Neural underpinning of a respiration-associated resting-state fMRI network
Figures
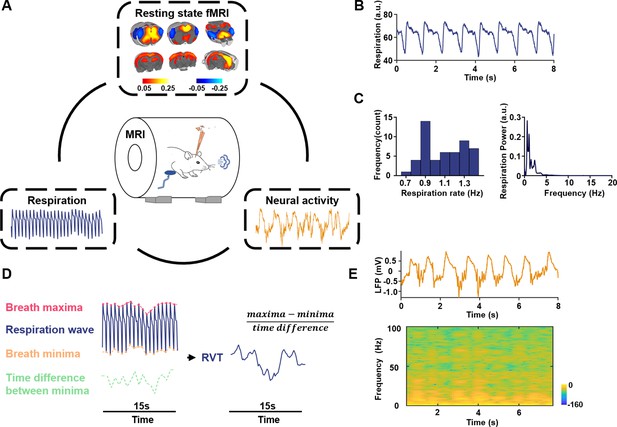
Simultaneous recordings of fMRI, electrophysiology and respiration signals in rats.
(A) Experimental design—simultaneous measurement of the resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI), electrophysiology, and respirational signals. Top: anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) seedmap; bottom left: respiration signal; bottom right: local field potential (LFP). (B) Exemplar respiration signal waveform. (C) Left: distribution of the respiration rate across all scans; right: power of the respiration signal averaged across all scans. (D) Computing respiration volume per time (RVT) from the respiration waveform. (E) Exemplar denoised LFP signal. Top: LFP time series; bottom: LFP power spectrogram.
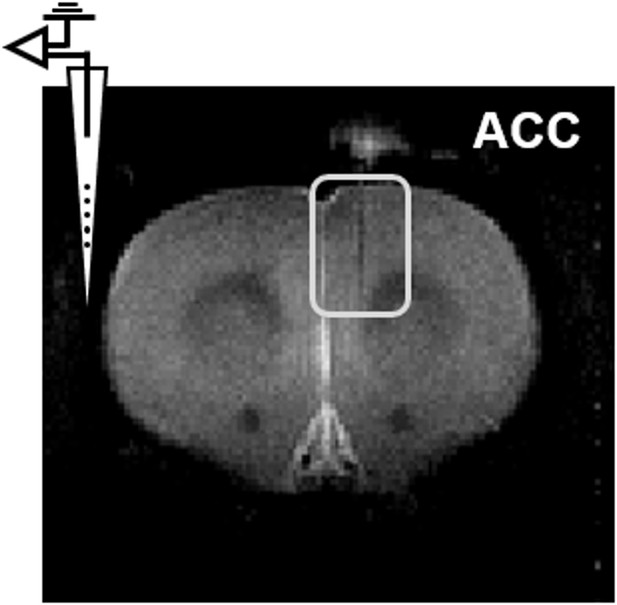
Representative image confirming the electrode location in the anterior cingulate cortex.
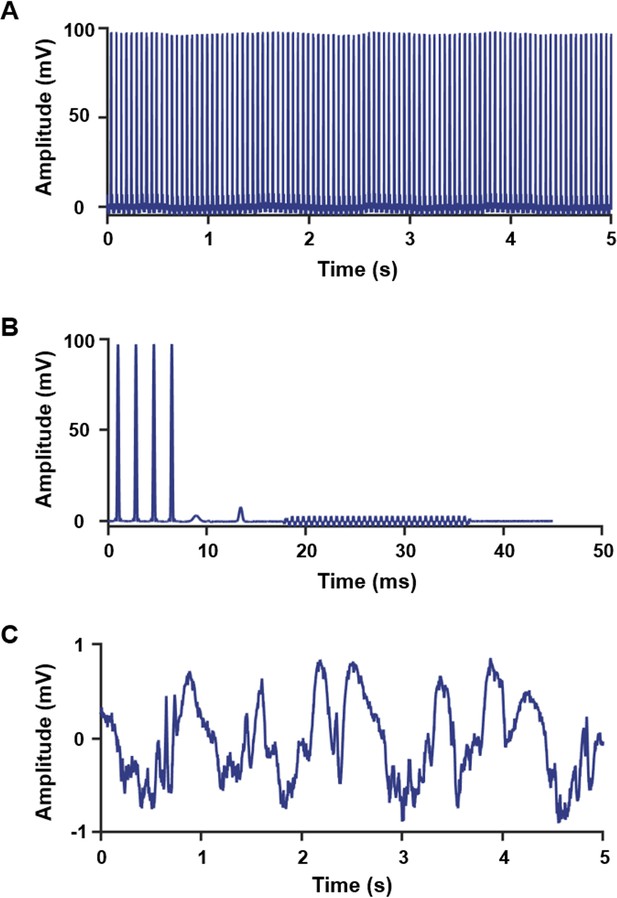
Removal of MRI artifacts from the electrophysiology signal.
(A) An example of raw electrophysiology signals before the denoising of MRI artifacts; (B) an example of the MRI artifact template. (C) Local field potential (LFP) after MRI artifact denoising.
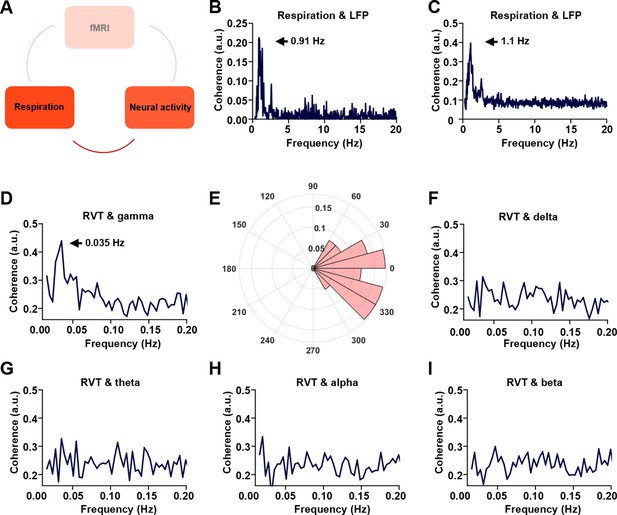
Phase-locking relationship between slow respiration variations and neural activity.
(A) The relationship between respiration and neural activity. (B) Respiration–local field potential (LFP) coherence from one sample scan. (C) Respiration–LFP coherence averaged across all scans. (D) Coherence between respiration volume per time (RVT) and gamma-band power (40–100 Hz), with the peak at 0.035 Hz. (E) Phase lag between RVT and gamma-band power. In contrast, no obvious coherence is observed between RVT and delta-band power (1–4 Hz, F), theta-band power (4–7 Hz, G), alpha-band power (7–13 Hz, H), or beta-band power (13–30 Hz, I).
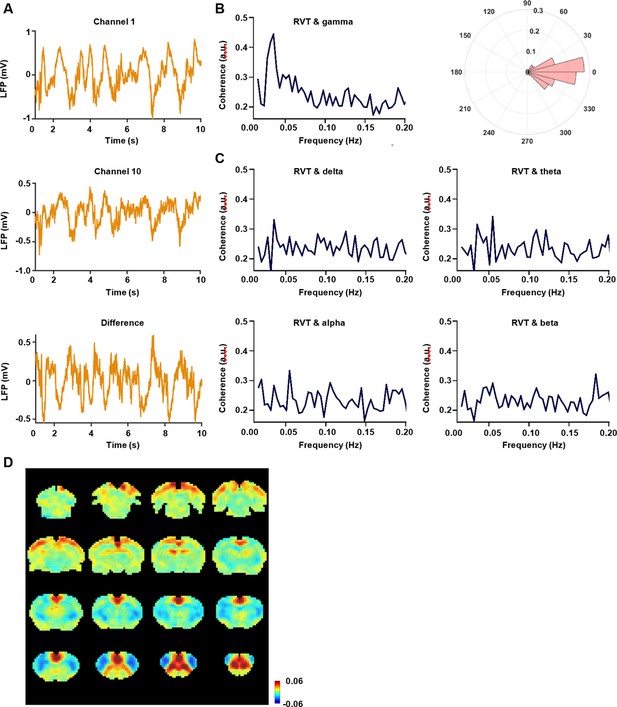
Electrophysiology results obtained using the differential subtraction method.
(A) Exemplar electrophysiology signals from two separate channels: channel 1 (top) and channel 10 (middle), as well as the subtracted signal between the two channels (bottom). Results in panels B–D are all based on the subtracted electrophysiology signal. (B) Left: coherence between the respiration volume per time (RVT) and gamma-band power (40–100 Hz). Right: phase lag between the RVT and gamma-band power. (C) Coherence between the RVT and delta-band power (1–4 Hz), theta-band power (4–7 Hz), alpha-band power (7–13 Hz), and beta-band power (13–30 Hz), respectively. (D) Gamma-band power-derived resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) correlation map.
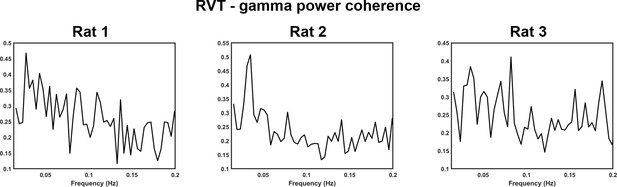
Respiration volume per time (RVT)–gamma power coherence in individual animals in the lightly sedated state.
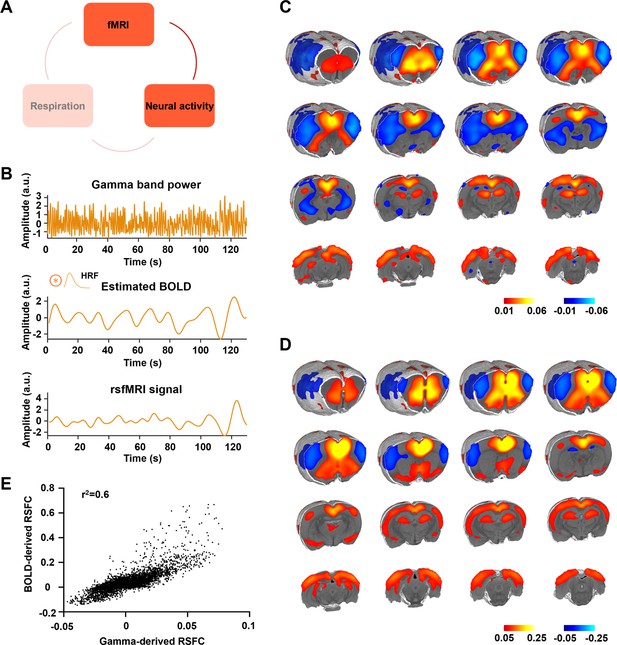
Gamma power is associated with the resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) signal.
(A) The relationship between neural activity and rsfMRI signal. (B) Top: exemplar gamma-band power in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC); middle: estimated blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal by convolving the gamma-band power with the hemodynamic response function (HRF); bottom: measured BOLD signal from the same brain region. (C) Gamma power-derived correlation map. (D) Seedmap of the right ACC. (E) Voxel-to-voxel spatial correlation between (C) and (D).
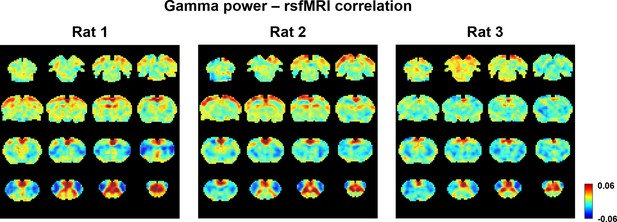
Gamma power–resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) correlation maps in individual animals in the lightly sedated state.
Difference of RSFC maps before and after respiration volume per time (RVT) regression.
(A) Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) (right side) seedmap after RVT regression; (B) difference of right ACC seedmaps before and after RVT regression; (C) gamma-band power-derived correlation map after RVT regression; (D) difference of gamma-band power-derived correlation maps before and after RVT regression.
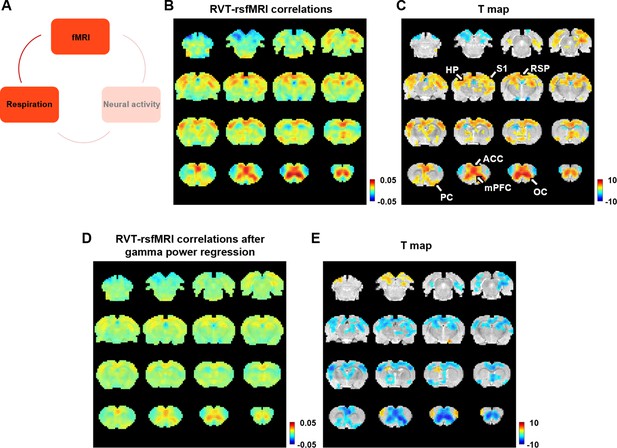
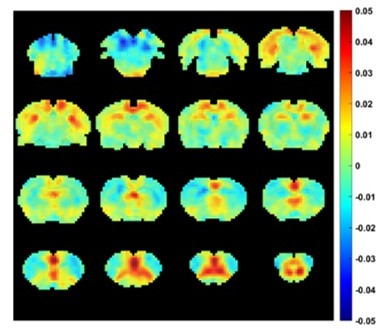
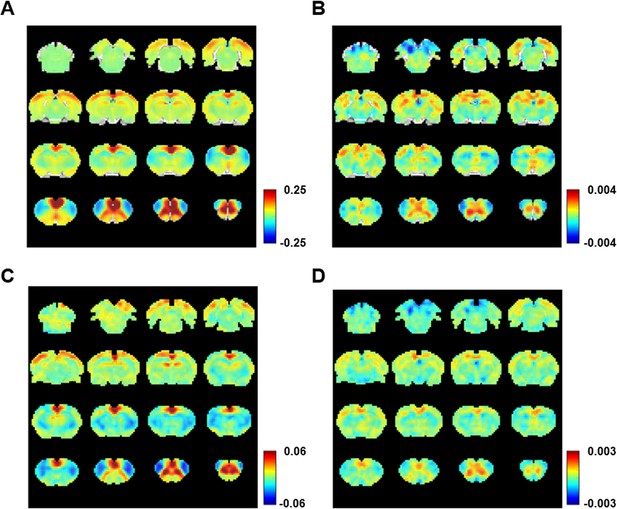
Correlation between slow variations of respiration and resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) signal.
(A) The relationship between respiration and rsfMRI signals. (B, C) Voxel-wise correlations between the respiration volume per time (RVT) and rsfMRI signals. (B) Unthresholded correlation map averaged across scans. (C) Thresholded T-value map (one-sample t-test, p < 0.05, false discovery rate [FDR] corrected). Brain regions displaying significant RVT–rsfMRI correlations include the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), orbital cortex (OC), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), piriform cortex (PC), hippocampus (HP), retrosplenial cortex (RSP), and primary somatosensory cortex (S1). (D) Voxel-wise correlations between the RVT and rsfMRI signals after the gamma-band power are regressed out from both signals. (E) Difference of correlation maps before and after gamma power regression (paired t-test, p < 0.05, FDR corrected).
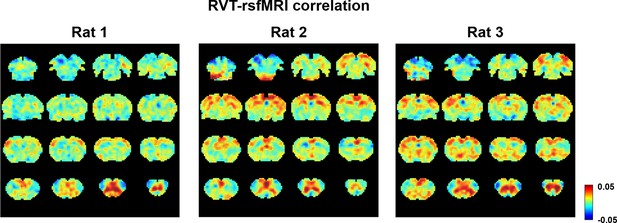
Respiration volume per time (RVT)–resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) correlation maps in individual animals in the lightly sedated state.
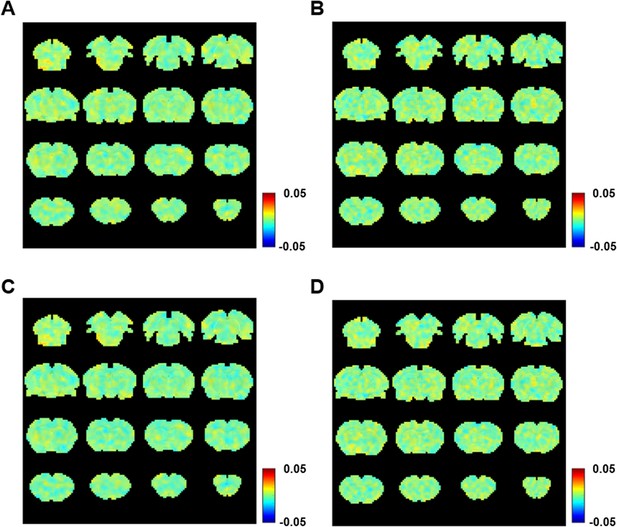
Voxel-wise correlations between the resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) signal and RETROICOR regressor with the regression of the white matter and ventricle signals in (A) light sedation and (B) isoelectric state.
Voxel-wise correlations between the rsfMRI signal and RETROICOR regressor without the regression of the white matter and ventricle signals in (C) light sedation and (D) isoelectric state.
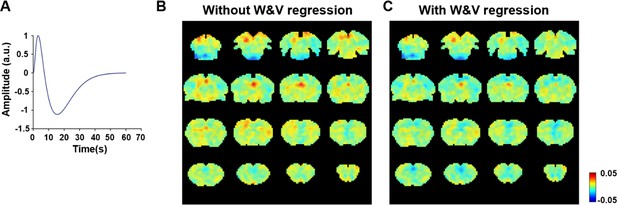
Voxel-wise correlations between the estimated time course of respirational artifacts and resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) signals.
(A) Respiratory response function. Voxel-wise correlations between the estimated time course of respirational artifacts and rsfMRI signals without (B) and with (C) the regression of the white matter and ventricle signals.
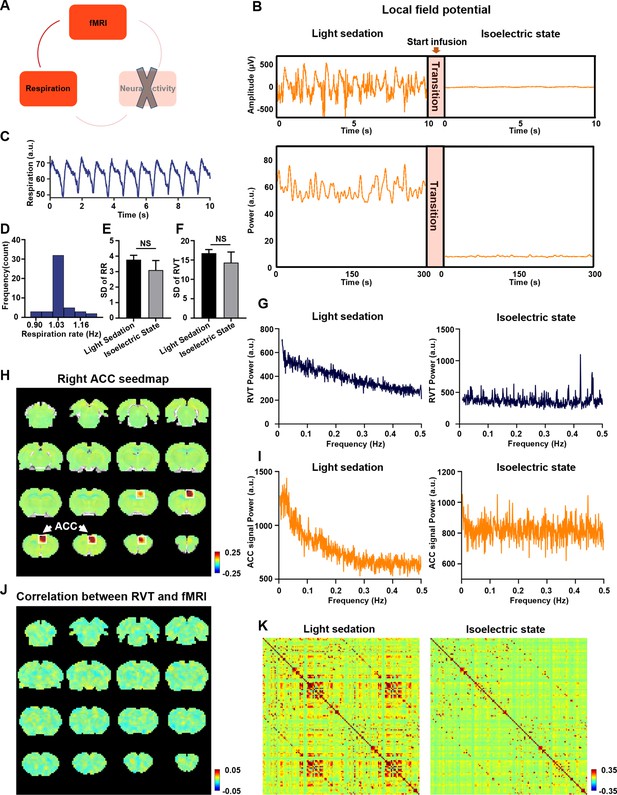
Respiration–resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) relationship at the isoelectric state.
(A) Determining the relationship between slow respiration variations and the rsfMRI signal after silencing the brain-wide neural activity. (B) Silencing neural activity at the isoelectric state induced by sodium pentobarbital. Top: LFP amplitude; bottom: LFP power; arrow: infusion of sodium pentobarbital. (C) Respiration signal at the isoelectric state. (D) Distribution of respiration rate (RR) across scans. (E) Variance of RR, quantified by the standard deviation (SD) of RR in the light sedation and isoelectric states. (F) Variance of respiration volume per time (RVT), quantified by the SD of RVT in the light sedation and isoelectric states. There is no significant difference in the SD of the RR (E, two-sample t-test, t = −1.0, p = 0.32) or the SD of RVT (F, two-sample t-test, t = −0.87, p = 0.39) between the light sedation and isoelectric states. (G) Power spectrum of RVT during (left) light sedation and (right) the isoelectric state. (H) Seedmap of the right anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) at the isoelectric state. (I) Power spectra of the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal during (left) light sedation and (right) the isoelectric state. (J) Voxel-wise correlations between RVT and the rsfMRI signal at the isoelectric state. (K) Brain-wide ROI-based RSFC matrices at (left) light sedation and (right) the isoelectric state (132 ROIs in total).
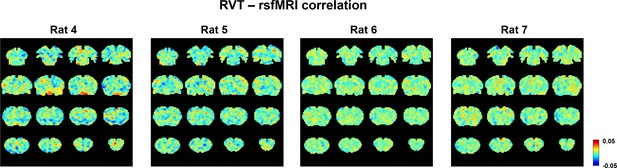
Respiration volume per time (RVT)–resting-state fMRI (rsfMRI) correlation maps in individual animals in the isoelectric state.
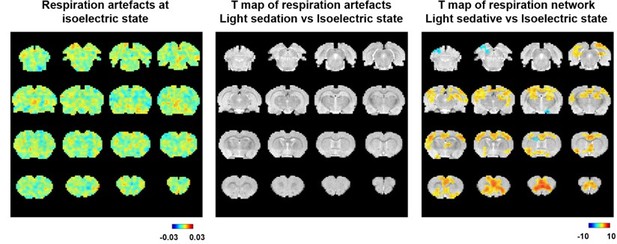
Left, voxel-wise correlations between the estimated time course of respirational artifact, estimated by convolving RVT with the respiration response function, and rsfMRI signals at the isoelectric state.
The same artifactual pattern during light sedation is shown in Figure 4 —figure supplement 3. Middle, statistical comparison of the respiration artifactual patterns between light sedation and isoelectric states (t-test, threshold p = 0.05, FDR corrected). Right, statistical comparison of the respiration-related brain network patterns between light sedation and isoelectric states (t-test, p < 0.05, FDR corrected).