The multi-tissue landscape of somatic mtDNA mutations indicates tissue-specific accumulation and removal in aging
Figures
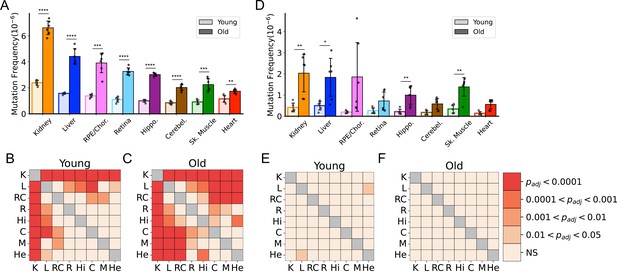
Frequency of somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutations increase with age and is tissue-specific.
(A) The frequency by which single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) were detected in all sequenced bases in either young (~5-months of age) or old (26-months of age) tissues arranged from highest to lowest SNV frequency in aged mice. (B) The frequency by which DNA insertions or deletions (In/Del) of any size are detected within all sequenced bases either young (~5-months of age) or old (26-months of age) tissues. For (A) and (B), significance between young and old within a tissue was determined by Welch’s t-test. *0.01 < p < 0.05, **0.001 < p < 0.01, ***0.0001 < p < 0.001, ****p<0.0001; error bars = standard deviation of individual data points shown. (C–D) Heatmaps of one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD for significant differences of SNV frequencies between tissues, within either young (C) or old (D) age groups. (E–F) Heatmaps of one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD for significant differences of In/Del frequencies between tissues, within either young (E) or old (F) age groups.
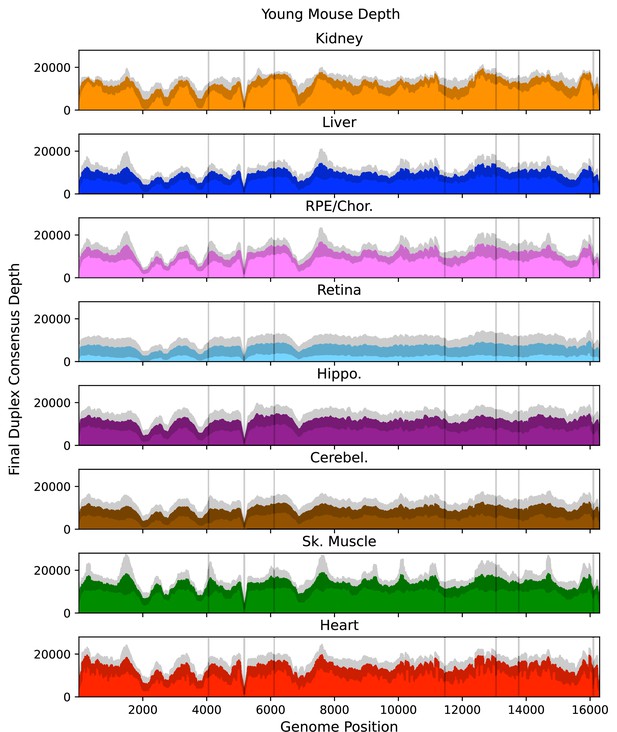
Mean post-consensus ‘duplex’ depth for young (4.5 months) tissues.
Variant occurring within the masked regions (vertical lines) or positions with less than a post-consusensus depth of 100× were ignored. Gray shading = standard deviation of the mean for N=5 mice.
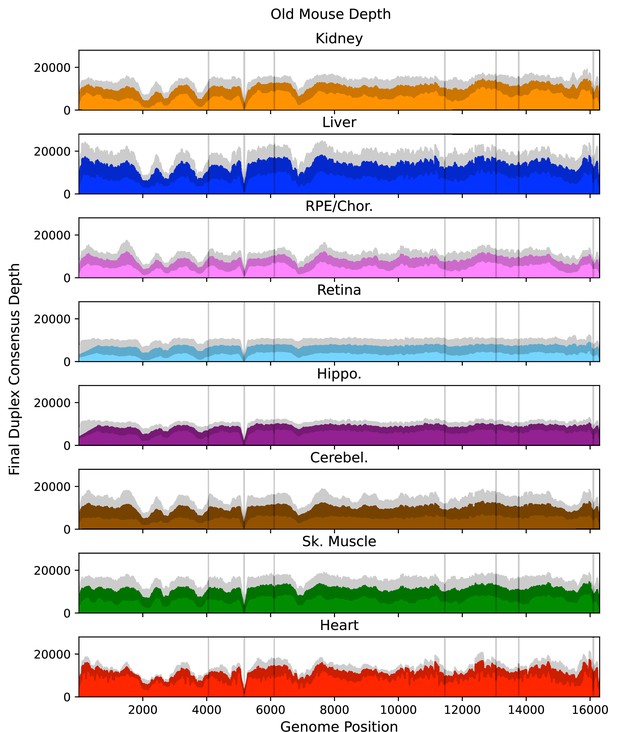
Mean post-consensus ‘duplex’ depth for old (26 months) tissues.
Variant occurring within the masked regions (vertical lines) or positions with less than a post-consusensus depth of 100× were ignored. Gray shading = standard deviation of the mean for N=6 mice.
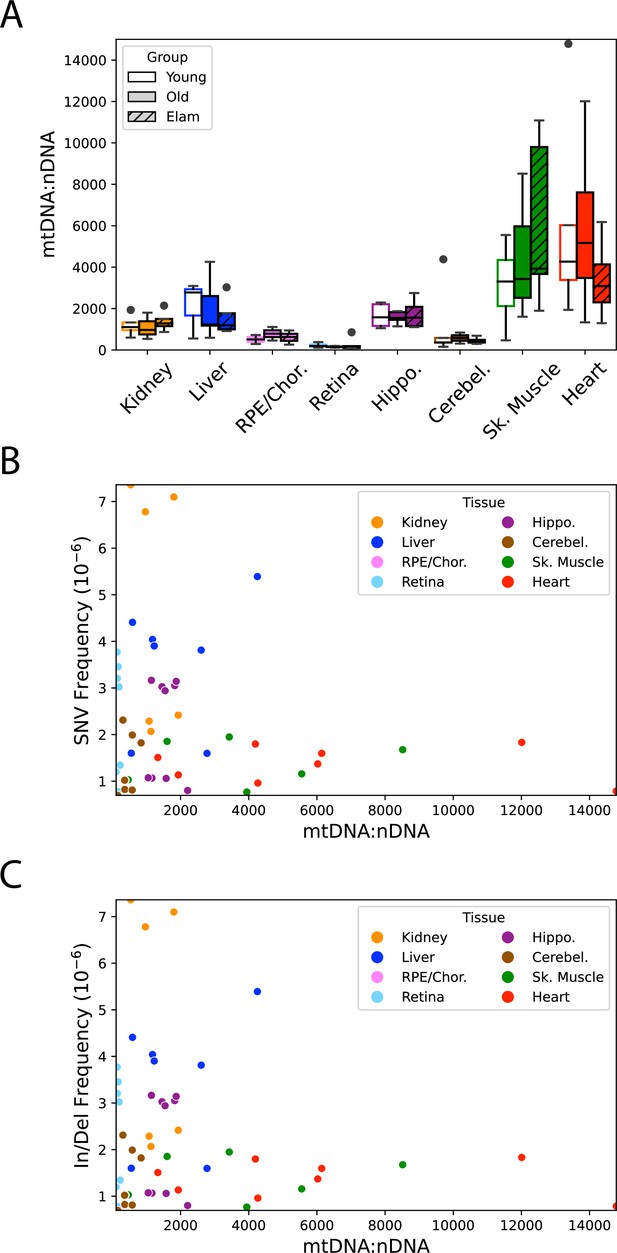
Mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) copy shows no correlation with age, intervention, or mutation frequency.
(A) mtDNA:nDNA ratio varies considerably between the eight tissue types, but does not change with age or treatment with elamipretide (ELAM). (B) Single-nucleotide variant (SNV) mutation frequency and (C) insertion/deletion (In/Del) mutation frequency do not correlate with mtDNA copy number, indicating that the tissue-specific differences in mtDNA frequency is not due to mtDNA content.
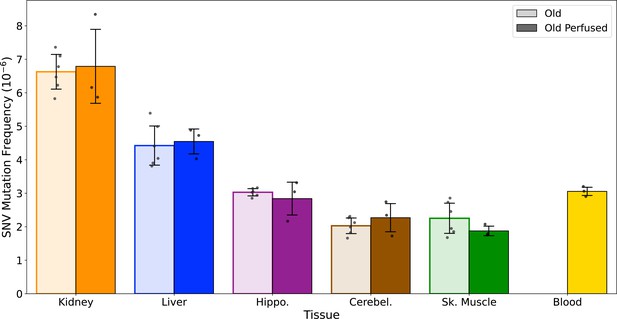
Blood does not significantly contribute to the differences in mutation frequency observed across tissues.
A separate cohort of NIA male aged mice (26 months, N=3) were transcardially perfused with 1× PBS prior to organ harvest. Collected tissues (kidney, liver, hippocampus, cerebellum, and skeletal muscle, and whole blood) were processed for duplex sequencing (Duplex-Seq) using the same protocol as used in the main aging cohorts. Significance tested with Welch's t-test. Error bars=standard deviation.
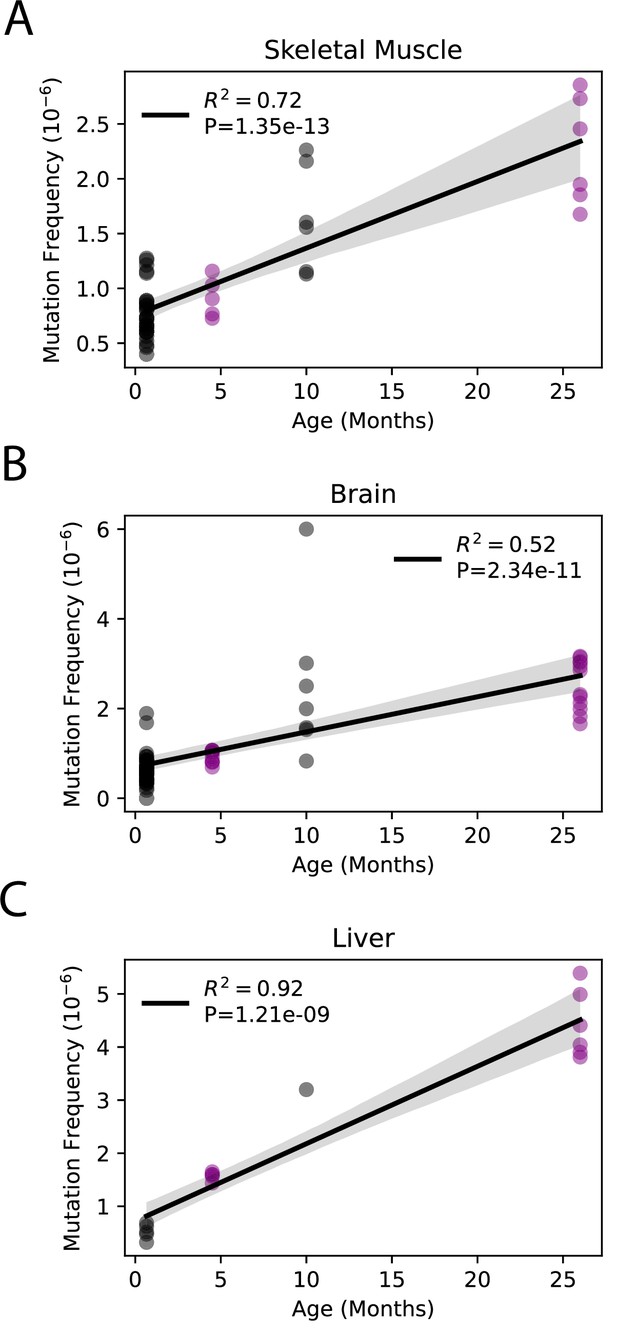
Somatic single-nucleotide variant (SNV) mutations increase linearly with age.
Linear regression of total SNV mutation frequency vs. age in (A) skeletal muscle, (B) brain, and (C) liver. Black = data from Arbeithuber et al.; purple = data from this study; shaded area = 95% confidence interval of linear regression.
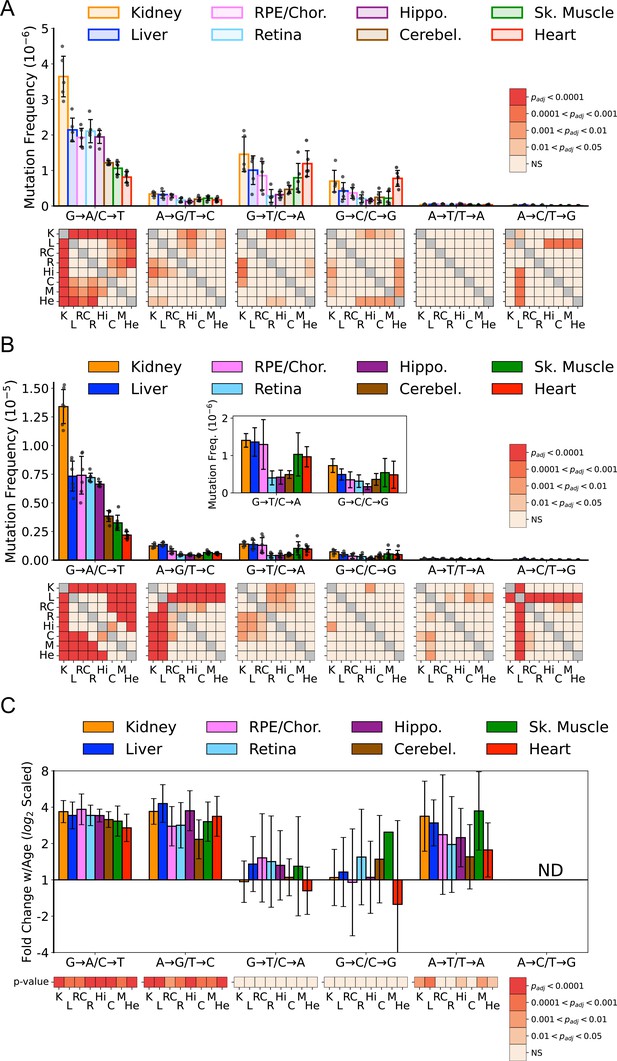
Mutation spectra of somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutations demonstrate tissue-specific distribution of mutation types.
(A) Single-nucleotide variant (SNV) frequency by mutation type for young (~5-months of age) tissues shows that replication/deamination-linked G→A/C→T mutations largely dictate overall SNV mutation burden and predominate in all young tissues except heart. Tissues of the central nervous system: eye retina, brain hippocampus, and brain cerebellum have the lowest frequencies of G→T/C→A and G→C/C→G transversions whereas they are highest in kidney and heart. Heatmaps show adjusted p-value from one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD for significant differences of SNV frequencies between young tissues within each mutation class. (B) SNV frequency by mutation type for old (26-month-old) tissues shows age-specific changes to mutation spectra. Heatmaps show one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD for significant differences of SNV frequencies between old tissues within each mutation class. (C) Fold-change of frequency from young to old age calculated for each tissue and spectra and shown with log2 scaling. Heatmap shows whether fold-change values of old relative to young mice are significantly different from fold-change 0 (no change). K=kidney; L=liver; RC = retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE)/choroid; R=retina; Hi = hippocampus; C=cerebellum; M=skeletal muscle; He = heart.
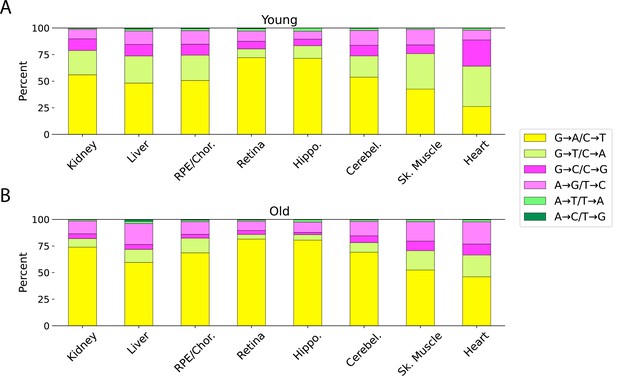
Relative proportion of different mutation types varies across tissues.
(A) Young. (B) Old.
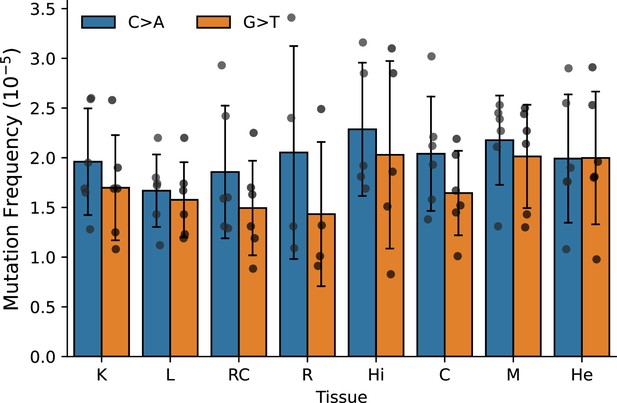
The single-strand consensus G→T and C→A frequency does not vary across tissues in old mice.
K=kidney; L=liver; RC = retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE)/choroid; R=retina; Hi = hippocampus; C=cerebellum; M=skeletal muscle; He = heart. Significance tested with Welch's t-test. Error bars = standard deviation.
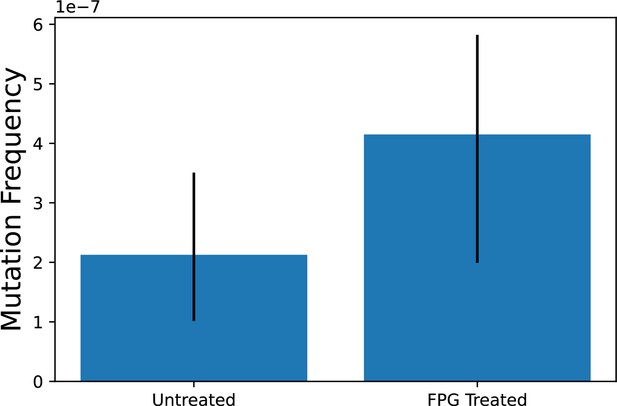
Treatment with FPG does not affect the G→T/C→T mutation frequency.
Skeletal muscle from old skeletal muscle was treated with FPG (New England Biolabs) post adapter ligation but before the first PCR, using the manufacturer’s instructions. Untreated with processed the same way, but without the addition of FPG. Error bars = 95% Wilson confidence interval.
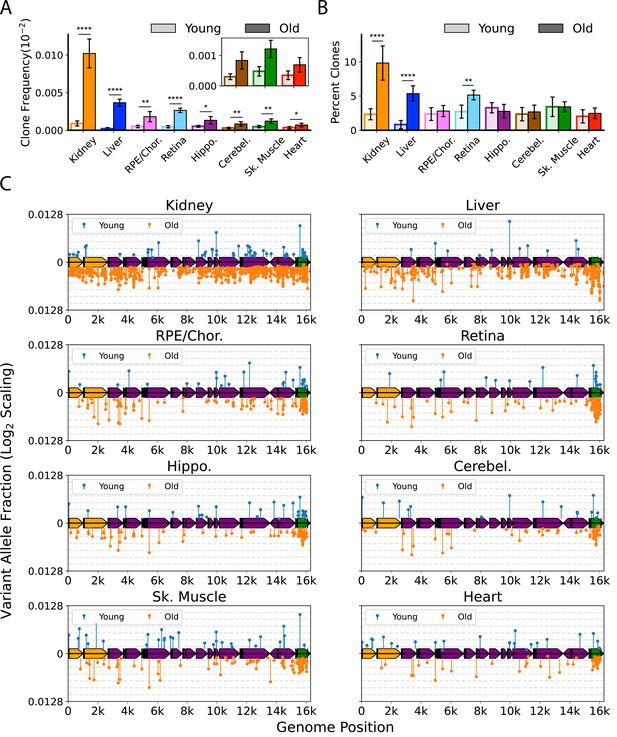
Clonal expansion of somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutations is tissue-specific.
(A) Frequency of mtDNA clones detected in each tissue shows an increase in detection of clones with age in all tissues. Note that y-axes are set for each tissue (N=5 for young; N=6 for old, error = ± standard deviation). (B) Percentage of total mutations found in heteroplasmic clones for each tissues shows that only kidney, liver, and retina have significant increases in relative ‘clonality’ with age. For (A) and (B), significance between young and old within a tissue was determined by Welch’s t-test. *0.01 < p < 0.05, **0.001 < p < 0.01, ***0.0001 < p < 0.001, ****p<0.0001; error bars = standard deviation of individual data points shown. (C) Lollipop plots show the mtDNA genomic location of clonal hetroplasmic mutations in young (top row, blue markers, n=5) and old (bottom row, orange markers, n=6) for each tissue type. Orange = rRNA; dark blue = tRNA; purple = protein coding; green = OriL or mitochondrial control region (mCR).
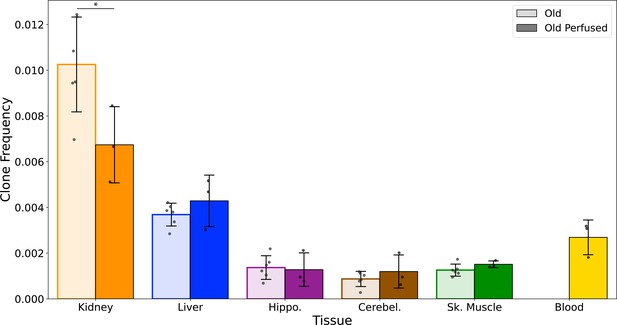
Mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) variant clones in blood are not a significant contributor to age-related to clonal expansions.
A separate cohort of NIA male aged mice (26 months, N=3) were transcardially perfused with 1× PBS prior to organ harvest. Collected tissues (kidney, liver, hippocampus, cerebellum, and skeletal muscle, and whole blood) were processed for duplex sequencing (Duplex-Seq) using the same protocol as used in the main aging cohorts. Error bars=standard deviation. Significance tested with Welch's t-test. *p < 0.05.
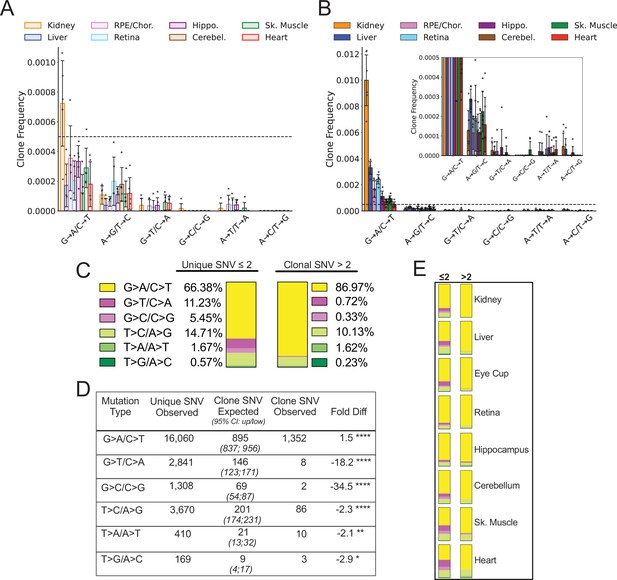
Spectral analysis of clonal somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutations suggests removal of reactive oxygen species (ROS)-linked mutations.
(A) Frequency of heteroplasmic clones in young mice shown as clone frequency for each mutation class and tissue. (B) Frequency of heteroplasmic clones in aged mice for each mutation class and tissue. Inset shows graph with adjusted axis to match young mice in (A) to better visualize lack of mutations in G→T/C→A and G→C/C→G mutation classes despite expansion of clonality with age. In both (A) and (B) the dotted line indicates frequency value of 0.005. (C) The combined distribution of mutation spectra for single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) for either unique mutations (detected two or less times) or clonal mutations (detected more than two times) for all aged tissues. (D) Table showing that, based on the mutation spectra of unique mutations, the observed number of SNV clones differs the number SNV clones expected if heteroplasmic clones arise randomly as a consequence of mutation burden. G→A/C→T and T→C/A→G clones are over-represented, while G→T/C→A and G→C/C→G clones are strongly under-represented based on Poisson sampling. ‘Fold Diff’ represents fold-change of observed clone values relative to expected. (E) Mutation spectra distributions for each aged tissue type mirrors the pattern of the combined aged samples with over/under representation of specific mutation types within observed clones. Mutation types are color coded as in (C).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Speadsheet containing the calculation of expected vs observed clone counts for Figure 5C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83395/elife-83395-fig5-data1-v2.xlsx
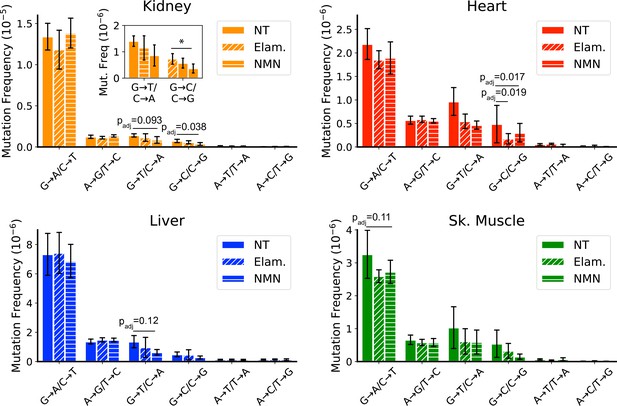
Late-life treatment with mitochondrially targeted interventions reduces somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutation burden and is consistent with a mechanism of active reactive oxygen species (ROS)-linked mutation removal.
Mutation spectra show that aged mice treated for 8 weeks with either elamipretide (Elam, diagonal striped bars) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN, horizontal striped bars) have decreased frequency of mutations compared to no-treated (NT) controls specifically in mutation types linked to oxidative damage, G→T/C→A and G→C/C→G, specifically for (A) kidney and (B) heart and trending for (C) liver. (D) Muscle trends lower for Elam-treated mice in G→A/C→T mutations. Error bars = ± standard deviation. Statistics calculated by one-way ANOVA for each mutation class within a tissue and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test compared to the untreated aged control group, significance=padj <0.05 and trend=padj <0.15.
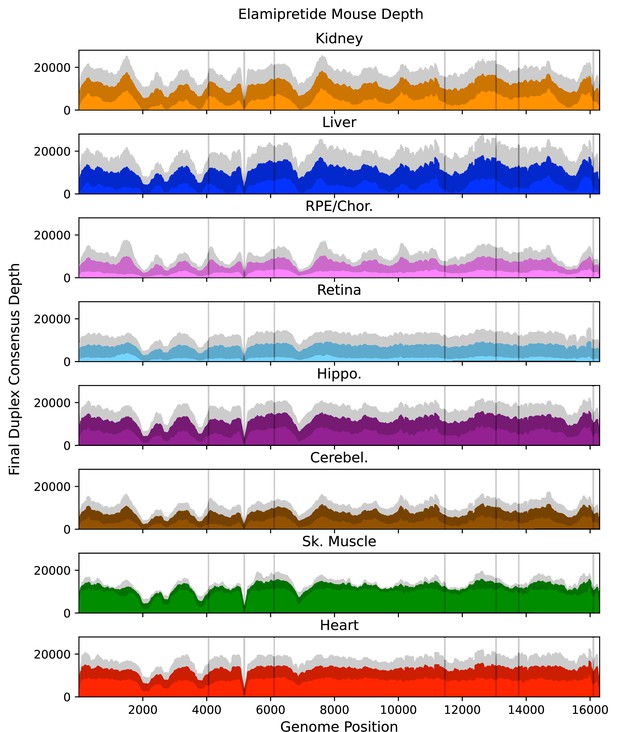
Mean post-consensus ‘duplex’ depth for aged (26 months) elamipretide-treated tissues.
Variant occurring within the masked regions (vertical lines) or positions with less than a post-consusensus depth of 100× were ignored. Gray shading = standard deviation of the mean for N=5 mice.
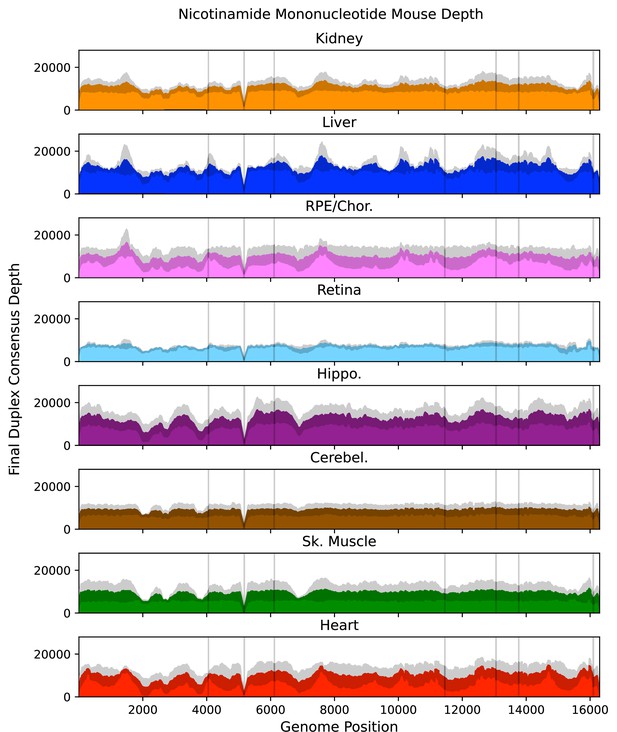
Mean post-consensus ‘duplex’ depth for aged (26 months) nicotinamide mononucleotide-treated tissues.
Variant occurring within the masked regions (vertical lines) or positions with less than a post-consusensus depth of 100× were ignored. Gray shading = standard deviation of the mean for N=3 mice.
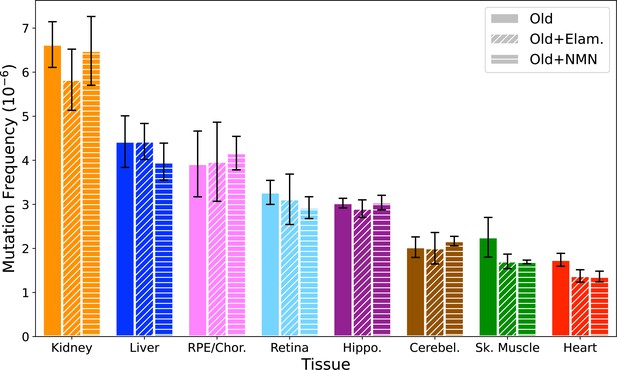
Elamipretide (Elam) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) do not affect the overall mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutation frequency.
Overall point mutation frequency for Old (NT), Old+Elam, and Old+NMN separated by tissue. Dunnett’s test with untreated old as the control was used to test for significance. N=6 for Old, N=5 for Elam, and N=3 for NMN. Error bars = standard deviation.
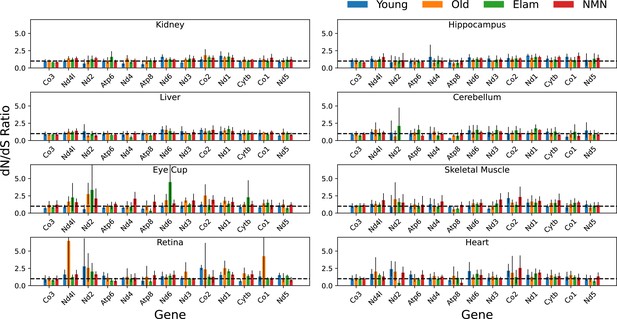
Per gene dN/dS ratio shows no apparent selection across age, tissues, and interventions.
Variants for each sample were separated by protein coding gene and the dN/dS ratio calculated using the dNdScv R package using the median depth for each gene as a covariate. dN/dS ratios from the same tissue and age or treatment group were averaged. N=5 for Young, N=6 for Old (NT), N=5 for Elam, and N=3 for NMN. Error bars = standard deviation.
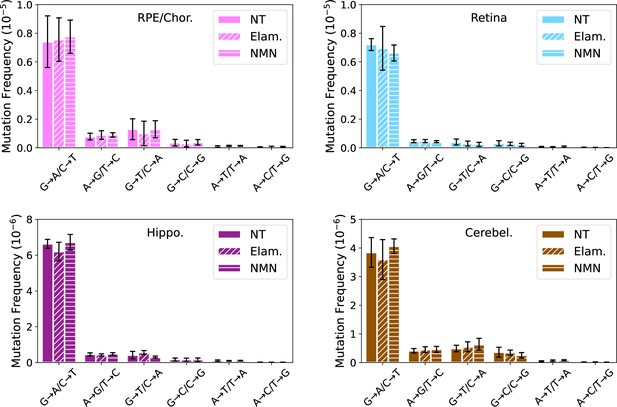
Late-life treatment with mitochondrially targeted interventions does not reduce somatic mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) mutation burden in retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE)/choroid (pink), retina (cyan), hippocampus (purple), or cerebellum (brown).
One-way ANOVA for each mutation class within tissue with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test compared to untreated aged control group was performed with no significant differences or trends detected. N=6 for no-treatment (NT), N=5 for Elam, and N=3 for NMN.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
File containing Supplementary Tables 1-5.
Table 1. Sequence of the 96 defined unique molecular identifier (UMI) duplex sequencing adapters. Sequence is provided in 5’→3’ orientation. Complementary UMI sequences are highlighted in red. Table 2. Sequence of the mouse-specific capture probes against the mtDNA. Sequence is provided 5'→3’ orientation. Biotin moiety is denoted by ‘/5Biosg/’. Table 3. Summary of duplex sequencing data. Summary of the samples sequenced, including assay performance metrics, including mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) enrichment specificity, family size, and consensus metrics, bases sequenced, sequencing depth, mutation counts, and mutation frequencies. Table 4. Mitochondrial genome (mtDNA) to nuclear genome (nDNA) copy number ratio data. Summary of the samples used to determine mtDNA and nDNA copy numbers. ND = not determined. Table 5. Genome coordinates of regions masked in the analysis. Coordinates are 1-indexed and columns are in .bed format order.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83395/elife-83395-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of all detected mutations.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83395/elife-83395-supp2-v2.zip
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83395/elife-83395-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf





