Binding and sequestration of poison frog alkaloids by a plasma globulin
Figures
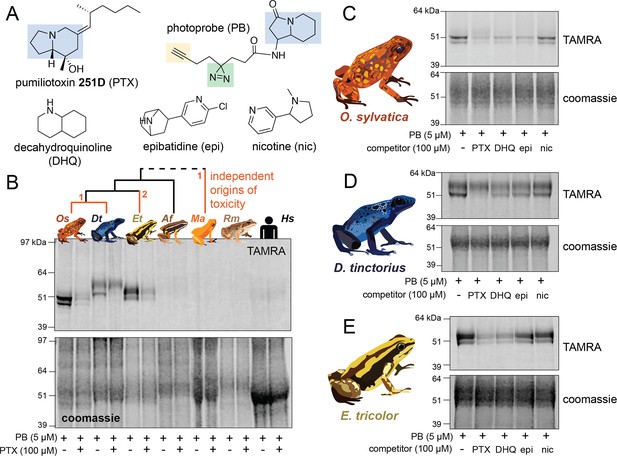
Alkaloid-like photocrosslinking probes show binding and competition in poison frog plasma.
(A) Structures of alkaloid-like photocrosslinking probe and alkaloids tested, with the functional group in blue, the diazirine group in green, and the terminal alkyne in yellow. In (B–E), the top images show the TAMRA signal, which visualizes photoprobe binding, and the bottom images show coomassie staining of the same gel to assess total protein concentration in each well. (B) Plasma from different species (Oophaga sylvatica – Os, Dendrobates tinctorius – Dt, Epipedobates tricolor – Et, Allobates femoralis – Af, Rhinella marina – Rm, and humans – Hs, from left to right) shows different plasma photoprobe-binding activity and competition. Orange lines on phylogeny indicate independent evolutionary origins of chemical defense in Dendrobatidae and Mantellidae, with the number representing the number of times the phenotype arose along that branch. (C) Oophaga sylvatica plasma shows crosslinking, and competition with pumiliotoxin (PTX), decahydroquinoline (DHQ), and epibatidine (epi), but not nicotine (nic). (D) Dendrobates tinctorius plasma shows crosslinking and competition with PTX, slight competition with DHQ and epi, and no competition with nic. (E) Epipedobates tricolor plasma shows crosslinking and competition with PTX and DHQ, but not with epi or nic.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Raw data for the gels shown in Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig1-data1-v2.zip
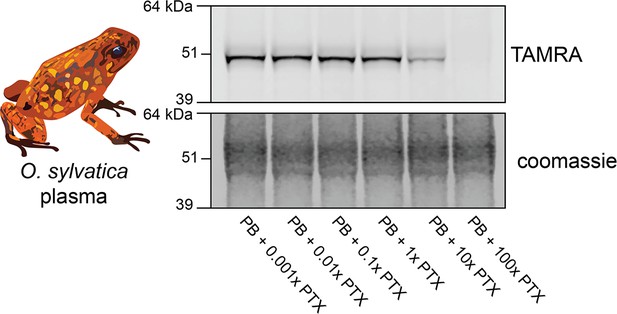
O. sylvatica dose response of photoprobe competition.
Plasma from O. sylvatica shows crosslinking to the photoprobe, and competition by pumiliotoxin 251D (PTX) occurs when there is 10:1 PTX:photoprobe concentration in the reaction.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for the gel shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig1-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
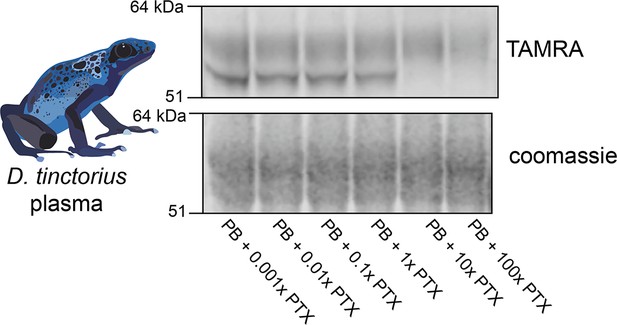
D. tinctorius dose response of photoprobe competition.
Plasma from D. tinctorius shows crosslinking to the photoprobe, and competition by pumiliotoxin (PTX) occurs when there is 10:1 PTX:photoprobe concentration in the reaction.
-
Figure 1—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data for the gel shown in Figure 1—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig1-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
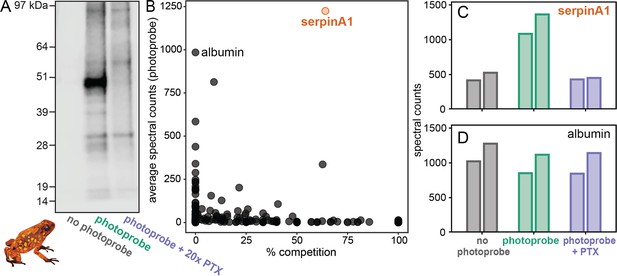
Proteomics identifies a serpinA1-like protein as the main pumiliotoxin (PTX)-binding protein in Oophaga sylvatica plasma.
(A) Streptavidin blot of the proteins pulled down from O. sylvatica plasma across the three conditions: no photoprobe, photoprobe, and photoprobe plus competitor PTX. (B) Quantitative proteomics output in terms of percent competition defined as 100% − average spectral counts in the photoprobe + PTX condition divided by average spectral counts in the photoprobe only condition. Average was taken across two replicates. SerpinA1-like protein and albumin are annotated. (C) The number of spectral counts across conditions for the serpinA1-like protein, each replicate is shown individually. (D) The number of spectral counts across conditions for the albumin protein, each replicate is shown individually.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Raw data for the blot and proteomics shown in Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig2-data1-v2.zip
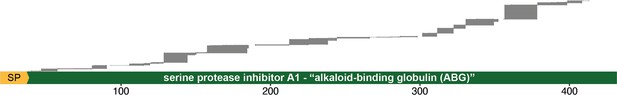
Peptide coverage over alkaloid-binding globulin (ABG) protein sequence.
All unique peptides from one replicate of the proteomics were mapped onto the protein sequence of O. sylvatica ABG, showing that there were peptides covering the full length of the protein.
-
Figure 2—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for the proteomics shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig2-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
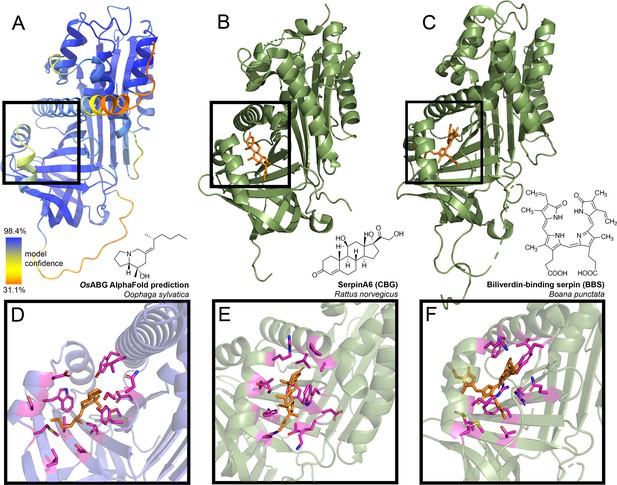
Predicted alkaloid-binding globulin (ABG) structure and binding pocket resembles that of other small molecule binding serpins.
(A) AlphaFold structure predicted with the protein sequence of the Oophaga sylvatica ABG, with color representing model confidence and predicted binding pocket based on molecular docking simulation indicated with a black box. (B) Crystal structure for rat SerpinA6/corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG), with the cortisol molecule shown in orange (PDB# 2V95). (C) Crystal structure for tree frog Boana punctata biliverdin-binding serpin (BBS), with biliverdin shown in orange (PDB# 7RBW). (D) Close-up of predicted binding pocket of pumiliotoxin (PTX) in O. sylvatica ABG, with residues proximal to PTX highlighted in magenta. The structure of PTX is indicated on the top right. (E) Close-up of cortisol binding in CBG (PDB# 2V95), with proximal residues highlighted in magenta. Cortisol structure is displayed on the top right. (F) Close-up of biliverdin binding in BBS (PDB# 7RBW), with some proximal residues highlighted in magenta. Biliverdin structure is shown on the top right.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Raw data for the structure prediction shown in Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig3-data1-v2.zip
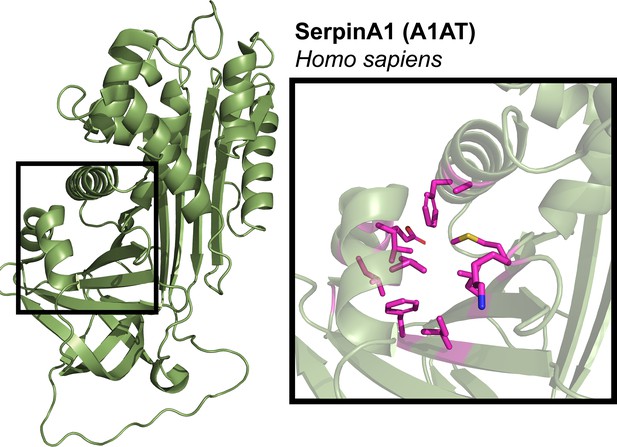
Structure of A1AT protein.
Crystal structure for human SerpinA1/alpha-1-antitrypsin (PDB# 1HP7) contains the structural elements of other serpin-binding pockets (black box), however is not documented to have small molecule binding capabilities. Black box shows close-up of A1AT (PDB# 1HP7), with pocket residues highlighted in magenta.
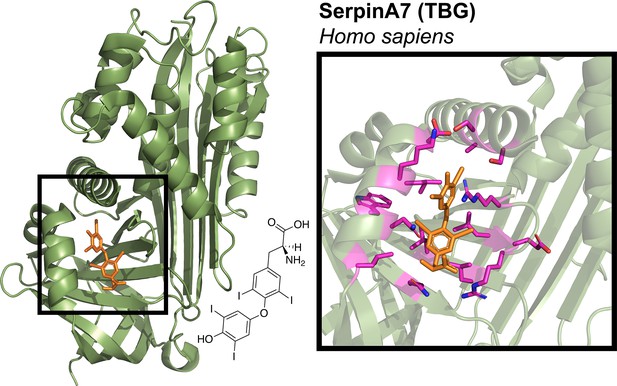
Structure and binding pocket of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) protein.
Crystal structure for human SerpinA7/TBG (PDB# 2RIW) binds thyroxine (orange) in the same structural pocket as other serpins. Black box shows close-up of thyroxine-binding pocket of TBG (PDB# 2RIW), with proximal residues highlighted in magenta. Thyroxine structure is displayed on the top right.

Alignment of binding pocket residues.
Alignment of proximal residues (within 5 angstroms of small molecule) across small molecule binding serpins OsABG, biliverdin-binding serpin (BBS, PDB# 7RBW), corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG, PDB# 2V95), and thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG, PDB# 2RIW) shows that most residues that may be involved in coordinating small molecule binding are not conserved, despite the structural conservation of the binding pocket. Percentages indicate the total percent identity of the protein sequences, the small number above each residue indicates the position of that amino acid in the protein sequence. Only proximal residues are shown, blank spaces are not representative of any specific sequence or spacing.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for the alignment shown in Figure 3—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig3-figsupp3-data1-v2.zip
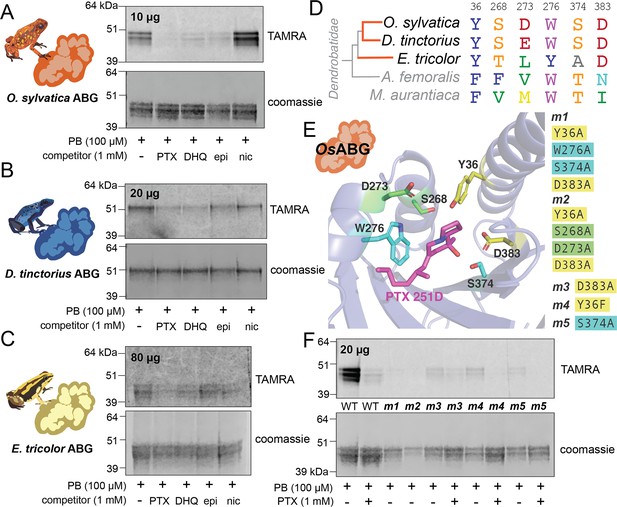
Recombinant expression and binding pocket mutants confirm plasma-binding activity and binding pocket predictions.
(A) Photoprobe crosslinking and competition with different compounds of 10 μg recombinantly expressed and purified OsABG recapitulates the binding activity seen in the plasma (Figure 1C). (B) Photoprobe crosslinking with 20 μg recombinantly expressed Dendrobates tinctorius alkaloid-binding globulin (ABG) shows crosslinking, and competition with pumiliotoxin (PTX) and decahydroquinoline (DHQ). (C) Photoprobe crosslinking with 80 μg recombinantly expressed Epipedobates tricolor ABG shows crosslinking, and competition with PTX and DHQ. (D) Alignment of protein sequence of proteins homologous to OsABG across species shows conservation of certain amino acids. Coloring of amino acids is based on the RasMol ‘amino’ coloring scheme, which highlights amino acid properties. (E) Potential binding residues were identified from the molecular docking simulation. Five different mutants were made based on specific amino acids in the binding pocket, with either a combination of four different alanine substitutions (m1 – yellow and teal residues, and m2 – yellow and green residues) or a single substitutions at D383 (m3), Y36F (m4), or S374A (m5). P8TX is shown in magenta. Oxygen atoms on the molecules are highlighted in red, nitrogen in blue. (F) Quadruple binding pocket mutants (m1 and m2) lose binding activity of the photoprobe, single amino acid substitutions (m3, m4, and m5) show reduced photoprobe binding and retained competition with PTX.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Raw data for the gels shown in Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig4-data1-v2.zip
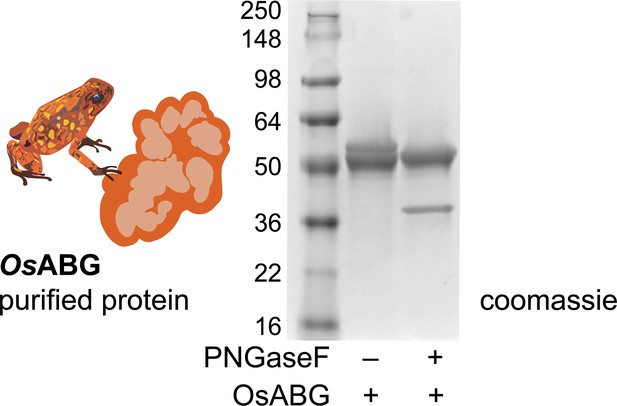
Glycosylation of recombinant OsABG.
Purified O. sylvatica doublet collapses when treated with PNGase deglycosylation enzyme.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for the coomassie gel shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
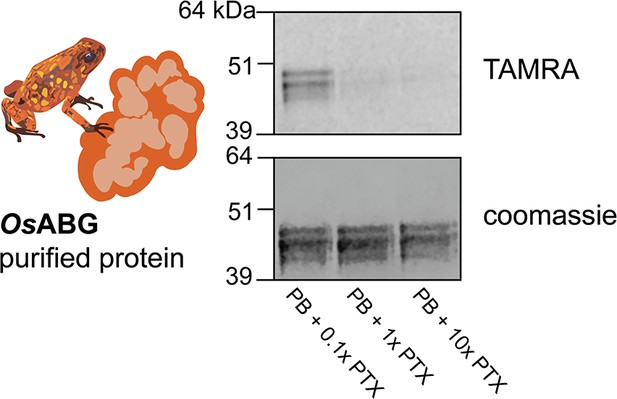
Dose response of crosslinking OsABG.
Purified O.sylvatica alkaloid-binding globulin (ABG) shows crosslinking to the photoprobe and competition by pumiliotoxin (PTX) when there is a 1:1 PTX:photoprobe concentration.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data for the gels shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig4-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip

Recombinant expression and purification of alkaloid-binding globulin (ABG) proteins in insect cells.
HIS blot and coomassie of the recombinantly expressed and purified O. sylvatica alkaloid-binding globulin (OsABG) and binding pocket mutants show a clear doublet pattern in both reduced (R) and non-reduced (NR) conditions.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for the blots and gels shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig4-figsupp3-data1-v2.zip
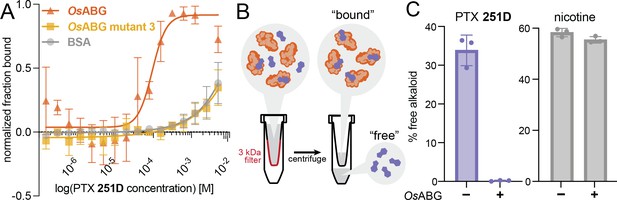
OsABG sequesters free pumiliotoxin (PTX) in solution.
(A) Microscale thermophoresis (MST) of labeled OsABG with PTX finds that binding is of higher affinity than that of OsABG mutant 3 (D383A) and bovine serum albumin (BSA). (B) A 3-kDA molecular weight cut off (MWCO) centrifuge filter was used to separate ‘free’ versus ‘bound’ alkaloids in solutions with and without OsABG present, to later be quantified with liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS). (C) The percent of ‘free’ PTX 251D (purple) dropped when OsABG was present, however the amount of ‘free’ nicotine (gray) remained unchanged by the presence of OsABG.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Raw data for the microscale thermophoresis (MST) and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) data shown in Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig5-data1-v2.zip
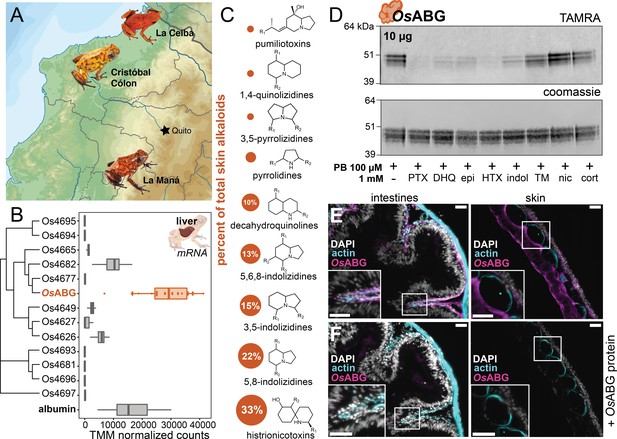
OsABG is expressed in the liver and binds ecologically relevant alkaloids.
(A) Wild Oophaga sylvatica were collected across three locations in Ecuador, n = 10 per location. (B) The liver expression level of OsABG was higher than that of other members of the serpinA family found in the genome, and of albumin. (C) Dorsal skin alkaloids fell into nine different classes, with the size of the circle representing the averaged percent of total skin alkaloid load. (D) Photoprobe binding with recombinantly expressed OsABG was competed by pumiliotoxin (PTX), decahydroquinoline (DHQ), epi, a histrionicotoxin-like compound (HTX), and indolizidine ring without R groups (indol), and slightly by a mixture of skin toxins from the wild specimens (TM). Photoprobe binding was not competed by nicotine (nic) or cortisol (cort). (E) Custom anti-OsABG antibody staining (magenta) in the skin and intestines, with actin stain (blue) and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, shown in white). (F) Pre-incubation of anti-OsABG with purified OsABG protein in the skin and intestines shows loss of OsABG staining, indicating specific staining activity. White bars represent 50 μm.
-
Figure 6—source data 1
Raw data for the gene expression, gels, and immunohistochemistry shown in Figure 6.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig6-data1-v2.zip
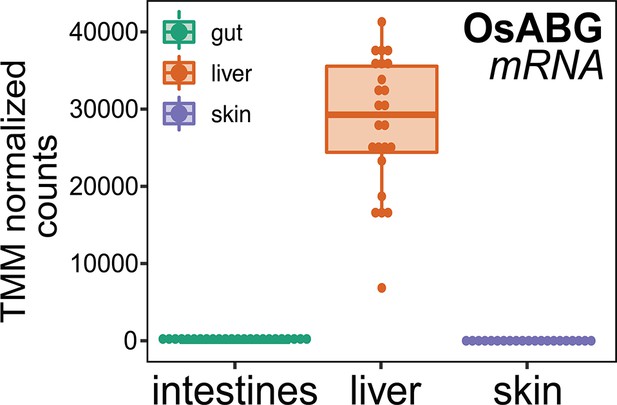
OsABG expression in intestines, liver, and skin.
Comparison of mRNA expression levels across tissues found high expression in the liver, and low to no expression in the skin and intestines.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Raw data for the gene expression data shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig6-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
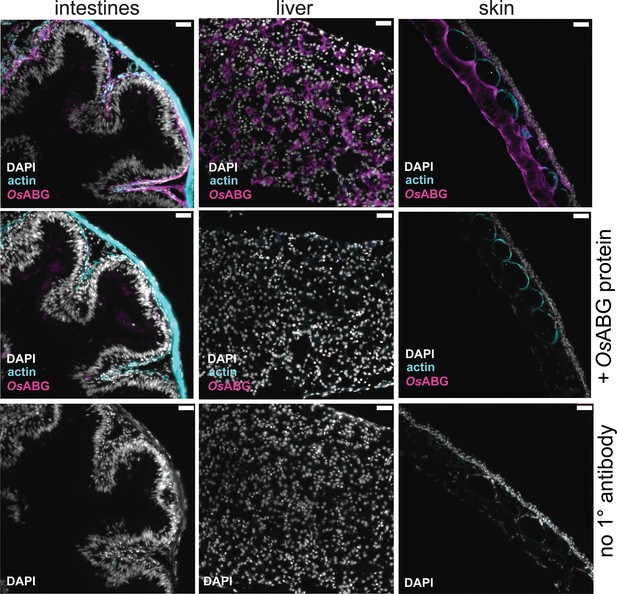
OsABG protein presence in intestines, liver, and skin.
Immunohistochemical staining of O. sylvatica intestines, liver, and skin with custom anti-OsABG primary antibody, anti-actin, and DAPI. Second row shows staining of O. sylvatica intestines, liver, and skin with custom anti-OsABG primary antibody pre-incubated with OsABG protein, anti-actin primary antibody, and DAPI stain. Third row shows negative control staining of O. sylvatica intestines, liver, and skin with no primary antibodies added.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Raw data for the immunohistochemistry shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig6-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
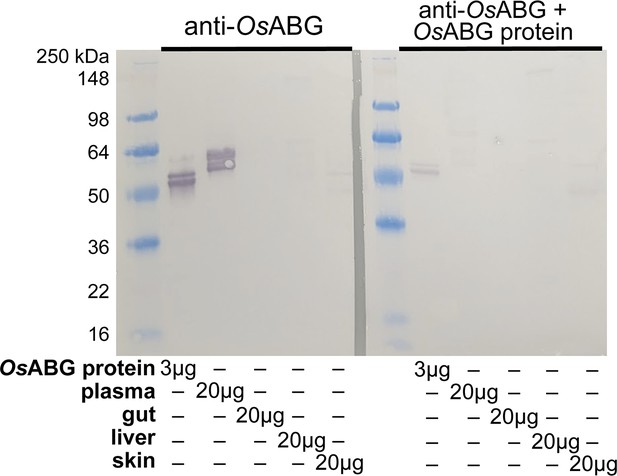
Western blot of anti-OsABG protein.
Western blot using custom anti-OsABG antibody against purified OsABG protein, O. sylvatica plasma, intestines, liver, and skin. The second blot has the same conditions but the primary antibody was pre-incubated with purified OsABG protein prior to blotting, to test the specificity of the antibody.
-
Figure 6—figure supplement 3—source data 1
Raw data for the western blot shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85096/elife-85096-fig6-figsupp3-data1-v2.zip
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene (Oophaga sylvatica) | OsABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032869 | Consensus sequence from three individuals |
| Gene (Dendrobates tinctorius) | DtABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032870 | Consensus sequence from three individuals |
| Gene (Epipedobates tricolor) | EtABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032871 | Consensus sequence from three individuals |
| Strain, strain background (Escherichia coli) | TOP10 | Invitrogen | Cat# C404010 | Chemically competent cells |
| Genetic reagent (Oophaga sylvatica) | O. sylvatica genome | This paper | GenBank: JARQOD000000000 | Annotation available with associated datadryad files |
| Genetic reagent (Allobates femoralis) | A. femoralis genome | This paper | GenBank: JARQOC000000000 | Annotation available with associated datadryad files |
| Genetic reagent (Epipdobates tricolor) | E. tricolor transcriptome | This paper | Available with datadryad files | |
| Genetic reagent (Dendrobates tinctorius) | D. tinctorius transcriptome | Alvarez-Buylla et al., 2022 | PMID: 35275922 | |
| Genetic reagent (Mantella aurantiaca) | M. aurantiaca transcriptome | This paper | Available with datadryad files | |
| Cell line (Spodoptera frugiperda) | Sf9 insect cell culture | Kemp Proteins | Proprietary insect cell expression technology | |
| Biological sample (Oophaga sylvatica) | Captive-bred little devil poison frogs | Understory Enterprises | ||
| Biological sample (Dendrobates tinctorius) | Captive-bred dyeing poison frogs | Josh’s Frogs | ||
| Biological sample (Epipedobates tricolor) | Captive-bred phantasmal poison frogs | Josh’s Frogs | ||
| Biological sample (Allobates femoralis) | Captive-bred brilliant-thighed poison frogs | Understory Enterprises | ||
| Biological sample (Mantella aurantiaca) | Captive-bred golden mantella | Josh’s Frogs | ||
| Biological sample (Homo sapiens) | Human plasma | Innovative Research | Cat# IPLANAH | |
| Biological sample (Oophaga sylvatica) | Field-collected little devil poison frogs | Moskowitz et al., 2022 | doi:10.1101/2022.06.14.495949 | Tissue from 30 individuals |
| Antibody | Anti-OsABG rabbit polyclonal antibody | This paper | Generated by Pocono rabbit farm, WB dilution 1:1000, IHC dilution 1:800 | |
| Antibody | Anti-actin mouse monoclonal antibody | Abcam | Cat# ab11003 | IHC dilution 1:800 |
| Antibody | Goat monoclonal anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 568 | Invitrogen | Cat# A-11011 | IHC dilution 1:400 |
| Antibody | Goat monoclonal anti-mouse Alexa Fluor 488 | Invitrogen | Cat# A-11001 | IHC dilution 1:400 |
| Recombinant DNA reagent | pENTR plasmid | Invitrogen | Cat# K240020 | D-TOPO cloning |
| Sequence-based reagent | OsABG_fwd | This paper | PCR primer | CACCATGAAACTTTTCGTCTACCTGTGTTTCAGC |
| Sequence-based reagent | OsABG_rev | This paper | PCR primer | CTATTTTGTTGGGTCTACTATTCTTCCGCTG |
| Sequence-based reagent | DtABG_fwd | This paper | PCR primer | CACCATGAAGCTTTTCGTCTTCCTATGTTTCAGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | DtABG_rev | This paper | PCR primer | CTATTTTGTTGGGTTTATTATTTTTCCATTCAAAATATCG |
| Sequence-based reagent | EtABG_fwd | This paper | PCR primer | CACCATGAAGCTTTTCATCTTCCTGTGTTTGAGCC |
| Sequence-based reagent | EtABG_rev | This paper | PCR primer | CTATTTTGTTGGGTCTATTATTCTTCCGGAGAAAAC |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032869 | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG mutant 1 | This paper | Y36A + W276A + S374A + D383A | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG mutant 2 | This paper | Y36A + S268A + D273A + D383A | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG mutant 3 | This paper | D383A | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG mutant 4 | This paper | Y36F | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | OsABG mutant 5 | This paper | S374A | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | DtABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032870 | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | EtABG | This paper | GenBank: OQ032871 | Custom expression and purification by Kemp Proteins in sf9 cell culture |
| Peptide, recombinant protein | Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# A2153-50G | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Monarch total RNA Miniprep Kit | NEB | Cat# T2010S | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Superstrand III First-Strand Synthesis kit | Invitrogen | Cat# 18080-400 | ligo(dT)20 primer used |
| Commercial assay or kit | Phusion High Fidelity DNA polymerase | Thermo Scientific | Cat# F-530 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NucleoSpin Gel and PCR cleanup | Takara Bio | Cat# 740609.50 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | pENTR/D-TOPO kit | Invitrogen | Cat# 45-0218 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Miniprep Kit | QIAGEN | Cat# 27106X4 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Sanger Sequencing | Azenta Life Sciences | M13F and M13R primers used | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Red-NHS 2nd Generation Labeling Kit | Nanotemper | Cat# MO-L011 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tapestation RNA screentape analysis | Agilent | Cat# 5067–5576; Cat# 5067–5578; Cat# 5067–5577 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Qubit Broad Range RNA kit | Invitrogen | Cat# Q10210 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | NEB Directional RNA sequencing Kit | NEB | Cat# E7765L | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Zymo RiboFree TotalRNA Library Prep Kit | Zymo Research | Cat# R3003-B | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Tapestation D1000 screentape analysis | Agilent | Cat# 5582; Cat# 5583 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Qubit dsDNA high sensitivity kit | Invitrogen | Cat# Q33231 | |
| Commercial assay or kit | Horse-Radish Peroxidase (HRP) substrate kit | Bio-Rad | Cat# 1721064 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘PTX 251D; pumiliotoxin 251D; PTX’ | Other | Pubchem_CID:6440480 | Custom-synthesized molecule produced by PepTech (Burlington, MA, USA) |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘decahydroquinoline; DHQ’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# 125741 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘epibatidine; epi’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# E1145 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘histrionicotoxin-like compound; HTX’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# ENAH2C55884A-50MG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘indolizidine; indol’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# ATE24584802-100MG | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘nicotine; nic’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# N3876-100ML | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘cortisol; cort’ | Sigma-Aldrich | Cat# H0888-1G | |
| Chemical compound, drug | ‘photoprobe, PB’ | Enamine | Cat# Z2866906198 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TBTA | Fisher | Cat# H66485-03 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Copper (II) sulfate | Fisher | Cat# BP346-500 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride | Fisher | Cat# J60316-06 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | TAMRA-N3 | Fisher | Cat# T10182 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | InstantBlue | Abcam | Cat# ISB1L | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Biotin-N3 | Click Chemistry Tools | Cat# 1265 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Trizol | Thermo Fisher | Cat# 15596018 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | Tissue-Tek OCT | Sakura Finetek | Cat# 4583 | |
| Chemical compound, drug | FluoShield aqueous mounting media containing DAPI | Abcam | Cat# ab104139 | |
| Software, algorithm | Byronic | Protein Metrics | v4.1.5 | |
| Software, algorithm | MAFFT nucleotide sequence alignment | Benchling | ||
| Software, algorithm | Clustal Omega AA sequence alignment | Benchling | ||
| Software, algorithm | AlphaFold | Jumper et al., 2021b | PMID: 34265844 | Through google collab notebook: https://colab.research.google.com/github/deepmind/alphafold/blob/main/notebooks/AlphaFold.ipynb |
| Software, algorithm | UCSF Chimera | Pettersen et al., 2004 | PMID: 15264254 | |
| Software, algorithm | Autodock Vina | Eberhardt et al., 2021 | PMID: 34278794 | v1.2.0 |
| Software, algorithm | GraphPad Prism | GraphPad Software | ||
| Software, algorithm | GNPS mass spec deconvolution + identification | Wang et al., 2016 | PMID: 27504778 | |
| Software, algorithm | R | CRAN | v4.0.4 | |
| Software, algorithm | Trim-galore! | Martin, 2011 | doi:https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200 | trim_galore --paired --phred33 --length 36 -q 30 --stringency 1 -e 0.001 |
| Software, algorithm | Kallisto | Bray et al., 2016 | PMID: 27043002 | |
| Software, algorithm | ClustalW | Thompson et al., 1994 | PMID: 7984417 | |
| Other | Nupage 4–12% Bis-Tris protein gel | Invitrogen | Cat# NP0323BOX | Pre-cast protein gels |
| Other | 3 kDa Amicon MWCO centrifuge filter | Millipore-Sigma | Cat# UFC800324 | Centrifugal molecular weight cutoff filters |
| Other | Monolith Premium Capillaries | Nanotemper | Cat# MO-K025 | Glass capillaries for microscale thermophoresis measurements |
| Other | Eclipse Plus C18 column | Agilent | Cat# 959961-902 | Chromatographic column for LC–MS/MS |
| Other | PTFE syringe filter | Thermo Scientific | Cat# 44504-NP | Consumable to filter samples prior to GC–MS analysis |
| Other | Glass vials with PTFE-lined caps | Fisher | Cat# 60940A-2 | Consumable to store samples prior to GC–MS analysis |
| Other | Superfrost Slides | VWR | Cat# 48311-703 | Slides used for IHC staining |
| Other | Hydrophilic PAP Pen | Vector laboratories | Cat# H-4000 | Hydrophilic barrier pen used in IHC staining protocol |





