A conserved function of Human DLC3 and Drosophila Cv-c in testis development
Figures
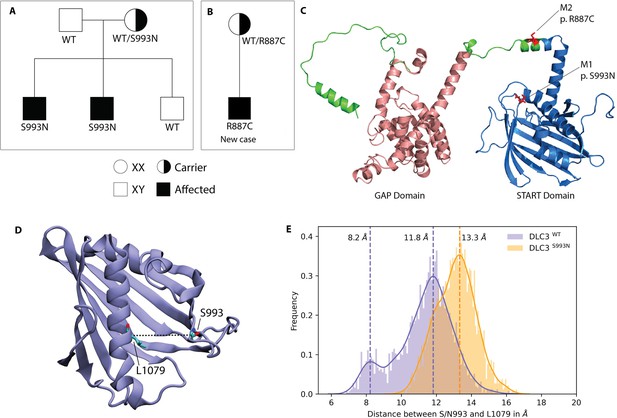
DLC3 variants associated to Differences of Sex Development (DSD) patients.
(A, B) Family diagrams showing the segregation of two different DLC3 alleles (panel A is modified from Ilaslan et al., 2018). (C) Structure of DLC3 GAP and StART domains showing the localization of the p.R887C and the p.S993N mutations. The protein is shown in cartoon representation, with the GAP domain represented in orange and the StART domain in blue. (D) Structure of the StART domain of human DLC3/StARD8. The distance between the Cα atoms of residues S/N993 and L1079 (shown in licorice representation) was used to determine the open and closed transitions arising from the motion of the Ω1 loop. (E) Distribution of the distance between the Cα atoms of S/N993 and L1079 in atomistic simulations of the WT and S993N systems.
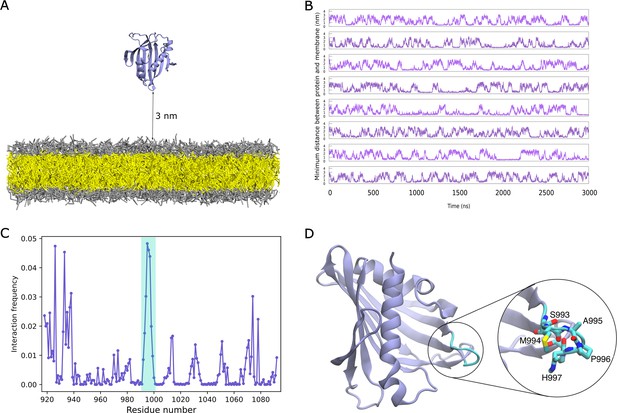
Binding of DLC3-StART domain to lipid bilayers.
(A) System setup containing the StART domain and a lipid bilayer. The protein is shown in cartoon representation, the lipid head-groups in grey and the tails in yellow. Water and ions beads are omitted for clarity. (B) Time-trace of minimum distance between the protein and the bilayer, for eight replicas. (C) Normalized interaction frequency for protein residues with bilayers. The shaded region in cyan represents the Ω1 loop of the domain. (D) Structure of the StART domain model from AlphaFold, with the Ω1 loop residues that exhibit the highest frequency of interaction highlighted in cyan.
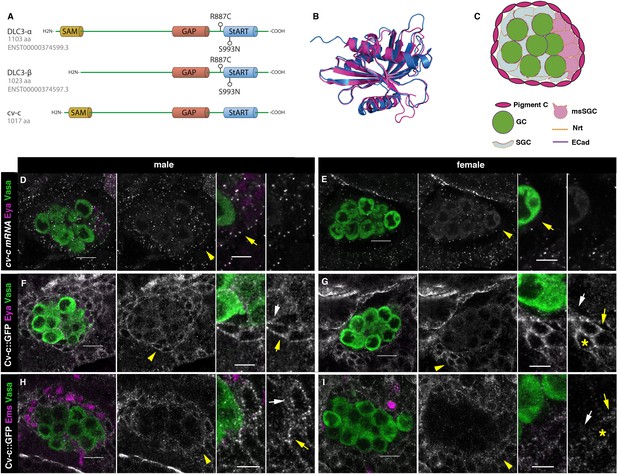
Cv-c and DLC3 structure and cv-c expression in the Drosophila gonad mesoderm.
(A) Linear representation of the DLC3-α, DLC3-β, and Cv-c proteins. The SAM domain is represented in yellow, the GAP domain in orange, and the StART domain in blue. (B) Alignment of the DLC3 (blue) and Cv-c (magenta) StART domains. (C) Schematic representation of the cell types in a Drosophila testis at st17. Germ cells, green; pigment cells, magenta; somatic gonadal cells, grey; male-specific somatic gonadal cells, pink. RNA in situ hybridization of male (D) and female (E) st17 embryos shows general transcription of cv-c in the mesoderm. The right panels in D–I are close ups of the arrowed region in the central panels. (D) In the testis, comparable levels of mRNA puncta can be detected in the somatic mesoderm and in the gonadal mesoderm cells surrounding the male germ cells as are clearly observed in the male-specific somatic gonad precursors (msSGPs) marked by Eya (magenta, indicated by an arrowhead in grey panels and an arrow in the close up). (E) In the ovary, marginal levels of cv-c mRNA expression are observed in the gonadal mesodermal cells, creating a halo of decreased number of puncta surrounding the female germ cells contrasting with the cv-c expressing adjacent somatic mesodermal cells (arrow in close up). (F–I) Cv-c::GFP protein expression in male and female embryos. (F, H) In the testis Cv-c::GFP is detected in the gonadal mesoderm surrounding the germ cells including the male msSGPs (Eya, magenta F) and the pigment cell precursors (Ems, magenta H). (G, I) In females, no substantial GFP signal is detected in the gonadal mesoderm surrounding the germ cells. Note in (F, H) that Cv-c::GFP signal in the gonad mesoderm cells allows tracing the testis contour, while in ovaries (G, I) this is not possible. Higher levels of Cv-c::GFP are present in the ectodermally derived trachea and hindgut. In close ups white arrows point to membranes close to the germ cells, yellow arrows to the membrane of gonad mesodermal cells. In males, Cv-c::GFP can be detected in the membranes between gonadal and somatic mesodermal cells (F, H) whilst in females GFP can only be detected outside the ovary in the membrane of the somatic mesoderm (G, I asterisks). Scale bar: 10 and 5 µm in close ups.
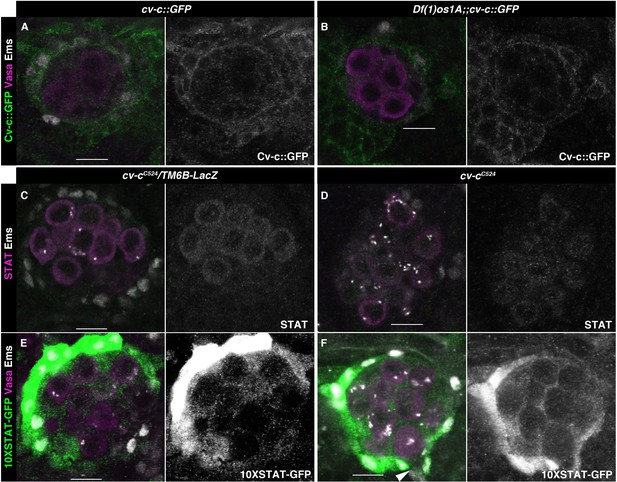
JAK/STAT pathway and cv-c-independent functions.
(A, B) cv-c::GFP stage 17 testis stained against GFP (green), Vasa (magenta), and Ems (grey) in a wild-type (A) or Df(1)os1A mutants. Cv-c expression and localization are unaffected by JAK/STAT lack of activation (right panels show Cv-c::GFP in grey). (C–F) JAK/STAT testis activity in cv-cC524 mutants in heterozygosis (C, E) or homozygous (D, F) testis. Neither STAT localization (magenta), (C, D) nor 10XSTAT-GFP reporter expression (green), (E, F) are modified in cv-cC524 mutants. Panels (C, D) are stained with anti-STAT (magenta or grey in right panels), (C–F) with anti-Ems (grey), (E, F) with anti-Vasa (magenta), and (C, F) with anti-GFP (green or grey in right panels). Scale bar: 10 µm.
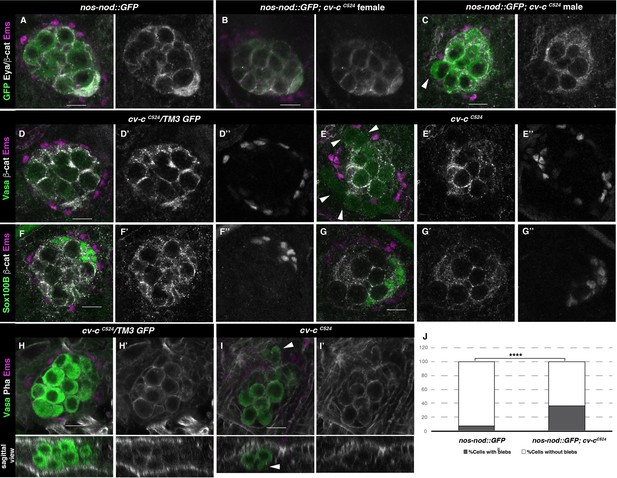
Gonad morphology in cv-c mutant embryos.
(A–C) Gonads with germ cells labelled with nos-nod::GFP (green), pigment cells with anti-Ems (magenta), and male-specific somatic gonad precursor (msSGP) with anti-Eya (nuclear grey staining) and the AJs with anti-β-catenin (grey membranes). Right panels show Eya and β-catenin channel. (A) In the control testis, germ cells are ensheathed by thin mesoderm extensions produced by the interstitial cells detectable by β-catenin staining. Similar germ cell ensheathment is observed in cv-cC524 ovaries (B), while in cv-cC524 testis (C) some germ cells become extruded from the gonad and are not enveloped by β-catenin (arrowhead). (D–G) Testes labelled with mesodermal specific markers to detect the pigment cells (Ems, magenta D–G) or the msSGPs (Sox100B, green F, G) in heterozygous (D, F) or cv-cC524 homozygous mutant embryos (E, G). Grey channels in right panels correspond to β-catenin in (D-G), Ems in (D, E), or Sox100B in (F, G). All mesoderm cell types are specified in cv-c mutant testis despite morphological aberrations resulting in the pigment cell layer’s discontinuity (compare D and F with E and G). (H–J) Testes stained with anti-Vasa (green) to label the germ cells and phalloidin (grey and right panels) to show actin filaments in heterozygous (H) or homozygous cv-cC524 mutants (I). Germ cells in mutant testes present protrusions compatible with migratory movements (arrowheads). Z sections are shown below H, I panels. Scale bar: 10 µm. (J) Quantification of blebbing cells in wild-type or mutant cv-c background using Fisher test; ****p value <2.2e−16 (nos::GFP N = 575 and nos::GFP;cv-cC524 N = 744) (Figure 3—source data 1).
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82343/elife-82343-fig3-data1-v2.xlsx
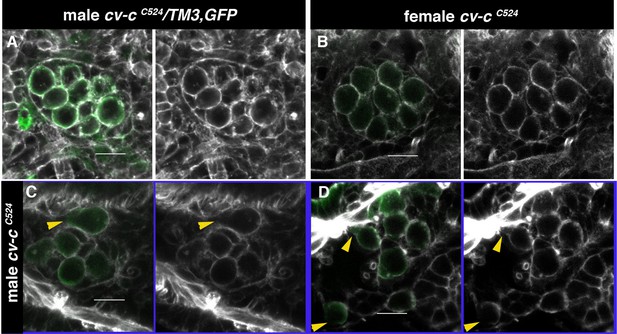
Actin cystoskeleton in cv-c mutants testes.
(A–D) Embryos labelled with phalloidin (grey) to reveal the filamentous actin cytoskeleton and with nos-nod::GFP (green) to label the germ cells. (A) In heterozygous males and (B) homozygous cv-cC524 mutant females, germ cells form a continuous filamentous actin structure around the cortex. (C, D) In homozygous cv-cC524 mutant males, the actin filament is discontinuous at the position where blebs form (arrowheads). Scale bar: 10 µm.
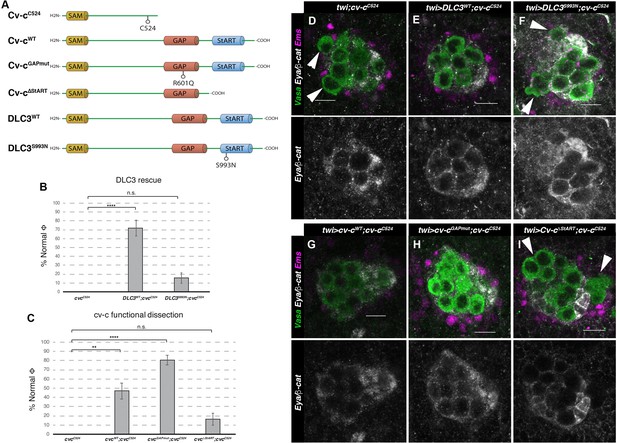
Rescue of cv-c mutant testes.
(A) Schematic representation of Cv-c and DLC3 protein variants studied. Rescue of the dysgenic testis of cv-cC524 homozygous mutant males after expressing the specified (B) DLC3 or (C) Cv-c protein variants under UAS control with the pan mesodermal twi-Gal4 line. Phenotypic rescue is shown as percentage of testes where all germ cells are encapsulated inside the testis. Representative images of testes in (D) control homozygous cv-cC524 animals, or homozygous cv-cC524 animals expressing in the mesoderm either (E) UAS-DLC3WT, (F) UAS-DLC3S993N, (G) UAS-Cv-cWT, (H) UAS-Cv-cGAPmut, or (I) UAS-Cv-cΔStART. Arrows in D, F, I point to extruded germ cells that are not surrounded by β-catenin. Testes are stained with anti-Vasa to label the germ cells (green), anti-Ems to label the pigment cells (purple), and anti-Eya and anti-β-catenin to label the male-specific somatic gonad precursors (msSGPs) and the membranes ensheathing the germ cells, respectively (grey in lower panels). Scale bar: 10 µm. Fisher test, Cv-cWT p = 0.0017 (N = 34), Cv-cGAPmut p < 0.0001 (N = 56), DLC3WT p < 0.0001 (N = 28), Cv-cΔStART p = 0.3005 (N = 31), and DLC3S993N p = 0.3180 (N = 38) (ns, p > 0.05; **p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001) (Figure 4—source data 1).
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82343/elife-82343-fig4-data1-v2.xlsx
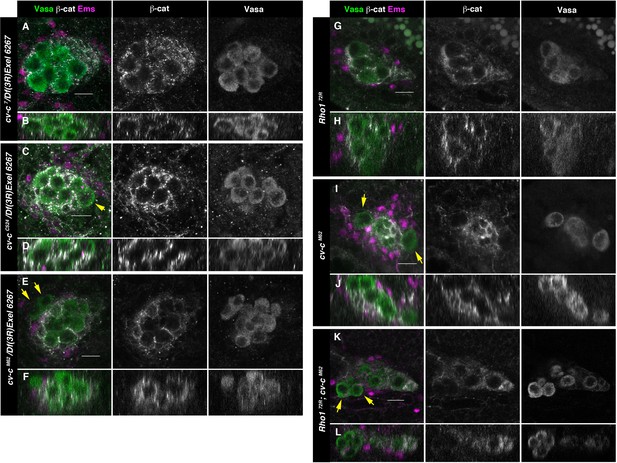
Testes in embryos with altered small GTPase regulation.
(A–L) Testes of various genotypes stained with anti-Vasa (green), β-catenin (grey), and Ems (magenta). β-Catenin and Vasa channels are shown separately in right panels. (A, B) No extruded gem cells are observed in hemizygous cv-c7/Df(3R)Exel6267 embryos carrying a cv-c7 allele which inactivates the RhoGAP domain’s function. (C, D) Hemizygous cv-cC524/Df(3R)Exel6267 or (E, F) cv-cM62/Df(3R)Exel6267 showing extruded germ cells. (G, H) Rho172R mutant embryos have smaller testes without extruded germ cells. (I, J) Homozygous cv-cM62 mutants present extruded germ cells. (K, L) Homozygous Rho172R cv-cM62 double mutant embryos present smaller testis with extruded germ cells. Arrows point to GCs outside the gonads. Note that β-catenin envelops all germ cells in (A, B) and (G, H) while in (C–F) and (I–L) some germ cells are not surrounded (arrows). Z sections are shown under all panels. Scale bar: 10 µm.
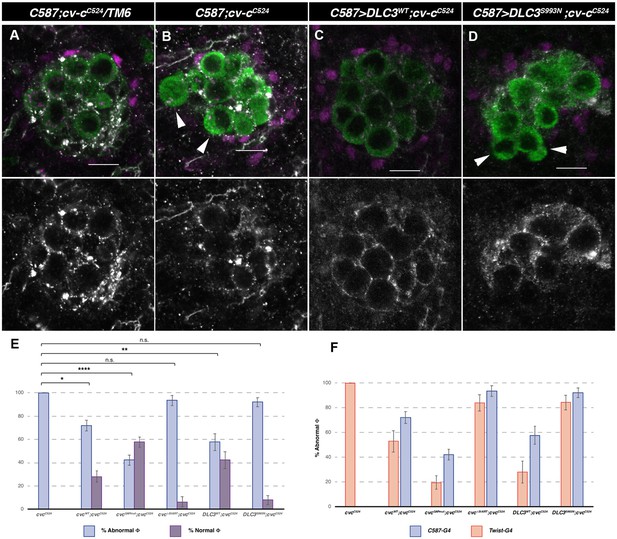
cv-cC524 homozygous mutant testes expressing different Cv-c and DLC3 protein variants exclusively in the somatic gonadal mesoderm with the c587-Gal4 driver line.
Representative images of testes in (A) heterozygous cv-cC524 animals, (B) control c587-Gal4 cv-cC524 homozygous animals or (C) homozygous cv-cC524 animals expressing either UAS-DLC3WT or (D) UAS-DLC3S993N. Arrowheads in B and D point to extruded germ cells that are not surrounded by E-Cad. DLC3WT expression rescues the cv-cC524 testis defects whilst DLC3S993N does not. Germ cells are stained with anti-Vasa (green); E-Cad, to label the membranes ensheathing the germ cells (grey) and anti-Ems to label the pigment cells (magenta). Scale bar: 10 µm. (E) Percentage of abnormal testes (blue bars) versus phenotypically wild-type rescued testis (purple bars) in the different genotypes analysed. (A testis is considered abnormal when one or more germ cells are extruded from the gonad.) (F) Comparison of rescue capability of the same UAS lines when expressed with the twi-Gal4 pan-mesodermal (orange bars) or the c587-Gal4 somatic gonadal cell driver lines (blue bars) shown as percentage of abnormal testes (Figure 5—figure supplement 1). Fisher test, Cv-cWT p = 0.0344 (N = 89), Cv-cGAPmut p < 0.0001 (N = 135), Cv-cΔStART p = 1 (N = 31), DLC3WT p = 0.0053 (N = 45), and DLC3S993N p = 0.5722 (N = 50) (ns; * p > 0.05; **p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001).
-
Figure 5—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82343/elife-82343-fig5-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
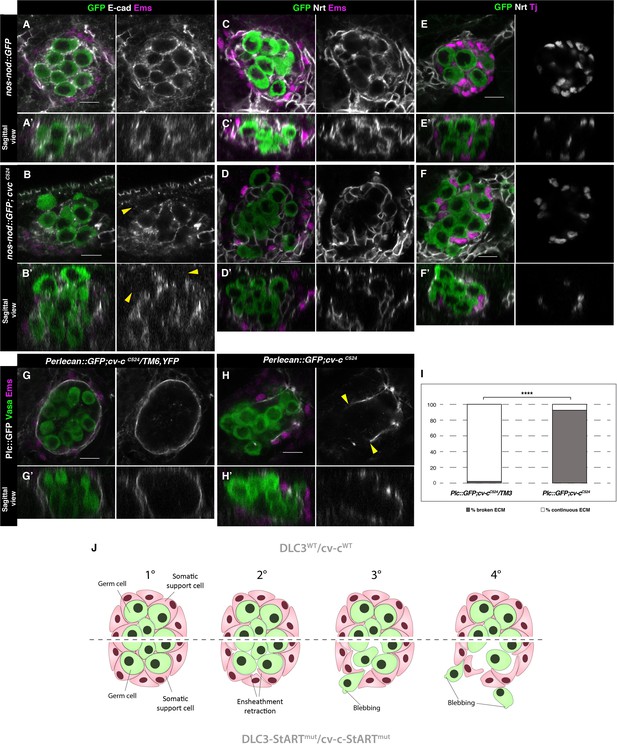
Ensheathment defects in cv-c mutant testes.
(A, C, E) Wild-type and (B, D, F) cv-cC524 testes. Germ cells are labelled with nos-nod::GFP (green A–F) and labelled in grey with anti-E-cad (A–B) or anti-Nrt (C–D) to highlight the ensheathing membranes (grey in right panels). (A, A’) In the wild-type E-cad highlights contacts between the germ cells and the interstitial somatic gonadal cells surrounding each germ cell reflecting their correct ensheathment. (B, B’) In cv-c mutant testes, several germ cells inside the testis and all the extruded ones (arrowheads) are not surrounded by E-cad labelling membranes indicating incorrect ensheathment. (C, C’) Neurotactin in the wild-type testis reflects correct germ cell ensheathment. (D, D’) In cv-cC524 mutants little Neurotactin expression is detected inside the testis. Nuclei of Tj-labelled somatic gonadal cells (magenta and grey in right panels) are detected between the GCs inside wild-type testes (E, E’) but not in cv-cC524 mutant testes (F, F’). (G, G’) Heterozygous and (H, H’) homozygous cv-cC524 testes labelling the extracellular matrix with Perlecan::GFP (Pcl, grey in right panels) and stained with anti-Vasa (green) and anti-Ems (magenta) to label the GCs and the pigment cells, respectively. (G, G’) The wild-type testis is enclosed by a Perlecan containing extracellular matrix (white). In cv-cC524 mutant testis a discontinuous extracellular matrix is observed where the GCs are outside the gonad (H, H’, yellow arrowheads). Z sections are shown under all panels. Scale bar: 10 µm. (I) Quantification of broken and continuous Perlecan Extracellular matrix (ECM) layer in cv-cC525 heterozygous or homozygous mutants using Fisher test; ****p value less than 0.0001 (cv-cC524/TM6B N = 54 and cv-cC524 N = 24) (Figure 6—source data 1). (J) Interpretation of the testis degeneration in wild type and DLC3/Cv-c mutants. (1) The StART domain of DLC3/Cv-c has a Rho-independent function stabilizing cell interactions between germ cells and somatic support cells. Stable cell–cell interaction among the cells of the gonadal niche allows them to settle down in the testis. (2) In DLC3S997N/Cv-cΔStART testis cell–cell interactions become compromised, cells lose their cohesion and separate from the gonadal niche. (3) After losing communication with somatic cells, germ cells become extruded from the gonadal niche initiating an erratic migrating behaviour. (4) Progressive loss of germ cells leads to gonad degeneration.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82343/elife-82343-fig6-data1-v2.xlsx
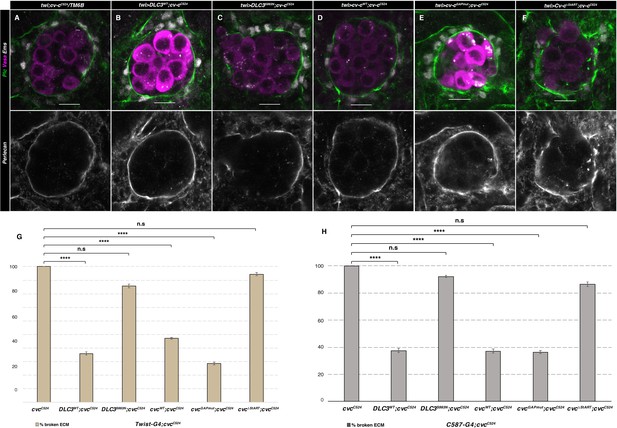
ECM rescue of cv-c mutant testes.
Representative images of testes in (A) control twi-Gal4; cv-cC524 heterozygous animals or homozygous cv-cC524 animals expressing in the somatic mesoderm cells either (B) UAS-DLC3WT, (C) UAS-DLC3S993N, (D) UAS-Cv-cWT, (E) UAS-Cv-cGAPmut, or (F) UAS-Cv-cΔStART. Germ cells are stained with anti-Vasa (magenta), pigment cells with anti-Ems (grey) and the ECM surrounding the gonad with anti-Perlecan (green and grey in lower panels). Scale bar: 10 µm. Comparison of rescue capability of the same UAS lines when expressed with the twi-Gal4 pan-mesodermal (G) or the C587-Gal4 somatic gonadal cell (H) driver lines shown as percentage of broken ECM detected by abnormal Perlecan distribution. Fisher test, (G) UAS-DLC3WT p = 0.0001 (N = 39), UAS-DLC3S993N p = 0.1442 (N = 28), UAS-Cv-cWT p = 0.0001 (N = 74), UAS-Cv-cGAPmut p < 0.0001 (N = 42), and UAS-Cv-cΔStART p = 1 (N = 18). (F) UAS-DLC3WT p < 0.0001 (N = 32), UAS-DLC3S993N p = 0.5435 (N = 38), UAS-Cv-cWT p < 0.0001 (N = 35), UAS-Cv-cGAPmut p < 0.0001 (N = 44), and UAS-Cv-cΔStART p = 0.2385 (N = 22) (ns, p > 0.05; ****p < 0.0001) (Figure 6—source data 1).
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/82343/elife-82343-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.xlsx
Videos
In vivo gonad coalescence of a control heterozygous cv-cC524/+ testis.
The germ cells are labelled with nos-nod::GFP and the male-specific somatic gonadal precursors with six-moe::GFP. Movie taken from st14 (prior to gonad coalescence) up to st16 (after coalescence).
In vivo gonad coalescence of a homozygous cv-cC524 testis.
The germ cells are labelled with nos-nod::GFP and the male-specific somatic gonadal precursors with six-moe::GFP. Movie runs from st14 (prior to coalescence) to st16 (after coalescence) when germ cell extrusion becomes noticeable (arrow). Note that the early stages of testis development are normal until the germ cell extrusion begins at later stages.
Selected planes from the testis presented in Video 2 to show more clearly the extrusion of an internal germ cell (asterisk).
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Rho172R | Strutt et al., 1997 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | y[1]w[*];Mi{y[+mDint2]=MIC}cv-c[MI00245] | BDSC | RRID:BDSC_30677 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | P{Sxl-Pe-EGFP.G}G5b, w* | BDSC | RRID:BDSC_32565 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | w1118; P{10XStat92E-GFP}1 | BDSC | RRID:BDSC_26197 | Bach et al., 2007 |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | cv-cM62 | Denholm et al., 2005 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | cv-c7 | Denholm et al., 2005 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | cv-cC524 | Denholm et al., 2005 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-cv-cWT | Sotillos et al., 2018 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-cv-cGAPmut | Sotillos et al., 2018 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-cv-cΔStART | Sotillos et al., 2018 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Myc-DLC3WT | Sotillos et al., 2018 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | nos-nod::GFP | A. González Reyes | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | c587-Gal4 | E. Matunis | RRID:BDSC_67747 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | six4-moe::GFP | S. DiNardo | Sano et al., 2012 | |
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Vasa::GFP | P. Lasko | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | Perlecan::GFP | Morin et al., 2001 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | twist-G4 | Greig and Akam, 1993 | ||
| Genetic reagent (Drosophila melanogaster) | UAS-Myc-DLC3S993N | This paper | Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | XhoI DLC3WT::pBS | This paper | Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | XhoI DLC3 S993N::pBS | This paper | Methods | |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pUASt::Myc-DLC3S993N | This paper | Methods | |
| Sequence-based reagent | DLC3S993N-For | This paper (Sigma-Aldrich) | PCR primers | 5’-TGTACCACTATGTCACCGACA-A-CATGGCACC-3’ |
| Sequence-based reagent | DLC3S993N-Rev | This paper (Sigma-Aldrich) Methods | PCR primers | 5’-TGGGGTGCCATG-T-TGTCGGTGACATAGTG-3’ |
| Antibody | Rat monoclonal anti-VASA | DSHB | AB_760351 | (1:20) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-Nrt | DSHB | AB_528404 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | rat monoclonal anti-DE-cad | DSHB | AB_528120 | (1:50) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-STAT | E. Bach | Flaherty et al., 2010 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | Mouse monoclonal anti-β-catenin | DSHB | AB_528089 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | mouse monoclonal anti-Eya | DSHB | AB_528232 | (1:100) |
| Antibody | guinea pig polyclonal anti-Ems | U. Walldorf | Walldorf and Gehring, 1992 | (1:5.000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-Sox100B | S. Russell | Nanda et al., 2009 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | guinea pig polyclonal anti-Tj | A. González-Reyes | Díaz-Torres et al., 2021 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | rabbit polyclonal anti-Perlecan | A. González-Reyes | Díaz-Torres et al., 2021 | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Rabbit polyclonal anti-GFP | Invitrogen | A11122 | (1:300) |
| Antibody | Chicken polyclonal anti-GFP | Abcam | ab13970 | (1:500) |
| Antibody | mouse anti-βgal | Promega | Z378A | (1:1000) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A-11029 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-21424 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A-21236 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | A-11034 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-21429 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A-21245 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Guinea Pig IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-21435 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Guinea Pig IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 647 | Invitrogen | A-21450 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Rat IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 | Invitrogen | A-48262 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Rat IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 555 | Invitrogen | A-48263 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Goat polyclonal anti-Chicken IgY (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor Plus 488 | Invitrogen | A32931 | (1:400) |
| Antibody | Donkey polyclonal anti-Goat IgG (H+L) Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 555 | Invitrogen | A-21432 | (1:400) |
| Software | ImageJ/Fiji | Fiji | http://fiji.sc/ | |
| Software | AdobePhotoshop/Illustrator | Adobe | https://www.adobe.com/ | |
| Software | Prism | GraphPad | https://www.graphpad.com/data-analysis-resource-center/ | |
| Software | Imaris | Oxford Instruments | https://imaris.oxinst.com/ | |
| Software | SeqBuilder/SeqMan | DNASTAR | https://www.dnastar.com/ | |
| Commercial assay, kit | DIG RNA Labelling Kit | Roche | 11 175 025 910 | |
| Commercial assay, kit | Qiagen Plasmid Midi Purification Kit | Qiagen | 12143 | |
| Other | Rhodamine Phalloidin (1:100) | Invitrogen | R415 | High-affinity F-actin probe conjugated to red fluorescence dye TRITC |
| Other | VECTASHIELD Mounting Medium | Vector Laboratories | âH-1000 | Antifade Mounting Medium for preserving fluorescence |
| Other | DAPI (1:10.000) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 62248 | Blue-fluorescent DNA stain |
| Other | Pfu polymerase | Promega | M774A | PCR polymerase |
| Other | DpnI restriction enzyme | Roche | 10742988001 | DNA restriction enzyme |
| Other | Halocarbon oil 27 | Sigma | H8773 | Inert oil to avoid Drosophila embryos/tissues desiccation. |





