Role of cytoneme structures and extracellular vesicles in Trichomonas vaginalis parasite-parasite communication
Figures
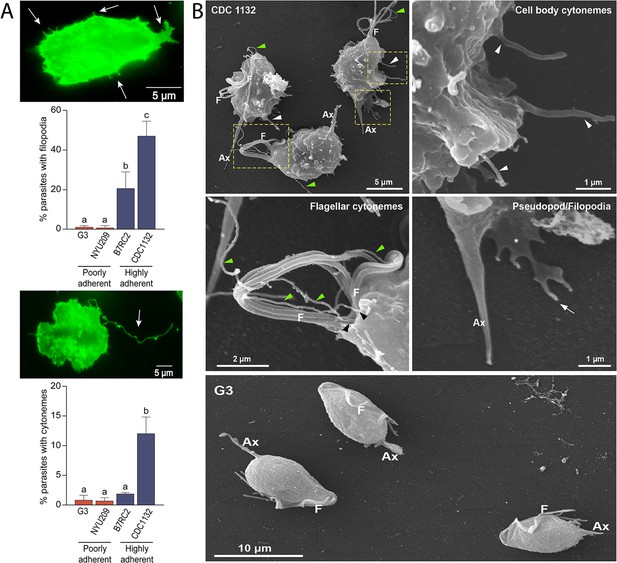
Adherent T. vaginalis strains form abundant membrane protrusions.
(A) Quantification of the percentage of parasites containing filopodia (top) or cytonemes (bottom) in their cell surface. The presence of filopodia/cytonemes in two poorly adherent (G3 and NYU209) and two highly adherent strains (B7RC2 and CDC1132) was analyzed. Three independent experiments by duplicate were performed, and 100 parasites were randomly counted per sample. Data are expressed as percentage of parasites with filopodia and cytonemes ± standard deviation. ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (α=0.95) was used to determine significant differences. (B) SEM reveals a myriad of projections originating from the surface of parasites from CDC1132 strain. Cytonemes protruding from cell body and flagellar base region are indicated by white and green arrowheads, respectively. Pseudopodia (*) and filopodia (arrow) are also seen. The surface protuberances appear to be close ended. Almost no protrusions were observed arising from the surface of poorly adherent parasites (G3). F, flagella; Ax, axostyle.
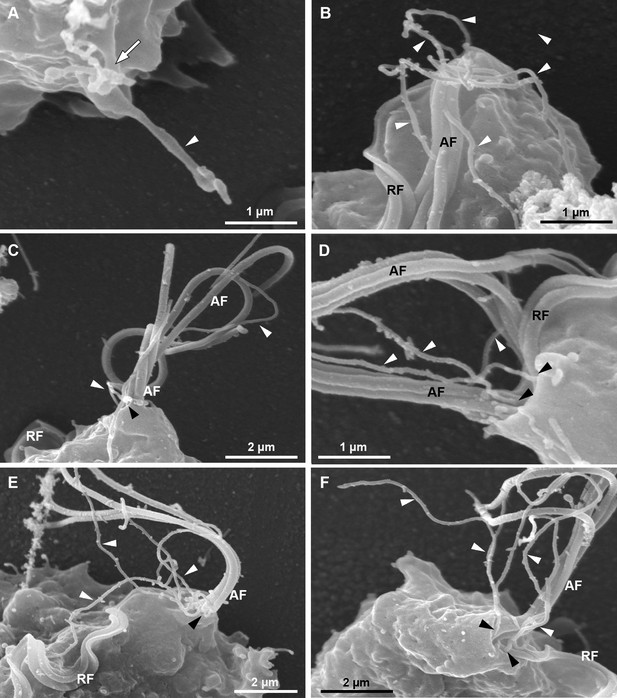
SEM of detailed views of cytonemes protruding from the surface of CDC1132 parasites.
A–D are insets from Figure 1B. (A) A tubular projection protruding from the cell body is seen (arrowhead). Notice that the cytoneme is branched in the region where it emerges from the cell surface (arrow). (B–F) Flagellar cytonemes (white arrowheads). These tubular extensions are originated from the same region where the anterior (AF) and recurrent (RF) flagella emerge (black arrowheads).
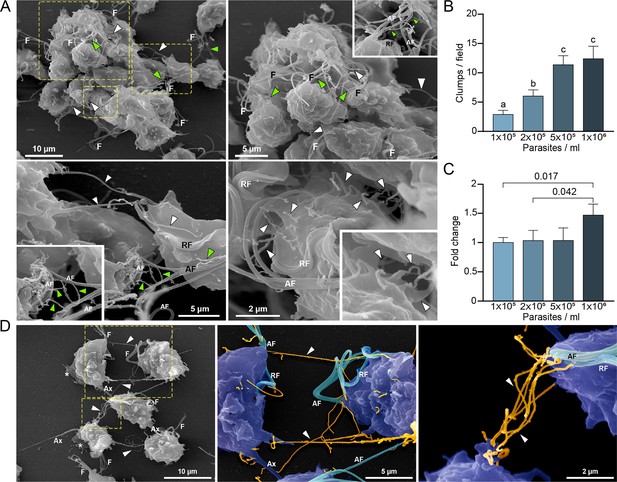
Cytonemes are associated to clumps formation.
(A) Cytonemes emerging from flagella base (green arrowheads) and cell body (white arrowheads) are frequently observed connecting adjacent cells inside clumps of parasites by SEM. F, flagella; AF, anterior flagella; RF, recurrent flagellum. (B) Quantification of clumps per field at different parasite densities (parasites/ml). Twenty fields were counted by duplicate in three independent experiments. A clump was defined as an aggregate of ∼5 or more parasites. Data are expressed as number of clumps for field ± standard deviation. ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (α=0.95) was used to determine significant differences. (C) Quantification of the number of CDC1132 parasites containing cytonemes at different parasite densities (parasites/ml). Three independent experiments by duplicate were performed, and 100 parasites were randomly counted per sample. Data are expressed as −fold change compared to the number of parasites containing cytonemes at density 1×105 parasites/ml ± the standard deviation of the mean. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments. (D) Cytonemes (orange) are observed connecting two parasites (blue) by SEM (arrowheads). F, flagella; AF, anterior flagella; RF, recurrent flagellum; Ax, axostyle.
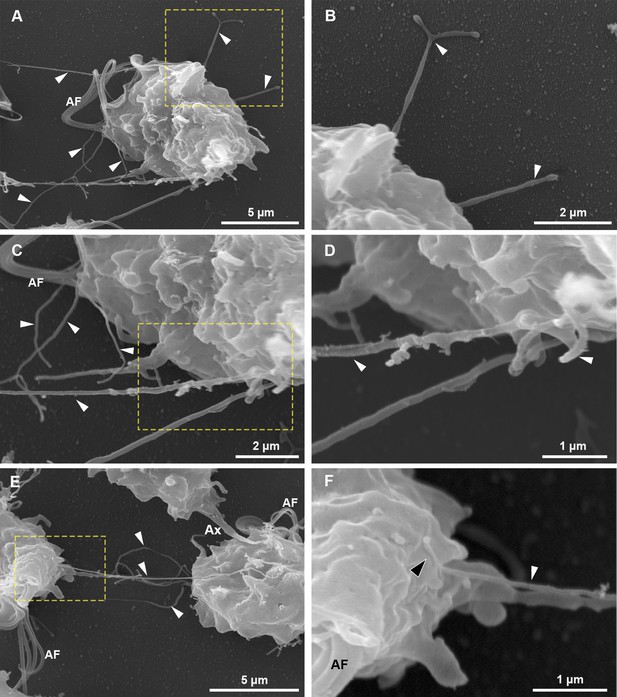
SEM of detailed views and insets from Figure 2D.
(A–D) Branched and unbranched cytonemes are seen (white arrowheads). (E–F) A cytoneme connecting two parasites. In (F), the closed tip of cytoneme is seen in contact with the surface of the adjacent parasite (black arrowheads). AF, anterior flagella; RF, recurrent flagellum.
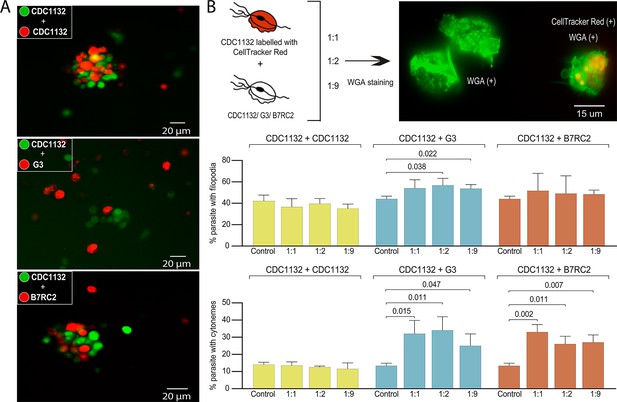
Cytoneme formation is induced by interaction between different strains.
(A) CDC1132 parasites stained with CFSE (green) were co-incubated with CDC1132, G3, or B7RC2 stained with Cell Tracker CMTPX Dye (red) for 1 hr. The interaction between different strains was evaluated by analyzing the capacity to form clumps. As G3 is a poorly adherent strain, the observation of smaller clumps when incubated with CDC1132 is expected. (B) Percentage of CDC1132 parasites containing filopodia or cytonemes during co-incubation with different strains. CDC1132 parasites were stained with Cell Tracker Red (red) and co-incubated for 1 hr with different ratio (1:1, 1:2, and 1:9) of unstained CDC1132, G3, and B7RC2. Then, all the parasites were stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA; green), and the number of CDC1132 parasites (identified as the parasites stained red and green) containing filopodia (middle panel) and cytoneme (lower panel) were analyzed. As control, the number of cytonemes and filopodia of CDC1132 parasites (without co-incubation) was quantified. Data are expressed as percentage of CDC1132 parasites with filopodia and cytonemes ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments.
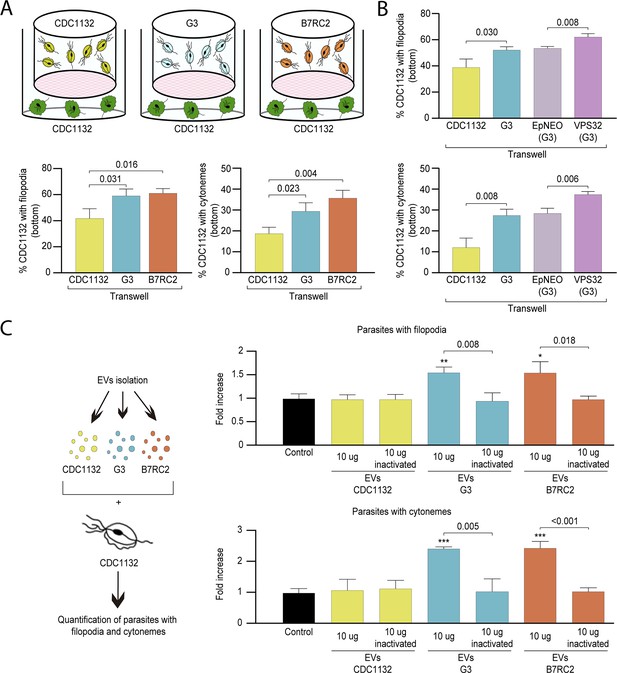
Cytoneme formation is induced by paracrine communication.
(A) Using a cell culture insert assay, CDC1132 parasites (bottom) were co-cultured with CDC1132, G3, and B7RC2 strains (transwell) for 1 hr. Then, the number of CDC1132 parasites (bottom) containing filopodia and cytonemes was quantified by wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining. Data are expressed as percentage of parasites with filopodia and cytonemes ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments. (B) Using a cell culture insert assay, CDC1132 parasites (bottom) were co-cultured with CDC1132, G3, G3 transfected with an empty plasmid (EpNEO) and G3 transfected with VPS32 (transwell) for 1 hr. Then, the number of CDC1132 parasites (bottom) containing filopodia and cytonemes was quantified by WGA staining. Data are expressed as percentage of parasites with filopodia and cytonemes ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments. (C) Extracellular vesicles (EVs; 10 µg) isolated from G3, B7RC2, and CDC1132 parasites were incubated with wild-type CDC1132 parasites for 1 hr. As control, CDC1132 parasites were incubated with the same volume of the PBS solution or 10 µg of inactivated EVs from different strains. Then, the parasites were stained with WGA, and the number of parasites containing cytonemes and filopodia was quantified. Data are expressed as a mean −fold increase compared to control (without EVs) ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001).
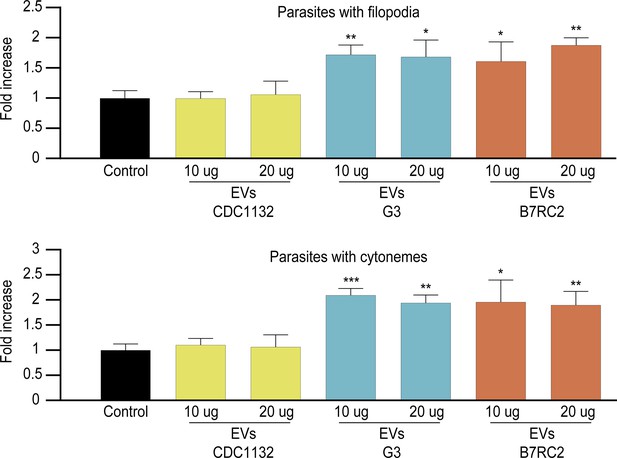
Effect of CDC1132 incubation with different concentrations of extracellular vesicles (EVs).
EVs (10 or 20 µg) isolated from G3, B7RC2, and CDC1132 parasites were incubated with wild-type CDC1132 parasites for 1 hr. As control, CDC1132 parasites were incubated with the same volume of the PBS. Then, the parasites were stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA), and the number of parasites containing cytonemes and filopodia was quantified. Data are expressed as a mean −fold increase compared to control (without EVs) ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001).
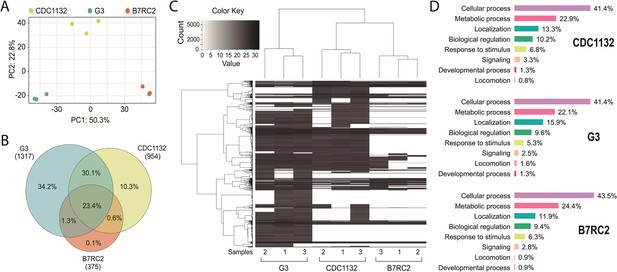
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from different strains contain different protein cargo.
EVs’ proteomic analysis. (A) Principal-component analysis plot representing proteomics data from the comparative analysis of three independent samples of EVs isolated from CDC1132, G3, and B7RC2 strains. (B) Venn diagram depicting proteins shared among EVs isolated from G3, B7RC2, and CDC1132 strains. The numbers in parenthesis indicate the quantity of proteins identified in EVs isolated from each strain. The percentages in the diagrams represent the proteins shared by the different vesicles populations considering the total number of proteins identified in the three strains (1480 proteins). (C) Heatmap of proteins present EVs of G3, B7RC2, and CDC1132 strains. Three independent isolated samples of EVs isolates from each strain were analyzed (1, 2, and 3). Each horizontal line representing an individual protein. Color gradient represents the protein abundance. Note that a dendrogram resulted from a hierarchical clustering analysis of proteins using Pearson correlation as a distance metric indicates that the proteins of EVs from different strains were distinct from each other. (D) Proteins identified in the proteome of EVs from G3, B7RC2, and CDC1132 were identified using Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) analysis and sorted into functional groups based on gene ontology biological processes.
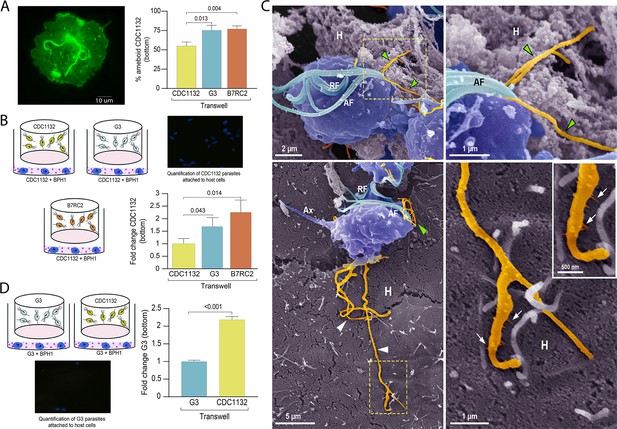
Communication between different parasite strains affects attachment to the host cell.
(A) Using a cell culture insert assay, CDC1132 parasites (bottom) were co-cultured with CDC1132, G3, and B7RC2 strains (transwell) for 1 hr. Then, the percentage of amoeboid CDC1132 parasites in the bottom was quantified by wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining. Data are expressed as percentage of ameboid parasites ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments. (B) Cell Tracker Blue CMAC labeled CDC1132 parasites were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with NhPRE1 prostate cell monolayers cultured onto coverslips in 24-well plates, accompanied by co-culture with CDC1132, G3, and B7RC2 utilizing a cell culture insert assay (1:2 bottom: transwell parasite ratio). Coverslips were washed to remove non-attached parasites and mounted, and the number of attached parasites was quantified by fluorescence microscopy. Data are expressed as fold change related to the attachment of CDC1132 parasites co-incubated with CDC1132 strain inside the transwell ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments. (C) Cytonemes (orange) protruding from the flagellar base (green arrowheads) and cell body (white arrowheads) of CDC1132 parasites (blue) are observed in contact with host cells (H) by SEM. In the lower panels, thin extensions branching (arrows) from the cytoneme are seen in close contact with the BPH1 cells. AF, anterior flagella; RF, recurrent flagellum; Ax, axostyle. (D) Cell Tracker Blue CMAC labeled G3 parasites were incubated for 60 min at 37°C with NhPRE1 prostate cell monolayers cultured on coverslips in 24-well plates, accompanied by co-culture with G3 and CDC1132 utilizing a cell culture insert assay (1:2 bottom: transwell parasite ratio). Coverslips were washed to remove non-attached parasites, mounted, and quantified by fluorescence microscopy. Data are expressed as fold change related to the attachment of G3 parasites co-incubated with G3 strain in the transwell ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Student T-tests (α=0.95) were used to determine significant difference between treatments.
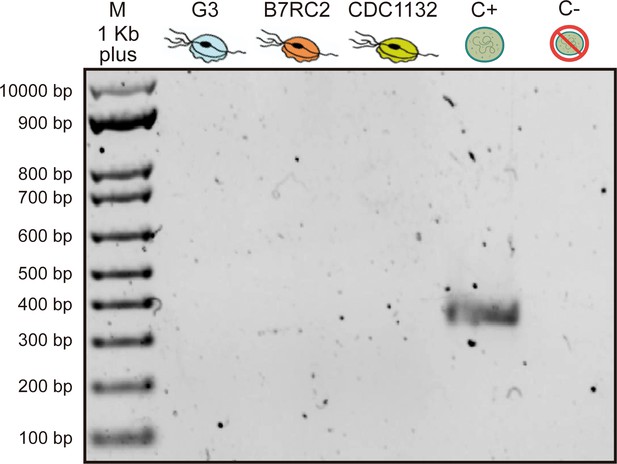
PCR gel electrophoresis results for detection of Mycoplasma contamination.
Lane 1: DNA size marker; lane 2: G3 strain parasite; lane 3: B7RC2 strain parasite; lane 4: CDC1132 strain parasite; lane 5: positive control template; and lane 6: ultrapure water (negative control).
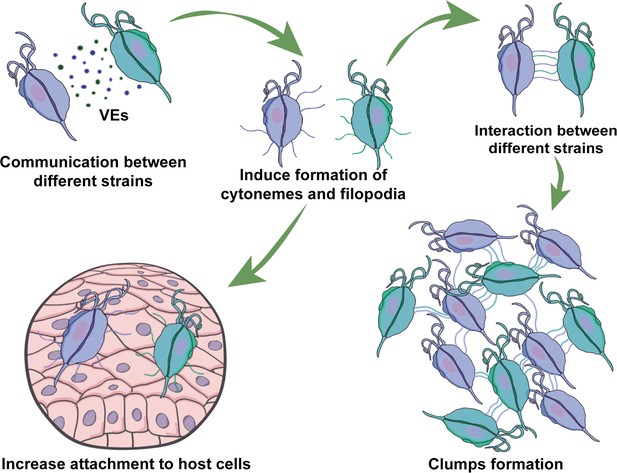
Visual summary of role of extracellular vesicles (EVs) and cytonemes in T.vaginalis parasite: parasite communication.
Different T. vaginalis strains release EVs that have specific protein content and affect the formation of filopodia and cytonemes of recipient parasites. The communication among parasites from different strains affects their attachment to host cells, most likely as a result of the increased formation in filopodia and cytonemes structures.
Videos
Live-cell microscopy revealed the presence of filamentous structures extending from the surface of T. vaginalis.
Cytonemes protruding from CDC1132 parasites in contact with BPH1 cells by videomicroscopy.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of proteins identified in isolated extracellular vesicles (EVs) from G3, CDC1132, and B7RC2 strains by mass spectrometry.
LFQ(label-free quantitation) intensity: Untargeted label-free quantitation of proteins.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86067/elife-86067-supp1-v2.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86067/elife-86067-mdarchecklist1-v2.pdf





