Homeostatic control of an iron repressor in a GI tract resident
Figures
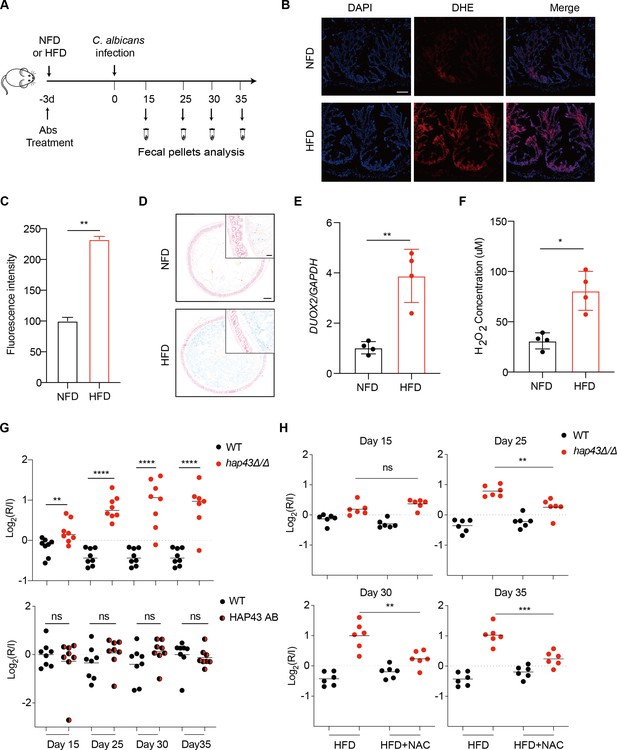
Deletion of HAP43 significantly increases the commensal fitness of C. albicans in gastrointestinal (GI) tract of mice fed a high-Fe diet (HFD).
(A) As depicted in the schematics, mice were fed a normal Fe (NFD) or HFD for 3 d prior to C. albicans inoculation. The mice continuously received the same diet during the course of experiments. (B) Colonic reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in mice receiving an NFD or HFD diet for 3 d. Cryostat colonic sections were incubated with dihydroethidium (DHE) and DAPI. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Quantitative analysis using fluorescence intensity of DHE (a) in the colon. (D) Colonic samples were collected from mice fed either an NFD or HFD, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded, sectioned, and stained with Prussian blue for iron. Representative Prussian blue-stained colonic samples confirmed higher iron deposits in mice receiving HFD (iron blue, nucleus red). Scale bar, 200 μm; inset, 50 μm. (E) The expression of DUOX2 mRNA in the colonic tissue of mice receiving NFD or HFD. Values were normalized to the expression levels of GAPDH. (F) The effect of iron on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) levels in NFD or HFD-treated mice (n = 4 mice per group). (G) Mutant lacking HAP43 exhibits enhanced commensal fitness in HFD-treated mice. Mice (n = 8 mice per group) fed an HFD were inoculated by gavage with 1:1 mixtures of the wild-type (WT) and either hap43Δ/Δ mutant or HAP43 reintegrant (HAP43 AB) cells (1 × 108 CFU per mice). The fitness value for each strain was calculated as the log2 ratio of its relative abundance in the recovered pool from the host (R) to the initial inoculum (I), and was determined by qPCR using strain-specific primers that could distinguish one from another. (H) Treatment of the antioxidant N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is able to partially but significantly abrogate the commensal fitness of Hap43 mutant in HFD-fed mice. During the course of experiments, mice (n = 6 mice per group) fed HFD were received drinking water supplemented with or without NAC (1.5 g/L) and then inoculated by gavage with 1:1 mixtures of the wild-type (WT) and hap43Δ/Δ mutant cells (1 × 108 CFU per mice). Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001; by unpaired Student’s t-test (C, E, F, G, H).
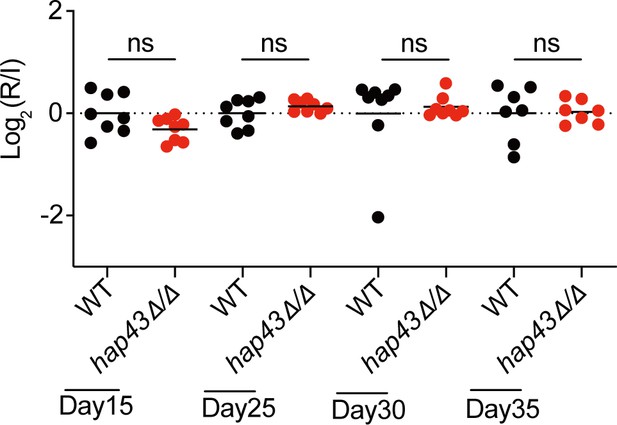
Mutant lacking HAP43 exhibits no change in commensal fitness in normal Fe diet (NFD)-treated mice.
Mice (n = 8) fed a normal Fe diet (NFD) were inoculated by gavage with 1:1 mixtures of the wild-type (WT) and hap43Δ/Δ mutant cells (1 × 108 CFU per mice). The fitness value for each strain was calculated as the log2 ratio of its relative abundance in the recovered pool from the host (R) to the initial inoculum (I), and was determined by qPCR using strain-specific primers that could distinguish one from another. ns, no significance; by unpaired Student’s t-test.
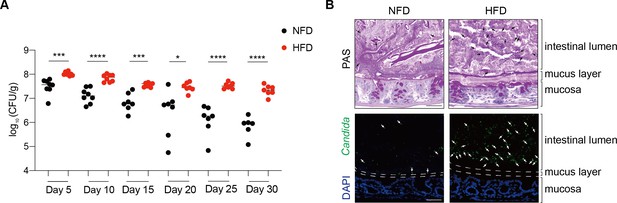
A high-Pi diet significantly promotes the intestinal colonization of C. albicans.
(A) Cells of SC5314 strain (108 CFU/mouse) were separately inoculated into groups of mice fed normal Fe diet (NFD) or high-Fe diet (HFD) (n = 8) by gavage. The intestinal colonization of C. albicans strain was measured by counting the cell numbers present in fresh fecal pellets from days 5–30 post-inoculation. The abundance of C. albicans cells was determined as fungal load (log10 CFU/g feces). Bars represent the mean; *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 by unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) The images shown are colons stained with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) or an anti-Candida antibody (green) or DAPI (blue). The dotted lines represent the boundary between the epithelial surface and the intestinal lumen. The arrows indicate the presence of C. albicans. Images are representative of at least three mice. Scale bar, 50 μm.
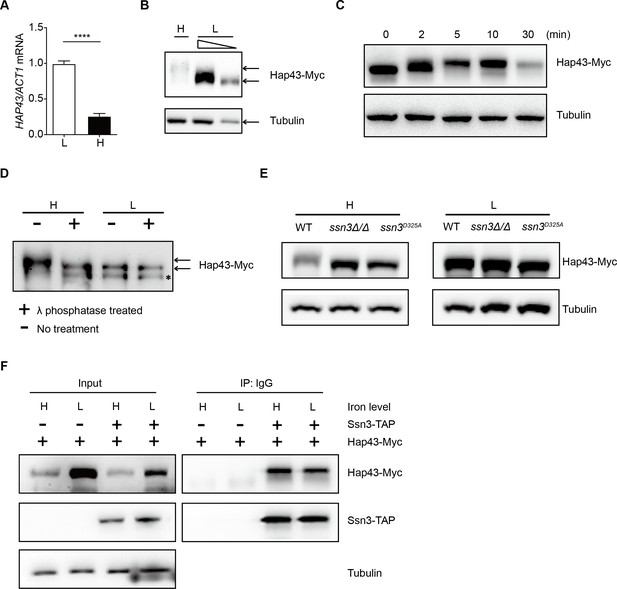
High iron triggers Hap43 phosphorylation that is modulated by the protein kinase Ssn3.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis for HAP43 mRNA in WT strain grown under iron-replete (H, high iron) or iron-depleted (L, low iron) conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ****p<0.0001; by unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) Immunoblots of C-terminally tagged Hap43 (Hap43-Myc) in WT cells propagated under iron-replete (H) or iron-depleted (L) conditions. To better display the mobility-shift on protein, we added additional lane and loaded smaller quantities of total proteins from low-iron culture. α-tubulin, internal standard. (C) Time course for electrophoretic mobility of Hap43-Myc in WT cells during a shift from iron-depleted to iron-replete conditions. (D) Immunoblots of purified Hap43-Myc protein either treated (+) or not treated (-) with λ phosphatase. Note that higher amounts of total proteins from high-iron cultures were loaded. * indicates a presumed Hap43-Myc C-terminal proteolysis product. (E) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc recovered from WT, ssn3Δ/Δ or SSN3D325A cells under iron-replete (H) or iron-depleted (L) conditions. α-tubulin, internal standard. (F) Hap43-Myc is co-immunoprecipitated with Ssn3-TAP. WT strains containing only Ssn3-TAP or both Ssn3-TAP and Hap43-Myc were grown under iron-replete (H) or iron-depleted (L) conditions. Lysates were prepared under nondenaturing conditions, and IgG-sepharose affinity column was used to immune-precipitate Ssn3-TAP and interacting proteins.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig2-data1-v2.zip
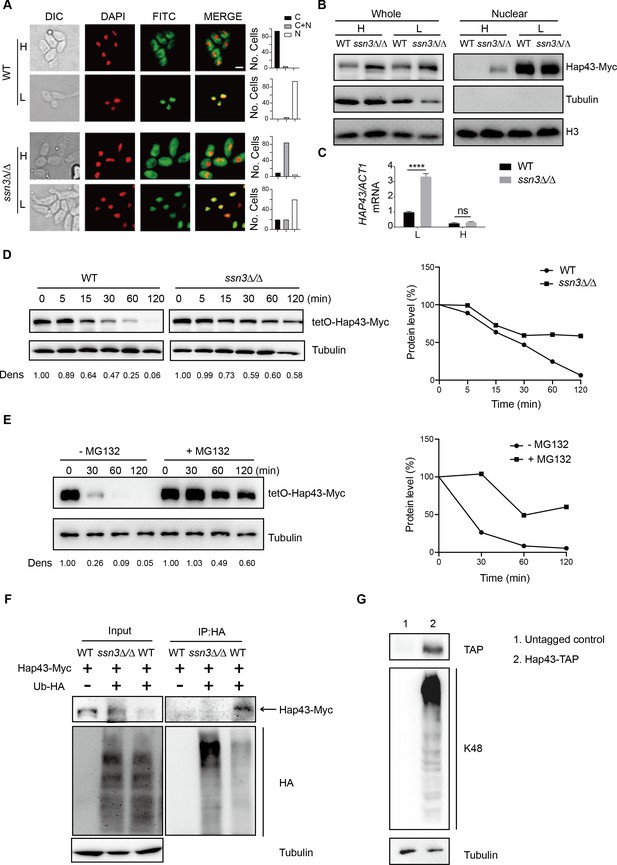
Ssn3-modulated phosphorylation induces cytoplasmic localization and protein degradation of Hap43 by ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
(A) Left panels: indirect immunofluorescence of Hap43-Myc in WT and ssn3Δ/Δ mutant strains grown under iron-replete (H, high iron) or iron-depleted (L, low iron) conditions. DIC represents phase images, DAPI represents nuclear staining, FITC represents Hap43-Myc staining, and Merge represents the overlay of Hap43-Myc and nuclear staining. Right panels: quantification of the cellular distribution of Hap43. Each bar represents the analysis of at least 100 cells. C representing >90% cytoplasmic staining, N > 90% nuclear staining, and C + N a mixture of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc in whole cell extracts and nuclear fraction of WT or ssn3Δ/Δ mutant cells propagated under iron-replete (H) or iron-depleted (L) conditions. Cellular contents were separated into cytosolic and nuclear fractions according to the protocol described in ‘Materials and methods.’ The nuclear marker H3 and cytoplasmic marker α-tubulin were used to display the purities of nucleus and cytoplasm. (C) qRT-PCR analysis for HAP43 mRNA in WT and ssn3Δ/Δ strains grown under iron-replete (H) or iron-depleted (L) conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; ****p<0.0001; by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s test. (D) Hap43 protein is stabilized in a ssn3Δ/Δ mutant. WT or ssn3Δ/Δ strains stably expressing doxycycline-inducible Myc-tagged Hap43 (TetO-Hap43-Myc) were treated with doxycycline. Cells were harvested in the exponential phase of growth, washed to remove doxycycline, and resuspended in fresh iron-replete medium. The turnover of Hap43-Myc in WT or ssn3Δ/Δ cells was then evaluated following the tetO promoter shut-off by removal of doxycycline through time-course experiments. Right panel: Hap43-Myc quantification after intensity analysis using ImageJ. (E) Similar to (D), after treatment with doxycycline, WT cells (a copy of ERG6 was deleted) stably expressing doxycycline-inducible Myc-tagged Hap43 (TetO-Hap43-Myc) were harvested, washed, and treated with or without the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 (100 μM). The turnover of Hap43-Myc in WT cells was evaluated through time-course experiments. Right panel: Hap43-Myc quantification after intensity analysis using ImageJ. (F) Detection of Hap43 ubiquitination in C. albicans. WT and ssn3Δ/Δ mutant strains were engineered by stably expressing either Hap43-Myc alone or both Hap43-Myc plus tetO-HA-Ub. Both strains were incubated under iron-replete plus 50 μg/ml doxycycline conditions and cell extracts were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA-conjugated beads followed by western blot analysis with anti-Myc antibodies for detection of ubiquitinated Hap43. (G) Detection of Hap43 polyubiquitination in C. albicans. The WT strain was engineered by stably expressing Hap43-TAP and grown under iron-replete conditions. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with lgG-sepharose followed by western blot analysis with anti-K48 linkage antibody for detection of K48-linked polyubiquitination of Hap43.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig3-data1-v2.zip
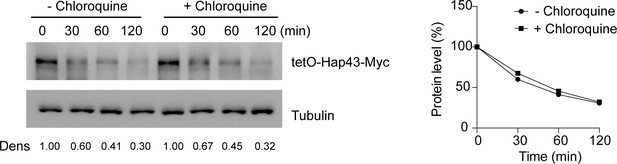
Chloroquine had no effect on Hap43 degradation under high iron conditions.
After treatment with doxycycline, the WT cells stably expressing doxycycline-inducible Myc-tagged Hap43 (TetO-Hap43-Myc) were harvested, washed, and treated with or without the lysosomal protease inhibitor chloroquine (100 mM). The turnover of Hap43-Myc in WT cells was evaluated through time-course experiments. Right panel: Hap43-Myc quantification after intensity analysis using ImageJ. For raw blots, see Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig3-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
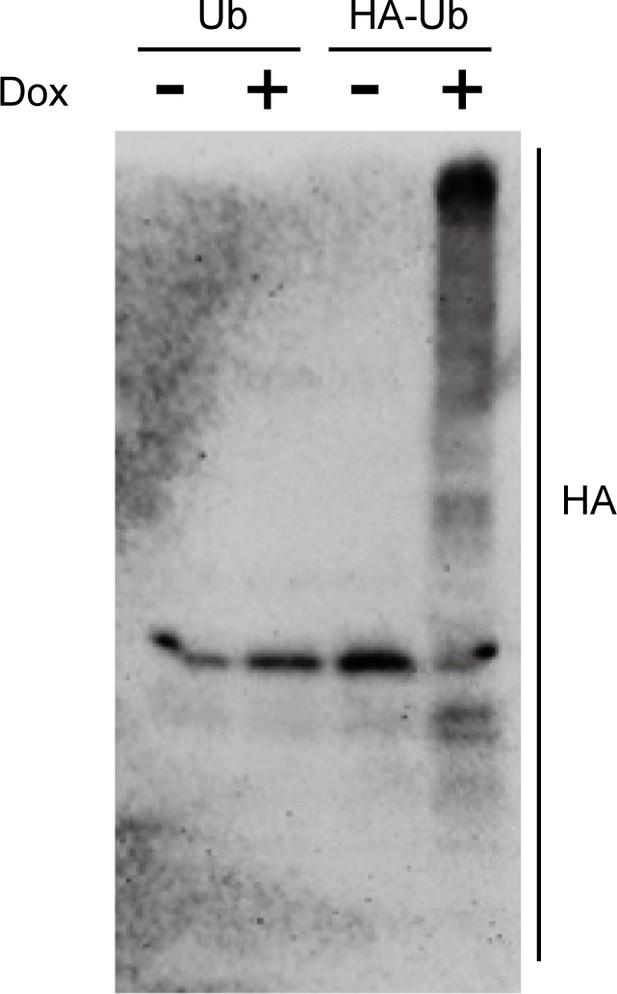
Immunoblots showing the induction of an epitope-tagged 3xHA-ubiquitin under the control of the doxycycline (DOX)-inducible promoter.
C. albicans cells co-expressing 3xHA-tagged ubiquitin and Hap43-Myc as well as Hap43-Myc cells were incubated in YPD supplemented with 50 μg/ml Dox for 6 hr. Log-phase cells were collected and lysed, followed by immunoblots of whole cell extracts with anti-HA antibodies. For raw blots, see Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1.
-
Figure 3—figure supplement 2—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig3-figsupp2-data1-v2.zip
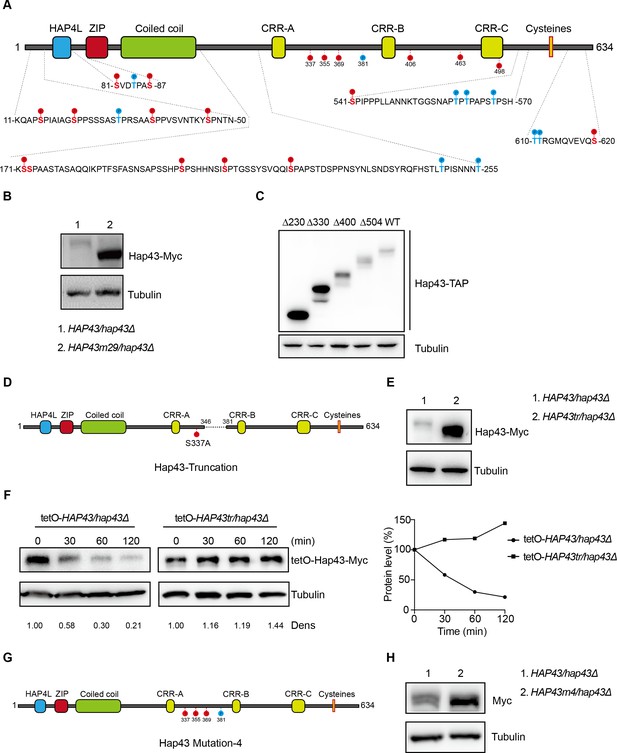
The critical phosphorylation sites are essential for Hap43 stabilization.
(A) Schematic representation of C. albicans Hap43. Putative phosphorylation sites predicted by the Kinasephos 2.0 server and Cdk8-dependent phosphorylation sites are represented. (B) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc in strains expressing either the WT or the amino acid mutation (HAP43m29; all 29 putative S/T phosphorylation sites were replaced with alanine residues) allele of Hap43. Cells were treated at high iron conditions. (C) Immunoblots of Hap43-TAP in WT and truncation mutant strains grown under iron-replete conditions. (D) Schematic representation of C. albicans Hap43 truncation. Hap43 truncation mutation (HAP43tr) was generated by deleting the 36 residues (346–381 aa) of Hap43 in HAP43S337A strain. (E) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc in strains expressing either the WT or the truncation mutation (HAP43tr) allele of Hap43. Cells were treated at high iron conditions. (F) Strains expressing either the WT or the truncation mutation (HAP43tr) allele of Hap43 under control of the inducible tetO promoter were treated with doxycycline. Cells were harvested in the exponential phase of growth, washed to remove doxycycline, and resuspended in fresh iron-replete medium (YPD). The turnover of Hap43-Myc in WT or truncation mutant cells was then evaluated following the tetO promoter shut-off by removal of doxycycline, through time-course experiments. Right panel: Hap43-Myc quantification after intensity analysis using ImageJ. (G) Schematic representation of C. albicans Hap43 mutation-4 (HAP43m4). Four putative S/T phosphorylation sites (S337/S355/S369/T381) in Hap43 were individually replaced with alanine residues. (H) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc in strains expressing either the WT or the amino acid substitution (HAP43m4) allele of Hap43. Similar to (E), cells were treated at high iron conditions.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 4.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig4-data1-v2.zip
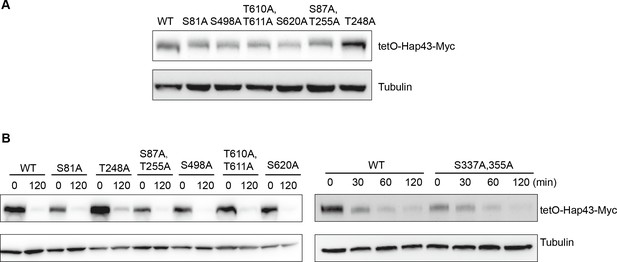
The Hap43 mutants harboring serine/threonine-to-alanine substitutions in its one or two putative phosphorylation sites showed the WT-like degradation patterns of Hap43 under high iron conditions.
(A) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc in strains expressing the indicated amino acid substitution allele of Hap43. Cells were treated at high iron conditions. (B) Strains expressing the indicated amino acid substitution allele of Hap43 under control of the inducible tetO promoter were treated with doxycycline. Cells were harvested in the exponential phase of growth, washed to remove doxycycline, and resuspended in fresh iron-replete medium. The turnover of Hap43-Myc in WT or relative mutant cells was then evaluated at 2 hr following the tetO promoter shut-off by removal of doxycycline. For raw blots, see Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1.
-
Figure 4—figure supplement 1—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig4-figsupp1-data1-v2.zip
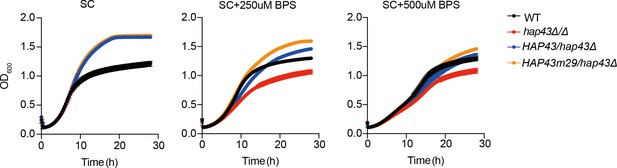
The mutants harboring amino acid substitutions or fragment truncation showed no defects in vegetative growth.
Growth curve analysis of HAP43 mutant strain harboring 29-point mutations in YPD liquid medium supplemented with 250 μM or 500 μM the impermeable iron chelator bathophenanthroline disulfonate (BPS) at 30°C. OD600 readings were obtained every 15 min in a BioTek Synergy 2 Multi-mode Microplate Reader.
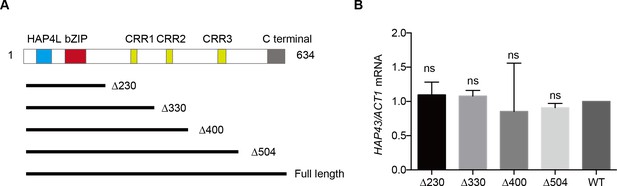
The critical phosphorylation region is essential for Hap43 stabilization.
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating the Hap43 truncation proteins used as part of this study. The positions of the major domains identified in individuals with Hap43 are indicated. Numbers indicate the positions of the first and last amino acids, relative to the full-length protein. (B) qRT-PCR analysis for HAP43 mRNA in WT and truncation mutant strains grown under iron-replete conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; compared to WT, by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test (B).
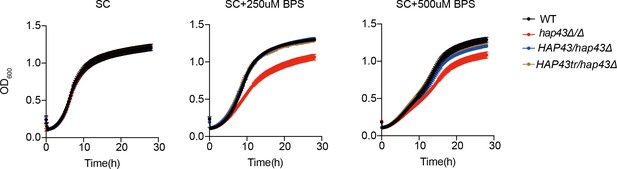
The mutants harboring amino acid substitutions or fragment truncation showed no defects in vegetative growth.
Growth curve analysis of Hap43 truncation in YPD liquid medium supplemented with 250 μM or 500 μM the impermeable iron chelator bathophenanthroline disulfonate (BPS) at 30°C. OD600 readings were obtained every 15 min in a BioTek Synergy 2 Multi-mode Microplate Reader.
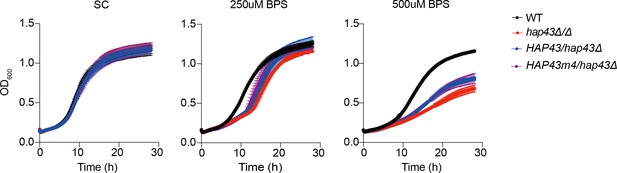
The HAP43 mutant-4 strain (HAP43m4/hap43Δ) harboring amino acid substitutions showed no defects in vegetative growth.
Growth curve analysis of indicated strains in SC liquid medium supplemented with 250 uM or 500 uM the impermeable iron chelator bathophenanthroline disulfonate (BPS) at 30°C. OD600 readings were obtained every 15 min in a BioTek Synergy 2 Multi-mode Microplate Reader.
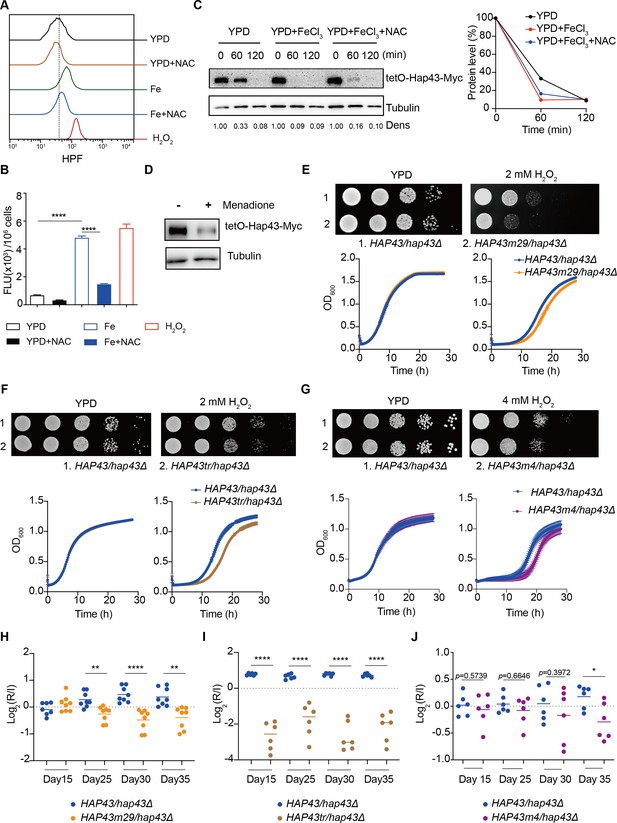
Hap43 phosphorylation is important for alleviating Fenton reaction-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) toxicity and for gastrointestinal (GI) colonization.
(A, B) Intracellular ROS production of C. albicans under different experimental conditions. C. albicans yeast cells were grown on YPD supplemented with indicated reagents. About 1 × 107 cells in exponential growth phase were collected, washed with PBS, stained with 5 mM of HPF, and analyzed using FACS (A) or the microplate reader (B). (C, D) Hap43 stability assay by immunoblots in WT strain stably expressing doxycycline-inducible Myc-tagged Hap43 (TetO-Hap43-Myc). Exponential-phase cells grown in iron-replete (YPD) medium supplemented with 50 μg/ml doxycycline were harvested, washed, and resuspended in fresh YPD medium only, YPD supplemented with 200 μM FeCl3, a combination of 200 μM FeCl3 and 20 mM N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) (C) or 20 μM menadione for 120 min (D). (E–G) Growth of different C. albicans strains, including WT (HAP43/hap43Δ), HAP43m29 mutant (E) or HAP43tr truncation mutant (F) or HAP43m4 mutant (G), under oxidative stresses. Top panel: strains were spotted with tenfold serial dilutions onto YPD or YPD supplemented with 2 mM H2O2 and grown for 2 d at 30℃. Bottom panel: growth curve analysis of strains in YPD liquid medium supplemented with 2 mM or 4 mM H2O2 at 30°C. OD600 readings were obtained every 15 min in a BioTek Synergy 2 Multi-mode Microplate Reader. (H–J) Each of the HAP43 mutants, including HAP43m29 mutant (H), HAP43tr truncation mutant (Hap43tr) (I), or HAP43m4 mutant (J), exhibits decreased commensal fitness in mice. Similar to Figure 1F, mice (n = 6 or 8) were inoculated by gavage with 1:1 mixtures of the WT and each of the Hap43 mutant strains (1 × 108 CFU per mice). The fitness value for each strain was calculated as the log2 ratio of its relative abundance in the recovered pool from the host (R) to the initial inoculum (I), and was determined by qPCR using strain-specific primers that could distinguish one from another. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ****p<0.0001; by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s test (B) or unpaired Student’s t-test (H–J).
-
Figure 5—source data 1
Uncropped images of gels and blots in Figure 5.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-fig5-data1-v2.zip
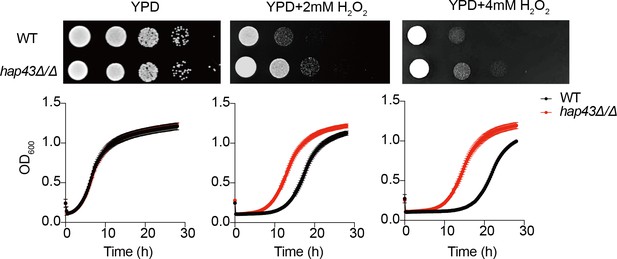
Growth of the hap43Δ/Δ mutant under oxidative stresses.
Top panel: WT and hap43Δ/Δ mutant cells were spotted with tenfold serial dilutions onto YPD or YPD supplemented with 2 mM or 4 mM H2O2 and grown for 2 d at 30℃. Bottom panel: growth curve analysis of WT and hap43Δ/Δ in YPD liquid medium supplemented with 2 mM or 4 mM H2O2 at 30°C. OD600 readings were obtained every 15 min in a BioTek Synergy 2 Multi-mode Microplate Reader.
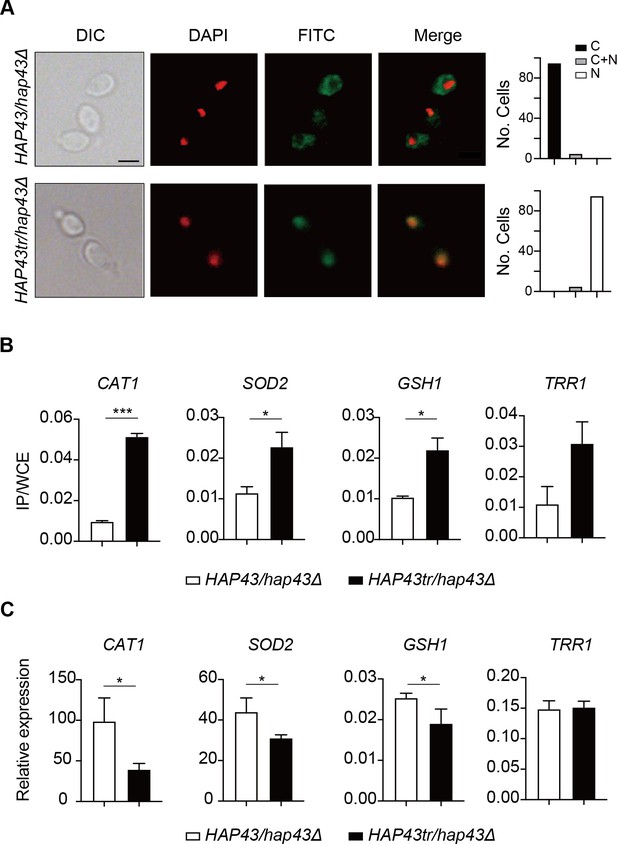
Iron-induced phosphorylation and degradation of Hap43 leads to de-repression of antioxidant genes.
(A) Left panels: indirect immunofluorescence of Hap43-Myc in HAP43/hap43Δ and HAP43tr/hap43Δ strains grown under iron-replete conditions. DIC represents phase images, DAPI represents nuclear staining, FITC represents Hap43-Myc staining, and Merge represents the overlay of Hap43-Myc and nuclear staining. Right panels: quantification of the cellular distribution of Hap43. Each bar represents the analysis of at least 100 cells. C representing >90% cytoplasmic staining, N > 90% nuclear staining, and C + N a mixture of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) ChIP of Hap43-Myc on the promoters that contain CCAAT boxes in a set of antioxidant genes. Overnight cultures of WT (HAP43/hap43Δ) and truncation mutant (HAP43tr/hap43Δ) cells were diluted in YPD plus 400 mM FeCl3 and grown to log phase at 30℃ before formaldehyde. Enrichment is presented as a ratio of qPCR of the indicated gene promoter IP (bound/input) over an ACT1 control region IP (bound/input) of the tagged strain, further normalized to the control strain. (C) qRT-PCR analysis for mRNA levels of a set of antioxidant genes in WT (HAP43/hap43Δ) and truncation mutant (HAP43tr/hap43Δ) strains grown under iron-replete conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; by unpaired Student’s t-test (B, C).
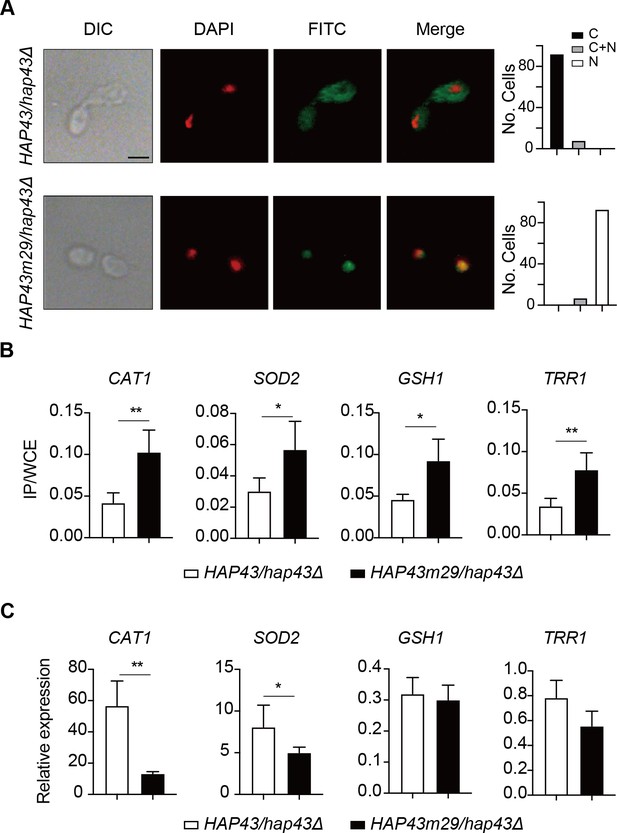
Iron-induced phosphorylation and degradation of Hap43 leads to de-repression of antioxidant genes.
Shown are the results about a comparison between WT and Hap43m29 mutant. (A) Left panels: indirect immunofluorescence of Hap43-Myc in HAP43/hap43Δ and HAP43m29/hap43Δ strains grown under iron-replete conditions. DIC represents phase images, DAPI represents nuclear staining, FITC represents Hap43-Myc staining, and Merge represents the overlay of Hap43-Myc and nuclear staining. Right panels: quantification of the cellular distribution of Hap43. Each bar represents the analysis of at least 100 cells. C representing >90% cytoplasmic staining, N > 90% nuclear staining, and C + N a mixture of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) ChIP of Hap43-Myc on the promoters that contain CCAAT boxes in a set of antioxidant genes. Overnight cultures of WT (HAP43/hap43Δ) and mutant harboring 29 substitutions (HAP43m29/hap43Δ) were grown and treated exactly the same way as described in Figure 6b. (C) qRT-PCR analysis for mRNA levels of a set of antioxidant genes in WT (HAP43/hap43Δ) and mutant harboring 29 substitutions (HAP43m29/hap43Δ) grown under iron-replete conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; by unpaired Student’s t-test (B, C).
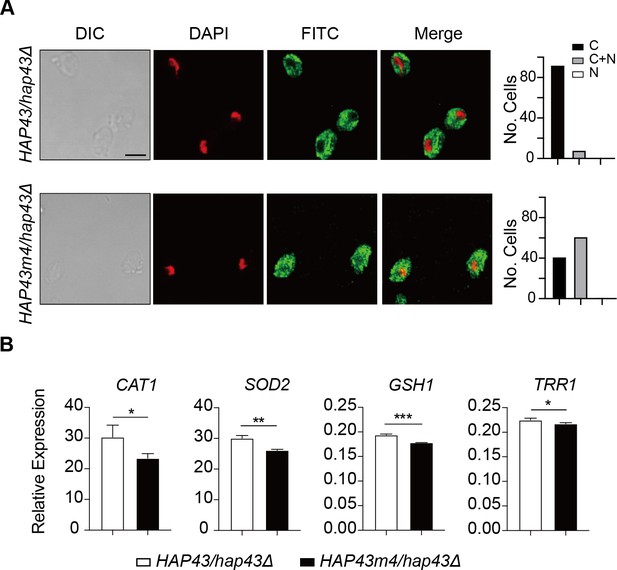
Iron-induced phosphorylation and degradation of Hap43 leads to de-repression of antioxidant genes.
Shown are the results about a comparison between WT and Hap43m4 mutant. (A) Left panels: indirect immunofluorescence of Hap43-Myc in HAP43/hap43Δ and HAP43m4/hap43Δ strains grown under iron-replete conditions. DIC represents phase images, DAPI represents nuclear staining, FITC represents Hap43-Myc staining, and Merge represents the overlay of Hap43-Myc and nuclear staining. Right panels: quantification of the cellular distribution of Hap43. Each bar represents the analysis of at least 100 cells. C representing >90% cytoplasmic staining, N > 90% nuclear staining, and C + N a mixture of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) qRT-PCR analysis for mRNA levels of a set of antioxidant genes in WT (HAP43/hap43Δ) and mutant harboring four amino acid substitutions (HAP43m4/hap43Δ) grown under iron-replete conditions. Transcript levels were normalized to the level of ACT1 mRNA. Results from three independent experiments are shown. All data shown are means ± SD. ns, no significance; *p<0.05; **p<0.01; by unpaired Student’s t-test (B).
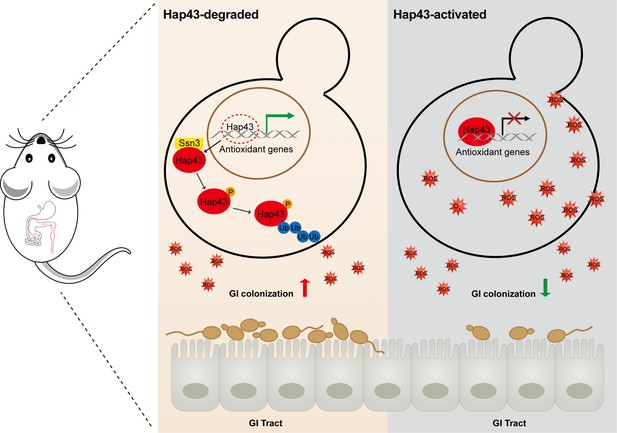
Model for the role of post-translational medication of Hap43 in promoting gastrointestinal (GI) commensalism of C. albicans.
In the iron-rich environment such as GI tract, the iron-responsive regulator Hap43 is subject to covalent post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation and ubiquitination, and causes cytoplasm-nuclear relocation and protein degradation via proteasome activity, thus serving as a positive signal to de-repress the expression of a set of antioxidant genes (e.g. CAT1 and SOD2), an event that is most effective in lowering cytotoxicity induced by iron-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and promotes C. albicans commensalism in GI tract.
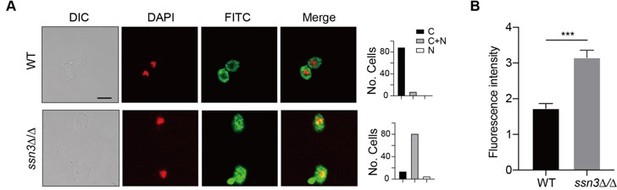
(A) Left panels: Indirect immunofluorescence of Hap43-Myc in WT and ssn3Δ/Δ mutant strains grown under iron-replete conditions. DIC represents phase images, DAPI represents nuclear staining, FITC represents Hap43-Myc staining, and Merge represents the overlay of Hap43-Myc and nuclear staining. Right panels: Quantification of the cellular distribution of Hap43. Each bar represents the analysis of at least 100 cells. C representing >90% cytoplasmic staining, N >90% nuclear staining, and C+N a mixture of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Quantification of fluorescence in images of A.
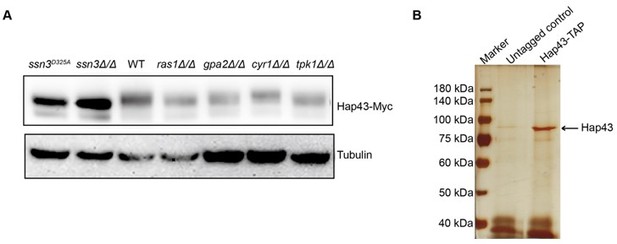
(A) Immunoblots of Hap43-Myc recovered from indicated C. albicans cells under iron-replete conditions. a-tubulin, internal standard. (B) Strain expressing Hap43-TAP was inoculated to YPD medium and grown overnight at 30oC for protein purification. Cell extracts were sequentially immunoprecipitated with lgG Sepharose and calmodulin Sepharose. Proteins were identified by gel electrophoresis separation and silver staining. The arrow represents Hap43.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Strains (a), plasmids (b), and primers (c) used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-supp1-v2.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/86075/elife-86075-mdarchecklist1-v2.docx





