A frameshift in Yersinia pestis rcsD alters canonical Rcs signalling to preserve flea-mammal plague transmission cycles
Figures
rcsDpe negatively regulates biofilm formation, while rcsDpstb positively regulates biofilm formation in Y. pestis.
(A) Schematic representation of the rcsD frameshift mutation that occurred during speciation of Y. pestis from its ancestor Y. pseudotuberculosis. rcsDpstb: rcsD from Y. pseudotuberculosis; rcsDpe: rcsD from Y. pestis; △rcsB, rcsB deletion; RcsDN-term: N-terminal fragment of RcsD; RcsD-Hpt: C-terminal HPt domain of RcsD. Crystal violet (CV) binding assay (B) and Congo red (CR) pigmentation assay (C) using Y. pestis KIM6+ (WT), an N-terminal deletion mutant (△rcsDN-term), and an rcsDpstb substitution strain (rcsDpe::rcsDpstb) and their derivatives that carry plasmids harbouring rcsDpe (prcsDpe) or rcsDpstb (prcsDpstb). (D) Schematic representation of the rcsD mutations constructed in this study. CV binding assay (E) and CR pigmentation assay (F) using Y. pestis KIM6+ (WT) and its derivative strains harbouring plasmids expressing different truncations of RcsD. CV assays in panels B and E were performed together. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Expression of RcsD-Hpt is initiated by an uncommon AUU start codon and negatively regulates biofilm formation in Y. pestis.
(A) Schematic representation of mutations introduced to the putative RBS and start codon of RcsD-Hpt. ATT–312→GGT or ATT–312→ATG indicate that the predicted ATT start codon was mutated to GGT or ATG, respectively. RBS* indicates that the putative RBS of RcsD-Hpt was mutated. Congo red (CR) pigmentation assay (B) and crystal violet (CV) binding assay (C) using Y. pestis KIM6+ (WT) and its derivative strains. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test, comparing each construct with WT. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. (D) Expression of RcsD in Y. pestis and its derivatives were detected by western blot analysis using an anti-Flag antibody (see Figure 2—source data 1 details). The 3xFlag and His6 epitope tags (FH) encoding sequences were fused to the C-terminus of rcsDpe and rcsDpstb. (E) Structure of RcsD-Hpt (103 residues) predicted by AlphaFold2. Conserved His50 is located at the a3 helix of RcsD-Hpt. (F) Structure comparison of RcsD-Hpt (103 residues) by AlphaFold2 (yellow) and HptB of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 (PDB 7C1l, cyan).
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw source data for Figure 2D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-fig2-data1-v2.zip
Characterization of proteins encoded by rcsDpe region, related to Figure 2.
(A) Schematic representation of mutations introduced to the putative but non-functional start codons. (B) Crystal violet (CV) biofilm assay using wild type (WT) and ΔrcsD strains complemented by the expression of putative rcsD-hpt genes. (C) CV biofilm using ΔrcsD strains complemented by the expression of rcsD-hpt with mutated start codons or the mutated conserved phosphorylation site. (D) Congo red (CR) pigmentation assay of ectopic expression of the 103-residue HPt domain with an AUU start codon or GGU codon, using a modified pBAD vector (without ATG codon) in the Y. pestis KIM6+ WT strain, or rcsD deletion mutant. (E and (F) Expression of RcsD in Y. pestis and its derivatives were detected by western blot analysis using an anti-Flag antibody. The 3xFlag tags were inserted to the C-terminus of RcsDpe and RcsDpstb. rcsDpe-flag* (ATT–312→GGT): the predicted start codon AUU was mutated to GGT (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1 for details). rcsDpe-flag** (inserting stop codon): a stop codon was introduced upstream of the frameshift site (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 2 for details). (G) Quantification of readthrough efficiency using a LacZ reporter assay. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 1E.
The original file of the full raw unedited blots and the uncropped blot with the relevant bands clearly labelled as Figure 2—figure supplement 1E.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 2
Raw source data for Figure 2—figure supplement 1F.
The original file of the full raw unedited blots and the uncropped blot with the relevant bands clearly labelled as Figure 2—figure supplement 1F.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-fig2-figsupp1-data2-v2.zip
The conserved His residue, H844, is important for the function of RcsD and RcsD-Hpt.
(A) Crystal violet (CV) assay of Y. pestis expressing rcsD and its H844A-relevant derivatives. CV assays in panel C of Figure 2—figure supplement 1 and panel A of Figure 2—figure supplement 2 were performed together. (B) CV assay of Y. pestis expressed with rcsD and its H844A-relevant derivatives. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
The frameshift mutation in rcsD alters the Rcs signalling pathway in Y. pestis.
Congo red (CR) pigmentation assay (A and C) and crystal violet (CV) biofilm assay (B and D) the derivatives of Y. pestis KIM6+ (wild type [WT]) and the rcsDpstb substitution strain. prcsF, plasmid expressing rcsF; prcsF (C125S), plasmid expressing rcsF with cysteine (C) to serine (S) substitution at position 125; pigaA, plasmid expressing igaA; pigaA (C413S), plasmid expressing igaA with cysteine (C) to serine (S) substitution at position 413. (E) CV binding assay using WT and a rcsC deletion mutant expressing RcsD-Hpt (rcsD-hpt). CR pigmentation assay (F and G) and CV biofilm assay (H) using two Y. pestis rcsC deletion mutants expressing different rcsC variants. CV assays in panels B, D, and H were performed together. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
The frameshift mutation in rcsD increases the phosphorylation of RcsB and represses the expression of HmsT.
(A) Crystal violet (CV) biofilm assays using a wild type (WT) (white), ΔrcsB (grey), or rcsB (D56Q) (black) mutant strain, each harbouring pUC19 vectors expressing rcsDpe or rcsDpstb. (B) Phosphorylation analysis of RcsB in the Y. pestis KIM6+ strain (WT) harbouring an RcsB expression plasmid (prcsB), a plasmid expressing RcsB fused with a 3xflag tag (prcsB-Flag), or a modified prcsB-Flag expression plasmid in which the conserved phosphorylation site Asp50 was mutated to Gln, and the Y. pestis rcsDpstb substitution strain harbouring the prcsB-Flag expression plasmid (see Figure 4—source data 1 for details). (C) Quantification of HmsT expression using a β-galactosidase assay. The lacZ reporter gene was fused with the hmsT promoter in plasmid pGD926. (D) Expression of HmsT was analysed by western blotting using an anti-Flag antibody (see Figure 4—source data 2 for details). Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with three replicates. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-test. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw source data for Figure 4B.
The original file of the full raw unedited blots and the uncropped blot with the relevant bands clearly labelled as Figure 4B.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-fig4-data1-v2.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Raw source data for Figure 4D.
The original file of the full raw unedited blots and the uncropped blot with the relevant bands clearly labelled as Figure 4D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-fig4-data2-v2.zip
The frameshift mutation in rcsD stabilizes the pgm locus in Y. pestis.
(A) Bacterial burdens in fleas infected with Y. pestis wild type (WT), rcsDpe::rcsDpstb and rcsDN-term strains after 0, 7, and 14 days of infection. (B) Cumulative blockage of fleas after 4 weeks of infection with Y. pestis WT, rcsDpe::rcsDpstb and ΔrcsDN-term strains. Two independent infection experiments are shown. (C) Percent of pgm locus loss in fleas infected with Y. pestis WT and rcsDpe::rcsDpstb after 4 weeks of infection. Ten infected fleas were used for this assay. Statistical analysis was performed using a Fisher’s exact test. (D) Percent of pgm locus loss in vitro with Y. pestis KIM6+ and mutants. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons were performed for statistical analysis of mutants with WT strain KIM6+. Error bars represent ± SD from three independent experiments with six replicates. ns, not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Genome-wide identification of genes regulated by the Rcs phosphorelay system in Y. pestis.
(A–C) Survival of C57BL/6 mice infected with Y. pestis Microtus strain 201 and its derivatives using an infectious dose of 40, 160, and 800 colony-forming units (CFU). (D) Venn diagram of upregulated and downregulated genes in Y. pestis strains growing at temperatures (26°C or 37°C). (E) qPCR analysis of hmsT and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) identified by RNA-seq. The screening threshold for DEGs was defined as |logFC|≥1, and p≤0.05. Error bars indicate SD from at least three samples. (F) Heatmaps showing the differential expression of genes identified through clusters of orthologous group (COG) analysis.
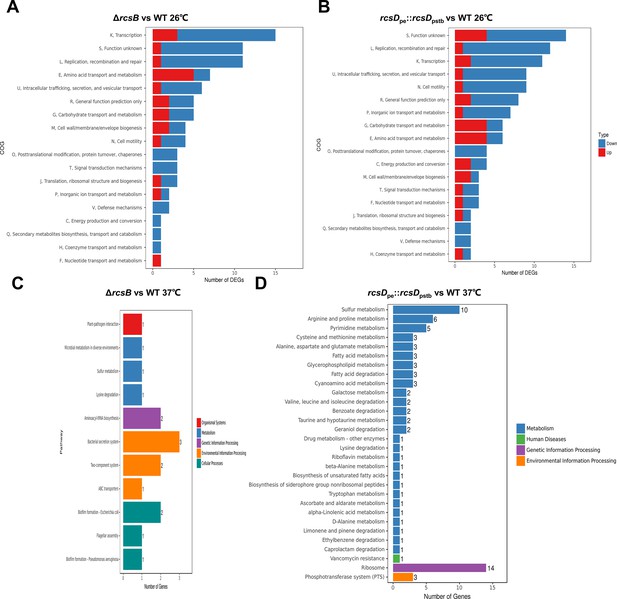
RNA-seq analysis of genes regulated by Rcs system, related to Figure 6.
(A–D) Clusters of orthologous groups (COG) analysis of RNA-seq gene expression data comparing the ΔrcsB strain and wild type (WT) (A), and rcsDpe::rcsDpstb with WT (B) at 26°C; ΔrcsB with WT (C), and rcsDpe::rcsDpstb with WT (D) at 37°C.
Genetic changes in Rcs genes during speciation of Y. pestis.
Acquisition events are indicated by green lightning symbols, loss of genetic material by a red cross, and mutation by blue circles. All comparisons shown are relative to Y. pseudotuberculosis. Increasingly darker shades of grey represent Y. pseudotuberculosis, and ancient strains from the Iron Age and the LNBA lineage, respectively. Increasingly darker shades of green represent branches one to four as annotated in the figure. Rcs-related genes and ISompC were considered as intact (dark blue), mutated (light blue), or absent (white). *: not analyzed. 1, present in all Y. pestis except branch 0 strain 0.PE4b; 2, rcsDN-term and rcsDC-term were located in a different genome site in the Nairobi (1.ANT), Angola (0.PE3), and Algeria3 (ORI) strains due to chromosome rearrangement; 3, indels are present in rcsDN-term in some strains I-3086 (0.PE4m) and A-1825 (2.MED1). MRCA, the most recent common ancestor. Figure 7 and nomenclature are adapted from Figure 1 of Demeure et al., 2019.
Predicted model of Rcs signal transduction and phosphoryl transfer in Y. pseudotuberculosis and Y. pestis.
In Y. pseudotuberculosis, full-length RcsD plays a dominant role while the lowly expressed RcsD-Hpt might play a moonlighting function. When Rcs is in ‘off’ state, RcsF is not activated leading to release from repression of IgaA, which interacts with RcsD. In this situation, RcsB, which might receive the phosphoryl group from another source such acetyl phosphate, is dephosphorylated by intact RcsD, which is then dephosphorylated by RcsC. When Rcs is in an ‘on’ state, activated RcsF interacts with IgaA, releasing the interaction of RcsD and IgaA. In this situation, RcsC transfers the phosphoryl group to RcsD, and then to RcsB, leading to an activated Rcs system. In Y. pestis, RcsD-Hpt might play a dominant role. Rcs system might be only slightly regulated by IgaA and RcsF pathway. In this situation, RcsC transfers the phosphoryl group to RcsD-Hpt, and then to RcsB, leading to an activated Rcs system. The arrows indicate direction of flow of phosphate and weight of the arrows correlates with the flow of amount of phosphate. Weight of the red inhibitor lines correlates with magnitude of inhibition. Phosphate is denoted as small circles with the letter P.
Evolutionary model for how genetic changes in the Rcs system fine-tunes biofilm formation to preserve virulence of flea bite-transmitted Y. pestis.
Functional rcsA and intact rcsD are encoded by ancestral Y. pseudotuberculosis. Biofilm formation was strongly repressed by the Rcs system due to the presence of RcsA. Y. pseudotuberculosis was transmitted between animals and the environment mainly by the faecal-oral route. Acquisition of pPla/pPCP1 and pFra/pMT1 plasmids led to the speciation of ancient Y. pestis, which was transmitted mainly between humans and occasionally by flea bites through early phase transmission. Once rcsA was pseudogenized, biofilm repression by rcsA was abolished, and biofilm blockage-mediated flea-borne transmission was established. rcsD subsequently underwent a frameshift mutation in most modern strains (bottom panel), which reduced biofilm formation leading to lower rates of spontaneous loss of the pgm locus compared to intermediate ancestral strains. Solid arrows indicate direction of flow of phosphate in our tested conditions, while the dashed arrows indicate the possible direction of flow of phosphate which might have existed in other conditions. Weight of the red inhibitor lines correlates with magnitude of inhibition. Phosphates are denoted as small green circles associated with the red arrows. The pPla/pPCP1 and pYmt/pFra refer to the two Y. pestis-specific plasmids that encode Pla and Ymt, respectively. Plague bacteria transmission between/and to rodents, humans, fleas, and the external environment is denoted by arrows in the lower section of each panel. The arrow weight indicates ecological importance. OM: outer membrane; PG: peptidoglycan; IM: inner membrane; H: histidine; D: aspartic acid; EPS: exopolysaccharides.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Strains used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp1-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 2
Plasmids used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp2-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 3
Primers and oligos used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp3-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 4
Differential expression of Y. pestis genes in Y. pestis mutant strains growing at temperatures (26°C or 37°C).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Mutations in Y. pestis during evolution involved in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp5-v2.docx
-
Supplementary file 6
Putative SD and start codon sites in rcsD in Enterobacteriaceae.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-supp6-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/83946/elife-83946-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf





