Taxonium, a web-based tool for exploring large phylogenetic trees
Figures
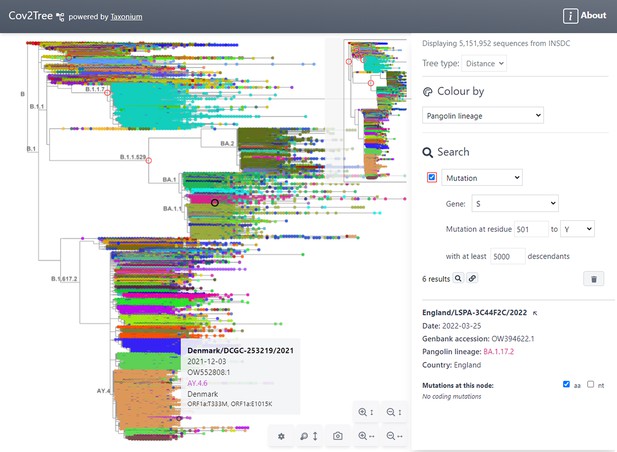
Tree exploration at unprecendented scale.
This figure presents a screenshot of the Taxonium web client displaying a 5,151,952 sequence tree of SARS-CoV-2 sequences. The left hand panel shows the zoomable tree with a minimap for orientation, and the right hand panel provides options for searching for nodes and for changing the colour scheme. Hovering over a node shows information in a tooltip, while clicking on a node displays further information in the right-hand panel. A search has been carried out for mutations at S:501 to Y, filtered to such nodes with at least 5,000 descendants, which are circled in red. Genomes are coloured by their PANGO lineage.
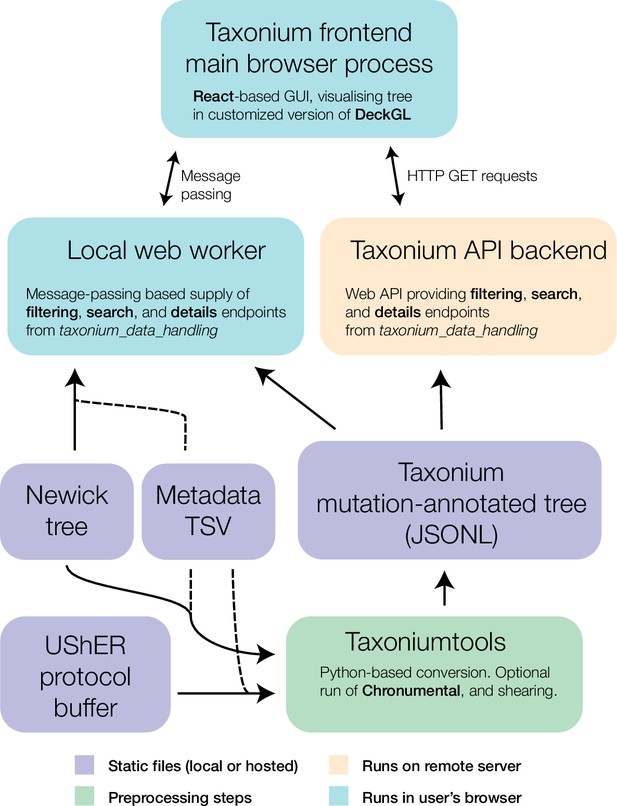
Components of the Taxonium project.
At the core of Taxonium is a graphical interface that runs in the web browser. It can connect either to a web-worker running in the same browser (for purely local use) or to an API web-server that serves parts of the tree on demand. Trees can be loaded from Newick format files with metadata TSVs (tab-separated value files), or from a specialised Taxonium JSONL (JSON-lines) format which is able to capture mutation-annotated trees. Taxonium JSONLs can be produced using the Taxoniumtools library.
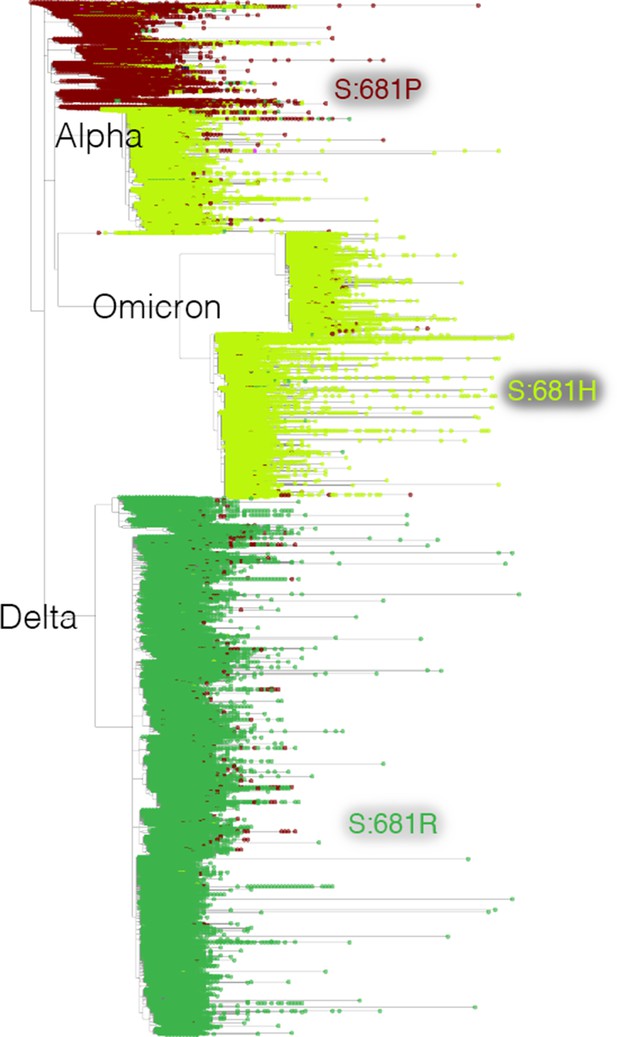
Mutation-annotated trees capture full sequence variation.
In this screenshot, genotype data at position Spike 681 is overlaid onto the full SARS-CoV-2 tree with Taxonium. This analysis can be reproduced by setting the ‘Color by’ field to genotype.
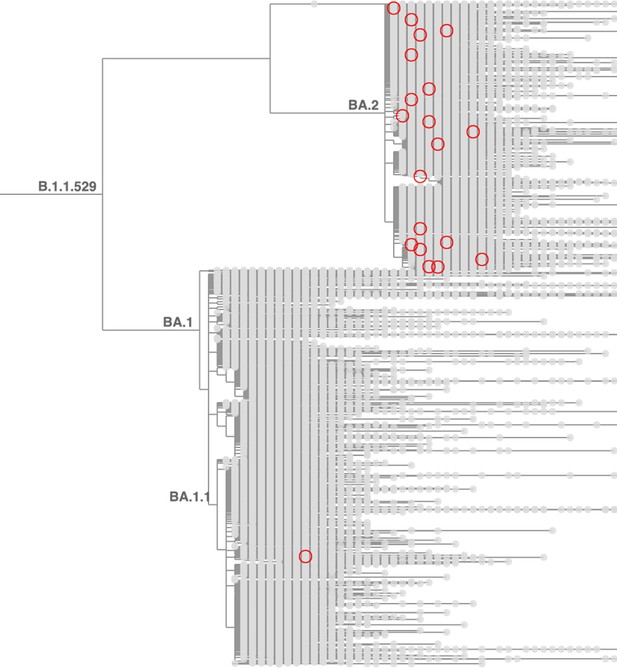
Taxonium reveals recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2.
This figure shows a tree zoomed in on Omicron (B.1.1.529), with 1,422,024 sequences until late May 2022. Circled nodes feature a mutation at S:452 to either M or Q which have more than 10 descendants. These (independent) mutation are much more common on the BA.2 genetic background, revealing epistasis.
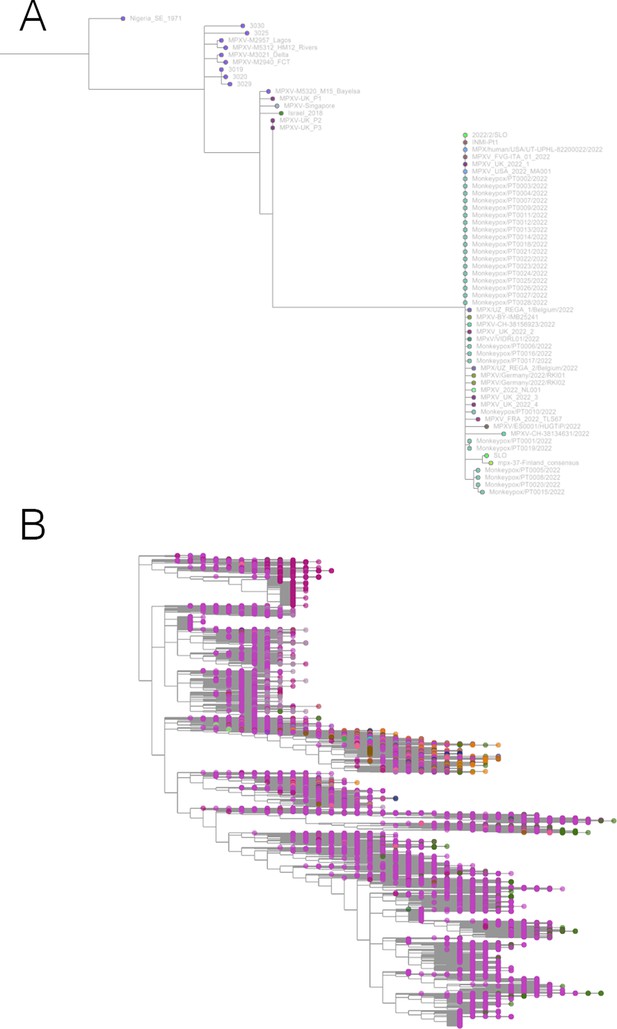
Taxonium has applications beyond SARS-CoV-2.
(A) Phylogeny of monkeypox sequences at mpx.taxonium.org. The large clade represents the current outbreak (B) NCBI’s taxonomy of 2.2 M species as explorable at taxonomy.taxonium.org.





