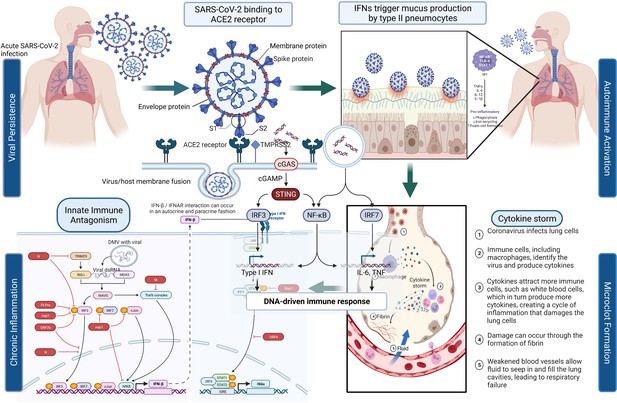
Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)
Figures
Tables
Table 1
Proposed molecular, pathobiological, and pathophysiological mechanisms related to Long COVID symptoms.
| Dysregulated system | Mechanism | Biological/molecular factor* | Signaling pathway | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomic | Autoimmune dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system; cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction (CVAD); post-intensive care syndrome (PICS); orthostatic intolerance (OI); syncope; postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS)-like dysfunction; (ME/CFS)-like dysfunction; antinuclear antibodies | ↑Ganglionic, adrenergic, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies ↑G-protein-coupled receptor autoantibodies | Sympathetic nervous system; cytokine storms; activation of renin–angiotensin system | Al-Kuraishy et al., 2021; Baig et al., 2020; Bisaccia et al., 2021; Escorihuela et al., 2020; Gunning et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020a; Nelson et al., 2019; Shaw et al., 2019; van Campen et al., 2020; Wu and Yang, 2020; |
| Cardiovascular | Myocardial hypertrophy; focal myocardial fibrosis; acute myocardial infarction; cardiac hypertrophy; endothelial dysfunction and coagulation activation; neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs); inflammation-coagulation (Factor XII); direct complement activation (inflammation) | ↑Thrombin ↓Plasmin ↓Fibrinolysis ↑ NT-proBNP ↑cTnI ↑Serum lactate dehydrogenase ↑Creatine kinase | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) signaling through an IDO-Kyn-dependent pathway (hypoxia induction) | Baldi et al., 2020; Basso et al., 2020; Flores et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2020; Hanneman et al., 2022; Lala et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2020b; Mueller et al., 2021; Parohan et al., 2020; Puntmann et al., 2020; Shi et al., 2020; Wallentin et al., 2020 |
| Endocrine | Damage to thyroid gland; thyroiditis/thyrotoxicosis | ↓Thyroxin-3, ↑ACE2, ↑TMPRSS2 | The Th17 and the AGE/RAGE signaling pathways | Clarke et al., 2022; Lazartigues et al., 2020; Wei et al., 2007; Wu et al., 2021 |
| Endothelial | Endothelialitis; thromboembolism; endothelial glycocalyx damage | ↑sP-Sel, vWF, and D-dimer ↑ Endothelin-1 (ET-1) ↓ Angiotensin II ↑Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines ↑Plasma heparinase | Bradykinin pathway | Buijsers et al., 2020; Flores et al., 2019; Mueller et al., 2021; Osburn et al., 2022; Scherbakov et al., 2020; Zha et al., 2022 |
| Gastrointestinal | Impaired barrier function; gut inflammation, altered serotonin metabolism and gut microbiota dysbiosis, Ruminococcus gnavus positively correlated with inflammatory markers; Clostridia was negatively correlated, fungal translocation leading to NF-κB activation and inflammation | ↑ Ruminococcus gnavus, ↑Fecal calprotectin ↑Plasma serotonin (5-hydroxytrytamine, 5-HT) | Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) signaling | Chandrashekhar Joshi and Pozzilli, 2022; Giron et al., 2022; Schultheiss et al., 2022 |
| Hematological | Vascular dysregulation; hypercoagulopathy; endothelialitis; hemostatic changes that leave the endothelium inflamed, pre-adhesive, and prothrombotic; thrombocytopenia, deep vein thrombosis | ↑Plasminogen activator inhibitor factor I (PAI) ↑Tissue factor (TF) ↑von Willebrand factor (vWF) ↑D-dimer ↓Hb ↑GM-CSF | p38 MAPK; Antibody-dependent cellular toxicity | Aird, 2007; Boisramé-Helms et al., 2013; Giustino et al., 2020; Hamming et al., 2004; Hamming et al., 2007; Hussman, 2020; Liu et al., 2020a; Rahman et al., 2021; Riphagen et al., 2020; Zachariah et al., 2020 |
| Immunological | Dysregulated and heightened immune system; prolonged inflammation leading to multiorgan dysfunction; cytokine release syndrome (CRS); Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS); neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs); pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) including Toll-like receptor (TLR); retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I)-like receptors; oxidative stress | ↑IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6 ↑IL- 8, IL-10 ↑IL-IL-12, IL-17 ↑IL-18 ↑IFN-γ, NF-κB; ↑IFN-I and IFN-III ↑TNF, ↑CXCL-10, ↑p38 MAPK ↑JAKs and STATs ↑GM-CSF ↑TGF- β ↑ESR | JAK/STAT; Toll-like receptor pathways (TLR-3 and TLR 7/8); AKT/mTOR/MAPK pathway; FcyRIIA; NF-κB p65 and p38 MAPK, 1/2 (STAT1/2) pathway | Blanco-Melo et al., 2020; Feng et al., 2019; Guo and Thomas, 2017; Jose and Manuel, 2020; Li and Verma, 2002; O’Shea et al., 2015; Pablos et al., 2020; Ronco and Reis, 2020; Tarentino and Maley, 1975; Tay et al., 2020; Tergaonkar et al., 2005; Totura et al., 2015; Wirth and Scheibenbogen, 2021; Ye et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhao and Zhao, 2020 |
| Neurological | Neuro-inflammation; coagulopathy; micro-thrombosis; aberrant immune response; metabolic brain disorders; stroke; Guillain–Barré syndrome; hemodynamic and coagulation disorders; arrhythmia; nervous system damage | ↑IL-18, IL-6, and IL-8 ↑CCL-11 ↑Neurofilament light (NFL) ↑Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) | Humoral and retrograde neural signals; blood–brain barrier (BBB) | Awogbindin et al., 2021; Castanares-Zapatero et al., 2022; Dando et al., 2014; Fernández-Castañeda et al., 2022a; Fernández-Castañeda et al., 2022b; Frere et al., 2022; Holmes et al., 2021; Lauer et al., 2018; Matschke et al., 2020; Pan et al., 2020; Poon et al., 2015; Proal and VanElzakker, 2021; Sahin et al., 2022; Song et al., 2020 ; Tate et al., 2022; VanElzakker, 2013; Wostyn, 2021; Wu et al., 2020 |
| Pancreatic | Direct insulin resistance and beta cell damage; indirect autoimmunity inflammation; stress and steroid-induced hyperglycemia | ↑PKR, PERK, ISR via viral RNA and Cytokine storm, IRS ↑IL-6 and TNF-α ↓REST (RE1-silencing transcription factor) ↑Amylase and lipase ↑HLA ↑Propionic acid ↑Isobutyric acid | Insulin signaling pathway, ISR | Shin et al., 2022 |
| Renal | Glomerulopathy; microangiopathy | ↑ACE2 receptor, ↑IFN-I and IFN-III | Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) disorders | Blanco-Melo et al., 2020; Hamming et al., 2004; Harmer et al., 2002; Nalbandian et al., 2021 Tay et al., 2020; Zou et al., 2020 |
| Respiratory | Pulmonary fibrosis; pulmonary thromboembolism; pneumonia; pulmonary vascular damage; cytokine release syndrome; dysbiosis (increased Staphylococcus cohnii and Pasteurella multocida); lipid metabolism; beta-oxidation; amino acid metabolism; and carbohydrate metabolism; hyperactivated T-lymphocytes and inflammatory macrophages; NETosis | ↑TNF-α, IL-1 ↑IL-IL-1β, IL-6 ↑IL-12 ↑MCP-1 ↑GM-CSF ↑CCL19 ↑CCR6 + Th17 ↑IL-8 (CXCL8) | Insulin/IGF signaling pathway Citrate cycle; respiratory electron transport chain; Th17 cell differentiation pathway | Ackermann et al., 2020; Budhraja et al., 2022; D’Errico et al., 2020; George et al., 2020; Griffin et al., 2020; Grosse et al., 2020; Jin et al., 2021; Jonigk et al., 2022; Kosuge et al., 2012; Medina-Enríquez et al., 2020; Morganstein et al., 2021; Sakr et al., 2020; Shin et al., 2022; Sidarta-Oliveira et al., 2020; Verdecchia et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2021; Yaméogo et al., 2011; Ye et al., 2020 |
| Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) | Kawasaki disease; cardiac involvement with macrophage activation; persistent T-cell immune response; mucosal barrier breakdown | ↑IL-6 and IL-1Ra | ??? | Feldstein et al., 2020; Sadanandam et al., 2020 |
-
*
↑ and ↓ arrows indicate increased and decreased levels, respectively, of biological and/or molecular factors.
Download links
A two-part list of links to download the article, or parts of the article, in various formats.
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Pathogenic mechanisms of post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC)
eLife 12:e86002.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.86002