Neurovascular anatomy of dwarf dinosaur implies precociality in sauropods
Figures
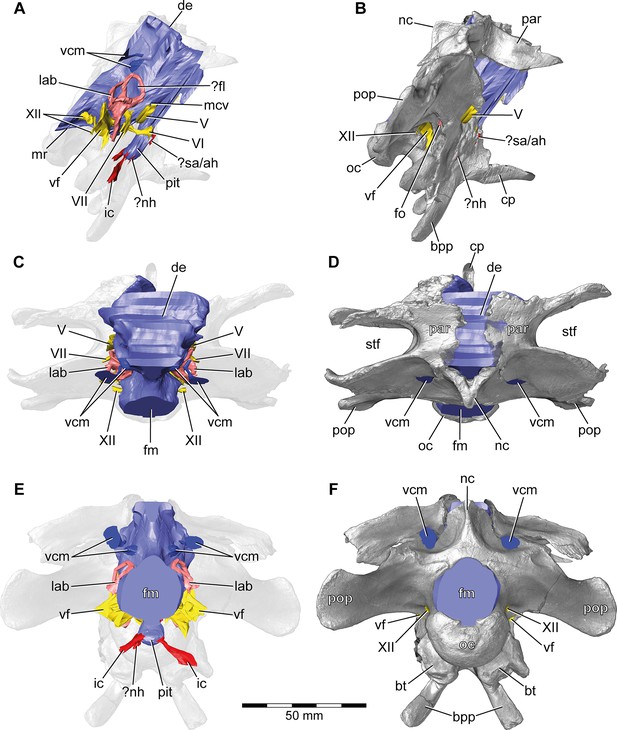
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D model of the braincase endocast with endosseous labyrinths and neurovascular canals of DFMMh/FV 581.1, 2, and 3 with transparent (A,C,E) and covering (B,D,F) volume rendering of the bony braincase in (A,B) right lateral, (C,D) dorsal, and (E,F) posterior view.
Note that scale mainly applies to posterior perspective (E,F).?fl, potential floccular recess; ?nh, potential canal for the neurohypophysis; ?sa/ah, potential sphenoidal artery/canal for the adenohypophysis; bpp, basipterygoid process; bt, basal tuber; cp, cultriform process; de, dorsal expansion; ic, internal carotid; fm, foramen magnum; fo, fenestra ovalis; lab, endosseous labyrinth; mcv, mid cerebral vein; mr, median ridge; nc, sagittal nuchal crest; oc, occipital condyle; par, parietal; pit, pituitary; pop, paroccipital process; stf, supratemporal fenestra; vcm, vena capitis media; vf, vagal foramen; V, trigeminal nerve; VI, abducens nerve; VII, facial nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve.
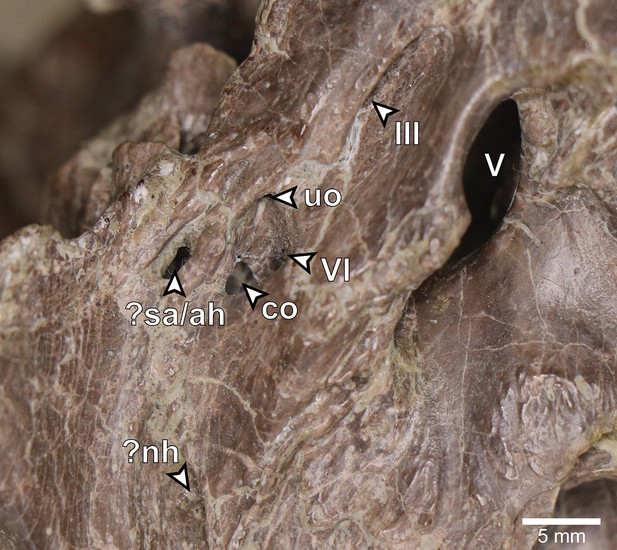
Europasaurus holgeri, close-up of left lateral aspect of DFMMh/FV 581.1.
?nh, potential opening for the neurohypophysis; ?sa/ah, potential sphenoidal artery opening/opening for adenohypophysis canal; co, connection between the abducens nerve canal (CN VI) and the pituitary fossa; uo, unclear opening; III, oculomotor nerve opening; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VI, abducens nerve opening.
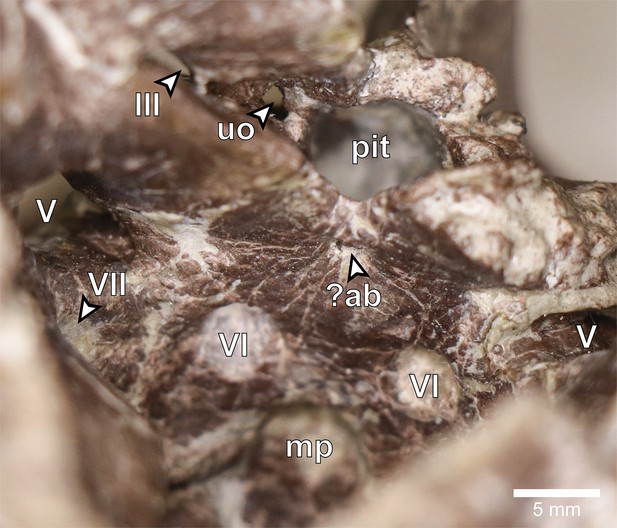
Europasaurus holgeri, close-up of anterior endocranial floor of DFMMh/FV 581.1 in dorsal view.
?ab, potential basilar artery opening; mp, median fossa producing the median protuberance on the ventral braincase endocast; pit, pituitary fossa; uo, unclear opening; III, oculomotor nerve opening; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VI, abducens nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening.
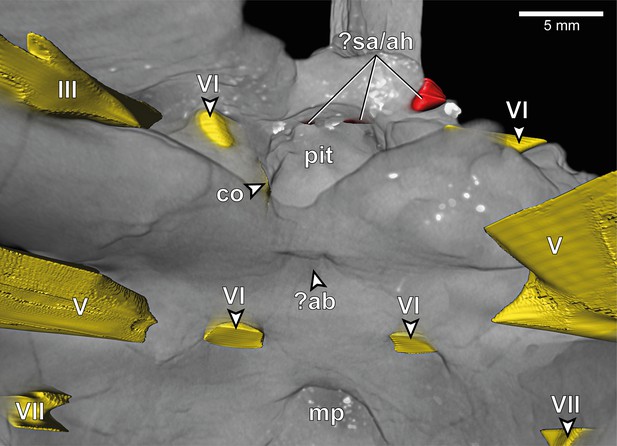
Europasaurus holgeri, close-up of 3D model of anterior endocranial floor of DFMMh/FV 581.1 in dorsal view.
?ab, potential basilar artery opening; ?sa/ah, potential sphenoidal artery opening/opening for adenohypophysis canal; co, connection between the abducens nerve canal (CN VI) and the pituitary fossa; mp, median fossa producing the median protuberance on the ventral braincase endocast; uo, unclear opening; pit, pituitary fossa; III, oculomotor nerve opening; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VI, abducens nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening.
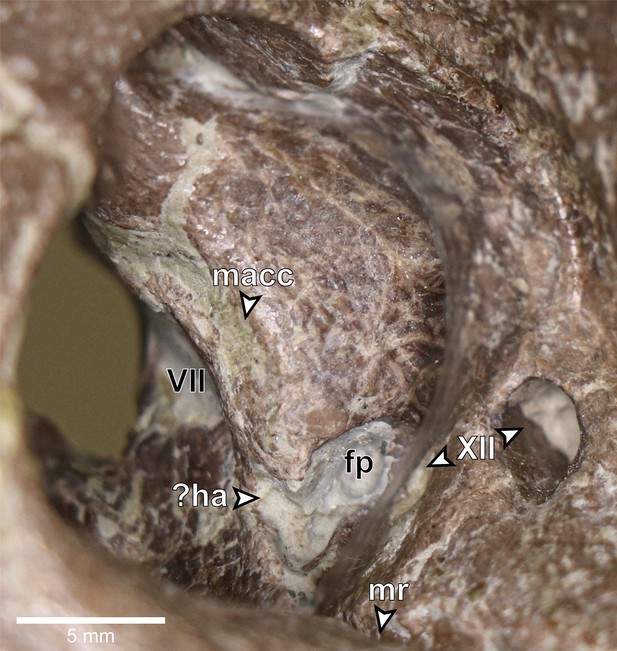
Europasaurus holgeri, close-up of right posterior endocranial wall of DFMMh/FV 581.1, viewed through the foramen magnum.
?ha, potential hiatus acusticus; fp, fenestra pseudorotunda; macc, medial aspect of common crus; mr, medial trough producing the median ridge on the ventral braincase endocast; VII, facial nerve opening; XII, hypoglossal nerve openings.
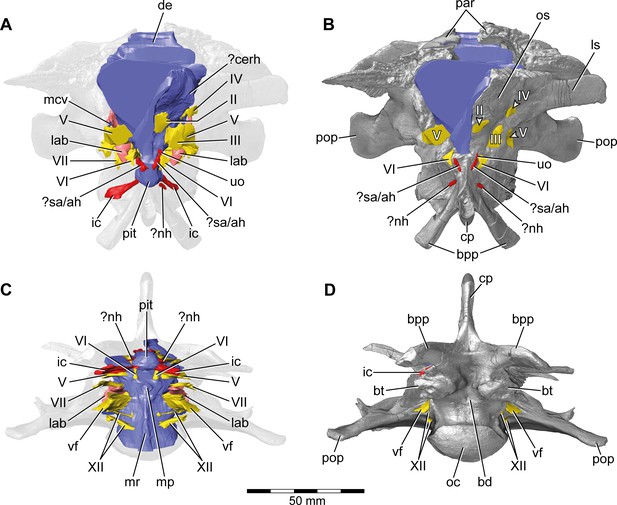
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D model of the braincase endocast with endosseous labyrinths and neurovascular canals of DFMMh/FV 581.1, 2, and 3 with transparent (A,C) and covering (B,D) volume rendering of the bony braincase in (A,B) anterior (C,D) and ventral view.
Note that scale mainly applies to ventral perspective (C,D). ?cerh, potential cerebral hemisphere; ?nh, potential canal for the neurohypophysis; ?sa/ah, potential sphenoidal artery/canal for the adenohypophysis; bd, blind depression; bpp, basipterygoid process; bt, basal tuber; cp, cultriform process; de, dorsal expansion; ic, internal carotid; fm, foramen magnum; lab, endosseous labyrinth; ls; laterosphenoid; mcv, mid cerebral vein; mp, median protuberance; mr, median ridge; oc, occipital condyle; os, orbitosphenoid; par, parietal; pit, pituitary; pop, paroccipital process; uo, unclear opening; vf, vagal foramen; II, optic nerve; III, oculomotor nerve; IV, trochlear nerve; V, trigeminal nerve; VI, abducens nerve; VII, facial nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve.
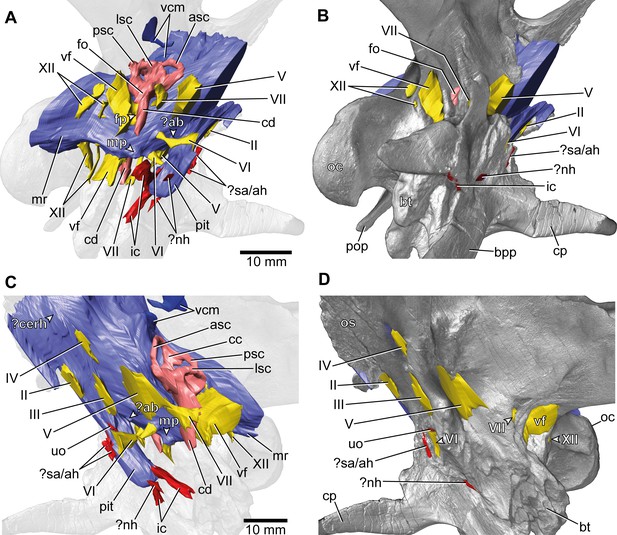
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D model of the braincase endocast with endosseous labyrinths and neurovascular canals of DFMMh/FV 581.1, 2, and 3 with transparent (A,C) and covering (B,D) volume rendering of the bony braincase in (A,B) right ventrolateral and (C,D) left lateral view.
?ab, potential basilar artery; ?cerh, potential cerebral hemisphere; ?nh, potential canal for the neurohypophysis; ?sa/ah, potential sphenoidal artery/canal for the adenohypophysis; bpp, basipterygoid process; bt, basal tuber; cp, cultriform process; ic, internal carotid; fo, fenestra ovalis; fp, fenestra pseudorotunda; mp, median protuberance; mr, median ridge; oc, occipital condyle; os, orbitosphenoid; pit, pituitary; pop, paroccipital process; uo, unclear opening; vcm, vena capitis media; vf, vagal foramen; II, optic nerve; III, oculomotor nerve; IV, trochlear nerve; V, trigeminal nerve; VI, abducens nerve; VII, facial nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve.
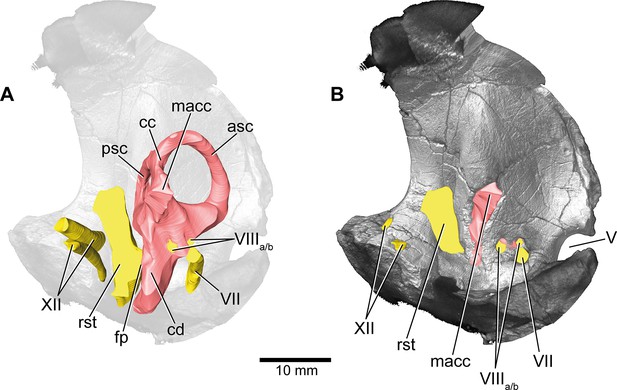
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D model of the left endosseous labyrinth region in DFMMh/FV 1077 with transparent (A) and covering (B) volume rendering of the bony braincase in medial view.
asc, anterior semicircular canal; cc, common crus; cd, cochlear duct; fp, fenestra pseudorotunda; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; macc, medial aspect of common crus; psc, posterior semicircular canal; rst, recessus scalae tympani; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VII, facial nerve; VIIIa/b, both branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve; XII, hypoglossal nerve.
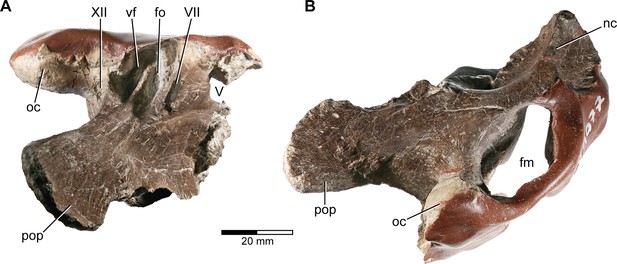
Europasaurus holgeri, fragmentary braincase DFMMh/FV 1077 in (A) ventral and (B) posterior view.
fm, foramen magnum; fo, fenestra ovalis; nc, nuchal crest; oc, occipital condyle; pop, paroccipital process; vf, vagal foramen; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening; XII, hypoglossal nerve opening.
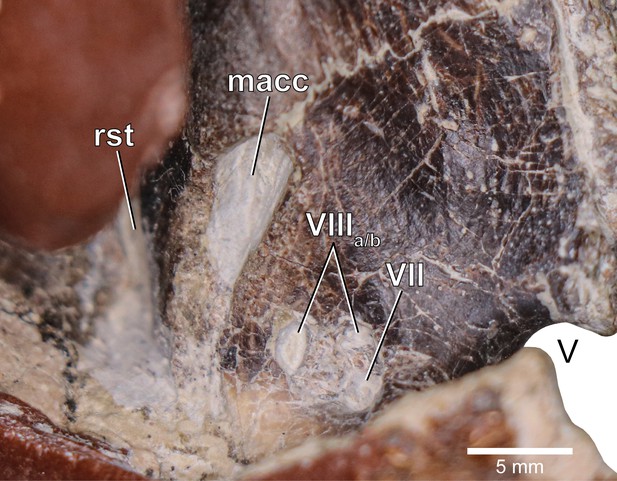
Europasaurus holgeri, close-up of medial aspect of the fragmentary braincase DFMMh/FV 1077.
macc, medial aspect of common crus; rst, recessus scalae tympani; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening; VIIIa/b, both openings of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
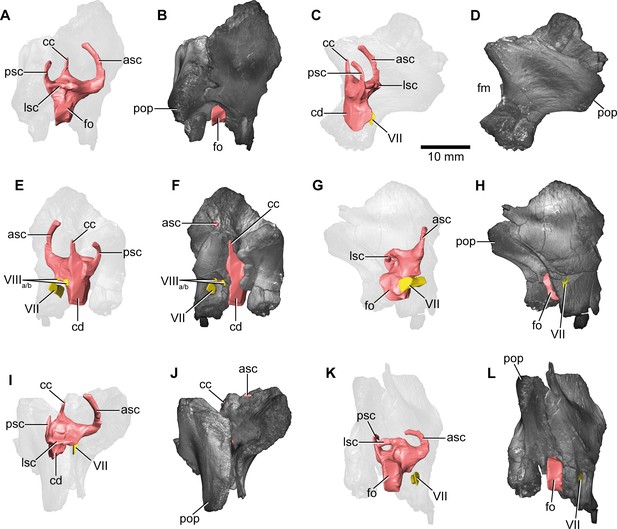
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D model of the right endosseous labyrinth in DFMMh/FV 466+205 with transparent (A,C,E,G,I,K) and covering (B,D,F,H,J,L) volume rendering of the bony braincase remains in (A,B) lateral, (C,D) posterior, (E,F) medial, (G,H) anterolateroventral, (I,J) dorsolateral, and (K,L) lateroventral view; in respect to the endosseous labyrinth.
Note that scale mainly applies to posterior perspective (C,D), and that VII and VIIIa/b are not shown in (A) and (B). asc, anterior semicircular canal; cc, common crus; cd, cochlear duct; fm, foramen magnum; fo, fenestra ovalis; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; pop, paroccipital process; psc, posterior semicircular canal; VII, facial nerve; VIIIa/b, both branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
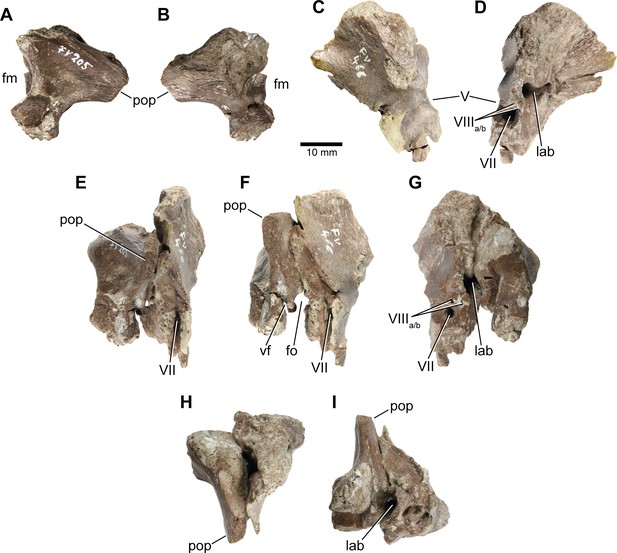
Europasaurus holgeri, isolated otoccipital (DFMMh/FV 205; A,B) and prootic (DFMMh/FV 466; C,D) in (A) posterior, (B) anterior, (C) lateral, and (D) medial view; prootic and otoccipital conjoined in (E) posterolateral, (F) lateral, (G) medial, (H) dorsal, and (I) ventral view.
Note that scale mainly applies to (A) and (B). fm, foramen magnum; fo, fenestra ovalis; lab, endosseous labyrinth; pop, paroccipital process; vf, vagal foramen; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening; VIIIa/b, both openings of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
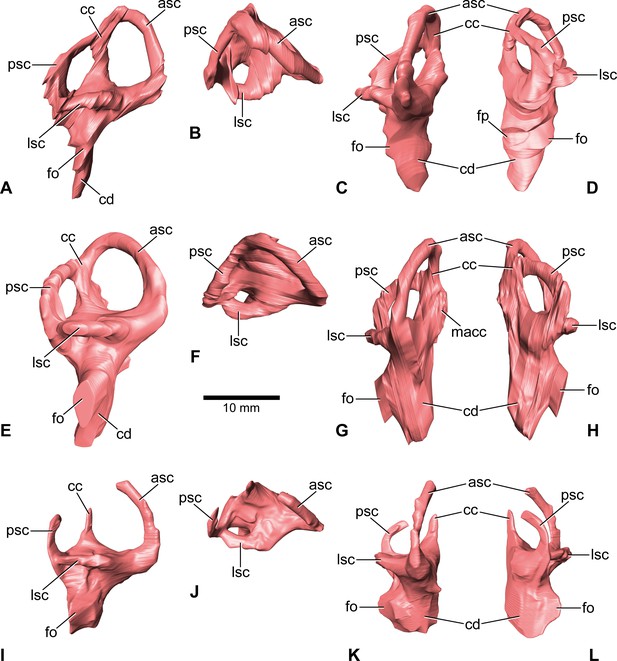
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D models of the endosseous labyrinth of DFMMh/FV 581.1 (A–D), DFMMh/FV 1077 (E–H; note that this model is mirrored) and DFMMh/FV 466+205 (I–L) in (A,E,I) lateral, (B,F,J) dorsal, (C,G,K), anterior and (D,H,L) posterior view.
Note that scale mainly applies to dorsal perspective (B,F,J). asc, anterior semicircular canal; cc, common crus; cd, cochlear duct; fo, fenestra ovalis; fp, fenestra pseudorotunda; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; macc, medial aspect of common crus; psc, posterior semicircular canal.
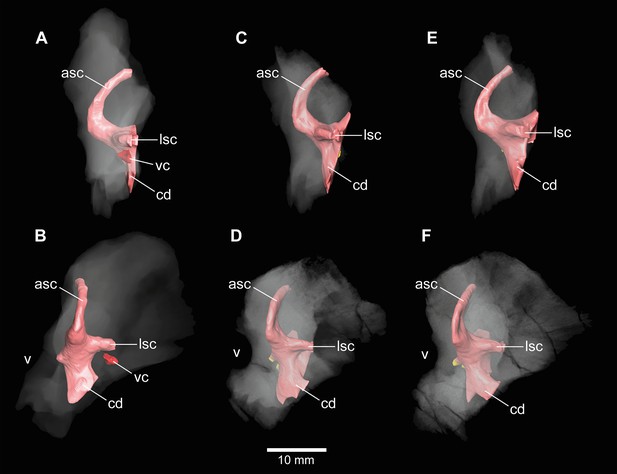
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D models of the anterior portions of the endosseous labyrinth in (A,B; note that this model is mirrored) DFMMh/FV 466, (C,D) DFMMh/FV 561 and (E,F) DFMMh/FV 964 in (A,C,E) lateral and (B,D,F) anterolateral view; in respect to the endosseous labyrinth.
Note that scale mainly applies to anterolateral perspective (B,D,F). asc, anterior semicircular canal; cd, cochlear duct; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; vc, vascular cavity; V, trigeminal nerve opening.

Europasaurus holgeri, isolated prootics (DFMMh/FV 466, A,B; DFMMh/FV 964, C,D; DFMMh/FV 561, E,F) in (A,C,E) lateral and (B,D,F) medial view.
Note that scale mainly applies to lateral perspective (A,C,E). lab, endosseous labyrinth; V, trigeminal nerve opening; VII, facial nerve opening; VIIIa/b, both openings of the vestibulocochlear nerve.
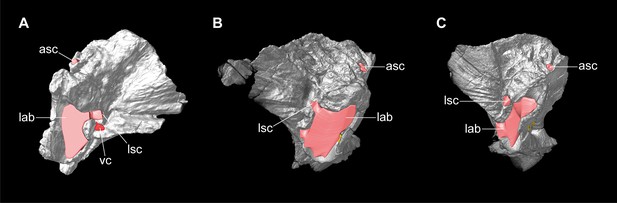
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D models of isolated prootics and inner features (DFMMh/FV 466, A; DFMMh/FV 561, B; DFMMh/FV 964, C) in (A–C) medial view.
Note that models are not scaled. asc, anterior semicircular canal; lab, endosseous labyrinth; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; vc, vascular cavity.
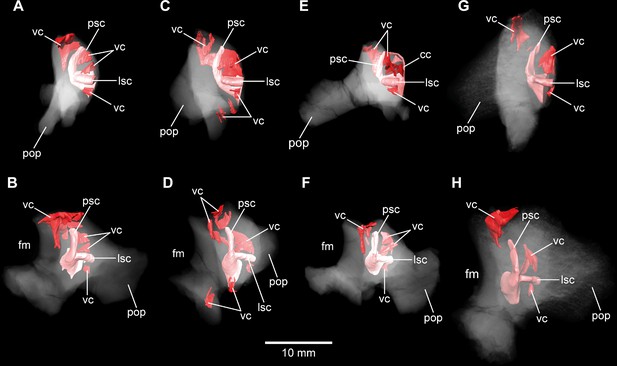
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D models of the posterior portions of the endosseous labyrinth in (A,B) DFMMh/FV 898, (C,D) DFMMh/FV 981.2, (E,F) DFMMh/FV 249, and (G,H) DFMMh/FV 205 in (A,C,E,G) anterolateral and (B,D,F,H) posterior view.
Note that scale mainly applies to posterior perspective (B,D,F,H). fm, foramen magnum; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; pop, paroccipital process; psc, posterior semicircular canal; vc, vascular cavity.
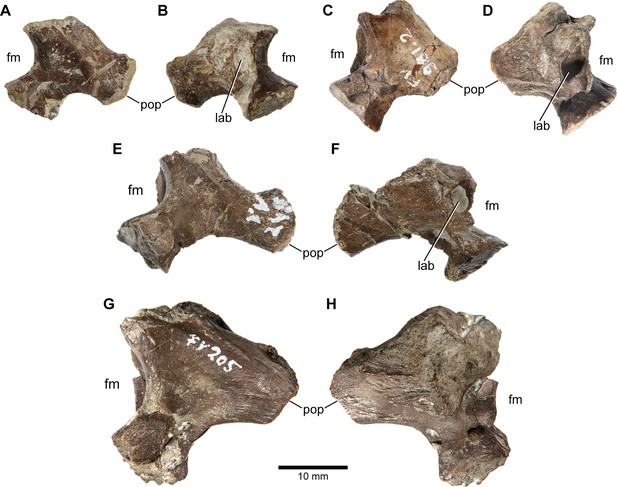
Europasaurus holgeri, isolated otoccipitals (DFMMh/FV 898, A,B; DFMMh/FV 981.2, C,D; DFMMh/FV 249, E,F; DFMMh/FV 205, G,H) in (A,C,E,G) posterior and (B,D,F,H) anterior view.
Note that scale mainly applies to posterior perspective (A,C,E,G). fm, foramen magnum; lab, endosseous labyrinth; pop, paroccipital process.
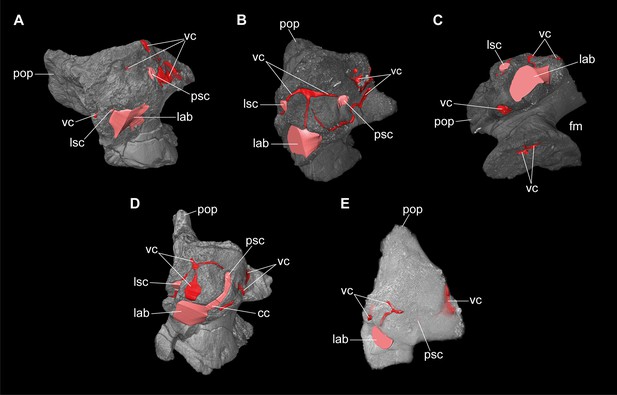
Europasaurus holgeri, 3D models of isolated otoccipitals and inner features (DFMMh/FV 898, A; DFMMh/FV 981.2, B,C; DFMMh/FV 249, D; DFMMh/FV 205, E) in (A,B,D,E) anterodorsomedial and (C) ventral view.
Note that models are not scaled. cc, common crus; fm, foramen magnum; lab, endosseous labyrinth; lsc, lateral semicircular canal; pop, paroccipital process; psc, posterior semicircular canal; vc, vascular cavity.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary information, scan details, and measurements.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82190/elife-82190-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82190/elife-82190-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





