean value used in scaling models.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Length of epidermal threads sampled using transmitted light microscopy.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
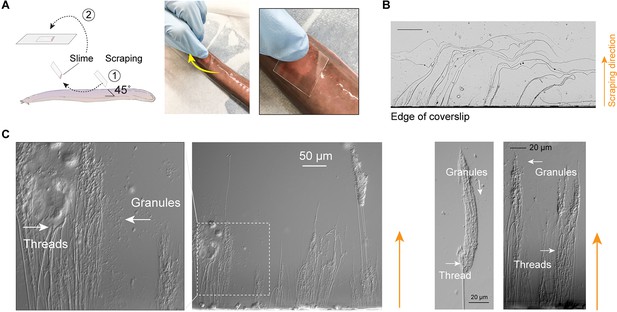
Release of epidermal threads.
(A) Schematic of sampling epidermal mucus using a coverslip scraped along the skin of an anesthetized hagfish. The coverslip was only gently pressed against the hagfish skin, as shown on the right. (B) Epidermal threads captured by the edge of coverslips, as viewed under light microscopy. (C) After scraping hagfish skin with the edge of a coverslip, ruptured epidermal thread cells (ETCs) and free granules and threads were evident near the coverslip edge. Enlarged area shows partially unraveled threads and granules.
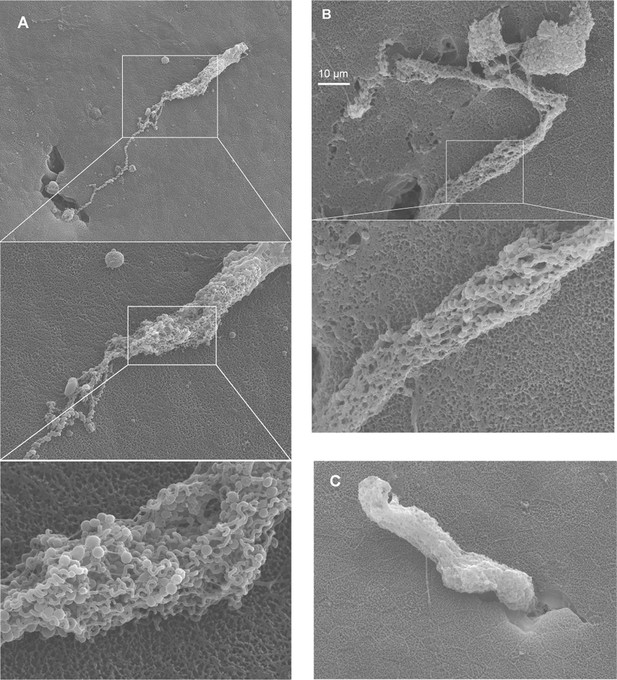
Release of epidermal threads.
(A–B) Granule clusters found on the epidermal surface, with helical threads still attached. (C) Partially released epidermal thread cell (ETC) granule cluster found on the epidermal surface.
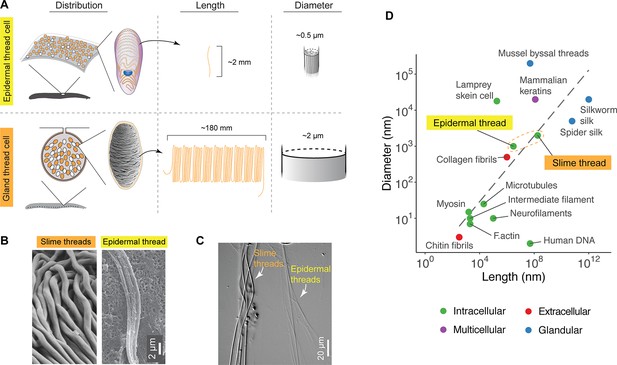
Comparison of distribution, size, and shape between epidermal and slime threads.
(A) A schematic comparison of the distribution of epidermal and gland thread cells, as well as the mean lengths and diameters of corresponding thread products. Data based on Pacific hagfish (Eptatretus stoutii). (B) A comparison of slime and epidermal threads viewed with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Note the epidermal thread has appeared to cleave into multiple sub-threads after being stretched (see also Figure 3—figure supplement 1). (C) Two types of threads collected from the same hagfish (viewed with differential interference contrast microscopy), highlighting their difference in diameter. (D) A size comparison of epidermal and slime threads in Pacific hagfish (E. stoutii) with other biofibers. Trend line represents a linear regression model based on all data points excluding human DNA. Colors denote different fiber production mechanisms (see Zeng et al., 2021).
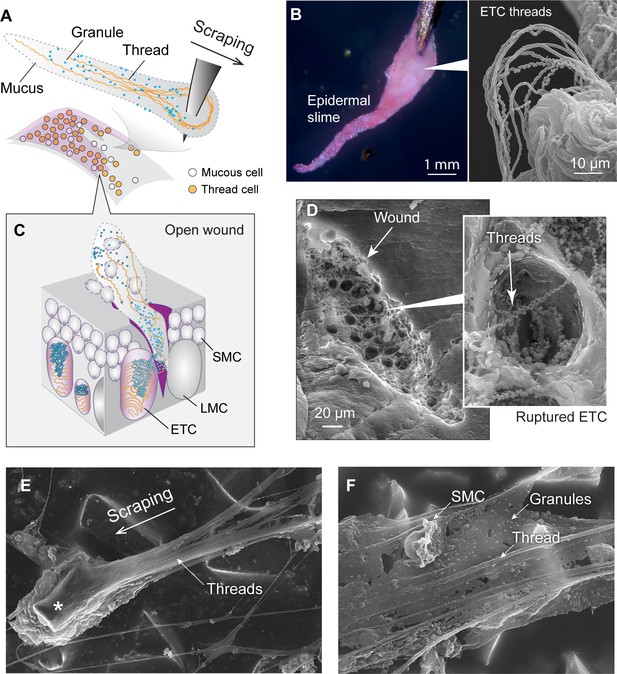
Formation and structure of epidermal slime produced by wounded skin.
(A) Schematic of epidermal slime formation when epidermis is wounded, with threads and granules from ruptured epidermal thread cells (ETCs) mixing with mucus from ruptured large mucous cells (LMCs). (B) Epidermal slime on pin tip, stained with eosin to show threads. (Right) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image of epidermal slime on pin tip, with enlarged areas showing stretched and unstretched threads. (C) A schematic of the slime formation by mixing of cellular contents from an open wound on epidermis. SMC, small mucous cell. (D) SEM images of a shallow abrasion wound, with insets showing damaged ETCs with partially released threads and granules. (E) Epidermal slime collected on sandpaper. Note the slime accumulated at the leading edge of the sand grain (asterisk) and the elongated slime at the trailing edge. (F) Thin film of epidermal slime collected by scraping with sandpaper, showing the scaffolding of mucus by threads, and the alignment of threads with the scraping direction. See more details in Figure 6—figure supplements 1–3.
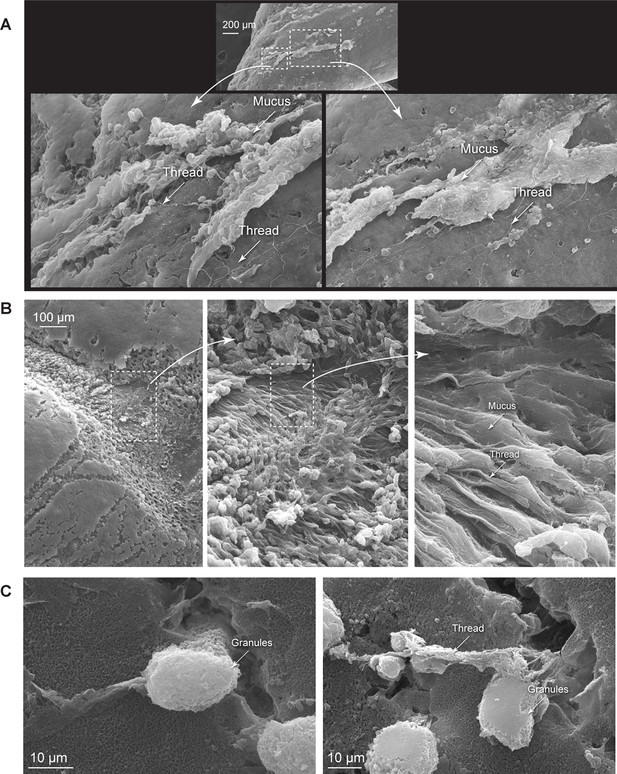
Formation of epidermal slime.
Newly wounded hagfish skin was fixed, dehydrated, and observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). (A–B) Formation of epidermal slime on abraded skin, with details showing the slime as a mixture of mucus, epidermal thread cell (ETC) threads and small mucous cells. (C) The release of ETC granules and threads from laceration wounds made with a scalpel.
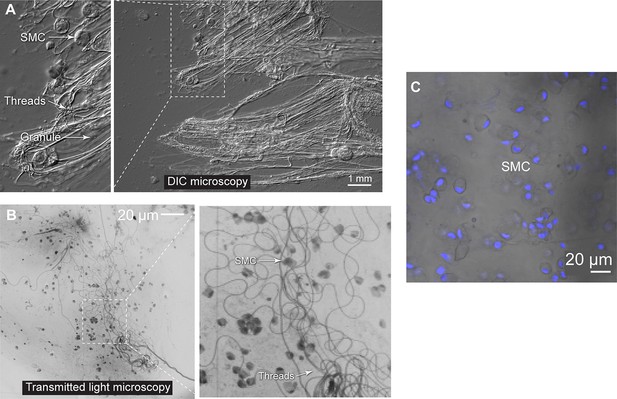
Structure of epidermal slime.
(A) Epidermal slime observed using differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, showing epidermal thread cell (ETC) threads, granules, and detached small mucous cells (SMC). (B) Epidermal slime collected after scraping hagfish skin with a pin and observed using bright-field microscopy, showing individual ETC threads. (C) Small mucous cells (SMC) appeared mostly intact in epidermal slime, although may have been ruptured. Here, we show small mucous cells with nuclei highlighted using DAPI.
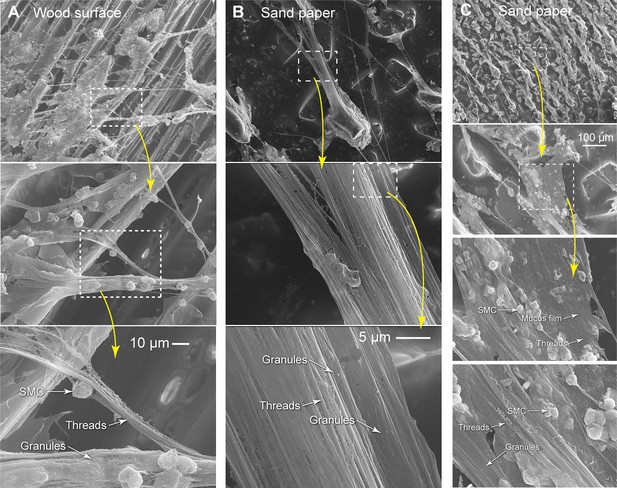
Structure of epidermal slime.
(A–C) After scraping hagfish skin with rough surfaces (sand paper and wood), we observed epidermal slime adhered to these surfaces using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The epidermal slime appeared as thin strings or sheets adhered to the protruding surfaces, with the rest trailing or crossing over gaps. From top to bottom, images show details of the epidermal slime with progressively increasing magnification. Dashed boxes denote enlarged areas.
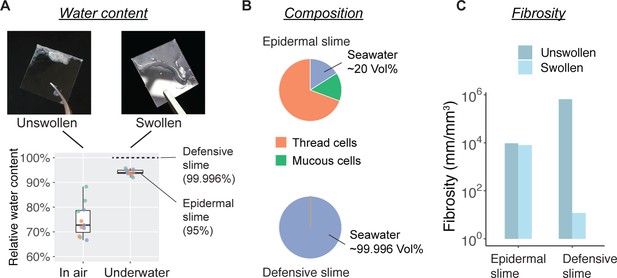
Water content and fibrosity of hagfish epidermal slime.
(A) The relative water content of epidermal slime collected by scraping a glass coverslip over blotted skin (unswollen) and underwater (swollen). Dots represent individual samples; colors represent different animals (N=3 for each group; see Materials and methods). (B–C) A comparison of slime composition (in relative volumes) and fibrosity between epidermal and defensive slimes. Note the high water content and low fibrosity of defensive slime produced with turbulent mixing after active ejection. See Figure 7—figure supplement 1f or more information on defensive slime.
-
Figure 7—source data 1
Water content of epidermal slime sampled from hagfish skin (blot-dried in air versus underwater).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-fig7-data1-v1.xlsx
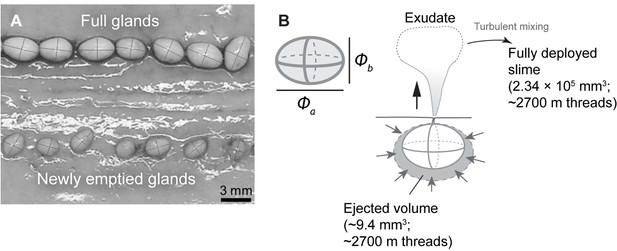
Morphometrics of hagfish defensive slime.
(A) Full glands and newly emptied glands on the same hagfish, showing difference in size and similarity in shape (see Schorno et al., 2018). We found that full and newly emptied glands share a similar aspect ratio of ~1.44 (see Materials and methods, Section ‘Fibrosity of defensive slime’). (B) Top left shows the configuration of major and minor axes for a slime gland. The right shows the configuration for estimating the volume of ejected gland exudate. The volume of ejected exudate per gland can be approximated as the volume difference between full and newly emptied glands (see Materials and methods, Section ‘Fibrosity of defensive slime’).
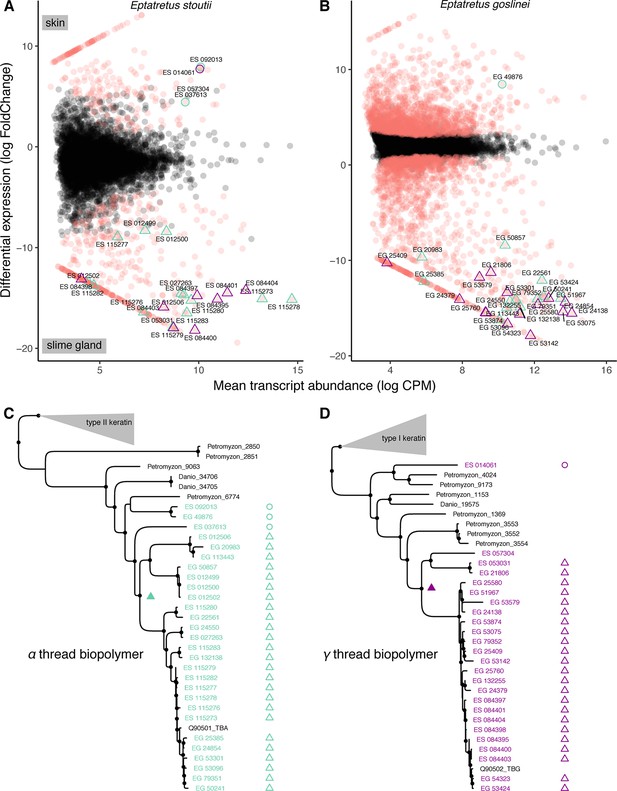
Molecular analyses suggest an epidermal origin of hagfish defensive slime threads.
(A and B) Differentially expressed transcripts (red) from skin versus slime gland RNAseq datasets (3× replicates each, from single specimens of Eptatretus goslinei; FDR <0.001). In both species, a low diversity of α and γ thread biopolymer genes are expressed in skin, while a large diversity of both α and γ thread biopolymer genes are expressed in slime gland. (C and D) Comparative phylogenomic analyses of α and γ thread gene trees (maximum likelihood) reveal slime gland- and hagfish-specific expansions of both α and γ intermediate filament genes. The presence of well-characterized, skin-specific α and γ thread orthologs from both lamprey (Petromyzon) and teleost (Danio) indicates that independent gene duplications of skin-expressed α and γ loci gave rise to a radiation of slime gland-specific transcripts. Open circles indicate skin expression; open triangles indicate slime gland expression; filled triangles indicate most parsimonious prediction of transition from ancestral skin expression to slime gland expression; small circles at nodes indicate greater than 80% support from either ultrafast bootstrap approximation or approximate likelihood ratio tests (Nguyen et al., 2015). Trees shown here are pruned from larger phylogenetic analyses. See Figure 8—figure supplements 1–2 and Materials and methods for details.
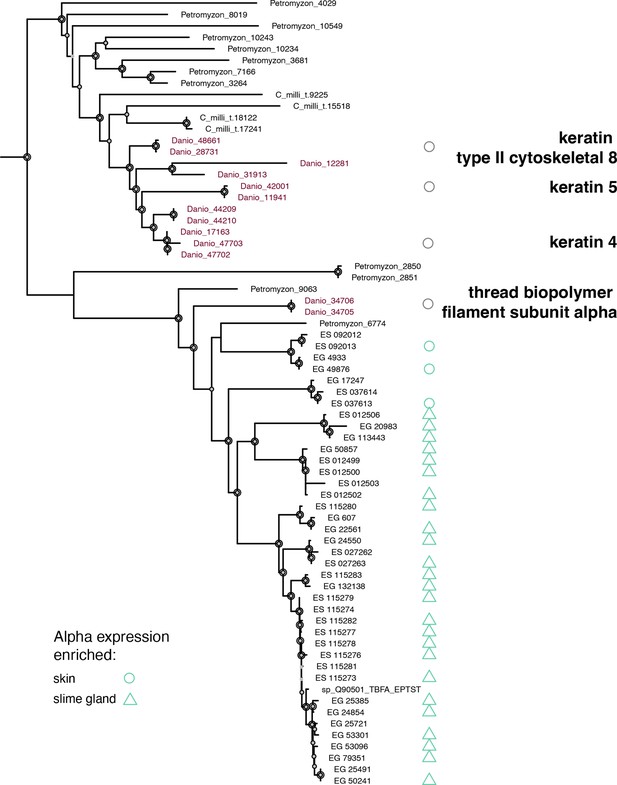
Phylogenetic analysis of vertebrate thread biopolymer alpha genes from selected taxa, rooted with its closest sister clade, which is comprised of type II keratins.
This tree was rooted with more distant outgroups that included glial acidic fibrillary protein and other neuronally expressed intermediate filament loci, not shown. Nodal support is given by ultrafast bootstrap and approximate likelihood ratio tests (Nguyen et al., 2015). Node symbol size indicates that at least one of those indices exceeds 70%, 80%, or 90% respectively relative to the size of the symbol. Danio rerio sequences were annotated using UNIPROT gene descriptions (Wang et al., 2021), which included expression information. Circles indicate skin expression. Triangles indicate slime gland expression. Teal symbols are derived from the present study. Gray circles are derived from public annotations. ES indicates Eptatretus stouti. EG indicates Eptatretus goslinei. ES and EG sequences that lack expression information have fewer than 50 transcripts per million (TPM). This analysis does not capture the complete evolutionary histories of outgroup genes and taxon sampling was purposefully limited. Therefore, outgroup sequences were pruned from this depiction. The rooted trefile alpha.tre, including all nodal support values, is available at https://github.com/plachetzki/ETC_GTC/tree/main/ES_EG_hagfish/trees.
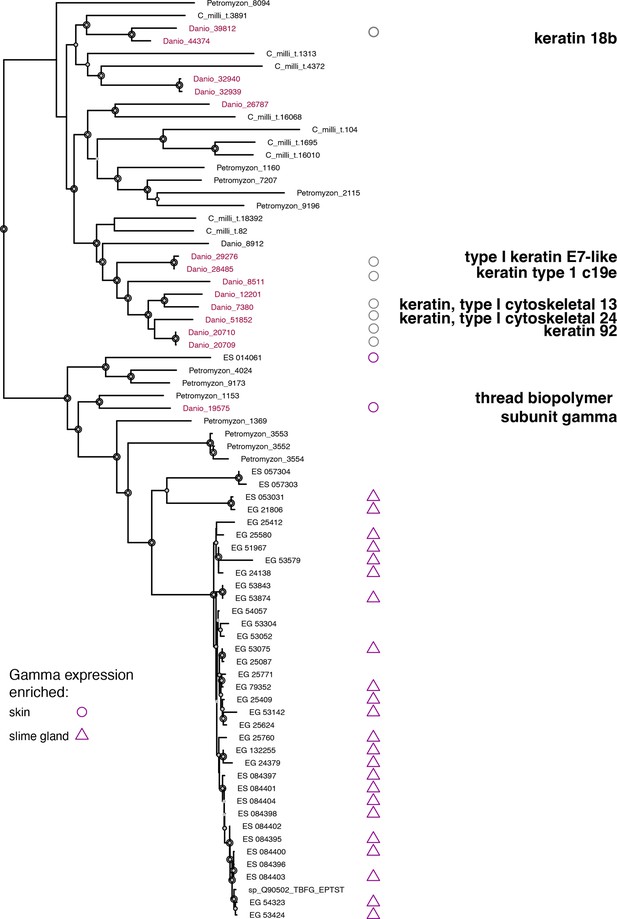
Phylogenetic analysis of vertebrate thread biopolymer gamma genes from selected taxa, rooted with its closest sister clade, which is comprised of type I keratins.
This tree was rooted with more distant outgroups that included desmins and other distantly related skin expressed keratins, not shown. Nodal support is given by ultrafast bootstrap and approximate likelihood ratio tests (Nguyen et al., 2015). Node symbol size indicates that at least one of those indices exceeds 70%, 80%, or 90% respectively relative to the size of the symbol. Danio rerio sequences were annotated using UNIPROT gene descriptions (Wang et al., 2021), which included expression information. Circles indicate skin expression. Triangles indicate slime gland expression. Purple symbols are derived from the present study. Gray circles are derived from public annotations. ES indicates Eptatretus stouti. EG indicates Eptatretus goslinei. ES and EG sequences that lack expression information have fewer than 50 transcripts per million (TPM). This analysis does not capture the complete evolutionary histories of outgroup genes and taxon sampling was purposefully limited. Therefore, outgroup sequences were pruned from this depiction. The rooted trefile gamma.tre, including all nodal support values, is available at https://github.com/plachetzki/ETC_GTC/tree/main/ES_EG_hagfish/trees.
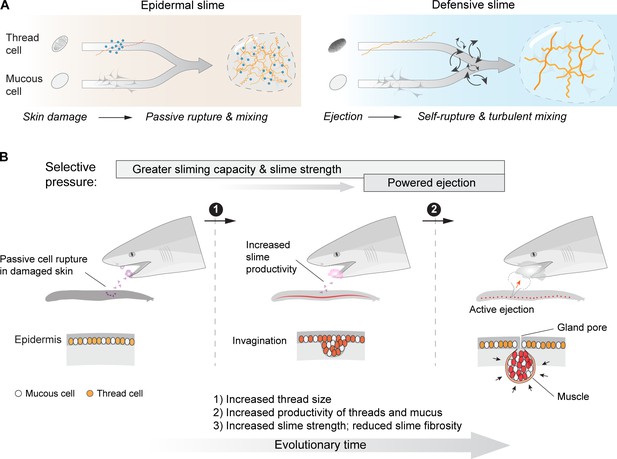
An epidermal origin of hagfish slime.
(A) A comparison of slime formation mechanism between epidermal and defensive slimes, highlighting their similarity in basic structural components and differences in mixing mechanism. Note a transition from passive slime formation to active ejection, as well as a transition in slime composition. (B) Schematic of two critical transitions in the evolution of hagfish slime glands. Specifically, selection for greater slime capacity likely drove an increase in the concentration of thread cells and mucous cells in epidermis and later in slime glands, while selection for active ejection likely was responsible for the acquisition of gland musculature and an enlarged gland cavity with a narrow pore (see Discussion). Bottom row highlights the invagination of epidermis (middle) as a possible intermediate state between the ancestral form (left) and muscularized slime glands seen in modern hagfishes (right).
Videos
Z-stack image sequences of eosin-stained hagfish epidermis from confocal laser scanning microscopy with transmitted light, taken in en face view.
Note a dense layer of epidermal thread cells (ETCs) and large mucous cells at the basal layer of epidermis. Each ETC is evident with a cluster of granules highlighted in red, while large mucous cells appear as voids.
Z-stack image sequences of hagfish epidermis from confocal laser scanning microscopy, taken in en face view.
Note the outermost epidermis is covered by a layer of small mucous cells, while epidermal thread cells (ETCs) are found at the basal layer.
Z-stack image sequences of hagfish epidermal thread cells (ETCs) based on confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Images were taken from eosin-stained epidermis, and the ETC granules are the brightest feature.
Three-dimensional reconstructions of epidermal thread cells (ETCs) based on confocal laser scanning microscopy, showing granule cluster and helical-shaped threads packed along the plasma membrane.
Experimentally induced formation of epidermal slime, demonstrated by scraping wet and blot-dried hagfish skin with a sharp pin head.
Scraping with a blunt pinhead did not lead to slime formation.
Different from condensed, adhesive hagfish epidermal slime, the defensive slime is highly diluted and not sticky.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (RNAseq data of hagfishes Eptatretus goslinei, Eptatretus stoutii) | Under BioProject PRJNA896978 at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra | |||
| Biological sample (hagfishes: Eptatretus goslinei, Eptatretus stoutii) | Wild-captured | |||
| Software, algorithm | R (https://www.r-project.org/) | |||
| Software, algorithm | Code (https://github.com/plachetzki/ETC_GTC) |
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary table.
(A) Morphological parameters of slime glands of Pacific Hagfish. (B) Comparison of fibrosity between defensive slime and epidermal slime.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/81405/elife-81405-supp1-v1.docx





