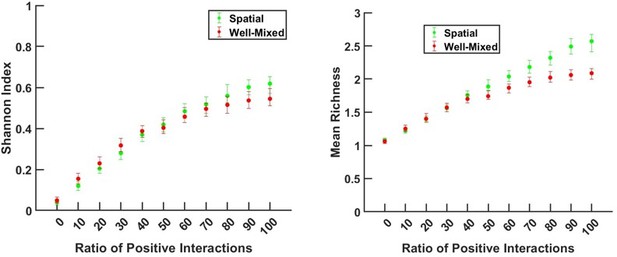
Spatial structure favors microbial coexistence except when slower mediator diffusion weakens interactions
Figures

A spatial environment favors coexistence more when interspecies facilitation is prevalent in the initial species pool.
(A) Species are engaged in metabolite-mediated interactions with other species. Each species produces a subset of mediators and consumes a subset. Each mediator can positively or negatively modulate the growth rate of the species it influences. In our model, consumption is present whenever there is an influence from a mediator on a species, regardless of whether the influence is facilitative or inhibitory. Production and consumption of mediators are indicated by open arrows. (B) In a one-dimensional (1D) spatial context, species and mediators are defined as functions of space that change over time because of population growth and dispersal as well as mediator production, consumption, and diffusion. A cartoon representation of the distributions of four species and three mediators are shown here over the spatial context (z). (C) Simulations were run at different ratios of facilitative to inhibitory interactions (fac:inh) for spatial (open blue squares) and well-mixed (filled blue circles) communities. Each ratio was run 500 times with the richness (number of species stably surviving at the end of a simulation) averaged over all the simulations. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples. Here, the species dispersal coefficient is cm2/hr. Boxes mark fac:inh ratios used in later simulations.
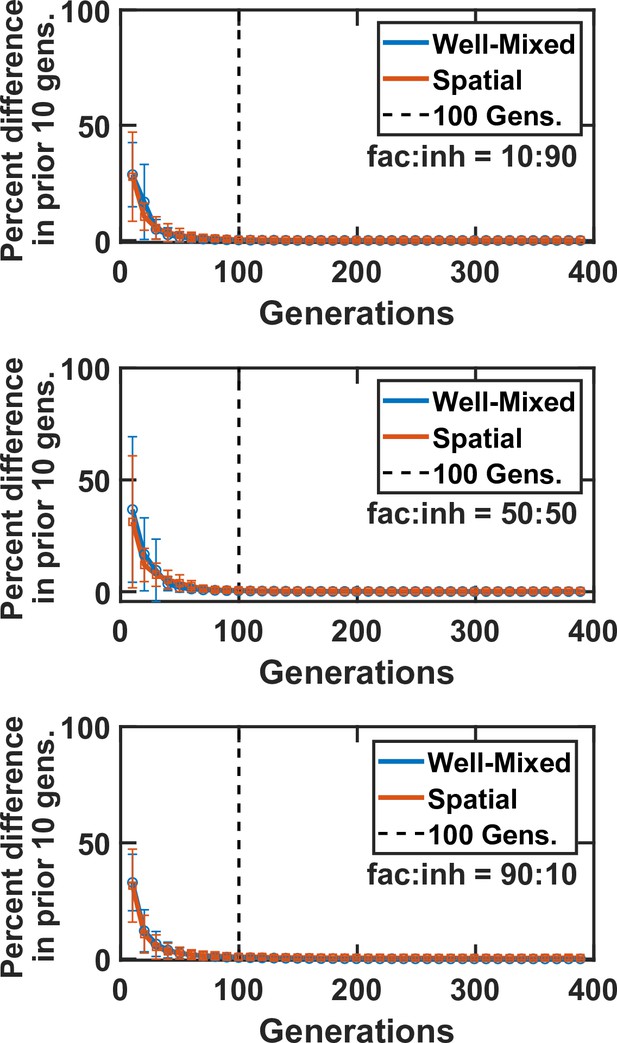
There is little change in community composition after 100 generations of growth.
Here, we examine a simple case with five species and three mediators. Markers and error bars show mean and standard deviation of the percentage change in the community composition over 10 generations of growth (one round of growth between dilutions). There was minimal change (less than 1% difference) after 100 generations of growth in both well-mixed and spatial contexts. This observation was consistent regardless of the initial ratio of facilitation to inhibition interactions, at fac:inh = 10:90 (top), 50:50 (middle), and 90:10 (bottom). In all cases, DCell = 5 × 10−9 cm2/hr and DMed = 1.8 × 10−2 cm2/hr.
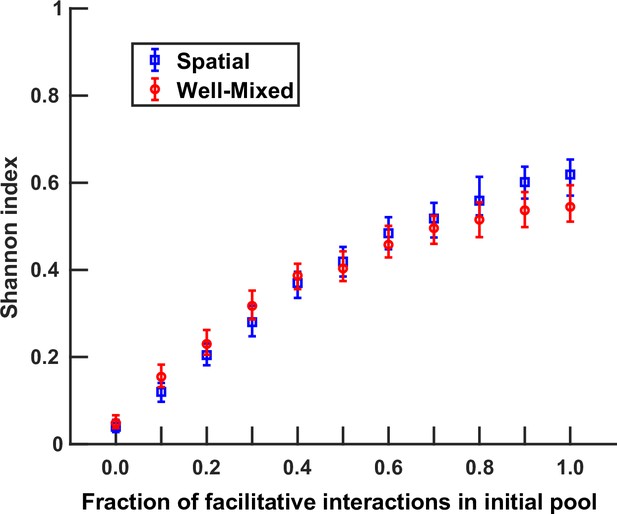
Shannon index shows the same overall trend as richness when comparing spatial versus well-mixed communities.
Similar to Figure 1C, simulations were run at different fac:inh ratios for both spatial communities (blue squares) and well-mixed communities (red circles). Each ratio was run 500 times with the richness (number of species stably surviving at the end of a simulation) averaged over all the simulations. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples. Here, the species dispersal coefficient is cm2/hr.
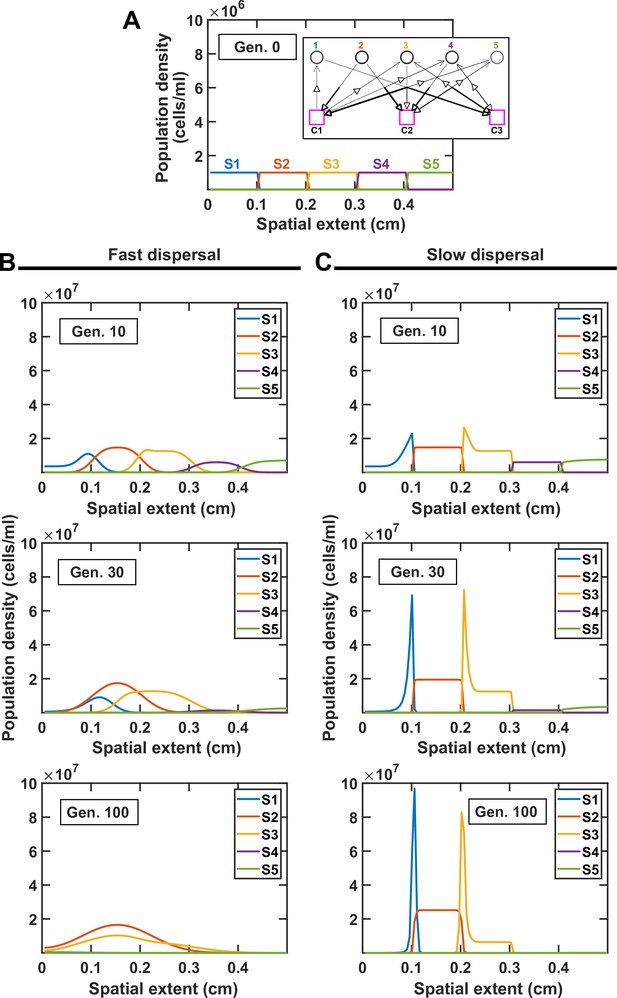
Comparing the spatial distribution of species at different dispersal rates illustrates the impact of dispersal on coexistence.
(A) Species are initially stacked over the spatial extent of the community. We examine a simple case with five species and three mediators (interaction network shown in the inset). Different progressions are observed at high (B, DCell = 5 × 10−6 cm2/hr) versus low (C, DCell = 5 × 10−9 cm2/hr) dispersal rates, leading to different coexistence outcome. In both cases, DMed = 1.8 × 10−2 cm2/hr.
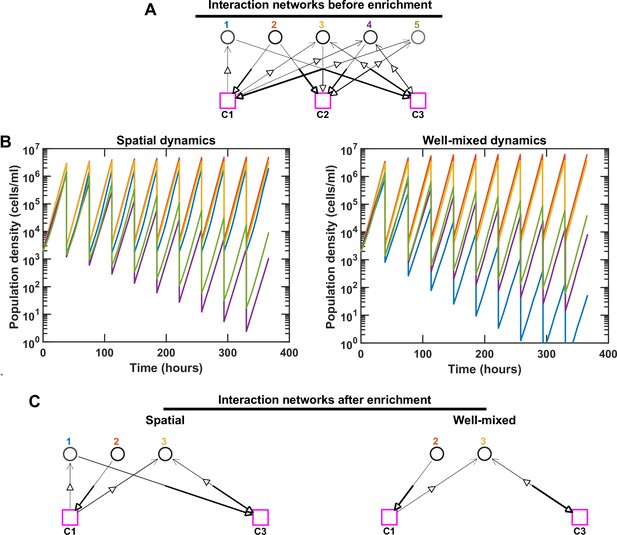
Species interactions and dynamics are different in spatial versus well-mixed environments, leading to different coexistence outcomes.
For simplicity, we consider an initial pool of five species with three mediators. We kept the same interaction network (A) in both spatial and well-mixed conditions and simulated the species dynamics. In the interaction network, hollow arrows indicate the flow of mediators (either production or consumption). The thickness of the lower end of each arrow shows the production rate and the thickness of the upper end of the arrow shows the strength of the mediator influence on the corresponding species. The basal growth rate of each species is shown as different shades of gray, with darker shades indicating larger basal growth rates. For spatial communities, the population density represents the sum of all densities across different spatial extents. We ran the simulation in both cases through 10 rounds of growth and dilution. Different population dynamics and ultimately different coexistence outcomes are observed in these cases after simulating 100 generations. Note that even though Species 4 and 5 in the spatial community and Species 1, 4, and 5 in the well-mixed community are still present in the final communities, because they exhibit a trend of decline in relative frequency, we consider them not to coexist (in accordance with our coexistence criterion, see Methods). (B, C) In this example, proximity of Species 1 to a beneficial Species 2 in the spatial community allows a strong boost in the growth of Species 1, leading to its coexistence with Species 2 and 3. In contrast, Species 1 in the well-mixed community receives a smaller portion of C1, not enough to allow Species 1 to keep up with the other species. In C, only coexisting species and mediators related to them are shown.
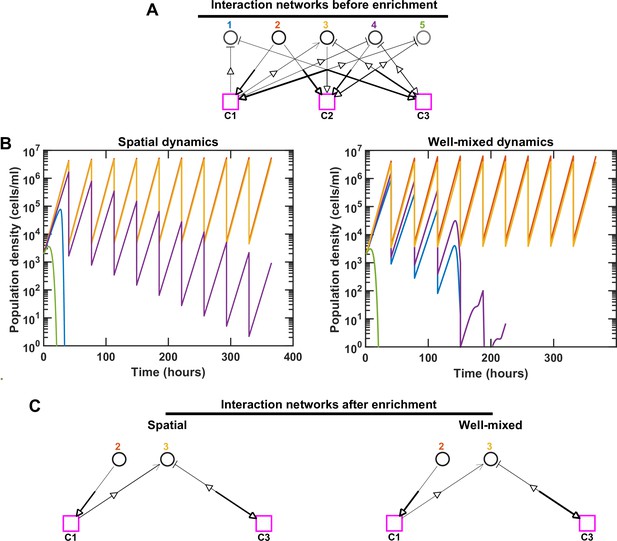
Species interactions and dynamics are different in spatial versus well-mixed environments, even when inhibition is prevalent.
For simplicity, we consider an initial pool of five species with three mediators, but rather than fac:inh = 90:10 in Figure 1—figure supplement 4, here we initially assign fac:inh = 10:90. We kept the same interaction network (A) in both spatial and well-mixed conditions and simulated the species dynamics. In the interaction network, hollow arrows indicate the flow of mediators (either production or consumption). The thickness of the lower end of each arrow shows the production rate and the thickness of the upper end of the arrow shows the strength of the mediator influence on the corresponding species. The basal growth rate of each species is shown as different shades of gray, with darker shades indicating larger basal growth rates. For spatial communities, the population density represents the sum of all densities across different spatial extents. We ran the simulation in both cases through 10 rounds of growth and dilution. Different population dynamics are observed in these cases. Note that even though Species 4 in the spatial community is still present in the final communities, because they exhibit a trend of decline in relative frequency, we consider them not to coexist (in accordance with our coexistence criterion, see Methods). (B, C) In this example, proximity of Species 1 to an inhibitory Species 2 in the spatial community leads to rapid exclusion of Species 1. Early extinction of Species 1 removes its inhibition of Species 4 and allows Species 4 to sustain longer in the spatial context compared to the well-mixed community. In C, only coexisting species and mediators related to them are shown.
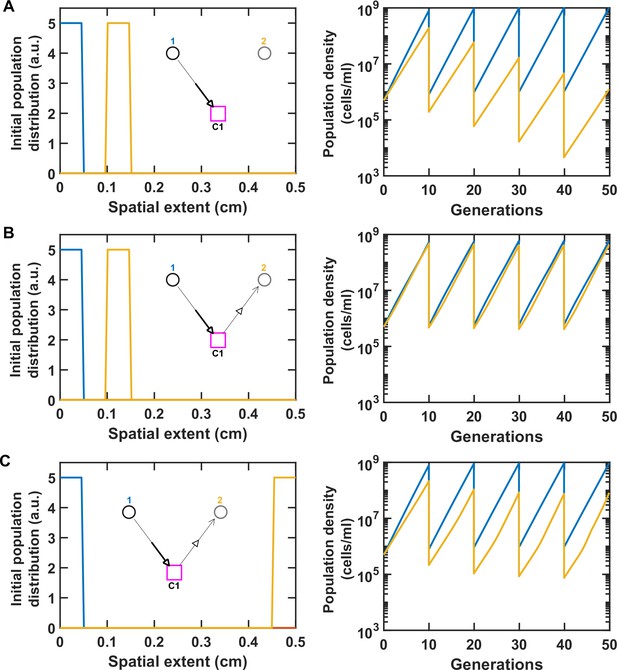
Spatial distance between species can modulate the strength of their interaction.
For simplicity, here we consider only two species engaged in commensalism (Species 1 providing a benefit to Species 2) through a single mediator (see insets). We examined a no-interaction control (A), versus when the species were initially close (B) or far (C) from each other within the spatial extent of the communities. All parameters are similar to Table 1, except the mediator diffusion coefficient which is chosen at DMed = 1.8 × 10−3 cm2/hr to exaggerate the impact of mediator diffusion in space. The panel on the left shows the initial distribution of the two populations in space and the panel on the right shows the population dynamics. Notably, the ratio of Species 1 to Species 2 drops by 10-fold, when Species 2 is farther away from Species 1 (C versus B). The basal growth rate of Species 1 and 2 are 0.1 and 0.08/hr, respectively. We ran the simulation for five rounds of growth and dilution.
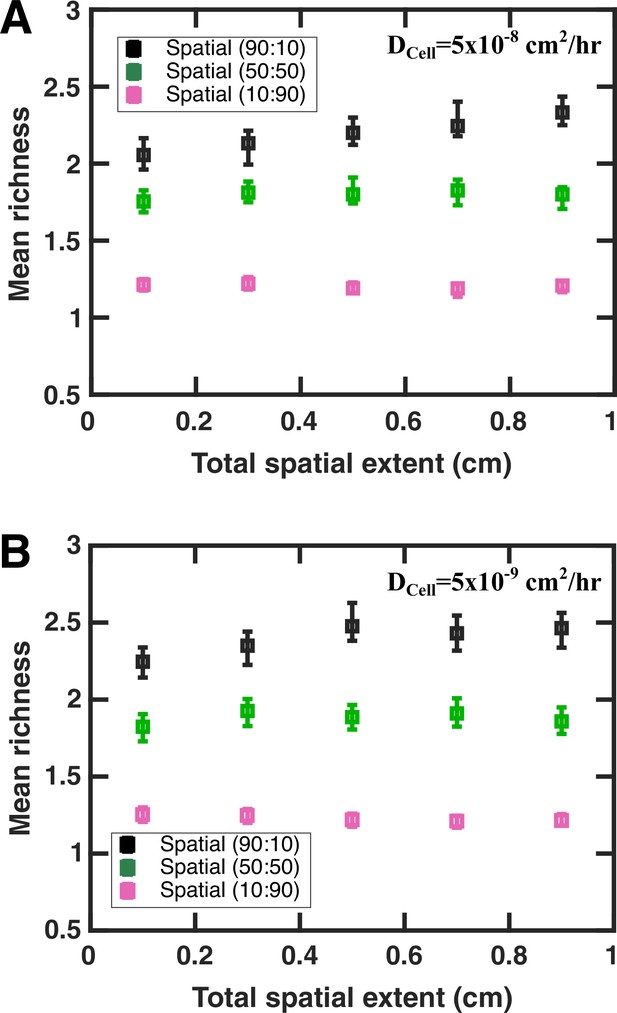
Within the same order of magnitude, the community’s spatial extent does not have a large impact on spatial coexistence.
All parameters other than the community’s spatial extent are kept fixed. Here, (A) DCell = 5 × 10−8 cm2/hr and (B) DCell = 5 × 10−9 cm2/hr. Legend shows the values of fac:inh assigned in the initial pool. In these simulations, the spatial resolution dz is kept at 0.05 mm in all cases and the initial extent of each species is 1/10th of the total spatial extent at the beginning of each simulation.
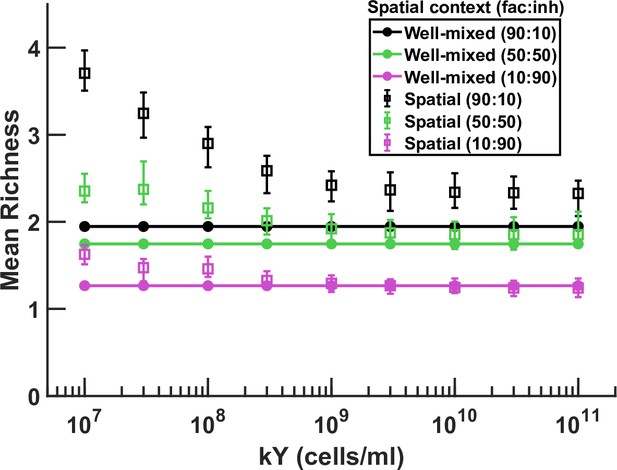
Imposing a local carrying capacity favors species coexistence.
All parameters other than the local carrying capacity kY are kept fixed. Imposing a local carrying capacity on the total cell number (see the equations described in Methods) lowers the competitive advantage of the most successful species and allows more coexistence. This is similar to the idea of strengthened intrapopulation competition in a spatially structured environment that has been discussed in depth in the past as one of the reasons that spatial environments can support more coexistence. To focus on the effect of interspecies interaction, we assume kY = 109 cells/ml in our other simulations throughout this manuscript to minimize the impact of kY (i.e. a forced intrapopulation competition) on our results.
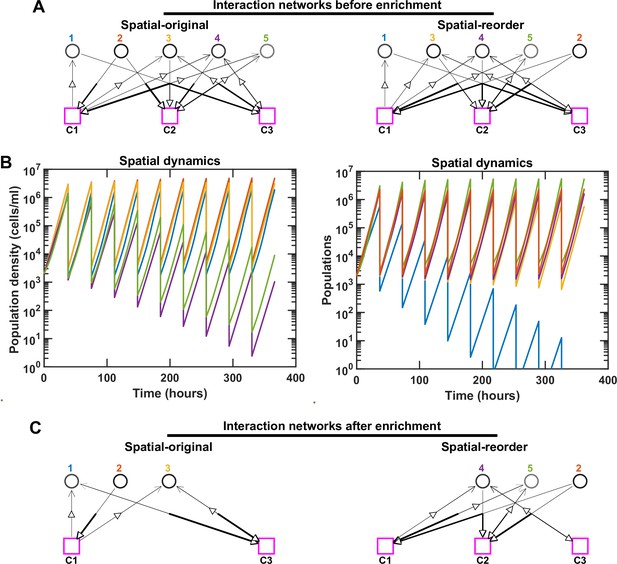
Rearranging the order of species can modulate the strength of interspecies interactions and impact spatial coexistence outcomes.
For simplicity, here we use the same examples as Figure 1—figure supplement 4 with five species and three mediators in the initial pool. We keep the same interaction network (A), but rearrange the initial order of species in the spatial community (original: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; reorder: 1, 3, 4, 5, 2). We ran the simulation in both cases through 10 rounds of growth and dilution. Different population dynamics and ultimately different coexistence outcomes are observed in these cases after simulating 100 generations. Note that even though Species 4 and 5 in the original community and Species 1 and 3 in the reorder community are still present in the final communities, because they exhibit a trend of decline in relative frequency, we consider them not to coexist (in accordance with our coexistence criterion, see Methods). (B, C) In this particular example, after changing the order, Species 1 and 3 receive less of the benefits from Species 2, leading to the emergence of Species 2, 4, and 5 as an alternative stable coexistence. In C, only coexisting species and mediators related to them are shown.
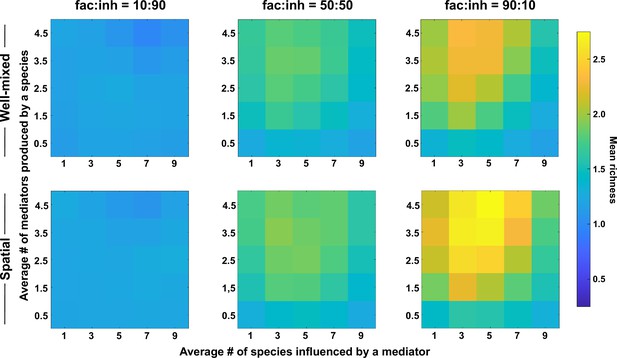
The number of metabolites produced and number of species influenced affect coexistence in spatial and well-mixed communities.
Different ranges of production and mediator influence values were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances and marked on the color bar. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The x-axis represents the average number of species influenced by a mediator and the y-axis represents the average number of mediators produced by each species. Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1.
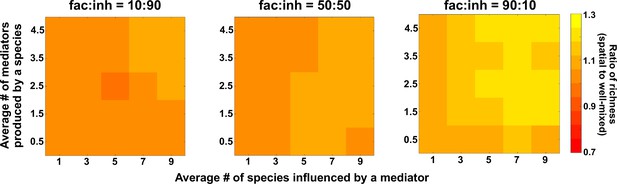
The number of metabolites produced and number of species influenced affect coexistence in spatial and well-mixed communities.
Different ranges of production and mediator influence values were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). The ratio of spatial to well-mixed mean richness values is calculated for 500 simulated instances and marked on the color bar. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The x-axis represents the average number of species influenced by a mediator and the y-axis represents the average number of mediators produced by each species.
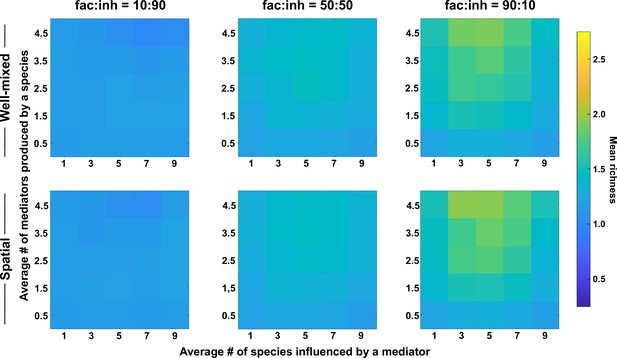
Coexistence is favored when many metabolites are produced and influence an intermediate number of species, even with weaker interactions.
Different ranges of production and mediator influence values were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances and marked on the color bar. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The x-axis represents the average number of species influenced by a mediator and the y-axis represents the average number of mediators produced by each species. Here, the maximum interaction strength magnitude = 0.05.
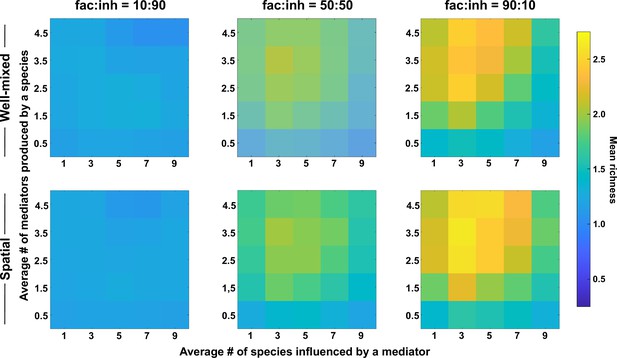
Coexistence is favored when many metabolites are produced and influence an intermediate number of species, even with stronger interactions.
Different ranges of production and mediator influence values were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances and marked on the color bar. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The x-axis represents the average number of species influenced by a mediator and the y-axis represents the average number of mediators produced by each species. Here, the maximum interaction strength magnitude = 0.5.
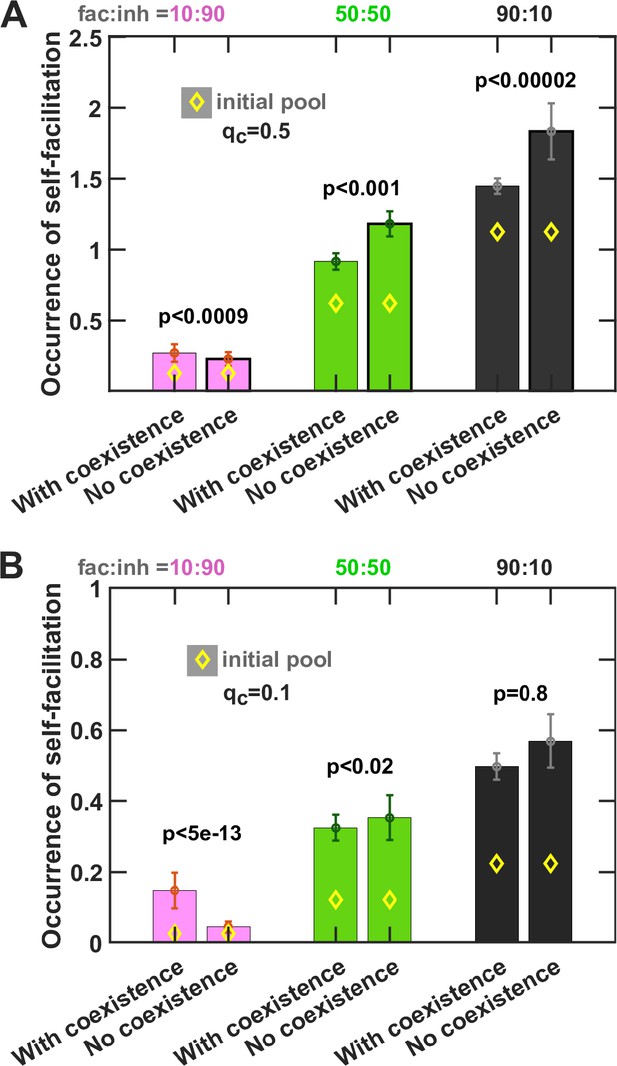
Self-facilitation is prominent among low-diversity outcomes.
We separated the outcomes based on whether one (No coexistence) or more species (With coexistence) emerged from enrichment and examined the occurrence of self-facilitation. Occurrence is defined here as the average number of self-facilitation links (i.e. production of a mediator that benefits its producer) divided by the number of species present in the community. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Here qc = 0.5 and qp = 0.5. Diamond markers (◊) show the occurrence in the initial pool of species before enrichment. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples using 500 total instances simulated. Mann–Whitney U test was used for comparison of occurrences between ‘No coexistence’ and ‘With coexistence’ cases to calculate the p values. More self-facilitation occurrence was associated with absence of coexistence when fac:inh was 50:50 or 90:10, but the reverse trend held when interactions within the initial pool were mostly inhibitory (fac:inh = 10:90).

Coexistence is higher where there is a balance between production and consumption of mediators.
Different average production and consumption rates were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) is calculated for 500 simulated instances. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Color bar represents the average richness. The x-axis represents the average production rate of mediators and the y-axis represents the average consumption rate of mediators. Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1.
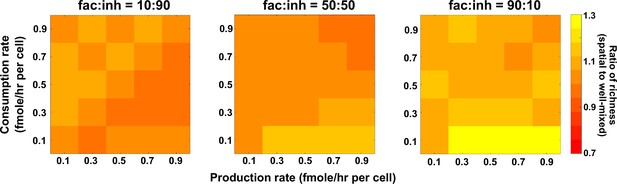
In spatial communities with many facilitation interactions among species, coexistence is favored at lower consumption rates of mediators.
Different average production and consumption rates were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). The ratio of spatial to well-mixed mean richness values is calculated for 500 simulated instances and marked on the color bar. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. The x-axis represents the average production rate of mediators and the y-axis represents the average consumption rate of mediators.
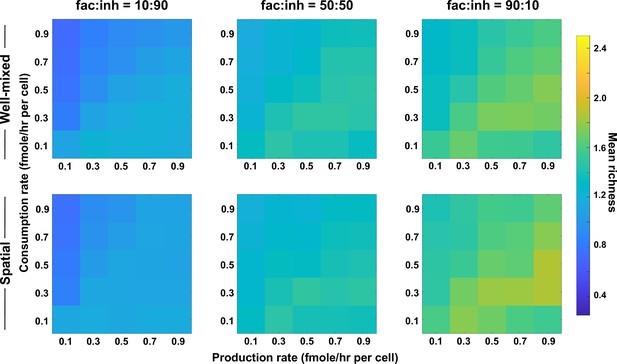
Coexistence is higher where there is a balance between production and consumption of mediators independent of the interaction strength (here, with weaker interactions).
Different average production and consumption rates were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) is calculated for 500 simulated instances. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Color bar represents the average richness. The x-axis represents the average production rate of mediators and the y-axis represents the average consumption rate of mediators. Here, the maximum interaction strength magnitude = 0.05.
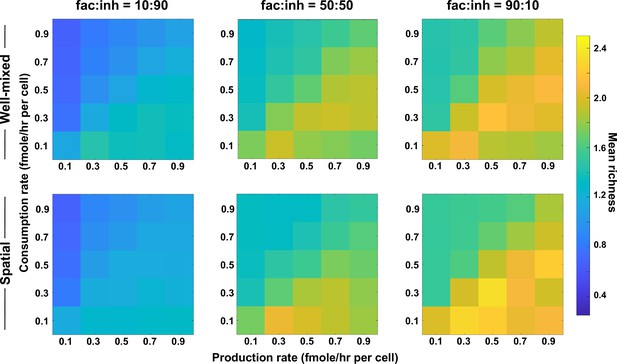
Coexistence is higher where there is a balance between production and consumption of mediators, independent of the interaction strength (here, with stronger interactions).
Different average production and consumption rates were analyzed for both well-mixed and spatial communities at three different fractions of fac:inh influences in the initial pool of species (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) is calculated for 500 simulated instances. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Color bar represents the average richness. The x-axis represents the average production rate of mediators and the y-axis represents the average consumption rate of mediators. Here, the maximum interaction strength magnitude = 0.5.

Lower dispersal rates allow more microbial coexistence.
Communities in spatially structured environments were simulated with different dispersal coefficients at three different fractions of fac:inh influences (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples.
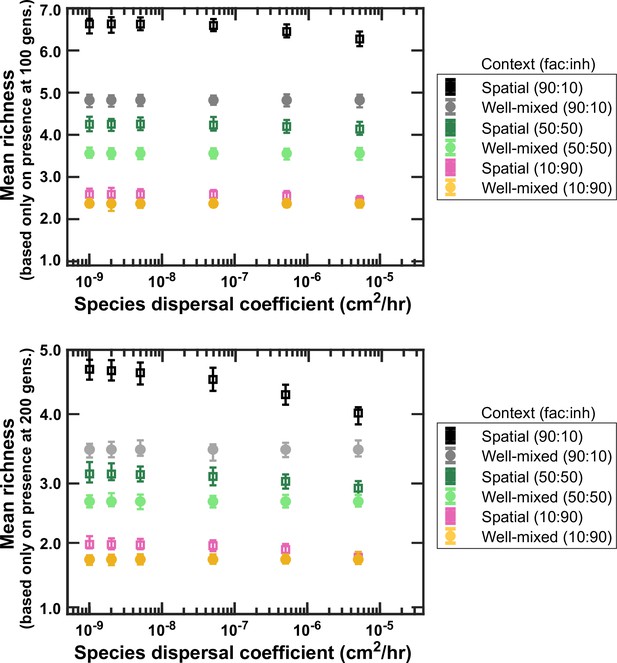
Lower dispersal rates allow more microbial coexistence.
Communities in spatially structured environments were simulated with different dispersal coefficients at three different fractions of fac:inh influences (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). Mean richness (here based on the average number of species present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations (top) or 200 generations (bottom). Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples. As expected, assessing species presence after 200 generations shows lower richness compared to 100 generations, since some species go extinct during the additional 100 generations. Nevertheless, both cases show a decreasing richness in spatial communities with larger dispersal coefficients (still richness stays higher than the well-mixed levels).
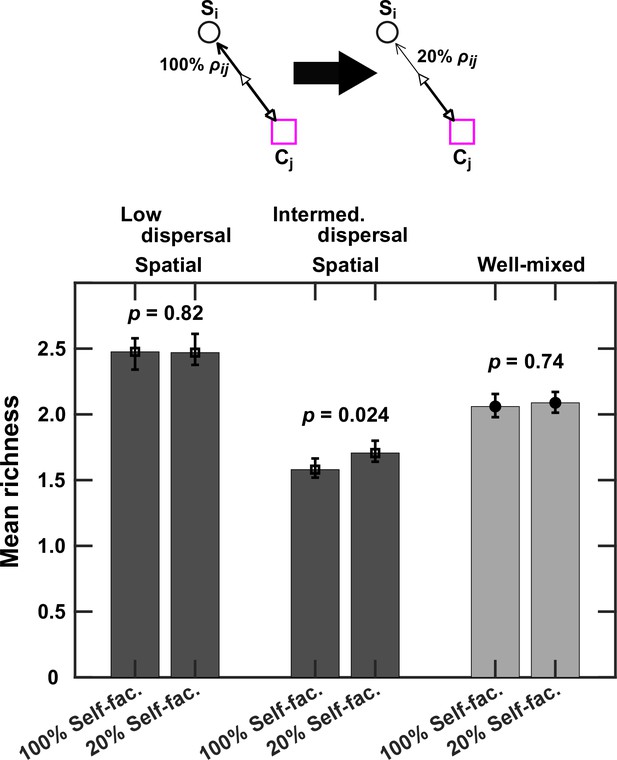
Self-facilitation contributes to lower richness at intermediate levels of dispersal.
For these cases, we use fac:inh = 90:10, because it showed the strongest change at intermediate dispersal values. Mean richness (i.e. average number of species stably present at the end of a simulation) was calculated for 500 simulated instances. In each instance, we simulated the enrichment and coexistence in the baseline case (100% ρij) as well as the same community when for self-facilitation links, the influence of the corresponding mediator on its producer was reduced by a factor of 5 (20% ρij). This is shown visually in the top schematic. This allows us to assess the impact of self-facilitation links in different conditions. We acknowledge that this assessment is not perfect, because weakening self-facilitation links in this way also reduces the beneficial influence of other species on Si that may happen via Cj. Nevertheless, we observe that at intermediate dispersal levels (Intermed. Dispersal, spatial; DCell = 5 × 10−6 cm2/hr), weakening self-facilitation links leads to more coexistence. In contrast, this effect is absent when dispersal levels are low (Low dispersal, spatial; DCell = 5 × 10−9 cm2/hr) or in well-mixed communities (Well-mixed). Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples.
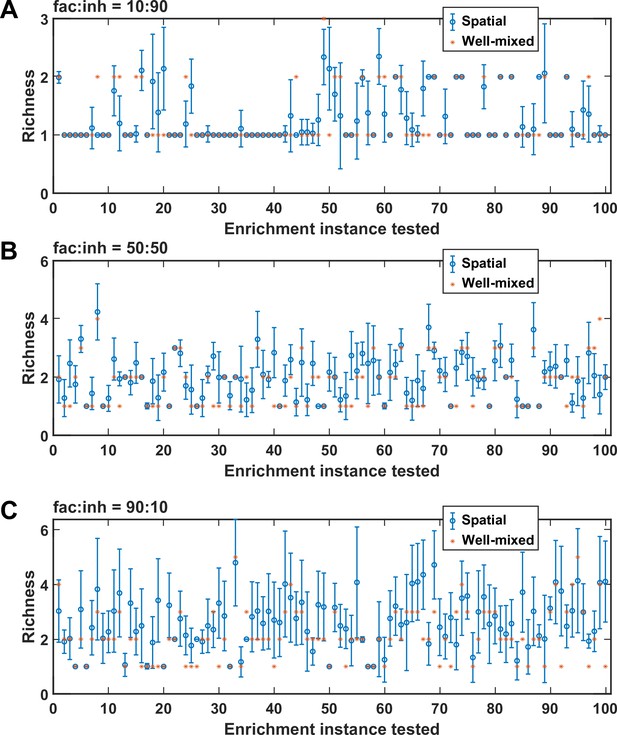
Rearranging the order of species affects spatial coexistence.
For each of the cases of (A) fac:inh = 10:90, (B) fac:inh = 50:50, and (C) fac:inh = 90:10, we simulated 100 instances and in each instance, we examined coexistence outcome (final richness) in 100 permutations of the order of species (as an example, 10, 3, 6, 1, 5, 7, 4, 2, 9, 8 would be a permutation of the order of the 10 species). Asterisks (*) show the calculated richness for the corresponding well-mixed community, and the circle (o) and the error bar show the mean and standard deviation of the richness values obtained for the 100 permutations tested. Overall, we observe that it is common to reach a different richness value when the order of species is changed.
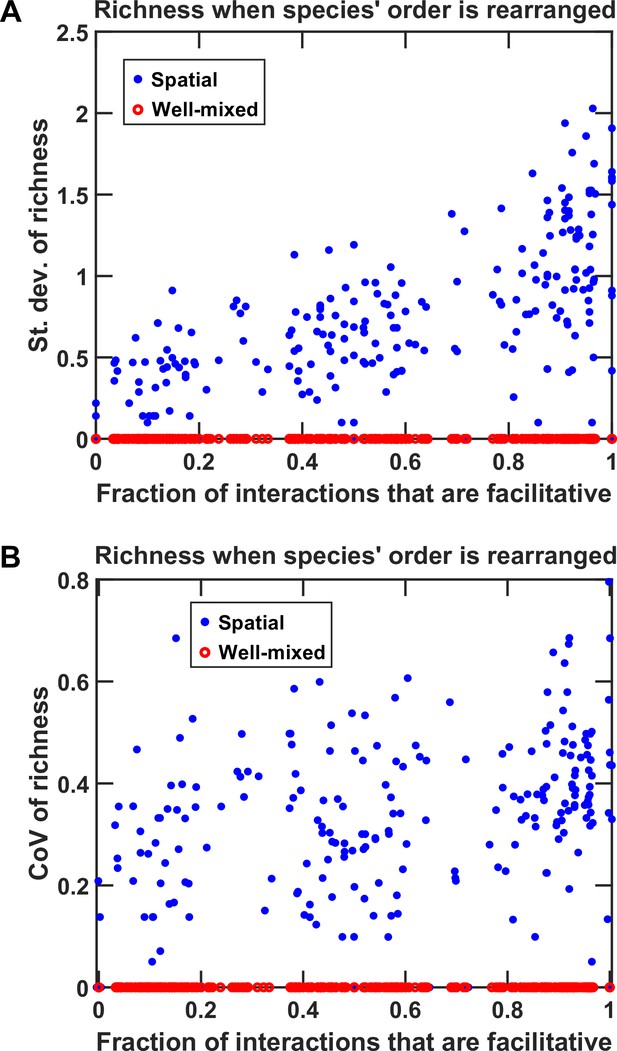
Rearranging the order of species affects spatial coexistence more in communities in which facilitation is prevalent.
Similar to Figure 4—figure supplement 3, we simulated 100 instances each of fac:inh = 10:90, 50:50, and 90:10, and in each instance, we examined coexistence outcome (final richness) in 100 permutations of the order of species. Red circles (○) show the calculated richness for the corresponding well-mixed community, and the blue filled circles (●). The standard deviation of the richness values obtained for the 100 permutations are shown in (A). The 95% confidence interval for the slope of the standard deviation of richness with respect to fp was 1.01 ± 0.13. The trend was maintained for the coefficient of variations of the 100 permutations as well (B). The 95% confidence interval for the slope of the standard deviation of richness with respect to fp was 0.48 ± 0.10. The Matlab function fitlm was used to estimate the slope and its standard error. Confidence intervals are calculated as , where is the inverse t coefficient, is the number of data points, and SE is the standard error of the slope.

At higher diffusion coefficients of mediators more coexistence is possible.
A range of metabolite diffusion coefficients were simulated in spatial communities (squares) at three different fractions of fac:inh influences (10:90, 50:50, and 90:10). We simulated corresponding well-mixed communities (circles) for comparison. Each condition was run 500 times with the richness (number of species stably surviving at the end of a simulation) averaged over all the simulations. Each simulation started with 10 species and 5 mediators and ran for 100 generations. Other simulation parameters are listed in Table 1. The error bars are 95% confidence intervals generated by bootstrapping 100 samples.
Tables
Parameters used in our simulations are listed.
| Parameter | Value (unit) |
|---|---|
| Number of instances examined () | 500 |
| Number of cell types in the initial pool () | 10 |
| Number of interaction mediators () | 5 |
| Total initial cell density (TID) | 104 (cells/ml) |
| Interaction strength saturation level () | 104 (cells/ml) |
| Population extinction threshold (ExtTh) | 0.1 (cells/ml) |
| Population dilution threshold (DilTh) | 107 (cells/ml) |
| Consumption rate () | 0.075–2.25 (fmol per cell per hour; avg. 0.15) Stochastic with a uniform distribution |
| Production rate () | 0.1–0.2 (fmol per cell per hour; avg. 0.1) Stochastic with a uniform distribution |
| Probability of production link per population () | 0.5 |
| Probability of influence link per mediator () | 0.5 |
| Maximum interaction strength magnitude () | 0.2 (1/hr) |
| Basal growth rate of species () | 0.1–0.2 (1/hr); stochastic with a uniform distribution |
| Number of generations for enrichment (nGen) | 100 |
| Dispersal coefficient for cells (DCell) | 5 × 10−9 (cm2/hr) |
| Diffusion coefficient for mediators (DMed) | 1.8 × 10−2 (cm2/hr) |
| Local carrying capacity per dz (kY) | 109 cells/ml |
| Total community spatial extent (Z) | 0.5 cm |
| Spatial resolution for species distributions (dz) | 0.005 cm |
| Cell growth update and uptake timescale (dtau) | 0.01 hr |
| Mediator diffusion time-step (dt) | 0.1dz2/DMed |
| Cell dispersal simulation time-step (dc) | 0.1dz2/DCell |