Associations of four biological age markers with child development: A multi-omic analysis in the European HELIX cohort
Figures

Participant flowchart.
See Supplementary file 1 for details on quality control of molecular data at sample and feature levels.

Study design schematic.
Source data for reproducing correlation plots are provided in Figure 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Source data for reproducing correlation plots in Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-fig2-data1-v2.csv
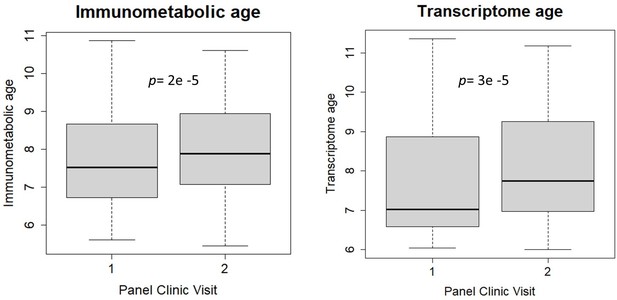
Comparison between immunometabolic and transcriptome age between first and second study visits.
Box plots (showing minimum, maximum, median, first quartile, and third quartile) of biological age measures at each panel study visit (approximately 6 months apart). Panel clinic 1 was part of the main Helix subcohort examination. p-values were calculated from paired t-tests.
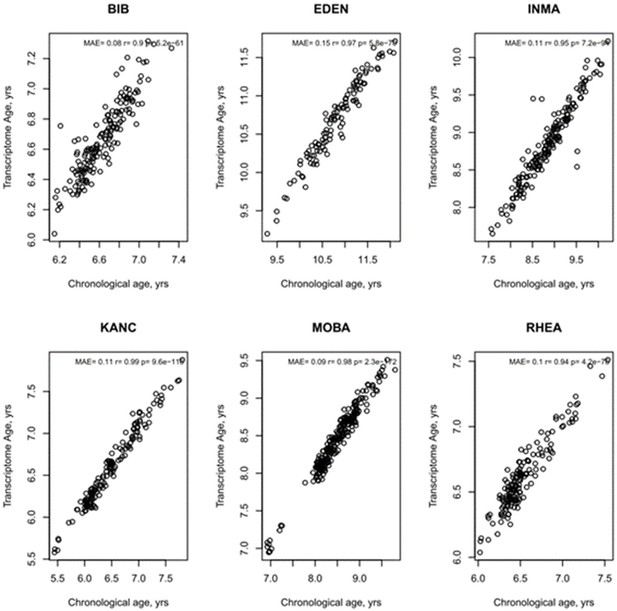
Age Prediction by study centre of transcriptome age.
MAE = mean absolute error. R and p values from Pearson’s correlation.
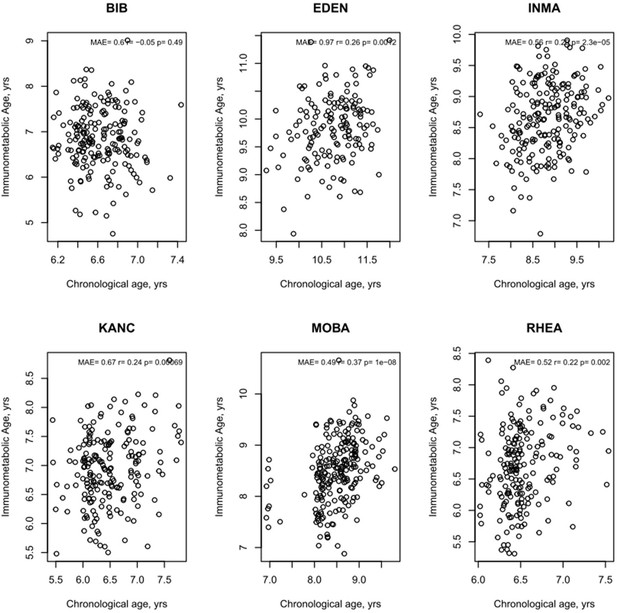
Age Prediction by study centre of immunometabolic age.
MAE = mean absolute error. R and p values from Pearson’s correlation.

Correlations between biological age indicators.
Heatmap shows partial Pearson’s correlations, adjusted for chronological age and study centre. * indicates p<0.05. Source data for reproducing plots is provided in Figure 3—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Source data for reproducing Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-fig3-data1-v2.csv

Associations between biological age measures and developmental measures.
Estimates were calculated using linear regression, adjusted for chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre. *indicates FDR <5%. Telomere length is expressed as a standard deviation (SD) decrease in length (multiplied by –1) to provide estimates indicative of accelerated biological age, as the other biological age indicators. Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. See Table 3 for numbers included in each analysis and exact point estimates and confidence intervals.
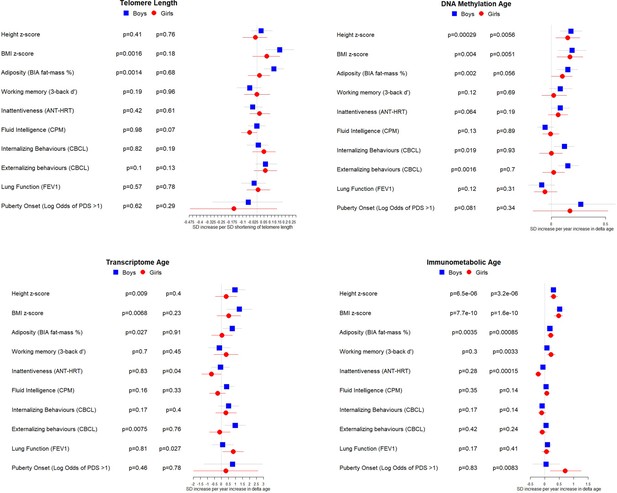
Associations between biological age measures and developmental measures, stratified by sex.
Estimates were calculated using linear regression, adjusted for chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre. Telomere length is expressed as a % decrease in length (multiplied by –1) to provide estimates indicative of accelerated biological age, as for the other biological age indicators. Error bars show 95% confidence intervals.
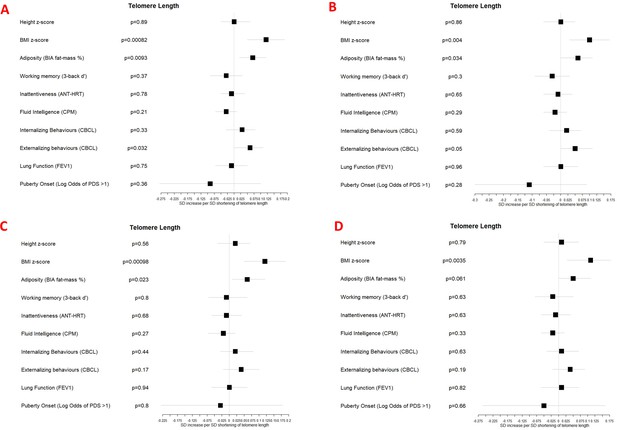
Associations between telomere length and developmental measures adjusted for (A) chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre; (B) as for A plus estimated cell counts; (C) as for A plus family affluence and social capital, birthweight, maternal active smoking, and child passive smoking; (D) as for C plus estimated cell counts.
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. Telomere length is expressed as a standard deviation decrease in length (multiplied by –1) to provide estimates indicative of accelerated biological age, as for the other biological age indicators.
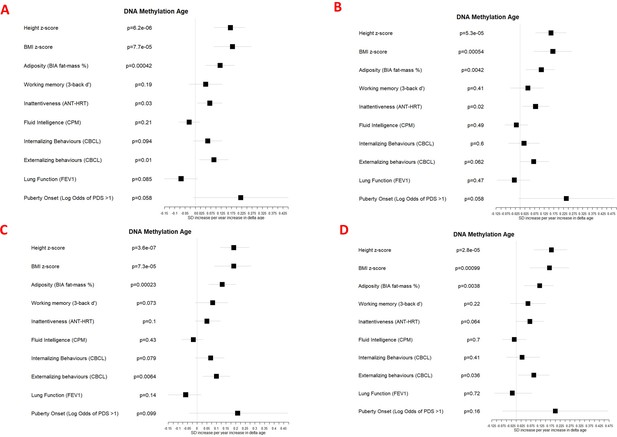
Associations between DNA methylation Δ age and developmental measures adjusted for (A) chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre; (B) as for A plus estimated cell counts; (C) as for A plus family affluence and social capital, birthweight, maternal active smoking, and child passive smoking; (D) as for C plus estimated cell counts.
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals.
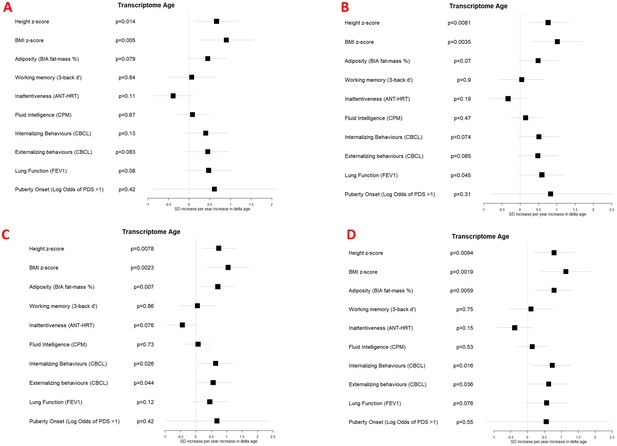
Associations between transcriptome Δ age and developmental measures adjusted for (A) chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre; (B) as for A plus estimated cell counts; (C) as for A plus family affluence and social capital, birthweight, maternal active smoking, and child passive smoking; (D) as for C plus estimated cell counts.
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals.
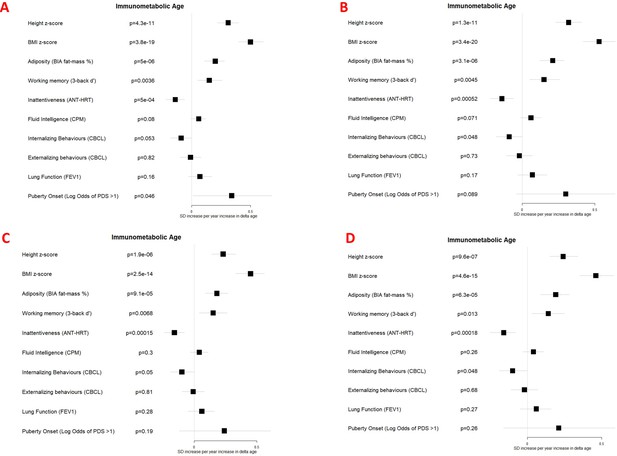
Associations between immunometabolic Δ age and developmental measures adjusted for (A) chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre; (B) as for A plus estimated cell counts; (C) as for A plus family affluence and social capital, birthweight, maternal active smoking, and child passive smoking; (D) as for C plus estimated cell counts.
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals.
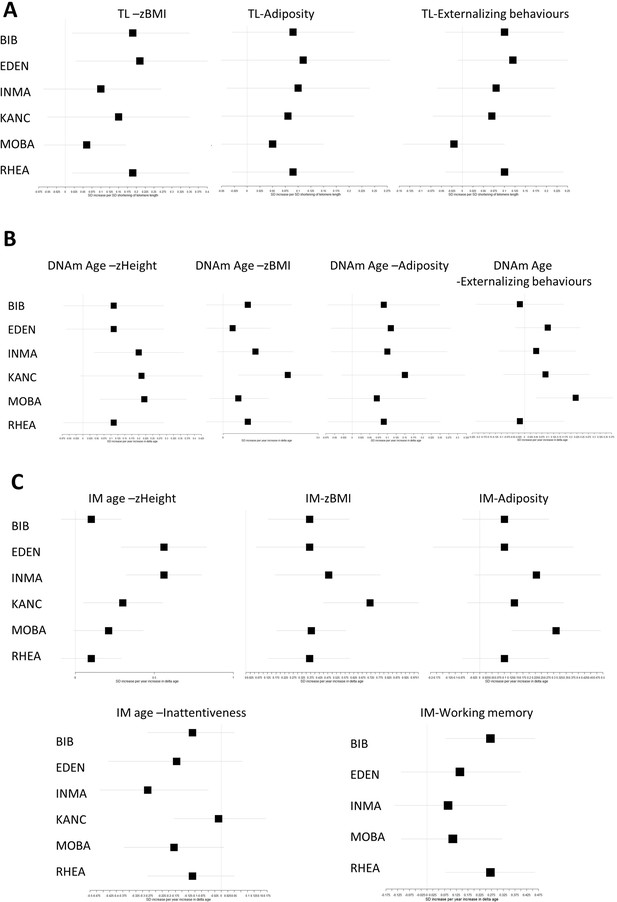
Associations between biological age measures and developmental measures, stratified by study centre (adjusted for chronological age, sex, and ethnicity).
Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. Associations at least at p<0.05 in the pooled analysis are shown for (A) telomere length (TL), (B) DNA methylation (DNAm) age, and (C) Immunometabolic (IM) age.
Tables
Summary Statistics for the study population.
| Telomere Length | DNA methylation age | Trancript-ome age | Immuno-metabolic age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) or Mean (SD) | N (%) or Mean (SD) | N (%) or Mean (SD) | N (%) or Mean (SD) | |
| N | 1162 | 1173 | 1007 | 1152 |
| Demographic factors | ||||
| Age (years) | 7.84 (1.54) | 7.84 (1.54) | 7.90 (1.50) | 7.86 (1.55) |
| Sex-Male | 639 (55) | 644 (54.9) | 547 (54.3) | 628 (54.5) |
| Sex-Female | 523 (45) | 529 (45.1) | 460 (45.7) | 524 (45.5) |
| Ethnicity-White | 1039 (89.4) | 1048 (89.3) | 905 (89.9) | 1032 (89.6) |
| Ethnicity-Pakistani/Asian | 96 (8.3) | 98 (8.4) | 76 (7.5) | 93 (8.1) |
| Ethnicity -Other | 27 (2.3) | 27 (2.3) | 26 (2.6) | 27 (2.3) |
| Cohort-BIB | 200 (17.2) | 203 (17.3) | 162 (16.1) | 191 (16.6) |
| Cohort-EDEN | 145 (12.5) | 146 (12.4) | 109 (10.8) | 149 (12.9) |
| Cohort-INMA | 212 (18.2) | 215 (18.3) | 184 (18.3) | 201 (17.4) |
| Cohort-KANC | 196 (16.9) | 198 (16.9) | 151 (15) | 197 (17.1) |
| Cohort-MOBA | 211 (18.2) | 212 (18.1) | 245 (24.3) | 222 (19.3) |
| Cohort-RHEA | 198 (17) | 199 (17) | 156 (15.5) | 192 (16.7) |
| Prenatal factors | ||||
| maternal non-active smoker during pregnancy | 988 (85) | 998 (85.1) | 859 (85.3) | 981 (85.2) |
| Maternal active smoker during pregnancy | 174 (15) | 175 (14.9) | 148 (14.7) | 171 (14.8) |
| Birthweight (kg) | 3.37 (0.5) | 3.37 (0.5) | 3.38 (0.52) | 3.38 (0.5) |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 39.57 (1.67) | 39.58 (1.67) | 39.59 (1.75) | 39.59 (1.66) |
| Family Capital | ||||
| Maternal Education (low) | 165 (14.7) | 166 (14.7) | 140 (14.4) | 157 (14.1) |
| Maternal Education (medium) | 391 (34.8) | 394 (34.8) | 328 (33.8) | 391 (35.1) |
| Maternal Education (high) | 568 (50.5) | 573 (50.6) | 503 (51.8) | 565 (50.8) |
| Family Affluence (low) | 133 (11.5) | 135 (11.5) | 112 (11.1) | 128 (11.1) |
| Family Affluence (medium) | 462 (39.8) | 466 (39.8) | 394 (39.2) | 450 (39.1) |
| Family Affluence (high) | 565 (48.7) | 570 (48.7) | 499 (49.7) | 572 (49.7) |
| Family Social Capital (low) | 513 (47.7) | 516 (47.5) | 422 (45.8) | 496 (46.7) |
| Family Social Capital (medium) | 264 (24.6) | 269 (24.8) | 228 (24.7) | 259 (24.4) |
| Family Social Capital (high) | 298 (27.7) | 301 (27.7) | 272 (29.5) | 307 (28.9) |
| Child factors | ||||
| No passive smoke exposure | 723 (63.8) | 732 (63.9) | 639 (64.5) | 718 (63.8) |
| Passive smoke exposure | 411 (36.2) | 413 (36.1) | 351 (35.5) | 407 (36.2) |
| Physical Activity-Low | 418 (36.9) | 420 (36.8) | 349 (35.3) | 416 (37.1) |
| Physical Activity-Medium | 336 (29.7) | 341 (29.9) | 295 (29.9) | 330 (29.4) |
| Physical Activity-High | 378 (33.4) | 381 (33.4) | 344 (34.8) | 375 (33.5) |
| KIDMED diet score | 2.81 (1.77) | 2.82 (1.78) | 2.88 (1.77) | 2.84 (1.76) |
| Developmental measures | ||||
| Height z-score | 0.4 (0.97) | 0.39 (0.98) | 0.39 (0.96) | 0.4 (0.98) |
| BMI z-score | 0.43 (1.2) | 0.43 (1.2) | 0.4 (1.15) | 0.42 (1.18) |
| Adiposity (BIA fat-mass %) | 6.76 (4.01) | 6.77 (4.01) | 6.52 (3.9) | 6.72 (3.95) |
| Working memory (3-back d') | 1.1 (1.01) | 1.1 (1.01) | 1.13 (1) | 1.1 (1.01) |
| Inattentiveness (ANT-HRT) | 301.97 (90.38) | 301.93 (90.46) | 297.69 (89.36) | 301.35 (89.84) |
| Fluid Intelligence (CPM) | 25.87 (6.33) | 25.86 (6.32) | 26.12 (6.26) | 25.95 (6.3) |
| Internalizing behaviors (CBCL) | 6.49 (5.9) | 6.48 (5.9) | 6.36 (5.89) | 6.52 (5.87) |
| Externalizing behaviors (CBCL) | 6.81 (6.5) | 6.82 (6.51) | 6.67 (6.49) | 6.74 (6.42) |
| Lung Function (FEV1) | 99.26 (13.46) | 99.25 (13.47) | 99.16 (13.02) | 99.17 (13.47) |
| Puberty not started | 250 (46.6) | 252 (46.5) | 254 (49.7) | 260 (48) |
| Puberty started (PDS >1) | 287 (53.4) | 290 (53.5) | 257 (50.3) | 282 (52) |
Associations between health risk factors and biological age measures.
Estimates were calculated using linear regression, adjusted for chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre. Bold indicates p<0.05 and *indicates FDR <5%. Telomere length is expressed as a standard deviation (SD) decrease in length (multiplied by –1) to provide estimates indicative of accelerated biological age, as the other biological age indicators. Telomere Length N=1162, DNA methylation age N=1173, Transcriptome age N=1007, Immunometabolic age N=1152.
| Telomere Length | DNA methylation age | TranScriptome age | Immunometabolic age | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD Decrease (95% CI) | p-value | Increase in years Δ Age (95% CI) | p-value | Increase in years Δ Age (95% CI) | p-value | Increase in years Δ Age (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Sex-Male | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Sex-Female | –0.27 (-0.39,–0.16) | 3.30E-06* | 0.07 (-0.01, 0.16) | 0.1 | 0 (-0.01, 0.02) | 0.73 | 0.06 (-0.01, 0.13) | 0.086 |
| Prenatal factors | ||||||||
| maternal non-active smoker during pregnancy | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Maternal active smoker during pregnancy | 0.07 (-0.1, 0.23) | 0.41 | 0.15 (0.03, 0.28) | 0.018 | 0 (-0.02, 0.02) | 0.88 | –0.04 (-0.14, 0.06) | 0.43 |
| Birthweight (kg) | –0.098 (-0.218, 0.023) | 0.11 | –0.021 (-0.114, 0.072) | 0.66 | 0.005 (-0.01, 0.02) | 0.51 | 0.102 (0.027, 0.177) | 0.0075 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | –0.012 (-0.048, 0.024) | 0.52 | 0.013 (-0.015, 0.041) | 0.35 | 0 (-0.005, 0.004) | 0.89 | 0.018 (-0.005, 0.04) | 0.12 |
| Family Capital | ||||||||
| Maternal Education (low) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Maternal Education (medium) | –0.06 (-0.26, 0.13) | 0.53 | 0.02 (-0.14, 0.17) | 0.84 | 0.01 (-0.02, 0.03) | 0.61 | 0.08 (-0.04, 0.2) | 0.21 |
| Maternal Education (high) | –0.1 (-0.29, 0.1) | 0.32 | –0.07 (-0.22, 0.08) | 0.37 | 0 (-0.02, 0.03) | 0.85 | 0.12 (0, 0.24) | 0.051 |
| Family Affluence (low) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Family Affluence (medium) | –0.15 (-0.34, 0.05) | 0.13 | –0.11 (-0.26, 0.03) | 0.13 | 0 (-0.03, 0.02) | 0.85 | 0.02 (-0.1, 0.14) | 0.8 |
| Family Affluence (high) | –0.27 (-0.47,–0.07) | 0.0081 | –0.14 (-0.29, 0.02) | 0.083 | 0.01 (-0.01, 0.04) | 0.35 | 0.09 (-0.04, 0.21) | 0.17 |
| Family Social Capital (low) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Family Social Capital (medium) | –0.06 (-0.21, 0.09) | 0.45 | –0.03 (-0.14, 0.09) | 0.62 | 0.02 (0.01, 0.04) | 0.012 | –0.04 (-0.14, 0.05) | 0.36 |
| Family Social Capital (high) | –0.15 (-0.3, 0) | 0.054 | –0.12 (-0.23, 0) | 0.048 | 0.02 (0.01, 0.04) | 0.011 | –0.06 (-0.15, 0.04) | 0.25 |
| Child factors | ||||||||
| No passive smoke exposure | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Passive smoke exposure | 0.05 (-0.08, 0.18) | 0.42 | 0.11 (0.02, 0.21) | 0.023 | 0.01 (0, 0.03) | 0.16 | –0.01 (-0.09, 0.07) | 0.76 |
| Physical Activity-Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Physical Activity-Medium | 0.09 (-0.06, 0.23) | 0.25 | –0.08 (-0.2, 0.03) | 0.15 | –0.01 (-0.03, 0.01) | 0.17 | 0.03 (-0.06, 0.12) | 0.56 |
| Physical Activity-High | 0.14 (-0.01, 0.29) | 0.067 | –0.1 (-0.22, 0.01) | 0.08 | 0 (-0.02, 0.01) | 0.69 | –0.06 (-0.15, 0.04) | 0.24 |
| KIDMED diet score | –0.03 (-0.064, 0.005) | 0.092 | 0.005 (-0.022, 0.031) | 0.74 | 0.004 (-0.001, 0.008) | 0.10 | –0.005 (-0.027, 0.016) | 0.64 |
Associations between biological age measures and developmental measures.
Estimates were calculated using linear regression, adjusted for chronological age, sex, ethnicity, and study centre.
| Telomere Length | DNA methylation age | Transcriptome age | Immunometabolic age | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | SD increase / odds ratio * per SD shortening (95% CI) | p-value | N | SD increase / odds ratio per year increase in Δ age (95% CI) | p-value | N | SD increase / odds ratio per year increase in Δ age (95% CI) | p-value | N | SD increase/ odds ratio per year increase in Δ age (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Height z-score | 1162 | 0 (-0.05, 0.06) | 0.89 | 1173 | 0.17 (0.09, 0.24) | 6.20E-06* | 1007 | 0.66 (0.13, 1.18) | 0.014 | 1152 | 0.31 (0.22, 0.4) | 4.30E-11* |
| BMI z-score | 1162 | 0.12 (0.05, 0.19) | 0.00082* | 1173 | 0.18 (0.09, 0.27) | 7.70E-05* | 1007 | 0.9 (0.27, 1.53) | 0.005* | 1152 | 0.5 (0.4, 0.61) | 3.80E-19* |
| Adiposity (BIA fat-mass %) | 1153 | 0.07 (0.02, 0.12) | 0.0093* | 1164 | 0.12 (0.05, 0.19) | 0.0004* | 999 | 0.45 (-0.05, 0.94) | 0.079 | 1144 | 0.2 (0.11, 0.28) | 5.00E-06* |
| Working memory (3-back d’) † | 882 | –0.03 (-0.09, 0.03) | 0.37 | 890 | 0.05 (-0.03, 0.13) | 0.19 | 784 | 0.06 (-0.51, 0.63) | 0.84 | 876 | 0.15 (0.05, 0.26) | 0.0036* |
| Inattentiveness (ANT-HRT) | 1142 | –0.01 (-0.05, 0.04) | 0.78 | 1153 | 0.07 (0.01, 0.13) | 0.03 | 997 | –0.39 (-0.85, 0.08) | 0.11 | 1135 | –0.14 (-0.22,–0.06) | 5.00E-04* |
| Fluid Intelligence (CPM) | 1156 | –0.03 (-0.07, 0.01) | 0.21 | 1167 | –0.03 (-0.08, 0.02) | 0.21 | 1001 | 0.08 (-0.3, 0.47) | 0.67 | 1147 | 0.06 (-0.01, 0.12) | 0.08 |
| Internalizing Behaviors (CBCL) | 1156 | 0.03 (-0.03, 0.08) | 0.33 | 1166 | 0.06 (-0.01, 0.13) | 0.094 | 1002 | 0.4 (-0.12, 0.93) | 0.13 | 1146 | –0.09 (-0.18, 0) | 0.053 |
| Externalizing behaviors (CBCL) | 1156 | 0.06 (0, 0.11) | 0.032 | 1166 | 0.09 (0.02, 0.16) | 0.01 | 1002 | 0.45 (-0.06, 0.97) | 0.083 | 1146 | –0.01 (-0.1, 0.08) | 0.82 |
| Lung Function (FEV1) | 911 | –0.01 (-0.07, 0.05) | 0.75 | 921 | –0.07 (-0.15, 0.01) | 0.085 | 795 | 0.47 (-0.06, 1.01) | 0.08 | 907 | 0.07 (-0.03, 0.17) | 0.16 |
| Puberty onset ‡ | 537 | 0.92 (0.76, 1.11) | 0.36 | 542 | 1.25 (0.99, 1.57) | 0.058 | 511 | 1.84 (0.41, 8.44) | 0.42 | 542 | 1.41 (1.01, 1.97) | 0.046 |
-
Bold indicates p<0.05 and *indicates FDR <5%.
-
*
Odds ratio provided for puberty onset only.
-
†
Not available in the Lithuanian KANC cohort.
-
‡
Only assessed in children over 8 years old.
Additional files
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx
-
Source code 1
R script for all data analyses.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-code1-v2.zip
-
Supplementary file 1
Number of samples and features before and after the quality control process.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Proportion of covariates missing for each biological age marker.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp2-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
Immunometabolic age clock coefficients.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp3-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Trancriptome age clock coefficients.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp4-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Overrepresentation analysis in ConsesuspathDB against KEGG and REACTOME pathways, of all transcripts contributing to the transcriptome clock.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp5-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Overrepresentation analysis in ConsesuspathDB against Gene Ontology (GO) biological process terms, of all transcripts contributing to the transcriptome clock.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp6-v2.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 7
Associations between biological age measures and developmental measures, in main analysis (model 1) and sensitivity analyses (models 2-4).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85104/elife-85104-supp7-v2.xlsx





