Male rodent perirhinal cortex, but not ventral hippocampus, inhibition induces approach bias under object-based approach-avoidance conflict
Figures
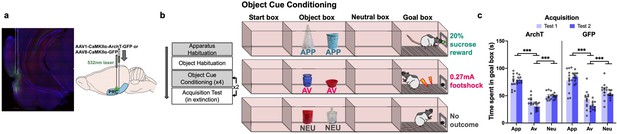
Object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task.
Rats expressing AAV1-CaMKIIa-ArchT-GFP (archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]) or AAV8-CAMKIIa-GFP (green fluorescent protein [GFP]) in the perirhinal cortex (PRC, a) underwent object cue conditioning to learn the outcomes associated with appetitive (APP), aversive (AV), and neutral (NEU) object pairs (b). Three-way ANOVA of acquisition data (mean ± SEM) indicated successful learning in both ArchT and GFP groups (c). Post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction applied. ***p<0.001.
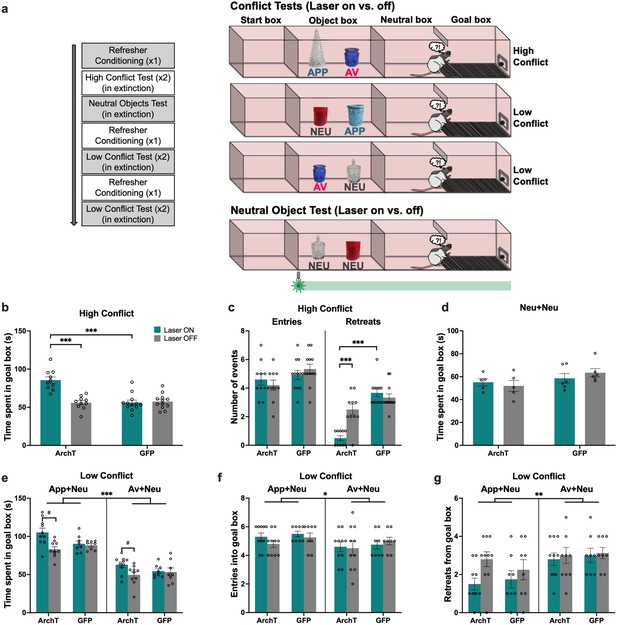
Impact of perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition on object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task performance.
(a) Rats (n=10 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=12 green fluorescent protein [GFP]) underwent a series of tests conducted in extinction: high conflict (APP+AV objects), neutral (NEU+NEU), and low conflict (APP+NEU or AV+NEU). (b–c) PRC inhibition (laser ON during the entire session) significantly increased time spent in the goal box and reduced the number of retreats in the high conflict test. (d) There was no effect of PRC inhibition on AA behavior in the neutral test. (e) Similar to the high conflict test, PRC inhibition increased time spent in the goal box in both low conflict tests. (f–g) PRC inhibition did not impact the number of entries or retreats in the App+Neu or Av+Neu low conflict tests, although there was a main effect of valence, with a greater number of entries for App+Neu and more retreats for Av+Neu. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for data shown in c,e-g, and two-way ANOVA was conducted for data in b,d. Post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction were conducted to further investigate significant interactions in all datasets except in d.***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.

Additional perirhinal cortex (PRC) rat data for the approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task.
(a) PRC inhibition did not impact rats’ goal box latency to enter (LTE) all compartments (box) of the runway in the high conflict test. (b) Exploration of appetitive (APP) and aversive (AV) objects did not differ during the high conflict test. (c–d) PRC inhibition did not impact rats’ goal box LTE in both sets of low conflict tests. (e–f) Exploration of objects did not differ during both sets of low conflict tests. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for all data shown.
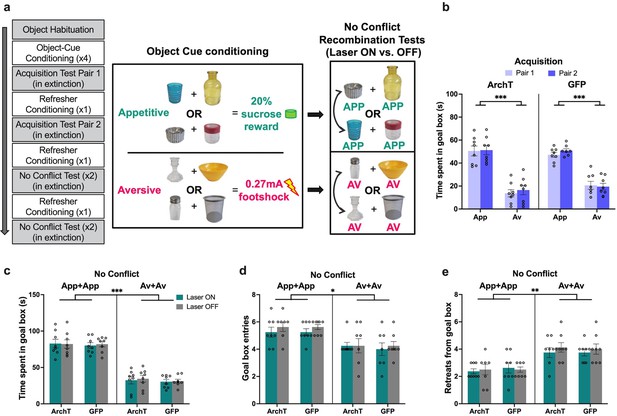
Impact of perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition on ‘no conflict’ approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task performance.
(a) A subset of rats (n=8 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=8 green fluorescent protein [GFP]) underwent a no conflict recombination task, in which they first learned a new set of appetitive (APP) or aversive (AV) object pairs and were then presented with recombined object pairs composed of objects of the same valence. (b) Both ArchT and GFP PRC rats successfully learned a new set of APP and AV object pairs for the no conflict recombination tests. (c–e) PRC inhibition did not affect AA behavior on the no conflict tests. A main effect of valence was observed for all measures, indicating intact valence retrieval for the recombined test pairs. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni corrections was conducted for all data shown. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.

Additional perirhinal cortex (PRC) rat data for the approach-avoidance (AA) no conflict recombination task.
(a–b) PRC inhibition had no effect on latency to enter (LTE) in the appetitive or aversive no conflict recombination tests. (c–d) Exploration of APP and AV objects did not differ during the no conflict recombination tests. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for all data shown.
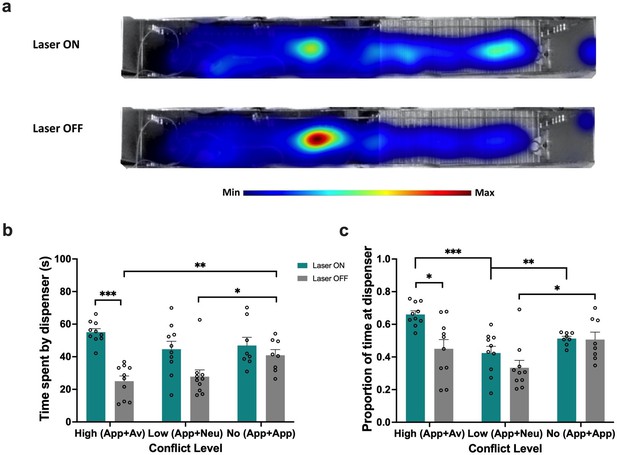
Perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition increases reward location approach behavior.
(a) Heatmap plots for the high conflict test. (b–c) PRC-inhibited rats spent more time by the sucrose dispenser, as measured by total time or proportion of time, in the high and low conflict tests but not in the no conflict test. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA, followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction was conducted for all data shown. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
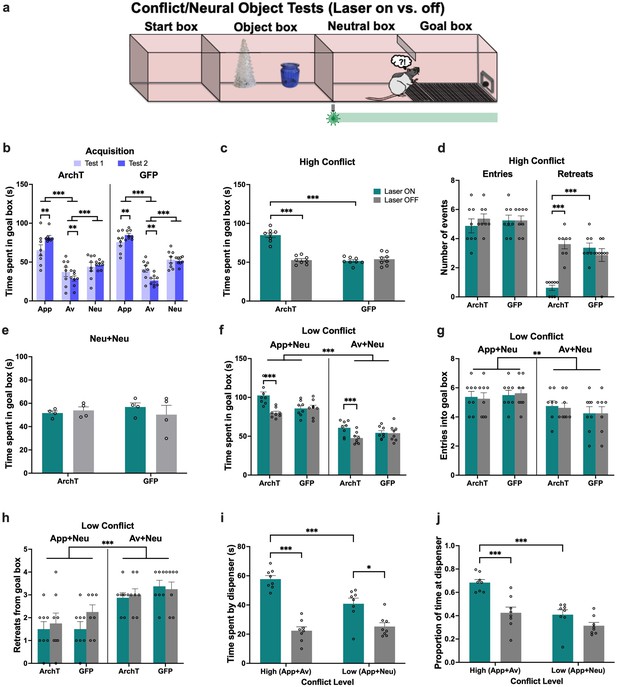
Perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition prior to the choice period of the runway task.
In a separate cohort of rats (n=8 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=8 green fluorescent protein [GFP]), (a) optogenetic inhibition was applied upon confinement to the neutral box of the runway task, after object exploration but prior to goal box entry (i.e., choice behavior). (b) All animals demonstrated object-outcome associations by acquisition test 2. (c–d) PRC inhibition significantly increased time spent in the goal box and reduced the number of retreats in the high conflict test. (e) There was no effect of PRC inhibition on AA behavior in the neutral test. (f) Similar to the high conflict test, PRC inhibition increased time spent in the goal box in both low conflict tests. (g–h) PRC inhibition did not impact the number of entries or retreats in the App+Neu or Av+Neu low conflict tests, although there was a main effect of valence, with a greater number of entries for App+Neu and more retreats for Av+Neu. (i–j) PRC-inhibited rats spent more time by the sucrose dispenser, as measured by total time or proportion of time, in the high and low conflict tests but not the no conflict test. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for all data shown shown except for data in panels c-e and i-j, which were subjected to two-way ANOVA. Significant interactions were followed up with post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.

Additional perirhinal cortex (PRC) rat data with optogenetic inhibition during the choice period for the approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task.
(a) PRC inhibition did not impact rats’ latency to enter (LTE) the object, neutral, and goal boxes in the high conflict test. (b) Exploration of App and Av objects did not differ during the high conflict test. (c–d) PRC inhibition did not impact rats’ goal box LTE behavior in both sets of low conflict tests. (e–f) Exploration of objects did not differ during both sets of low conflict tests. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for all data shown.
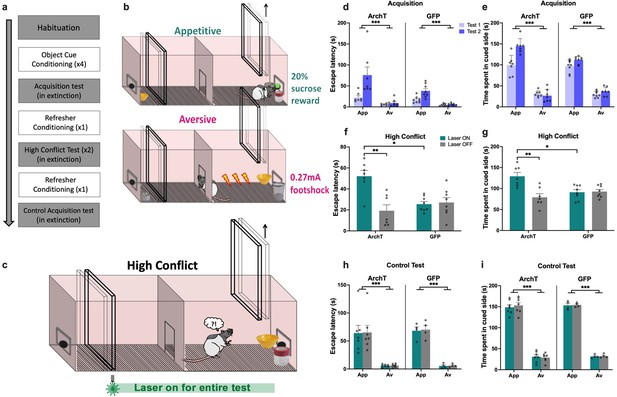
Impact of perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition on object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict shuttle box task performance.
(a) Timeline of paradigm. (b) Rats (n=7 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=8 green fluorescent protein [GFP]) first learned to stay to receive a reward when exposed to an appetitive object pair, and to escape to avoid footshock when exposed to an aversive object pair. (c) Rats were then exposed to a high conflict object pairing in extinction. (d–e) All rats demonstrated intact acquisition of AA behavior. (f–g) PRC inhibition led to an increased escape latency in the high conflict test and a greater amount of time spent in the cued side of the shuttle box. (h–i) PRC inhibition did not impact escape latency or time spent in the cued side in a subsequent control no conflict test. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for data shown in d-e, h-i and two-way ANOVA was conducted for data in f-g. Post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction were conducted to further investigate significant interactions in all datasets. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05.
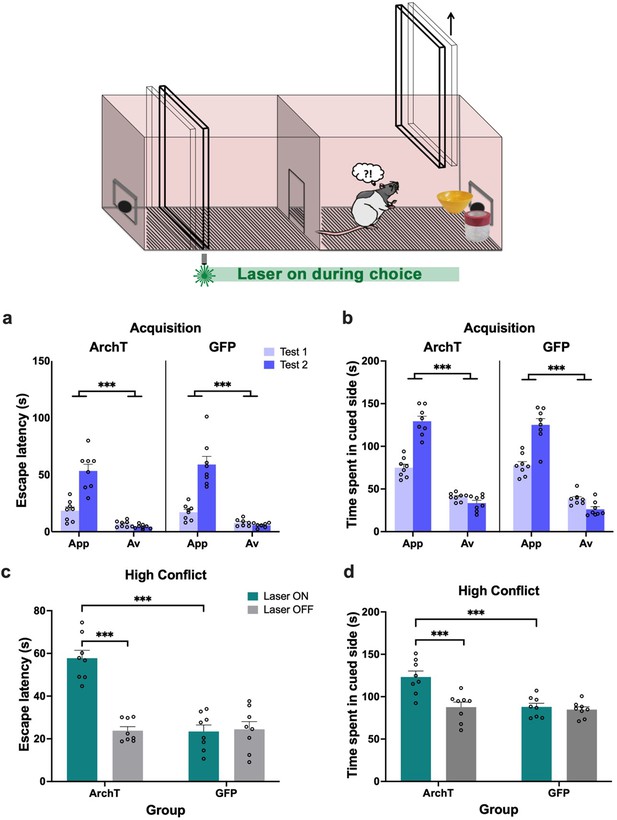
Perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition during the choice period of the object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict shuttle box task.
(a–b) All rats (n=8 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=8 green fluorescent protein [GFP]) demonstrated intact acquisition of AA behavior. (c–d) PRC inhibition led to an increased escape latency in the high conflict test and a greater amount of time spent in the cued side of the shuttle box. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for data shown in a-b, and two-way ANOVA was conducted for data in c-d. Post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction were conducted to further investigate significant interactions. ***p<0.001.
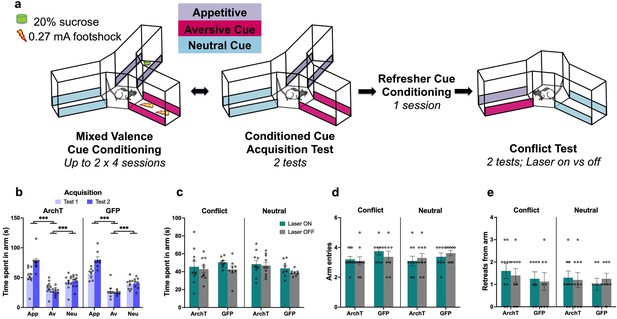
No effect of perirhinal cortex (PRC) inhibition on contextual approach-avoidance (AA) conflict behavior.
(a) PRC rats (n=10 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=8 green fluorescent protein [GFP]) underwent a contextual AA task known to be ventral hippocampus (vHPC)-dependent, in which they first learned the outcomes associated with appetitive, aversive, and neural cues and then underwent a conflict test in extinction. (b) Both ArchT and GFP rats demonstrated successful valence acquisition. (c–e) PRC inhibition had no effect on choice behavior during the conflict test. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA was conducted for all data shown, followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction in panel b data. ***p<0.001.
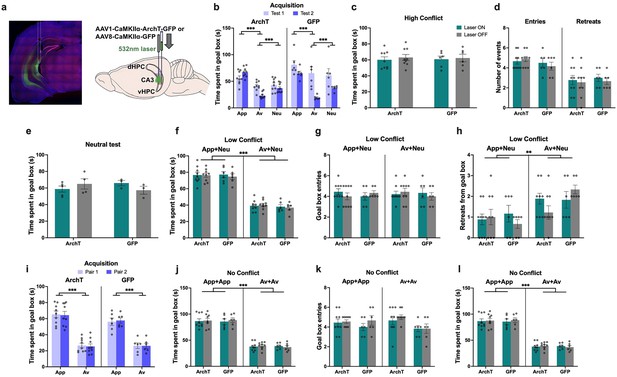
No effect of ventral CA3 (vCA3) inhibition on object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict runway task performance.
(a) Rats injected with archaerhodopsin T (ArchT) (n=9) or green fluorescent protein (GFP) (n=6) in the vCA3 underwent the object runway task. (b) Both groups learned the appetitive (App), aversive (Av), and neutral (Neu) object pairs successfully. (c–h) vCA3 inhibition did not impact any behavioral measure on the high conflict, neutral, or low conflict recombination tests. (i) Rats successfully learned a new set of object pairs for the no conflict recombination tests. (j–l) vCA3 inhibition did not impact performance on the no conflict recombination tests. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA and post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction (where significant interactions were found) were conducted for all data shown shown except for data in panels c-e, which were subjected to two-way ANOVA. ***p<0.001, **p<0.01.
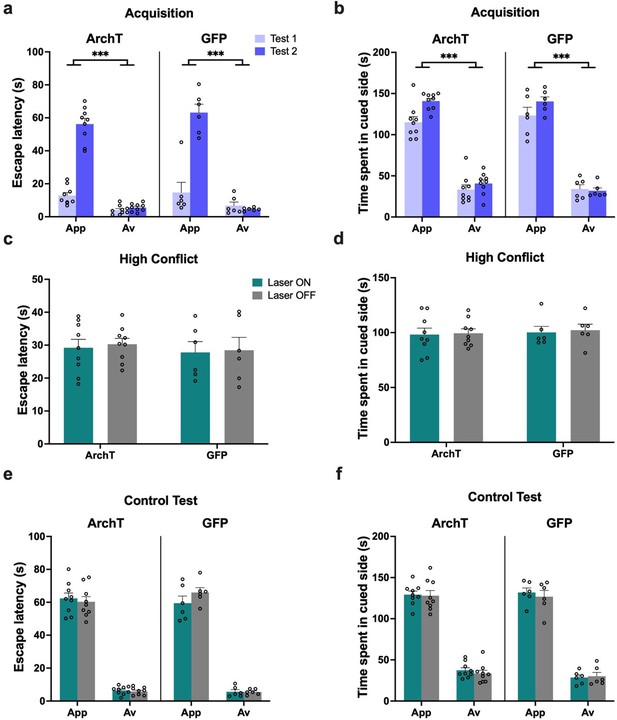
No impact of ventral hippocampus (vHPC) inhibition on object approach-avoidance (AA) conflict shuttle box task performance.
(a–b) Both archaerhodopsin T (ArchT) (n=9) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) ventral CA3 (vCA3) (n=6) rats demonstrated intact acquisition of AA behavior on the shuttle box task. (c–d) vCA3 inhibition had no effect on escape latency or time spent in the cued side in the high conflict test. (e–f) vCA3 inhibition also did not impact behavior on the control no conflict test. All figures show mean values ± SEM. Three-way ANOVA, followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction was conducted for data shown in a-b and e-f, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, and two-way ANOVA was conducted for data shown in c-d.
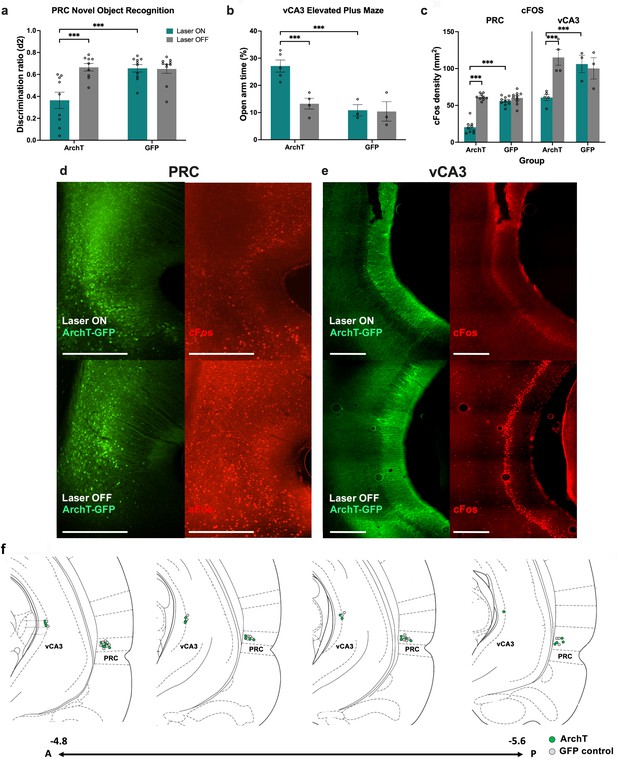
Effect of optogenetic inhibition on perirhinal cortex (PRC)- or ventral CA3 (vCA3)-dependent control tasks and cFos expression.
(a) PRC inhibition disrupted the ability of rats to discriminate a novel and familiar object on the novel object recognition task. (b) vCA3 inhibition increased time spent in the open arm of the elevated plus maze. (c–e) PRC and vCA3 inhibition was associated with decreased cFos levels in each respective area (PRC: n=18 archaerhodopsin T [ArchT]; n=20green fluorescent protein [GFP], vCA3: n = 9 ArchT, n = 6). (f) Schematic diagram showing placements of optic fibre tips in areas overlying the PRC and vCA3 in sections spanning - 4.8 to -5.6 relative to bregma. Scale bars depict 500 μm. Data figures show mean values ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA was conducted followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni correction for all data shown.***p<0.001.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain, strain background (Rattus norvegicus) | Long-Evans rats, male, 2–6 months old | Charles River | Cat#2308852, RRID:RGD_2308852 | |
| Antibody | Rb Anti-c-Fos rabbit polyclonal | Synaptic Systems | Cat# 226 003, RRID:AB_2231974 | TSA-IHC (1:5000) |
| Antibody | Peroxidase AffiniPure F(ab')2 Fragment Donkey Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L), donkey polyclonal | Jackson ImmunoResearch | Cat# 711-036-152, RRID: AB_2340590 | TSA-IHC (1:500) |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV- CaMKIIa-ArchT-GFP | Addgene/Ed Boyden | Cat# 99039-AAV1, RRID: Addgene_99039 | Inhibitory opsin |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pAAV-CaMKIIa-GFP | Addgene/Bryan Roth | Cat# 50469-AAV8, RRID: Addgene_50469 | Control virus |
| Software, algorithm | SPSS | IBM | https://www.ibm.com/spss | Version 26 |
| Software, algorithm | Ethovision XT | Noldus Information Technology | https://www.noldus.com/ethovision-xt | Animal tracking software/ hardware |
| Software, algorithm | Prism | GraphPad | https://www.graphpad.com/ | Version 8 |
| Other | NHS-Rhodamine | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 46406 | Rhodamine-based dye; TSA-IHC (1:500) |





