A critical evaluation of protein kinase regulation by activation loop autophosphorylation
Figures
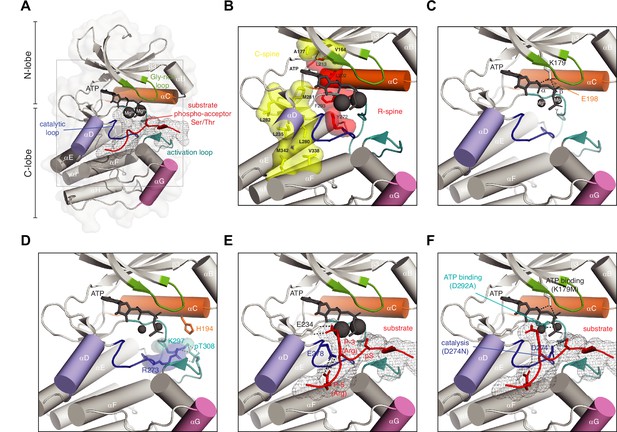
Anatomy of a protein kinase.
(A) Basic anatomy of a protein kinase. Important elements in catalysis and regulation are highlighted in color: glycine-rich loop (green), αC helix (orange), αD helix (purple), αG helix (pink), activation loop (teal), catalytic loop (blue), substrate peptide (red) (B) Regulatory (red) and catalytic (yellow) spines of a protein kinase that define the active conformation. Residue numbering according to Akt1 (PDB ID: 4ekk). (C) Conserved salt bridge between lysine in strand β3 and glutamate in αC helix that defines the active kinase conformation. (D) Network of hydrogen bonds that stabilizes the ordered conformation of the activation loop in Akt1 and anchors it to the surface of the kinase domain. (E) Substrate recognition by Akt1. Substrate peptide derived from GSK3β (gray mesh, red cartoon) makes specific interactions with conserved glutamates in the kinase domain of Akt1 via arginine side chains in the P-3 and P-5 positions. Residues C-terminal to the phospho-acceptor residue participate in an antiparallel beta-sheet interaction with the activation loop. (F) Ways to make an inactive kinase. Mutation of the β3 lysine (K179M), which abrogates ATP binding; mutation of the DFG aspartate (D292A), which abrogates magnesium and ATP binding; mutation of the catalytic aspartate (D274N), which prevents polarization of the substrate hydroxyl and blocks catalysis.
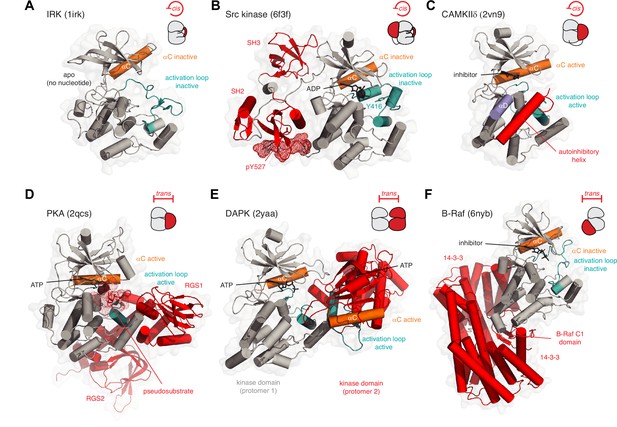
Kinase inhibition in cis and trans.
(A) Inhibition of insulin receptor kinase (IRK) in cis. The activation loop (teal) of IRK adopts a conformation in which it prevents the binding of ATP and displaces the αC helix into an inactive conformation. PDB ID: 1irk. (B) Inhibition of Src tyrosine kinase in cis. The regulatory SH3 and SH2 domains (red) help maintain the kinase domain (gray) in an inactive conformation. The activation loop (teal) adopts an inactive conformation in which Y416 is sequestered in an unphosphorylatable conformation and the nucleotide-binding site is occupied by ADP. The phosphorylated C-terminal tail of the kinase domain (pY527, red mesh) binds intramolecularly to the SH2 domain, thereby inhibiting its activation. PDB ID: 6f3f. (C) Inhibition of CAMKIIδ in cis. A C-terminal autoinhibitory helix (red) in CAMKIIδ occupies the substrate binding surface. PDB ID: 2vn9. (D) Inhibition of PKA in trans. In the absence of cAMP, the regulatory subunit of PKA (red) binds to the catalytic subunit and inserts its N-terminal pseudosubstrate segment (red mesh) into the substrate binding cleft. PDB ID: 2qcs. (E) Inhibition of DAPK in trans. Face-to-face dimerization of DAPK (one protomer of DAPK in red) blocks substrate binding. PDB ID: 2yaa. (F) Inhibition of B-Raf in trans. Binding of 14-3-3 proteins (red) to phosphorylated B-Raf traps its C1 and kinase domains in an autoinhibited conformation in which the kinase domain of Raf is incapable of forming the back-to-back dimer required for its activation. PDB ID: 6nyb.
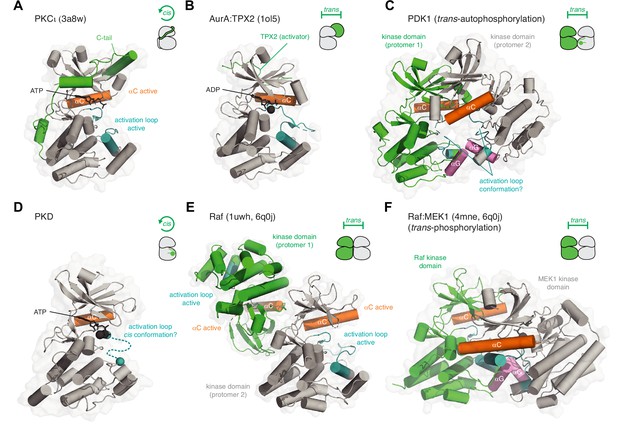
Kinase activation in cis and trans.
(A) Activation of PKCι in cis. The C-terminal AGC-specific extension of the kinase domain activates PKC by inserting various short linear motifs into regulatory pockets on the surface of the kinase domain. PDB ID: 3a8w. (B) Activation of AurA by TPX2 in trans. TPX2 inserts a hydrophobic motif into a pocket on the back side of the kinase domain N-lobe in an analogous manner to the hydrophobic motif of PKCι. PDB ID: 1ol5. (C) Activation of PDK1 by trans-autophosphorylation. Dimerization of the kinase domains via their αG helices (pink) drives trans-autophosphorylation of Ser241 in its activation loop. AlphaFold prediction. The mechanism of the reaction and conformation of the activation loop (teal) remains to be determined. (D) Activation of PKD1 by cis-autophosphorylation. Dissociation of an inactive face-to-face dimer of PKD1 kinase domains leads to activation loop cis-autophosphorylation. The mechanism of the reaction and conformation of the activation loop (teal) remains to be determined. (E) Activation of B-Raf by back-to-back dimerization of its kinase domains (trans). The back-to-back dimer interface stabilizes the active conformation of the αC helix (orange) and activation loop (teal) of each protomer. PDB ID: 1uwh, 6q0j. (F) Activation of MEK1 by Raf-mediated phosphorylation of its activation loop in trans. B-Raf and MEK1 form a heterodimer via their αG helices, homologous to the dimerization of PDK1. The mechanism of the reaction and conformation of the activation loop(s) (teal) remain to be determined. PDB ID: 4mne, 6q0j.

Interpreting biochemical evidence for cis and trans autophosphorylation.
(A) Common methods to assay autophosphorylation and their capacity to differentiate stoichiometric mono-phosphorylation (black), from sub-stoichiometric (blue) or super-stoichiometric (magenta) phosphorylation. (B) Common approaches to manipulate the monomer-dimer equilibrium of a kinase population in vitro to investigate its effect on autophosphorylation. (C) Hypothetical outcomes of dimerization in a kinase autophosphorylation assay. If autophosphorylation increases or decreases with increasing dimerization the reaction is autoactivated or autoinhibited, respectively, in trans. Both cis- and trans-autophosphorylation can be regulated in trans. An autophosphorylation reaction that is unaffected by dimerization is not subject to trans-autoregulation and likely proceeds in cis. (D) Catalytically inactive kinases can be phosphorylated in trans by an active kinase, but not in cis. This can be used to discriminate the reaction mode.
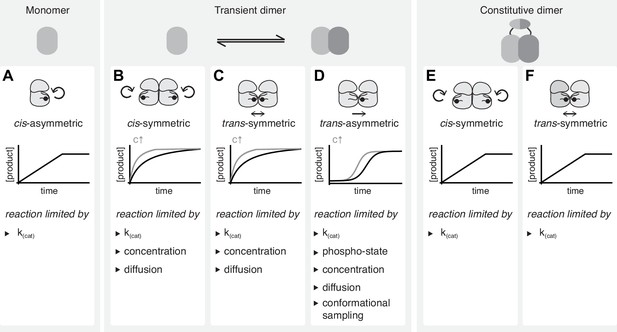
Interpreting kinetic evidence for cis- and trans-autophosphorylation.
(A) Kinases that do not dimerize can undergo autophosphorylation only in cis. These asymmetric reactions don’t require collision events and are limited only by their intrinsic catalytic rate. They result in linear reaction kinetics. (B) Autophosphorylation reactions that are dependent on transient dimerization include trans-autoactivated cis- and trans-autophosphorylation. Symmetric cis-autophosphorylation is triggered by the collision with a second kinase (assuming that the activating interaction is phospho-state independent) and, therefore, limited by diffusion and concentration, and proceeds with non-linear kinetics. (C) Symmetric trans-autophosphorylation is dependent on the collision of two unphosphorylated kinase molecules that phosphorylate each other in a reciprocal reaction which is substrate-limited and proceeds with non-linear kinetics. (D) In the asymmetric trans-autophosphorylation reaction, one kinase molecule (enzyme) stochastically adopts an ordered activation loop conformation and phosphorylates a second copy (substrate) that presents its activation loop. Upon phosphorylation, the catalytic rate of the kinase increases and the substrate is depleted. This leads to an initial lag phase followed by an exponential phase and a plateau. Such reactions are limited by stochastic conformational sampling and the changing catalytic activity of the population. (E) In the context of a constitutively dimeric kinase symmetric cis-autophosphorylation is limited only by the intrinsic catalytic rate and proceeds with linear kinetics. (F) In the context of a constitutively dimeric kinase symmetric trans-autophosphorylation is limited only by the intrinsic catalytic rate and proceeds with linear kinetics.
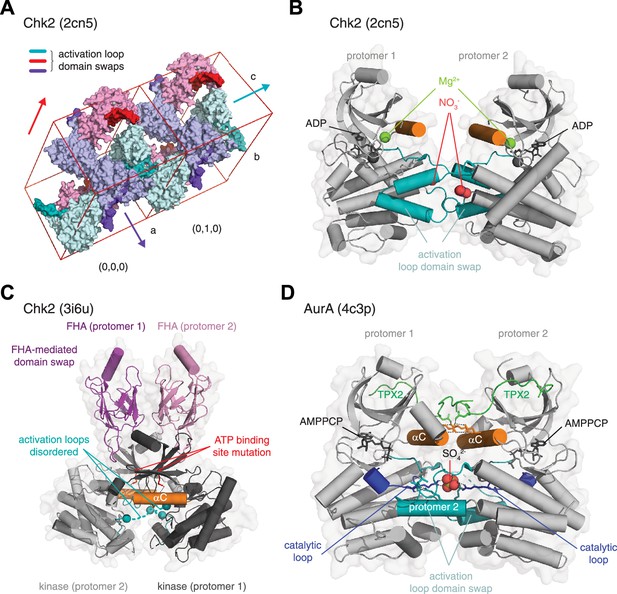
Interpreting crystallographic evidence for kinase dimerization.
(A) Crystal lattice formation in crystals of the checkpoint kinase (Chk2) domain in complex with ADP. The unit cell contains six molecules (cyan, purple, pink), which form dimers on three twofold crystallographic axes. These are mediated by the extended activation loops (dark color) of Chk2 that undergo activation loop exchange, in which residues 377–397 make either identical interactions with their crystallographically-related partner, or they make interactions with a neighboring molecule in the crystal lattice. Packing of the unit cells and, therefore, propagation of the lattice is mediated in part by the interactions of the activation loops of neighboring molecules. PDB ID: 2cn5. (B) Zoom in to the activation loop exchange of Chk2 in the 2cn5 lattice shown in A. The conformation of the Chk2 kinase domain is stabilized by reagents from the crystallization reservoir solution including nitrate (red spheres). One magnesium ion also occupies a non-physiological position in the kinase domain of each Chk2 molecule (green spheres). PDB ID: 2cn5. (C) Structure of a domain-swapped Chk2 construct containing both its regulatory FHA (magenta, pink) and catalytic kinase domains (gray, black). The asymmetric unit of the crystal lattice contains two molecules of Chk2 in which a face-to-face dimer of the kinase domains is mediated by a domain swap of the FHA domains of each protomer. The crystallized protein contains a kinase-inactivating point mutation of the β3 lysine (K249R), which abrogates ATP binding. The activation loops (teal) of each protomer are mainly disordered (dashed lines). PDB ID: 3i6u. (D) Structure of AurA in complex with TPX2. The asymmetric unit of the crystal lattice contains two molecules of AurA arranged in an asymmetric face-to-face dimer. A sulfate molecule in the center of the dimer stabilizes an exchange of the activation loop of each protomer by making a network of hydrogen bonds with the conserved arginine of the catalytic loop (blue, stick representation). Additional interactions that stabilize the dimer are mediated by electrostatic interactions between the αC helix (orange) and TPX2 (green). AurA was co-crystallized with AMPPCP, but is in an inactive conformation. PDB ID: 4c3p.
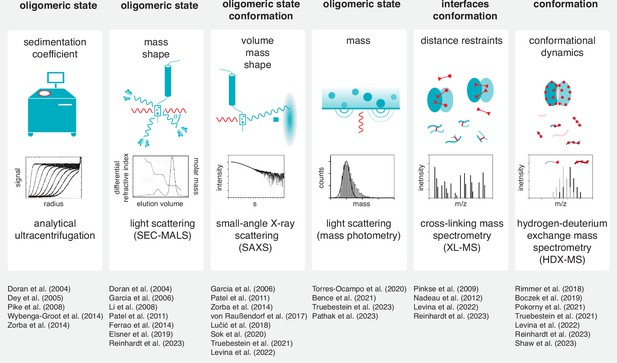
Tools to study kinase dimerization and autophosphorylation in solution.
Physical parameters that are measured by each technique are listed alongside the biological questions that can be addressed. Each technique is accompanied by a list of example studies in which the technique has been successfully applied. (Boczek et al., 2019; Doran et al., 2004; Garcia et al., 2006; Hajdusits et al., 2021; Li et al., 2008; Lučić et al., 2018; Nadeau et al., 2012; Pathak et al., 2023; Pinkse et al., 2009; Rimmer et al., 2018; Shaw et al., 2023; Sok et al., 2020; Torres-Ocampo et al., 2020).

The enigma of autophosphorylation.
(A) Activation loop autophosphorylation requires the activity of the kinase before it is itself phosphorylated on its activation loop. Logic dictates that the autophosphorylation reaction must, therefore, be mechanistically distinct from substrate phosphorylation. (B) Distinct mechanistic aspects of auto- and substrate phosphorylation. Substrate phosphorylation is always an asymmetric trans reaction while autophosphorylation can occur in distinct reaction modes. Sequence recognition can vary, depending on the structural context, such that the activation loop is not recognized as a substrate if supplied as a peptide in trans. The substrate sequence can also vary between the activation loop and downstream substrates. (C) Protein abundance levels were plotted against their RNA transcript levels from a proteome-wide screen in HEK293 cells. The abundance of kinases (black) is in the nanomolar range and relatively low in comparison to the total proteome (gray). Kinases that depend on activation loop autophosphorylation are generally expressed in the nanomolar concentration range, suggesting that trans-autoregulated kinases need a dedicated mechanism for dimerization. (D) Structure of the kinase domain of insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR) in a dimeric, face-to-face configuration in which the activation loop (purple-blue) of each protomer makes symmetric interactions with the catalytic site of the opposing protomer, presenting Y1135 of the activation loop in trans. PDB ID: 3d94. (ref = reference molecule). (E) Structure of the kinase domain of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) in a dimeric, face-to-face configuration in which the activation loop (salmon) of one protomer makes asymmetric contacts with the catalytic site of the opposing protomer, presenting Y647 of the activation loop in trans. PDB ID: 6pnx. (ref = reference molecule). (F) Activation loop trajectories of unphosphorylated insulin receptor kinase (IRK) (magenta), phosphorylated IRK (teal), IGFR in the trans, symmetric conformation (purple-blue), and FGFR in the trans, asymmetric conformation (salmon), displayed on the surface of the phosphorylated IRK kinase domain. PDB IDs: 1irk, 1ir3, 3d94, 6pnx. (G) B-factor plot for IRK kinase domain (apo structure, PDB ID: 1irk). High B-factors for the activation loop indicate that it is the most mobile (and least ordered) region of the kinase domain. (H) Zoom-in on the kinase-activation loop interactions observed in: phosphorylated IRK in complex with a substrate peptide (red), unphosphorylated IRK with its own activation loop in cis (magenta), IGFR with the activation loop of the opposing protomer in trans (symmetric, purple-blue), and FGFR with the activation loop of the opposing protomer in trans (asymmetric, pink). PDB IDs: 1irk, 1ir3, 3d94, 6pnx.





