Peptides that Mimic RS repeats modulate phase separation of SRSF1, revealing a reliance on combined stacking and electrostatic interactions
Figures
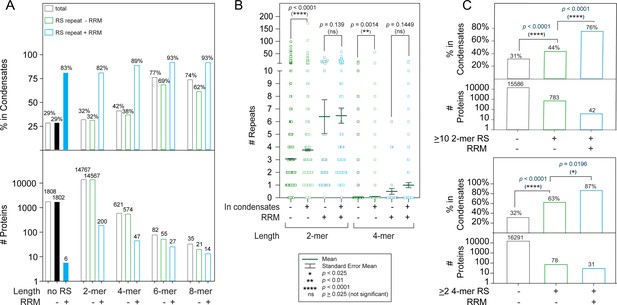
A combination of RS repeats and RRM domains is highly correlated with appearance in condensates.
(A) Increased RS repeat length leads to an increased likelihood of appearance in condensates. Percentage of proteins possessing indicated properties that appear in one of three major phase separation databases. The Pearson’s p-value (0.02) for the correlation between RS length and phase separation likelihood is shown in Supplementary file 1. Correlation between RS and RRM occurrence was analyzed by Fisher’s exact test (Supplementary file 3). (B) Correlation between number of 2-mer RS and 4-mer RS repeats with appearance in condensates. Proteins found in condensates are more likely to have a greater number of RS dipeptide and tetra-peptide repeats in the absence of RRM domains (-). The p-values presented were obtained using the Mann-Whitney test, which is suitable for non-normal distributions with different sample sizes (Widen et al., 2020). Bonferroni’s adjustment was applied to adjust the significance level to p-value = 0.025. (C) Proteins with >10 2 mer RS repeats or >2 4 mer RS repeats are more likely to phase separate, particularly when RRM domains are present. p-values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test (Supplementary file 4).
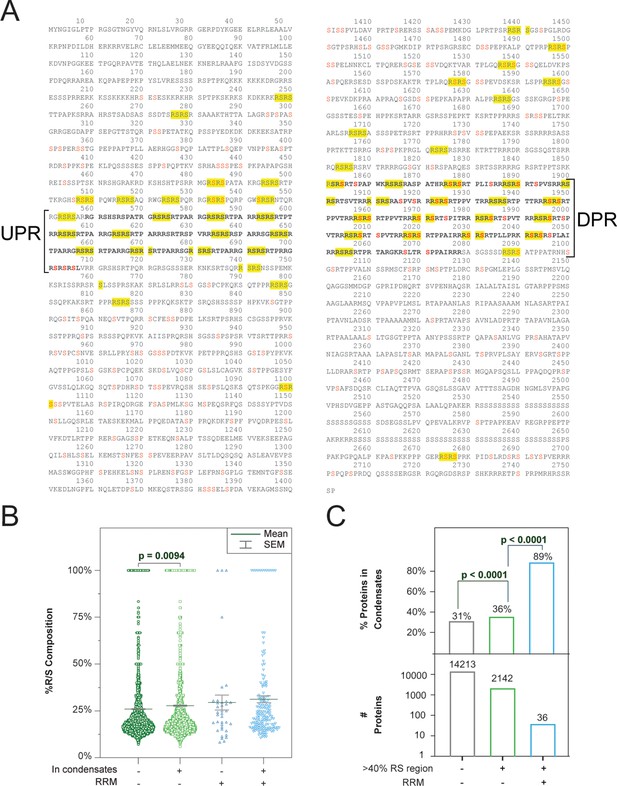
Increased repeat number and R/S percent composition correlate with increased phase separation.
(A) Amino-acid sequence of the protein SRRM2 with 56 4-mer RS repeats highlighted in yellow. Red serines can be phosphorylated according to the Uniprot database. Deletion of the undeca-repeat (UPR) and dodeca-repeat (DPR) regions results in dissociation of nuclear speckles (Xu et al., 2022). (B) Effect of percent R/S composition on the likelihood of phase separation. Each point indicates the 20-amino acid sequence in the protein that is densest in R/S. Percentages were calculated using LCD-Composer (Cascarina et al., 2021). Minimum density was set to 5%. p-values were obtained using the Mann-Whitney test. (C) Proteins with a 20-amino acid sequence of ≥40% R/S composition are more likely to be found in condensates, particularly when RRM domains are present. p-values were calculated using Fisher’s exact test.
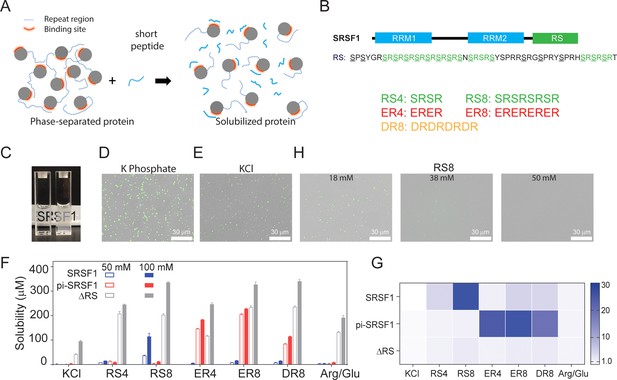
SRSF1 phase separation can be reduced using peptides that best mimic its RS repeats in their respective phosphorylation states.
(A) Schematic illustration of solubilizing phase-separating proteins using short peptides. Short peptides compete with RS repetitive regions, disrupting phase separation. (B) Domain architecture of SRSF1. The underlined serine residues in the SRSF1 RS domain can be phosphorylated, and the phosphorylated RS can be mimicked by ER and DR repeats. Short peptide co-solutes used in this study are shown below. (C) Phase separation of SRSF1. The left cuvette is SRSF1 solubilized in the RS8 peptide, and the right cuvette is SRSF1 in 140 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.4, 10 mM NaCl. The fluorescence image of 288 nM unphosphorylated SRSF1 in phosphate buffer (D), KCl buffer (E). SRSF1 is labeled with Alexa488 at N220C. (F) SRSF1 solubility using 50 mM or 100 mM of peptide as indicated. (G) Ratio of solubility in peptides to solubility in 100 mM Arg/Glu as determined in panel D. (H) The RS8 peptide can reduce phase-separation droplets of SRSF1.
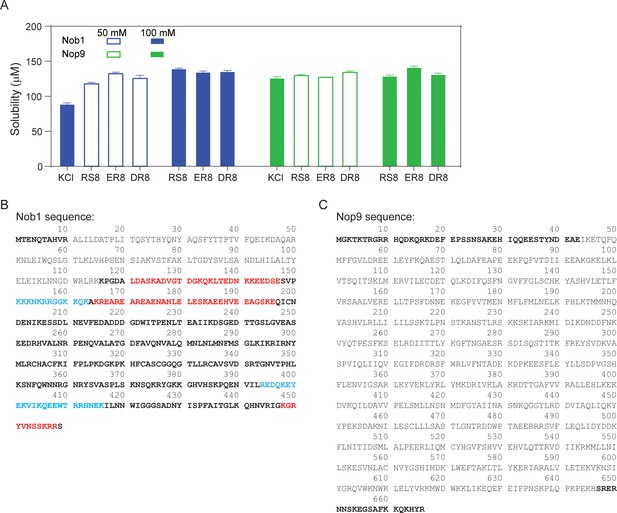
Repetitive peptides solubilize other proteins containing similar repetitive regions.
(A) Solubilizing effects of 8-mer Arg-Ser (RS8), Glu-Arg (ER8), and Asp-Arg (DR8) were tested on Nob1 (blue bars) and Nop9 (green bars) at peptide concentrations of 50 mM (open bars) and 100 mM (filled bars). A buffer of 100 mM KCl was used as a control. (B) Nob1 protein sequence. (C) Nop9 protein sequence. Unstructured regions are shown in bold fonts. The basic and acidic-basic residue regions are in cyan and red, respectively.
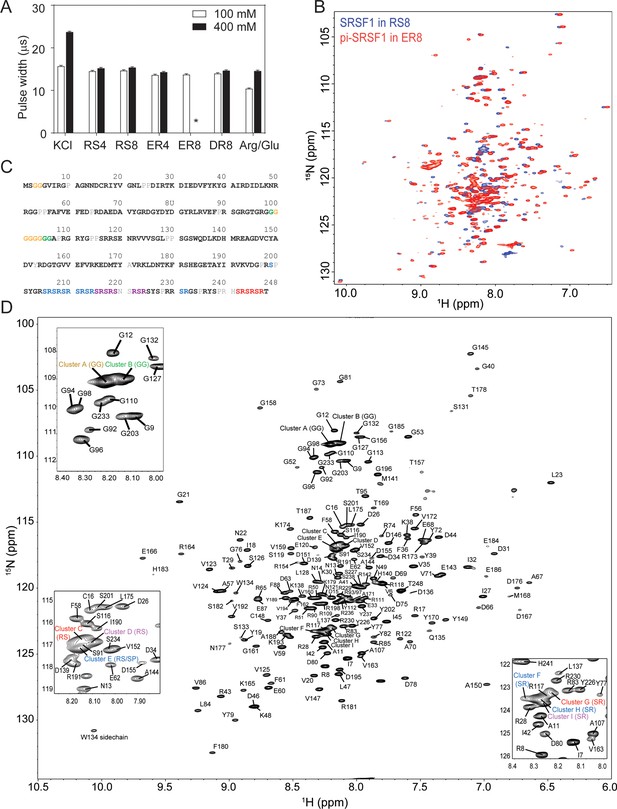
Short peptides are compatible with NMR experiments.
(A) NMR 90 degree pulse width. ER8 is insoluble at 400 mM and therefore its pulse width could not be determined, as indicated by *. (B) 15N-TROSY-HSQC overlay of SRSF1 in 100 mM RS8 and phosphorylated SRSF1 (pi-SRSF1) in 100 mM ER8. (C) Assigned residues in the SRSF1 protein sequence. Black bold fonts indicate non-overlapping residues. Gray fonts indicate unassigned residues. Color fonts indicate amino acids assigned to clusters. (D) Assignment of the SRSF1 amide groups.
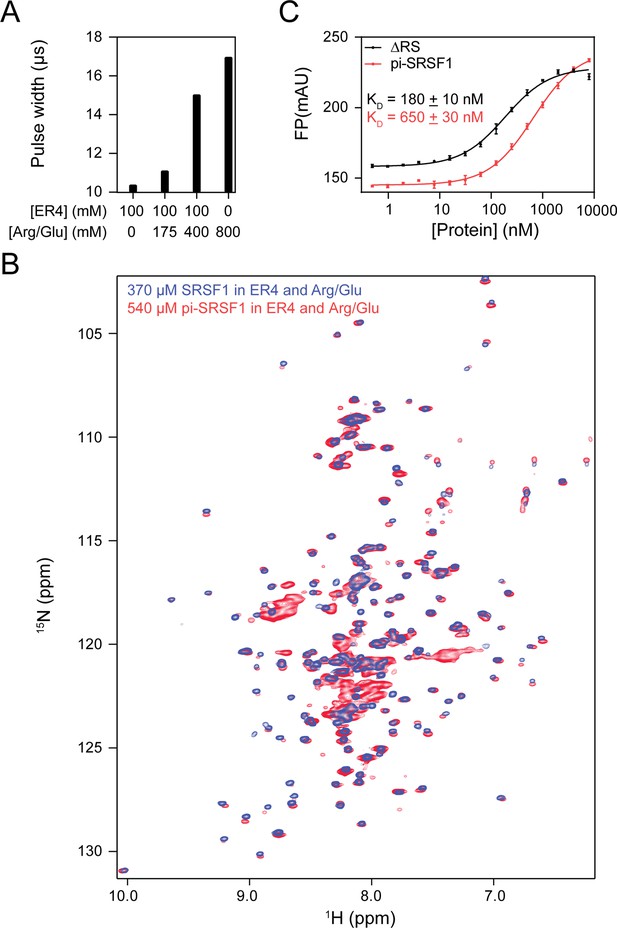
The buffer 100 mM ER4, 400 mM Arg/Glu, pH 6.4 was effective at solubilizing and optimizing spectral quality for both unphosphorylated and hyperphosphorylated SRSF1 at high enough concentrations for NMR assignment.
(A) Pulse width of various concentrations of ER4 and Arg/Glu. (B) 15N-TROSY-HSQC overlay of 370 µM SRSF1 (blue) and 540 µM phosphorylated SRSF1 (pi-SRSF1, red) in this buffer. (C) The buffer 100 mM ER4, 400 mM Arg/Glu, pH 6.4 did not abolish ligand binding. Fluorescence polarization assays for binding of SRSF1 constructs with a 5’ Alexa488-tagged RNA probe (UCAGAGGA). Both binding assays were performed in 100 mM ER4, 400 mM Arg/Glu, pH 6.5. Error bars represent SEM of three technical replicates.
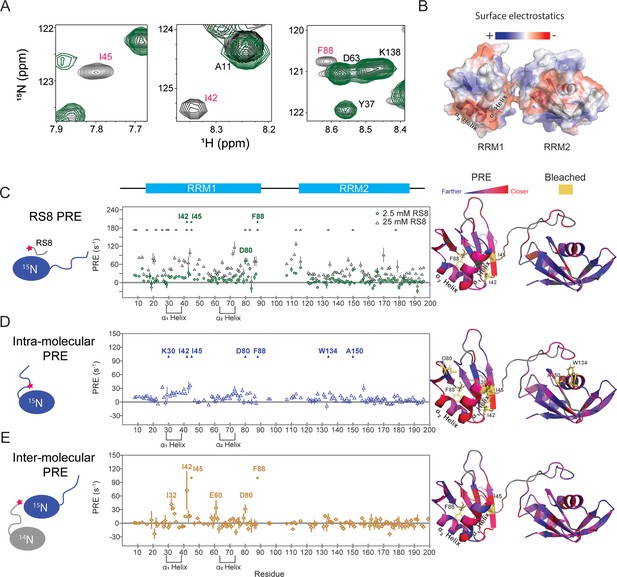
SRSF1 residues involved in interactions with the RS8 peptide are similar to those found in intra-, and homotypic inter-molecular interactions with the RS region.
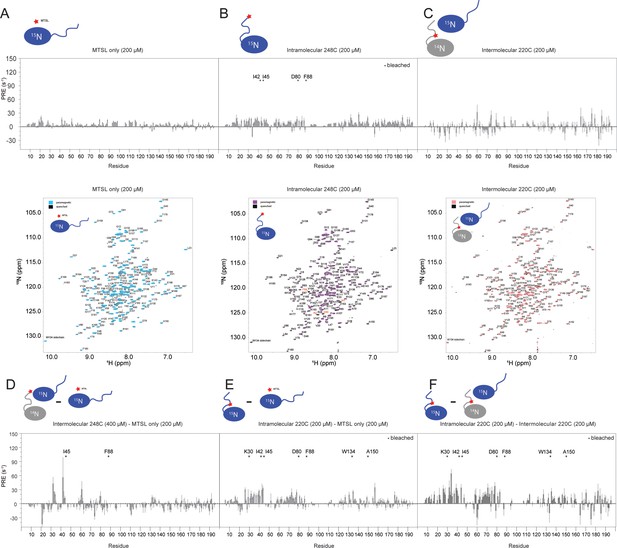
(A) 15N-TROSY-HSQC overlay of SRSF1 in 50 mM diamagnetic (gray) and 2.5 mM paramagnetic RS8 (green). The intensities of residues close to the probe become diminished. Bleached residues (indicated by red type) came in such close contact with RS8 that their intensities were diminished before the first observation time point (additional information in the methods section). The full spectra are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (B) Electrostatic surface of SRSF1 RRM1 and RRM2. The α1 helix on RRM1 has a large negatively charged surface area, and RRM1 possesses overall more negative charge. (C) PRE values induced by 2.5 or 25 mM paramagnetic RS8. (D) Intra-molecular PRE produced by the MTSL-labeled RS region (N220C). (E) Inter-molecular PRE produced by the MTSL-labeled NMR-inactive SRSF1 (T248C). The filled symbols indicate bleached residues. Yellow sticks in the molecular graphics on the right indicate bleached residues. Gray indicates residues whose PRE values are unavailable due to peak overlap or an inability to assign them. PyMOL molecular graphics were prepared using Xplor-NIH (see Materials and methods section for more information).
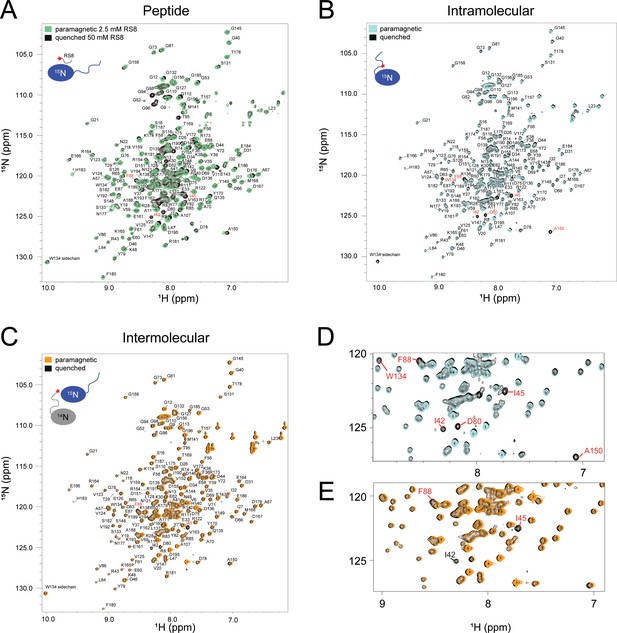
SRSF1 residues involved in interactions with the RS8 peptide are similar to those found in intra-, and homotypic inter-molecular interactions with the RS region.
15N-TROSY-HSQC overlay of samples used in (A) Peptide-SRSF1, (B) Intramolecular, and (C) Intermolecular PRE experiments. Spectra in which the paramagnetic center was active are color coded, and spectra in which the paramagnetic center was quenched with ascorbic acid are in black. Residues marked in red came in close enough contact to paramagnetic centers that PRE could not be quantified. We refer to these residues as bleached. (D) Expanded view of a section of interest from the intermolecular PRE spectrum. (E) Expanded view of a section of interest in the intermolecular PRE spectrum.
SRSF1 residues involved in interactions with the RS8 peptide are similar to those found in intra-, and homotypic inter-molecular interactions with the RS region.
PRE of MTSL alone (A), an intramolecular PRE experiment with the MTSL tag on the very C-terminal end of the protein (B), and an intermolecular PRE experiment replicating the conditions of the intermolecular interactions experiment (C). When these spectra are subtracted from the experiments displayed in the main text (D–F) the trend is still similar.
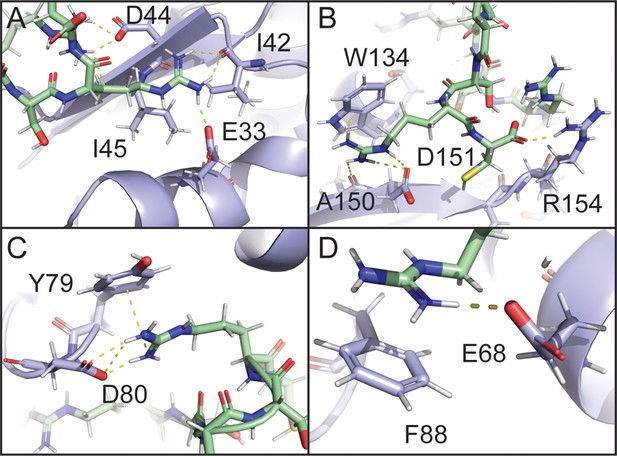
Electrostatic and cation-pi interactions are responsible for intermolecular interactions.
Molecular dynamics simulation of SRSF1 with four RS8 peptides.
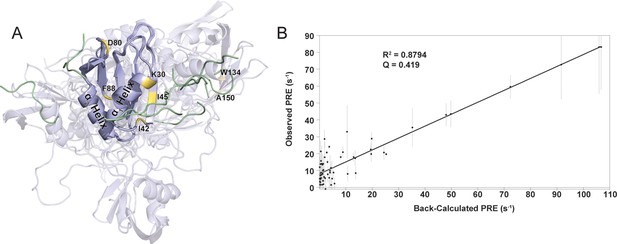
Fitting of MD simulation structure to PRE values.
(A) Sample 10-membered ensemble generated by Xplor-NIH. RRM1 (residues 16–90) is held in place while the N-terminus and linker are allowed full flexibility (shown as transparent cartoons). RRM2 residues (residues 121–196) are allowed to move as a group (shown as transparent cartoons). Peptides are shown in green cartoons. (B) Sample correlation plot between observed PRE values and PRE values back calculated from the structural ensemble. All residues with for which PRE is obtained are included. Of the structures generated, the top 25% had Pearson’s correlation coefficients between 0.916 and 0.941 (R2=0.839–0.885). These were used to create an MD simulation starting structure in which a single peptide was bound to each hotspot.
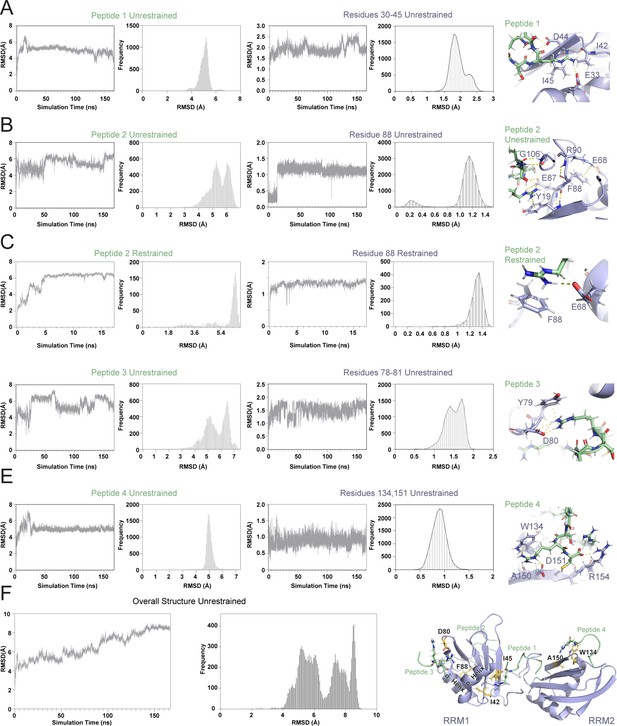
MD simulation trajectories of SRSF1 ΔRS interacting with four RS8 peptides.
Root mean standard deviation between the simulation starting structure and the structure at a given simulation time (A–E) Interactions between peptides (left) and the SRSF1 ΔRS residues with which they interact (right). Without restraints, peptides interacting with loop regions (B, D) showed shorter-lived equilibria. In a separate simulation, a restraint was placed on peptide 2 (C) to maintain a single structure for observation. (F) RMSD of entire structure over the MD simulation period.
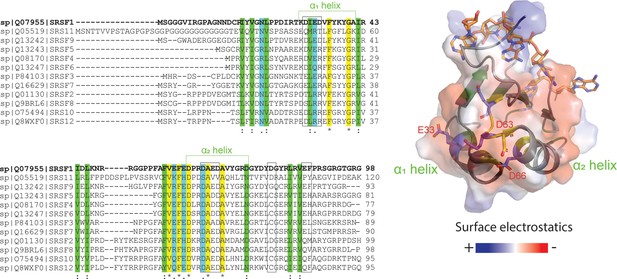
RRM1 residues responsible for SRSF1 phase separation are conserved throughout the SR protein family.
ClustalX alignment of RRM1 domains of the SR protein family, where yellow indicates identical amino acids, green and blue indicate conserved residues. Black boxes indicate PRE hotspots. Structure of RNA-bound SRSF1 RRM1 was obtained from PDB ID 6HPJ. Transparent electrostatic surface is displayed. Conserved electronegative residues opposite the RNA binding pocket are shown in sticks.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Effect of increasing length on phase separation for all possible dipeptide repeat combinations.
Lengths (x) analyzed are x=0, x>2, x>4, x>6, and x>8. p-values were obtained using a two-tailed correlation analysis. A p-value of <0.05 was considered an indicator that increasing repeat length correlated significantly with fraction of proteins found in condensates. A population-based error of was used to identify whether the sample size was large enough to draw conclusions from the data (as discussed in more detail in the methods section). Whether a repeat type passed both p-value and population-based error criteria is indicated in the right-most column.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Analysis of the effect of increasing repeat length when datasets are size-matched to either n=14 (sheet 1) or n=6 (sheet 2).
Percentage of proteins in condensates was found through Python’s random selection tool 50 different times for each population. Average and standard deviation are indicated at the top of the sheet.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Contingency tables analyzing the likelihood of RRM domain and RS repat co-occurrence both for proteins in condensates (left) and proteins not in condensates (right).
Values used correspond to those displayed in Figure 1A. p-values were obtained using Fisher’s exact test.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Contingency tables corresponding to the p-values shown in Figure 1C and Figure 1—figure supplement 1C.
Correlation between the fraction of proteins in condensates and the presence of a threshold number of short repeats or percentage R/S composition. p-values were obtained using Fisher’s exact test.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Values corresponding to the distance between peptides and hotspot residues at various timepoints in the MD simulation.
Distances (r) correspond to the length between the cysteine to which the paramagnetic center is attached and the NH hydrogen on the backbone of each residue under observation. Distances were measured using the Pymol measurement feature. Residue 42 is near to two peptides. Therefore, two distances are provided for residue 42. Bleached residues are expected to be within 12–15 Å of the paramagnetic center (Iwahara et al., 2007).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/84412/elife-84412-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





