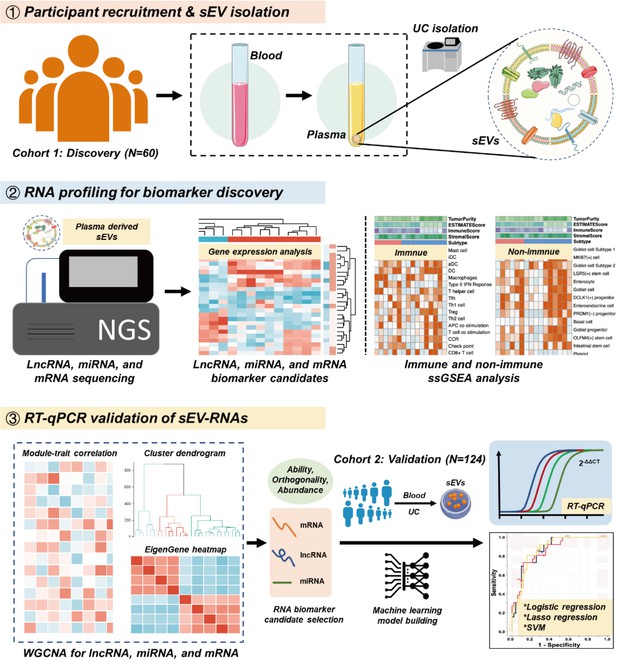
Circulating small extracellular vesicle RNA profiling for the detection of T1a stage colorectal cancer and precancerous advanced adenoma
Figures
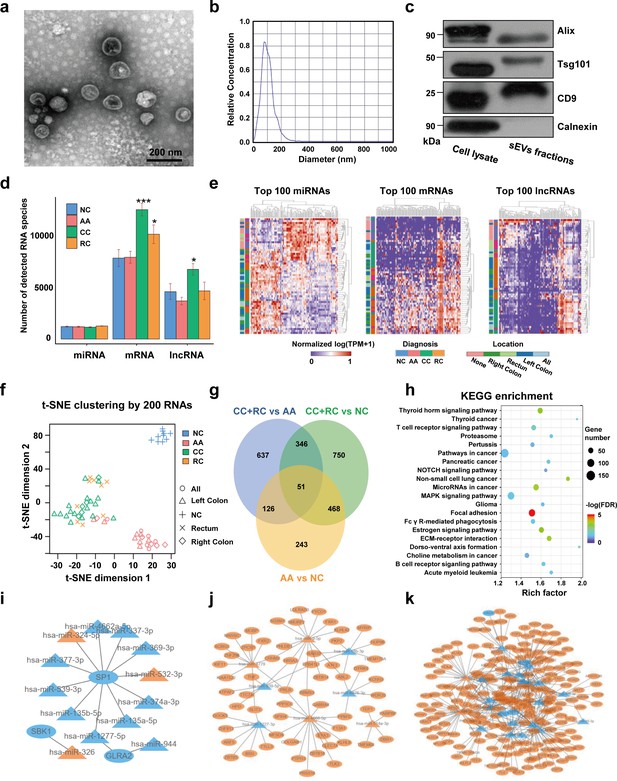
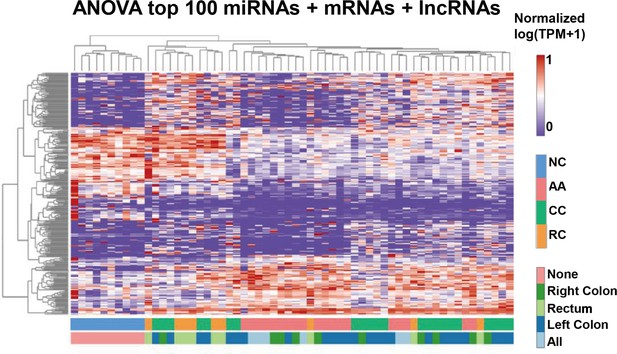
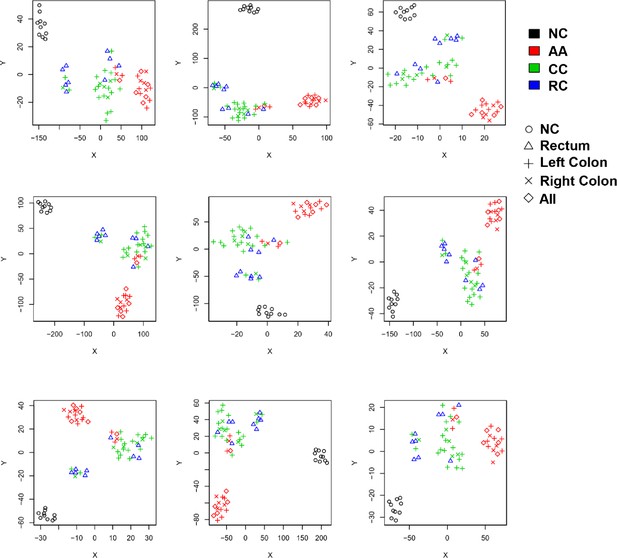
Transcriptome profiling of circulating sEVs.
(a) TEM images of circulating sEVs isolated from human plasma. (b) NTA results of circulating sEVs enriched from plasma. (c) WB results of sEV positive (Alix, TSG101, CD9) and negative (Calnexin) markers. (d) The numbers of detected RNA species in different groups. (e) The hierarchical clustering results of top 100 miRNAs (left panel), mRNAs (middle panel), and lncRNAs (right panel). (f) t-SNE clustering by those candidate RNAs. (g) A Venn diagram showed DEGs shared between different comparisons (CRC vs NC, AA vs NC, CRC vs AA). (h) KEGG enrichment of all those DEGs identified. (i–k) potential core regulatory networks between miRNAs and mRNAs in DEGs identified in three (i), two (j), and one (k) of all comparisons.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Original file for the western blot analysis in Figure 2C (anti-Alix, anti-CD9, anti-TSG101, and anti-Calnexin).
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-fig2-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Figures containing Figure 2C and original scans of the relevant western blot analysis (anti-Alix, anti-CD9, anti-TSG101, and anti-Calnexin) with highlighted bands and sample labels.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-fig2-data2-v1.zip
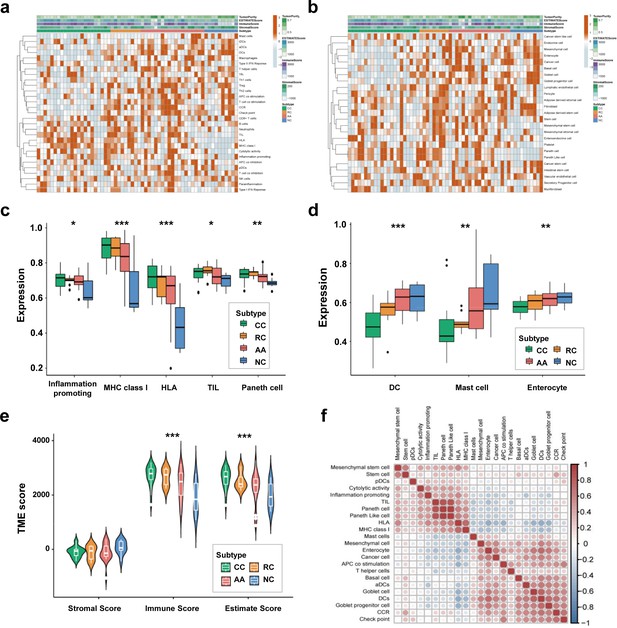
Cell-specific features of the sEV-RNA profile.
(a) The hierarchical clustering heatmap of immune cell-specific features of each sample. (b) The hierarchical clustering heatmap of stromal-related features of each sample. (c) Boxplot of cell-specific features overexpressed in CC and RC patients (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (d) Boxplot of cell-specific features overexpressed in NC participants (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (e) The violinplot of the microenvironmental scores in different subgroups (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).(f) Correlation among cell-specific features differentially enriched among different groups.
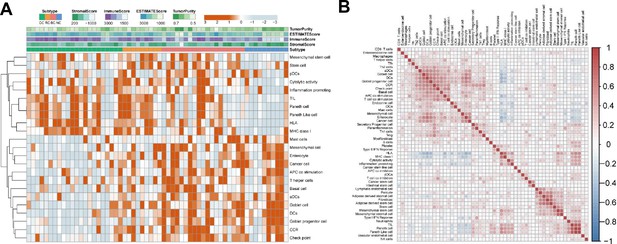
Cell-specific features of the sEV-RNA profile.
(A) The hierarchical clustering heatmap of different cell features in all sEV samples. (B) Correlation among all cell-specific features.
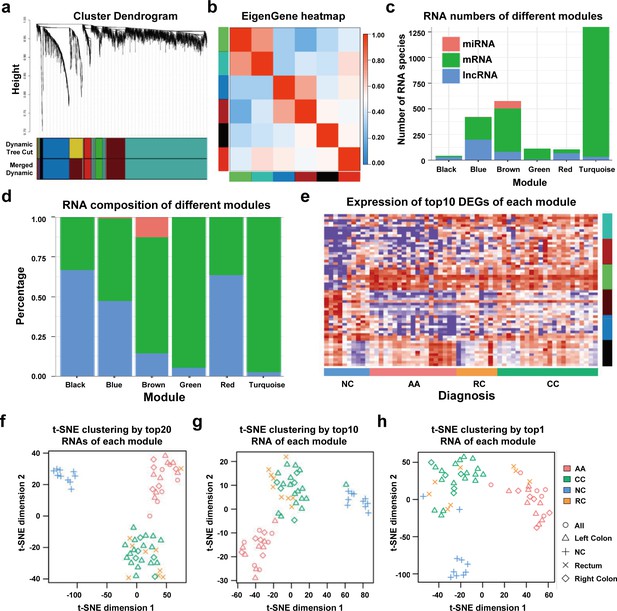
WGCNA analysis of sEV-RNAs.
(a) Gene coexpression module construction of all DEGs identified in sEV-RNAs. (b) The heatmap exhibited Pearson correlations among different modules. (c) Bar plot of module composition of different modules (all DEGs). (d) Percentage bar plot of the RNA composition of different modules (all DEGs). (e) A heatmap exhibited the expression levels of the top 10 DEGs in each module. (f) t-SNE clustering by the top 10 DEGs in each module. (g) t-SNE clustering by the top 5 DEGs in each module. (h) t-SNE clustering by the top1 DEGs in each module.
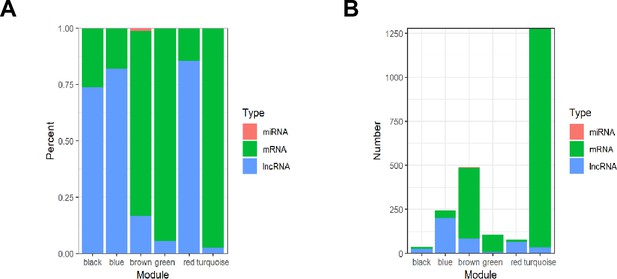
Proportions and numbers of RNA species in different modules.
(A) Percentage barplot of the RNA composition of different modules (only DEGs with kME >0.7). (B) Barplot of module composition of different modules (only DEGs with kME >0.7).
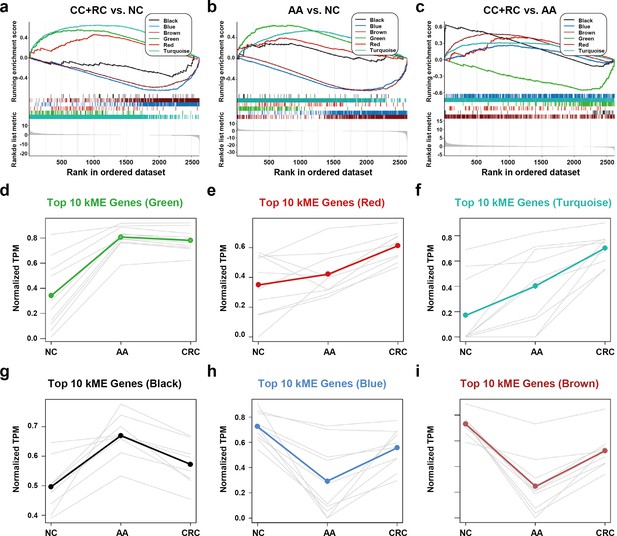
The expression trends of sEV-RNA modules.
(a–c) GSEA analysis of DEGs in different modules (a: CRC vs. NC; b: AA vs. NC; c: CRC vs. AA). (d-i) The expression trends of the Top 10 DEGs of each module among NC, AA, and CRC (d: green module; e: red module; f: turquoise module; g: black module; h: blue module; i: brown module).
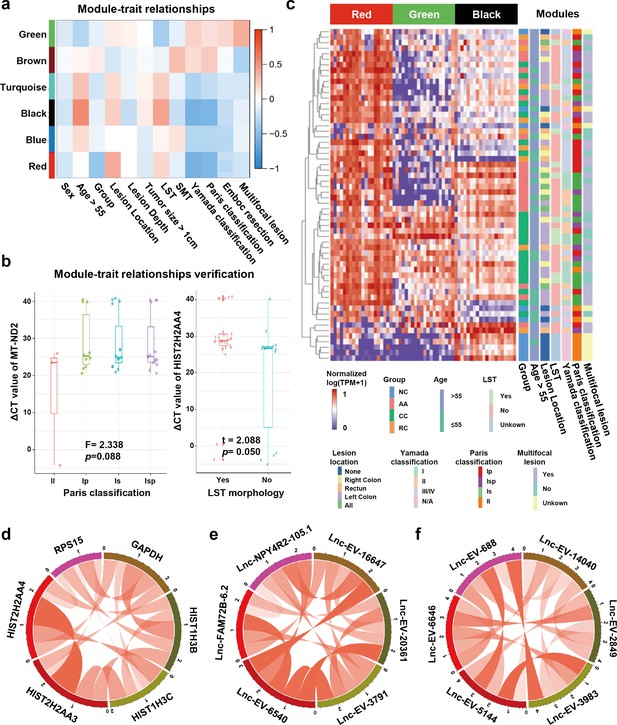
Module-trait correlation analysis of sEV-RNA modules.
(a) The heatmap exhibited the correlation between modules and clinical traits. (b) The RT-qPCR validation of representive module-trait correlation (left panel: correlation between MT-ND2 and Paris classification; right panel: correlation between HIST2H2AA4 and LST morphology). (c) The heatmap exhibited the sEV-RNA expression levels of red, black, and green modules. (d-f) Circos plot showed the inner correlations among sEV-RNAs in the module green (d), red (e), and black (f).
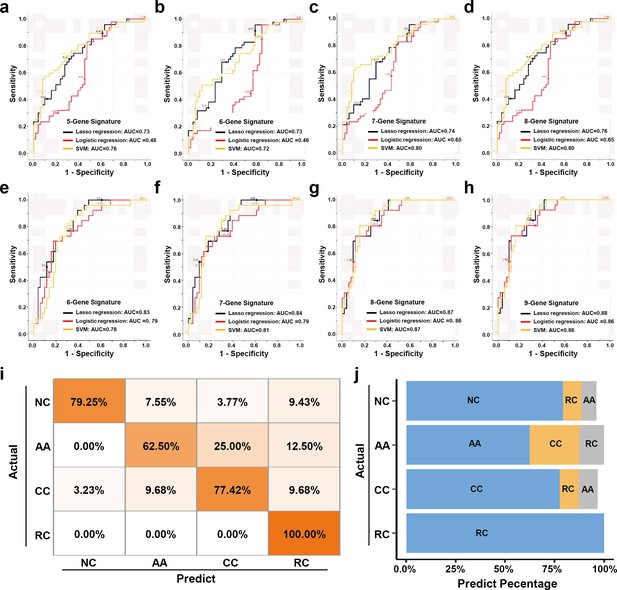
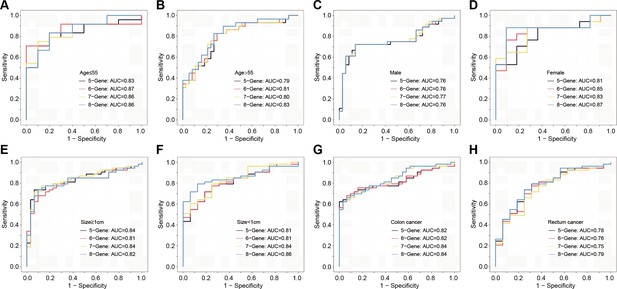
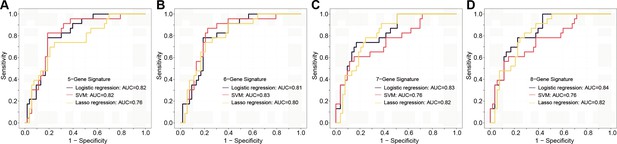
The plasma sEVs-RNA signature to detect early CRC and AA.
(a–d) The ROC analysis of different sEV-RNA signatures in the prediction of CRC patients by different algorithms (a: 5-gene panel; b: 6-gene panel; c: 7-gene panel; d: 8-gene panel). (e–h) The ROC analysis of different sEV-RNA signatures in the prediction of AA patients by different algorithms (e: 6-gene panel; f: 7-gene panel; g: 8-gene panel; h: 9-gene panel). (i) The QDA results of all 13 sEV-RNAs in classifying all samples. (j) Statistical summary of QDA performance in each sample group.
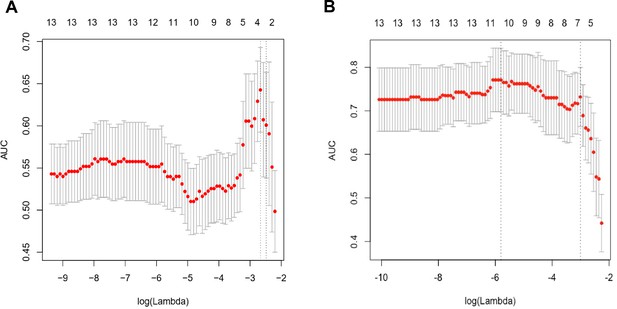
Lasso regression to construct multivariate prediction models.
(A) Performance of Lasso regression in variable selection to identify CRC. (B) Performance of Lasso regression in variable selection to identify AA.
The ROC analysis of different sEV-RNA signatures in the prediction of stage I CRC patients by different algorithms (a: 6-gene panel; b: 7-gene panel; c: 8-gene panel; d: 9-gene panel).
Tables
Selection of plasma sEVs-RNA candidates for AA and T1a stage CRC diagnosis.
| Candidate | AA vs NC | CRC vs NC | CRC vs AA | Module attribution | RNA Type | Amount | Finally seclected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-3615 | +* | + | -† | brown | miRNA | High | Yes |
| miR-330–5 p | + | + | - | brown | miRNA | Low | No |
| miR-425–5 p | + | + | - | NA | miRNA | High | Yes |
| miR-106b-3p | + | + | - | NA | miRNA | High | Yes |
| miR-589–5 p | + | + | - | NA | miRNA | Low | No |
| miR-181a-2–3 p | + | + | - | brown | miRNA | Low | No |
| Let-7f-5p | - | - | + | NA | miRNA | High | Yes |
| Let-7e-5p | - | - | + | NA | miRNA | High | No |
| miR-320a/b-3p | - | - | + | brown | miRNA | High | Yes |
| miR-664a-5p | - | - | + | brown | miRNA | Low | No |
| YBX3 | - | + | + | turquoise | mRNA | Low | No |
| C19orf43 | - | + | + | turquoise | mRNA | Medium | Yes |
| TOP1 | + | + | - | turquoise | mRNA | Medium | Yes |
| PPDPF | + | + | - | brown | mRNA | Medium | Yes |
| MT-ND2 | + | + | - | blue | mRNA | High | Yes |
| HIST2H2AA4 | + | + | - | green | mRNA | Medium | Yes |
| RPL10 | + | + | - | green | mRNA | High | No |
| RPS29 | + | + | - | blue | mRNA | High | No |
| IST1 | - | + | + | black | mRNA | Low | No |
| CSE1L | - | + | - | red | mRNA | Low | No |
| lnc-MSI1-2:1 | + | + | - | brown | lncRNA | High | Yes |
| lnc-FCGR1B-16:1 | - | + | + | red | lncRNA | Low | No |
| lnc-NPY4R2-105:1 | - | + | + | red | lncRNA | Medium | No |
| lnc-MKRN2-42:1 | - | + | + | turquoise | lncRNA | High | Yes |
| LNC_EV_9572(Chr8: 34358093–34456247) | + | + | - | black | lncRNA | High | Yes |
| LNC_EV_21004(Chr21: 8212554–8440060) | + | + | - | brown | lncRNA | High | No |
| LNC_EV_15260(Chr14: 49555875–49923916) | + | + | - | turquoise | lncRNA | High | No |
-
*
+: significant difference found in this comparision.
-
†
-: no significant difference found in this comparision.
CRC and AA prediction models established by Lasso regression.
Additionally, we adopted quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) to demonstrate the possibility of the plasma sEV-RNA signature for direct sample classification. An overall accuracy of 78% (ranging from 63% to 100%) was obtained for direct sample classification (Figure 7ij). Generally, the individuals classified into AA/CC/RC are considered as high-risk and should be advised to further endoscopic examination, and our QDA classifier provided a specificity of 79.25%, and a sensitivity of 99.0% (with only one CC sample missed) in identifying those high-risk individuals. Together, our RT-qPCR-based plasma sEVs-RNA signature could be a powerful and better alternative to FIT and FOBT tests in CRC and precancerous AA screening programs.
| Model type | Signature | RNAs | Lambda | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRC prediction | 5-RNA signature | Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, lnc-MKRN2-42:1 | 0.05 | 0.73 |
| 6-RNA signature | Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, lnc-MKRN2-42:1, LNC-EV-9572 | 0.035 | 0.73 | |
| 7-RNA signature | Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, lnc-MKRN2-42:1, LNC-EV-9572, HIST2H2AA4 | 0.03 | 0.74 | |
| 8-RNA signature | Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, lnc-MKRN2-42:1, LNC-EV-9572, HIST2H2AA4, miR-320a-3p | 0.02 | 0.76 | |
| AA prediction | 6-RNA signature | miR-425–5 p, Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, LNC-EV-9572 | 0.05 | 0.83 |
| 7-RNA signature | miR-425–5 p, Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, LNC-EV-9572, lnc-MKRN2-42:1 | 0.04 | 0.84 | |
| 8-RNA signature | miR-425–5 p, Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, LNC-EV-9572, lnc-MKRN2-42:1, HIST2H2AA4 | 0.1 | 0.87 | |
| 9-RNA signature | miR-425–5 p, Let-7f-5p, C19orf43, TOP1, PPDPF, LNC-EV-9572, lnc-MKRN2-42:1, HIST2H2AA4, MT-ND2 | 0.05 | 0.88 |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
CRC vs NC mRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp1-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 2
CRC vs NC miRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp2-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 3
CRC vs NC lncRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp3-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 4
AA vs NC mRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp4-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 5
AA vs NC miRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp5-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 6
AA vs NC lncRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp6-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 7
CRC vs AA mRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp7-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 8
CRC vs AA miRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp8-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 9
CRC vs AA lncRNA.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp9-v1.xls
-
Supplementary file 10
AA vs NC up-regulated Median_50 Log2FC_2 with Module sorted by FDR.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp10-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 11
CRC vs NC up-regulated Median_50 Log2FC_2 with Module sorted by FDR.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp11-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 12
Participants’ characteristics for the training and validation cohorts.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp12-v1.docx
-
Supplementary file 13
Transcripts and sequence of their primers and probes.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-supp13-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/88675/elife-88675-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx