Multiple antagonist calcium-dependent mechanisms control CaM kinase-1 subcellular localization in a C. elegans thermal nociceptor
Figures
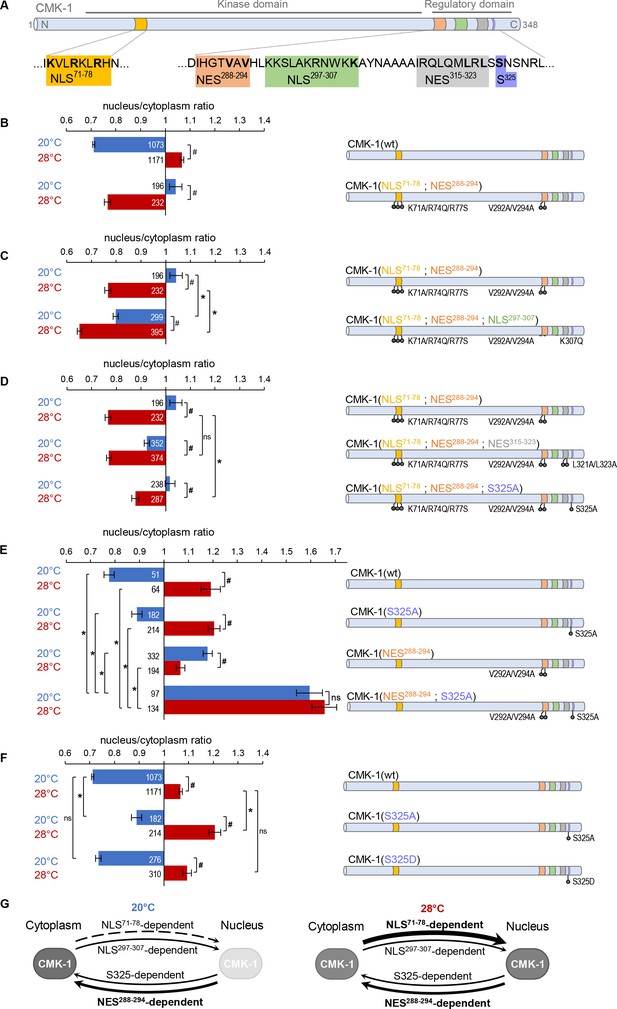
Multiple nuclear export sequence (NES) and nuclear localization signal (NLS) elements work in concert to regulate CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) localization.
(A) Schematic of CMK-1 with positions of the tested NES and NLS candidates and their sequence. (B–F) Subcellular localization of CMK-1::mNeonGreen reporters expressed in FLP and scored after 90 min at 20°C (blue) or at 28°C (red). Average nuclear/cytoplasm fluorescent signal ratio ( ± SEM, left) of wild type (wt) CMK-1 or indicated mutants as schematized (right). Detailed data distributions and ANOVA results are presented in Figure 1—figure supplement 1. #p<0.01 between temperature conditions; *p<0.01 between indicated genotypes; ns, not significant by Bonferroni post hoc tests. The numbers of animals scored in each condition (n) are indicated for each bar. Datasets for CMK-1(wt) and CMK-1(NLS71-78; NES288-294) are common across panels. (G) Updated model of the multiple elements controlling CMK-1 nuclear export and import. At 20°C, NLS71-78-dependent entry is not active (dashed arrow), leaving NES288-294 as the main drive for cytoplasmic accumulation (thick arrow). At 28°C, NLS71-78-dependent entry is active (thickest arrow), becoming the predominant drive to shift CMK-1 equilibrium toward the nucleus. The NLS297-307-dependent nuclear entry pathway and the S325-dependent cytoplasmic accumulation favoring pathway are two secondary pathways (thin arrows), whose activity mostly manifests when one or more of the remaining elements are impaired. For simplicity, the S325-dependent pathway is schematized like an export pathway. However, the S325-dependent pathway could also work via an enhanced cytoplasmic retention.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
Nuclear/cytoplasmic CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) expression ratio raw data for Figure 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
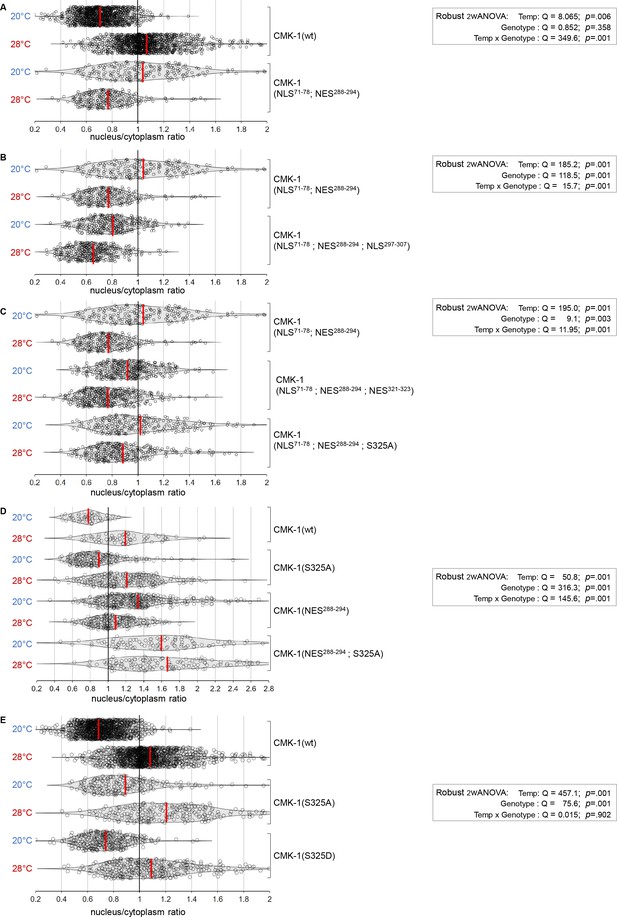
CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) localization data distributions and ANOVA results.
Violin plots with superimposed datapoints depicting the distribution of nucleus/cytoplasmic ratios of the indicated CMK-1::mNG reporters and robust ANOVA results. Red bars: average. (A) Data corresponding to Figure 1B. (B) Data corresponding to Figure 1C. (C) Data corresponding to Figure 1D. (D) Data corresponding to Figure 1E. (E) Data corresponding to Figure 1F.
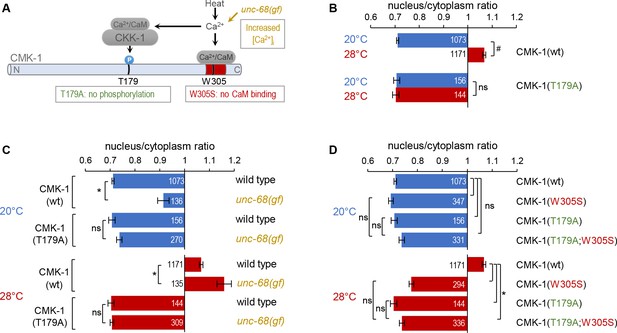
CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) T179 phosphorylation is required for CMK-1 nuclear entry downstream of intracellular calcium elevation.
(A) Schematic of calcium-dependent CMK-1 activation pathway involving CaM binding and CaM kinase kinase-1 (CKK-1) phosphorylation on T179. Illustration of the tested mutations and their effects. (B–D) Subcellular localization of CMK-1::mNeonGreen reporters expressed in FLP and scored after 90 min at 20°C (blue) or at 28°C (red). Average nuclear/cytoplasm fluorescent signal ratio ( ± SEM) of wild type (wt) CMK-1 or indicated mutants. Detailed data distributions and ANOVA results are presented in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. #p<0.01 between temperature conditions; *p<0.01 between indicated genotypes; ns, not significant by Bonferroni post hoc tests. The numbers of animals scored in each condition (n) are indicated for each bar. Datasets for CMK-1(wt) and CMK-1(T179A) are common across panels and CMK-1(wt) dataset is the same as in Figure 1.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Nuclear/cytoplasmic CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) expression ratio raw data for Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
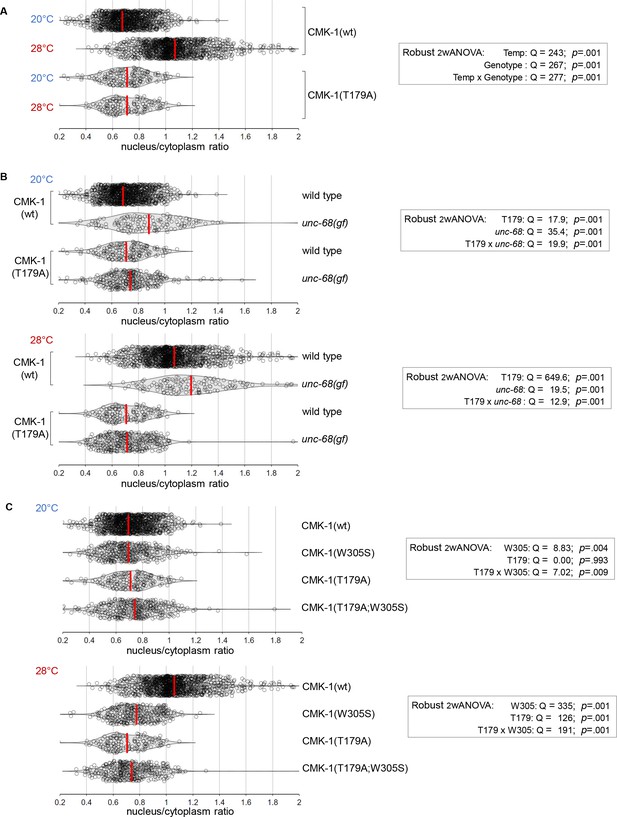
CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) localization data distributions and ANOVA results.
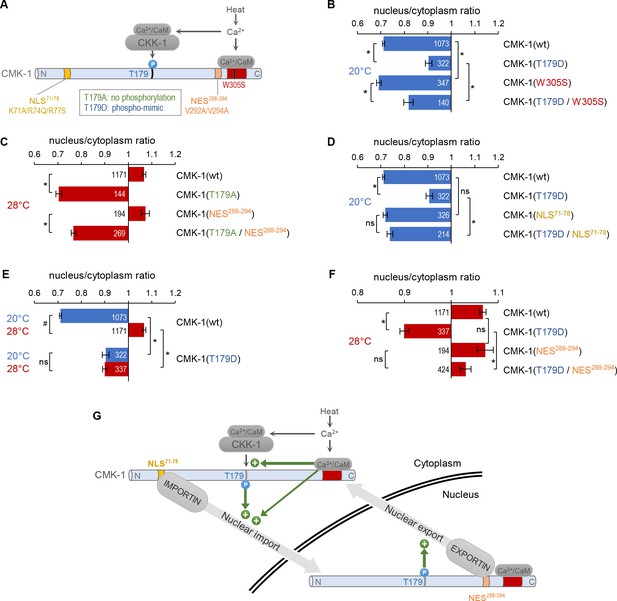
CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) T179 phosphorylation promotes both NLS71-78-dependent import and NES288-294-dependent export.
(A) Schematic of calcium-dependent CMK-1 activation pathways involving CaM binding and CaM kinase kinase-1 (CKK-1) phosphorylation on T179. Illustration of the tested mutations and their effects. (B–F) Subcellular localization of CMK-1::mNeonGreen reporters expressed in FLP and scored after 90 min at 20°C (blue) or at 28°C (red). Average nuclear/cytoplasm fluorescent signal ratio ( ± SEM) of wild type (wt) CMK-1 or indicated mutants. Detailed data distributions and ANOVA results are presented in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. #p<0.01 between temperature conditions; *p<0.01 between indicated genotypes; ns, not significant by Bonferroni post hoc tests. The numbers of animals scored in each condition (n) are indicated for each bar. Datasets for CMK-1(wt) and CMK-1(T179D) are common across panels and CMK-1(wt) dataset is the same as in Figures 1 and 2. (G) Schematic of the multiple cell stimulation-dependent pathways occurring downstream of calcium elevation (green arrows) and proposed to control CMK-1 nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling. CaM binding to CMK-1 can (i) directly promote nuclear import via NLS71-78-dependent pathway, fostered by an enhanced affinity for IMA-3 and (ii) favor CKK-1-dependent phosphorylation of T179. In turn T179 phosphorylation has a dual effect. First, it promotes NLS71-78-dependent nuclear entry. Second, it promotes NES288-294-dependent nuclear export. This mechanism is proposed to sustain an enhanced nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling activity and the progressive equilibrium shift toward the nucleus after prolonged heat-evoked FLP stimulation.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Nuclear/cytoplasmic CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) expression ratio raw data for Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx
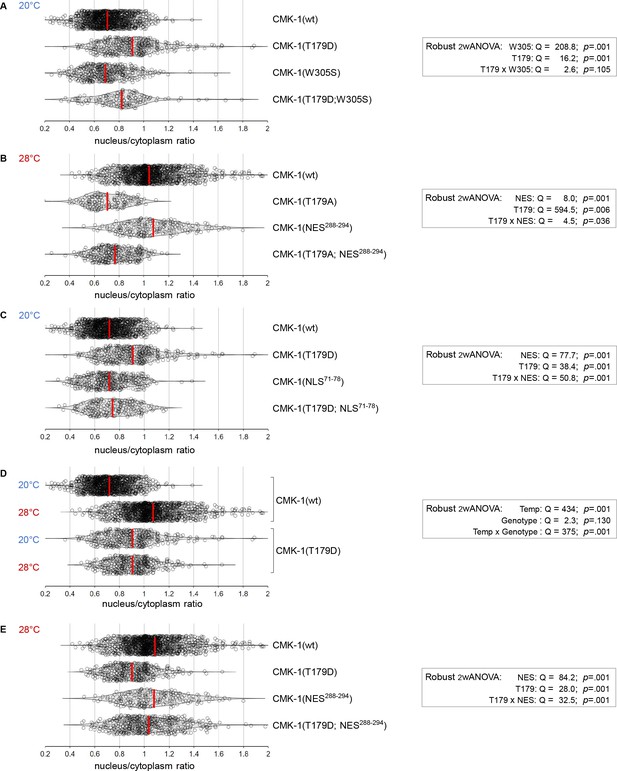
CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) localization data distributions and ANOVA results.
Violin plots with superimposed datapoints depicting the distribution of nucleus/cytoplasmic ratios of the indicated CMK-1::mNG reporters and robust ANOVA results. Red bars: average. (A) Data corresponding to Figure 3B. (B) Data corresponding to Figure 3C. (C) Data corresponding to Figure 3D. (D) Data corresponding to Figure 3E. (E) Data corresponding to Figure 3F.
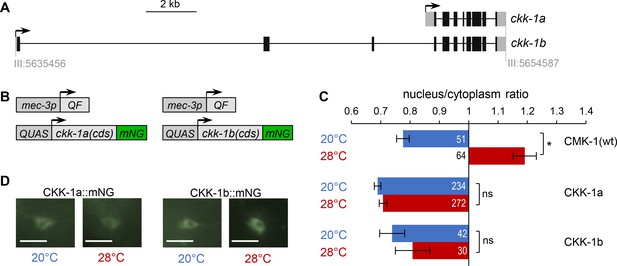
CaM kinase kinase-1 (CKK-1) subcellular localization in FLP.
(A) Schematic of ckk-1 gene locus showing genomic coordinates and the two predicted isoforms produced via alternative transcription start. Coding exon (black boxes), untranslated regions (gray boxes). (B) Schematic of the Q-system-based construct combinations used to drive mNeonGreen (mNG) fusion reporters for CKK-1a (B, left) and CKK-1b (B, right), respectively. (C) Subcellular localization of mNeonGreen reporters expressed in FLP and scored after 90 min at 20°C (blue) or at 28°C (red). Average nuclear/cytoplasm fluorescent signal ratio ( ± SEM) for the indicated reporters. Detailed data distributions presented in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. #p<0.01 between temperature conditions by Student’s t-test; ns, not significant. CMK-1 ratios are presented for comparison purpose. The numbers of animals scored in each condition (n) are indicated for each bar. (D) Representative fluorescence micrographs showing FLP signals. The nucleus is visible as a low-signal region (dark). Scale bars: 10 μm.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Nuclear/cytoplasmic CaM kinase-1 (CMK-1) and CaM kinase kinase-1 (CKK-1) expression ratio raw data for Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-fig4-data1-v1.xlsx
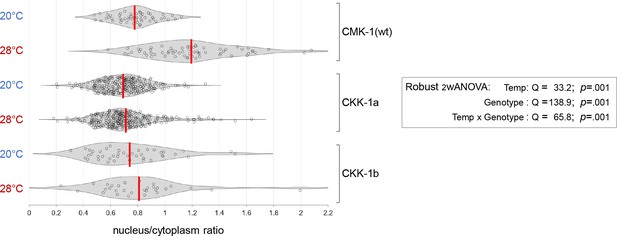
CaM kinase kinase-1 (CKK-1) localization data distributions and ANOVA results.
Violin plots with superimposed datapoints depicting the distribution of nucleus/cytoplasmic ratios of the indicated CMK-1::mNG and CKK-1::mNG reporters and robust ANOVA results. Red bars: average. Data corresponding to Figure 4C.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG439 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domSi439[mec-3p::cmk-1 (1–348)::mNG::unc-54 3’UTR] II | Expression of CMK-1(wt)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG703-704-705 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domEx703-704-705[mec-3p::cmk-1(V292A/V294A)::mNG, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(V292A/V294A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1032 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domSi439[mec-3p::cmk-1::mNG::3xFlag::unc-54 3’UTR] II;[unc-68(dom13)] V | Expression of CMK-1(wt)::mNG in FLP in unc-68 mutant background |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG900-901-902 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domEx900-901-902[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A)::mNG, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG700-701-702 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domEx700-701-702[mec-3p::cmk-1(W305S)::mNG, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(W305S)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG706-707-708 | Ippolito et al., 2021 | domEx706-707-708[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S)::mNG, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG709-710-711-1134-1135-1136 | This study | domEx709-710-711-1134-1135-1136 [mec-3p::cmk-1(T179D)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(T179D)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG744-745-746-812-813 | This study | domEx744-745-746-812-813[mec-3p::cmk-1(T179A)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(T179A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG906-907-908 | This study | domEx906-907-908[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/ T179D)::mNeonGreen, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/ R77S/T179D)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG909-910-911 | This study | domEx909-910-911[mec-3p::cmk-1(T179D/W305S)::mNeonGreen, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(W305S/T179D)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG924-925-926 | This study | domEx924-925-926[mec-3p::cmk-1(T179A/V292A/V294A)::mNeonGreen, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(T179A/ V292A/V294A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1015-1016-1017 | This study | domEx1015-1016-1017[mec-3p::cmk-1(T179A/W305S)::mNeonGreen, unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(W305S/T179A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1600-1601-1602 | This study | domEx1600-1601-1602[mec-3p::cmk-1(S325D)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(S325D)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1621-1622 | This study | domEx1621-1622[mec-3p::cmk-1(S325A)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(S325A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1727-1728-1729 | This study | domEx1727-1728-1729[mec-3p]::cmk-1(T179D/V292A/V294A)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP | Expression of CMK-1(T179D/V292A/V294A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1733-1734-1735 | This study | domEx1733-1734-1735[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A/L321A/L323A)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A/L321A/L323A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1739-1740-1741 | This study | domEx1739-1740-1741[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A/K307Q)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A/K307Q)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1748-1749-1750 | This study | domEx1748-1749-1750[mec-3p::QF]; [QUAS::ckk-1b::gfp]; [unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CKK-1b::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1751-1752-1753 | This study | domEx1751-1752-1753[mec-3p::QF]; [QUAS::ckk-1a::gfp]; [unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CKK-1a::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1793-1794-1795 | This study | domEx1793-1794-1795[mec-3p::cmk-1(V292A/V294A/S325A)::mNeonGreen; unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(V292A/V294A/S325A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1787-1788-1789 | This study | domEx1787-1788-1789[mec-3p::cmk-1(K71A;R74Q;R77S;V292A;V294A;S325A)::mNG]; [unc-122p::RFP] | Expression of CMK-1(K71A/R74Q/R77S/V292A/V294A/S325A)::mNG in FLP |
| Genetic reagent (C. elegans) | DAG1430-1431-1432 | This study | domEx1430-1431-1432[mec-3p::cmk-1(T179A)::mNeonGreen, unc-122p::RFP];[unc-68(dom13)]V | Expression of CMK-1(T179A)::mNG in FLP in unc-68 mutant background |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Plasmid name, cloning, and primer information.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/85260/elife-85260-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





