Major patterns in the introgression history of Heliconius butterflies
Figures
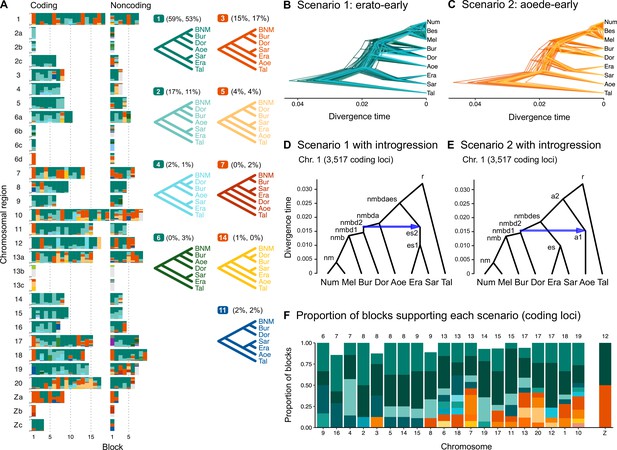
Ancestral gene flow at the base of Heliconius.
(A) Posterior probabilities of species trees for major Heliconius clades inferred from bpp analysis of 200-locus blocks (each spanning 1–3 Mb) across the genome under the multispecies coalescent (MSC) model with no gene flow. The y-axis shows the posterior probability of species trees and ranges from 0 to 1. Colors correspond to the nine most common maximum a posteriori (MAP) trees, summarized by lumping species in the melpomene-silvaniform clade (Bes, Num, Mel) into a single tip (BNM); see Figure 1—figure supplement 1 for full trees. Proportions of coding and noncoding blocks with each tree as a MAP tree are shown in parentheses. (B, C) Two scenarios of early divergence of Heliconius: (B) erato-early versus (C) aoede-early. Each tree is a MAP tree from a block having the MAP tree supporting one of these scenarios, with estimates of branch lengths (posterior means). (D, E) Phylogenetic and introgression histories estimated under an MSC model with introgression (MSC-I) corresponding to the two scenarios based on coding loci in chromosome 1 (3517 coding loci; see Figure 1—figure supplements 5 and 6). (F) Proportions of trees of scenarios 1 or 2 in each chromosome in order of increasing number of loci (used as a proxy for chromosome length). The Z chromosome (chr. 21) is placed at the right end. Number of blocks is shown on top of each bar. Tal: Eueides tales; Mel: H. melpomene; Bes: H. besckei; Num: H. numata; Bur: H. burneyi; Dor: H. doris; Aoe: H. aoede; Era: H. erato; Sar: H. sara.

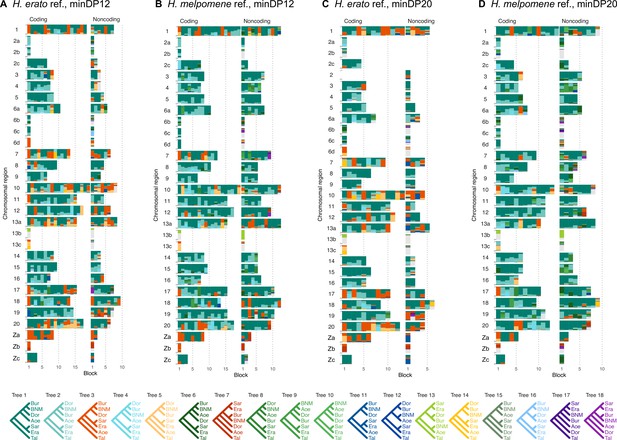
Posterior estimates of species trees from four versions of the 'etales-9spp' dataset (see ‘Methods’), using either H. erato (A, C) or H. melpomene (B, D) as a reference, and a read depth cutoff either 12 (A, B) or 20 (C, D).
See legend to Figure 1.
Posterior estimates of species trees from four versions of the 'etales-9spp' dataset (see ‘Methods’), using either H. erato (A, C) or H. melpomene (B, D) as a reference, and a read depth cutoff either 12 (A, B) or 20 (C, D), with the clade containing three species (Bes, Num, Mel) in the melpomene-silvaniform clade collapsed as a single species.
See legend to Figure 1.

Posterior means and 95% highest posterior density (HPD) intervals of introgression probabilities (φ), population sizes (θ), and divergence or introgression times (τ) under scenario 1 and scenario 2 multispecies coalescent model introgression (MSC-I) model in Figure 1D and E obtained from bpp analysis of the 'etales-8spp' dataset (see Supplementary file 1c for the number of loci).
A few chromosomal regions (2a, 2b, 6b, 6c, 6d, 13b, 13c) yielded too few loci (<100) and were excluded. Chromosome 21 is the sex (Z) chromosome.
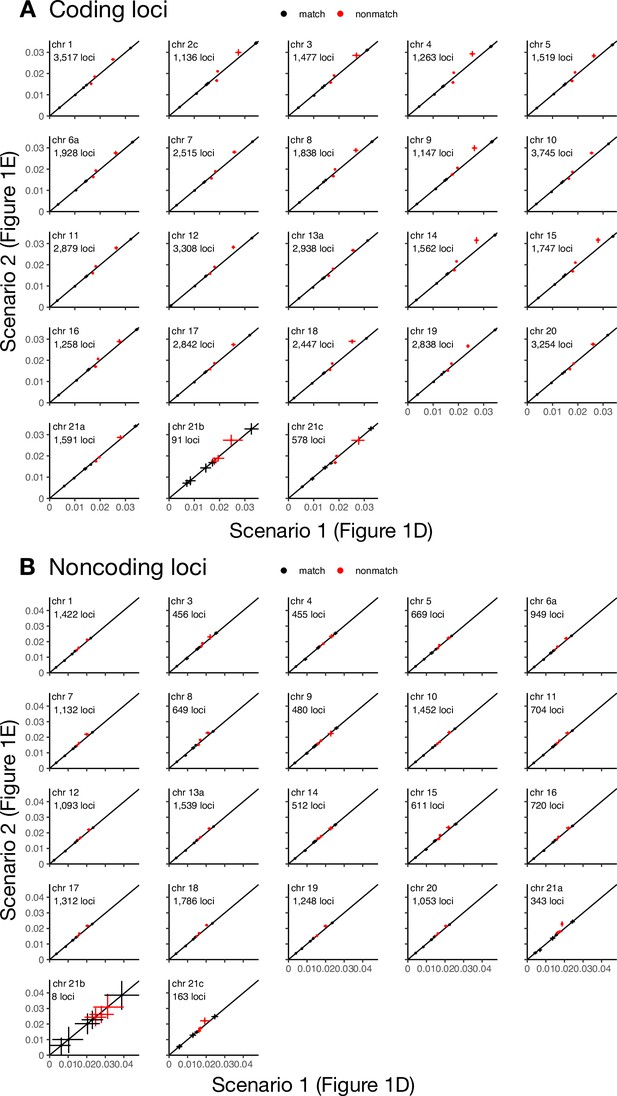
Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals of divergence times estimated under the multispecies coalescent with introgression (MSC-I) model of Figure 1D (erato-early, x-axis) versus estimates under the MSC-I model of Figure 1E (aoede-early, y-axis) using coding (A) or noncoding loci (B) of the 'etales-8spp' dataset.
Red points are divergence times unique to each model.
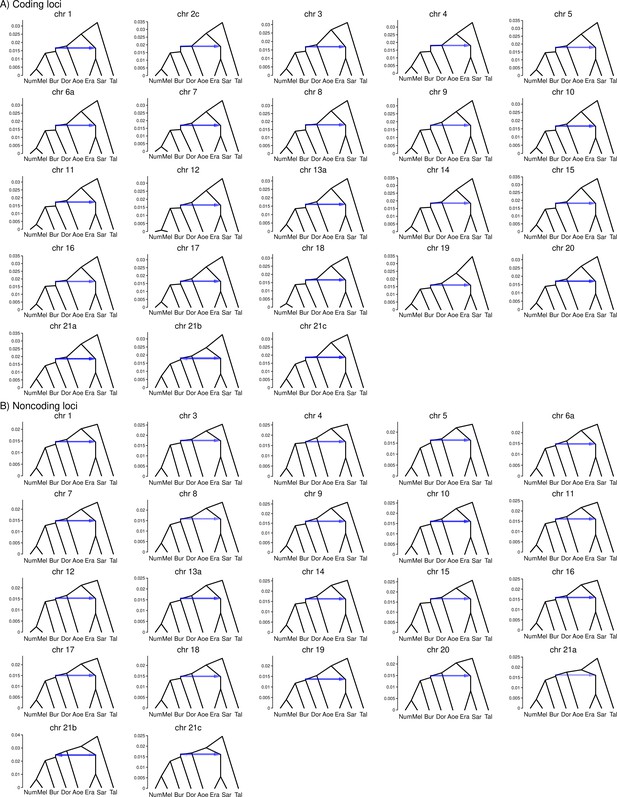
Posterior estimates of the species tree under the introgression model in Figure 1D (scenario 1: erato-early) obtained from bpp analysis of the 'etales-8spp' dataset for each chromosomal region.
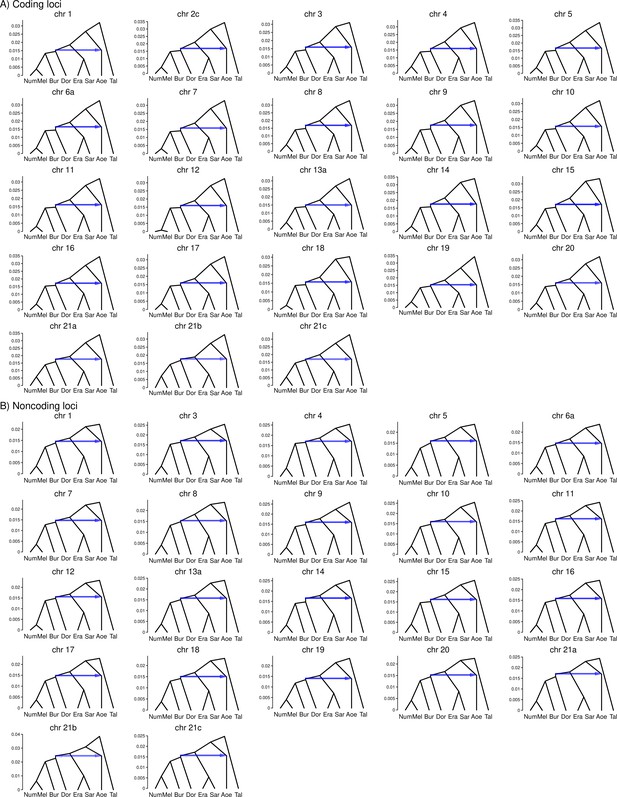
Posterior estimates of the species tree under the introgression model in Figure 1E (scenario 2: aoede-early) obtained from bpp analysis of the 'etales-8spp' dataset for each chromosomal region.

Maximum likelihood estimates (MLEs) of all parameters in the MSC-M model as well as internal branch lengths (Δτ = τ0 – τ1) by chromosomal region for all pairs of Heliconius species in the 'etales-9spp' dataset obtained from 3s analysis.
Error bars indicate two standard errors (not shown if standard errors were not reliably estimated). Columns are parameters in the model; rows are species pairs.
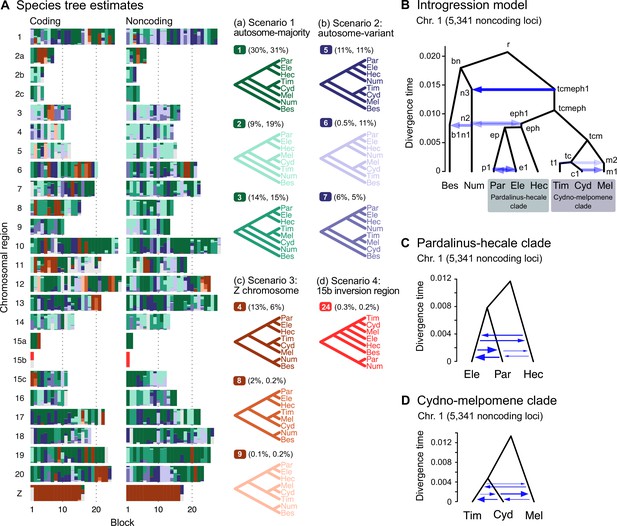
Major introgression events in the melpomene-silvaniform clade.
(A) Blockwise estimates of species trees of the melpomene-silvaniform clade inferred from 200-locus blocks across the genome under the multispecies coalescent (MSC) model with no gene flow using bpp (see Supplementary file 1l for data, Supplementary file 1m and n and Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for full results). Maximum a posteriori (MAP) trees are labeled in decreasing order of frequency among blocks. Proportions of coding and noncoding blocks with each tree as a MAP tree are shown in parentheses. (B) The multispecies coalescent with introgression (MSC-I) model events that can explain the three major groups of trees in (A). Branch lengths are based on posterior means of divergence/introgression times estimated from 5341 noncoding loci on chromosome 1 (Supplementary file 1q). Each internal node is given a label, which is used to refer to a population above the node, for example, the population between nodes r and bn is referred to as branch bn. Each horizontal arrow represents a unidirectional introgression event, for example, the arrow from tcmeph1 to n3 represents tcmeph→Num introgression at time τtcmeph1 = τn3 with probability φtcmeph1→n3. (C) Continuous migration (IM) model for the pardalinus-hecale clade, allowing bidirectional gene flow among the three species. (D) Multispecies coalescent with migration (MSC-M) model for the cydno-melpomene clade. For (C) and (D), branch lengths are based on estimates from noncoding loci in chromosome 1 (Figure 2—figure supplement 6, Supplementary file 1s–u), and arrow sizes are proportional to estimated migration rate (M = Nm). Bes: H. besckei; Num: H. numata; Par: H. pardalinus; Ele: H. elevatus; Hec: H. hecale; Tim: H. timareta; Cyd: H. cydno; Mel: H. melpomene.
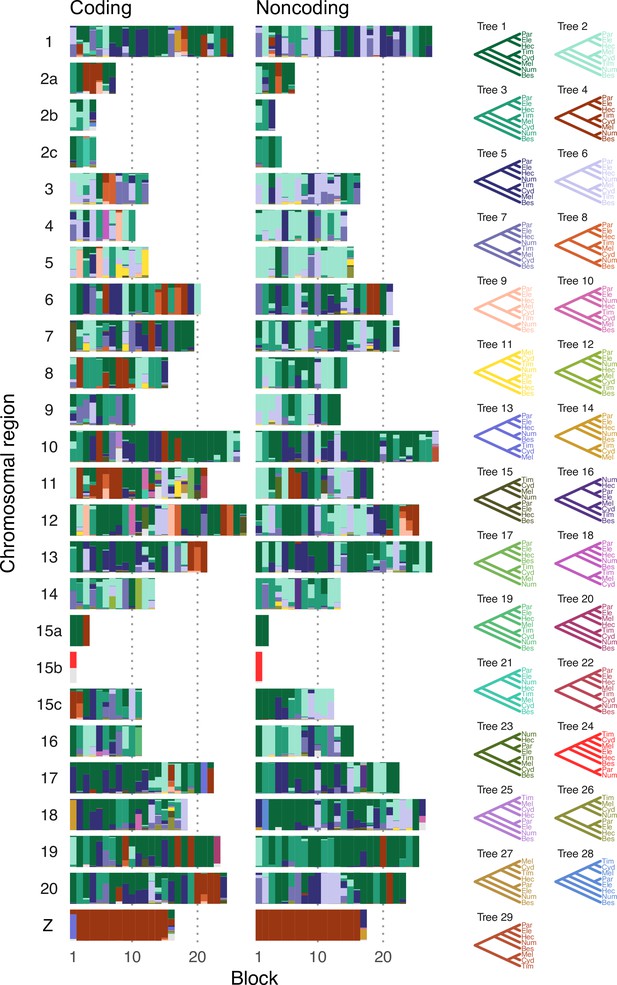
Posterior estimates of species trees of the melpomene-silvaniform clade inferred from 200-locus blocks across the genome from the bpp multispecies coalescent (MSC) analysis with no gene flow of the 'hmelv25-res' dataset.
Figure 2A shows a simplified version with fewer trees. See Supplementary file 1m and n.

Maximum likelihood estimates (MLEs) of all parameters in the multispecies coalescent with migration (MSC-M) model as well as internal branch lengths (Δτ = τ0 – τ1) by chromosomal region from species pairs in the 'hmelv25-all' dataset obtained from 3s analysis using (A) H. aoede or (B) H. erato as an outgroup.
Error bars indicate two standard errors (not shown if standard errors were not reliably estimated). Columns are parameters in the model; rows are species pairs. Full results are in Supplementary file 1o and p.

Estimated introgression history.
Estimated introgression history for each chromosomal region obtained under the model of Figure 2B and Figure 2—figure supplement 4D using (A) noncoding and (B) coding loci. Intensity of the horizontal edges is proportional to posterior mean of introgression probability, while the y-axis represents the divergence times in the units of the expected number of mutations per site. For posterior estimates of all parameters, see Supplementary file 1q and r.
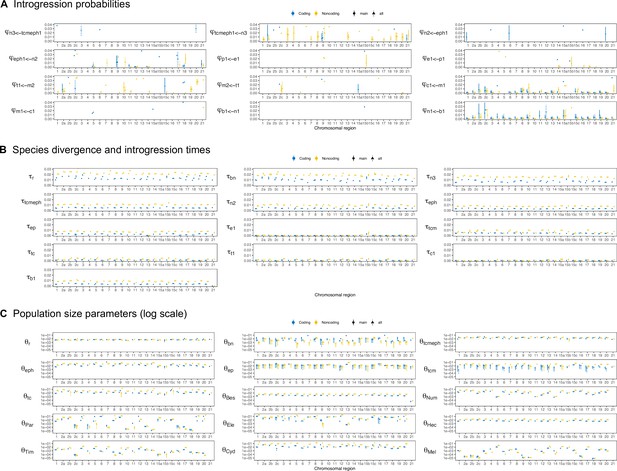
Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals of (A) introgression probabilities, (B) divergence or introgression times (τ), and (C) population sizes (θ) under the multispecies coalescent with introgression (MSC-I) model of Figure 2B using coding (blue) and noncoding data (yellow).
'main' (circle) is the main posterior peak; 'alt' (triangle) is an alternative posterior peak.
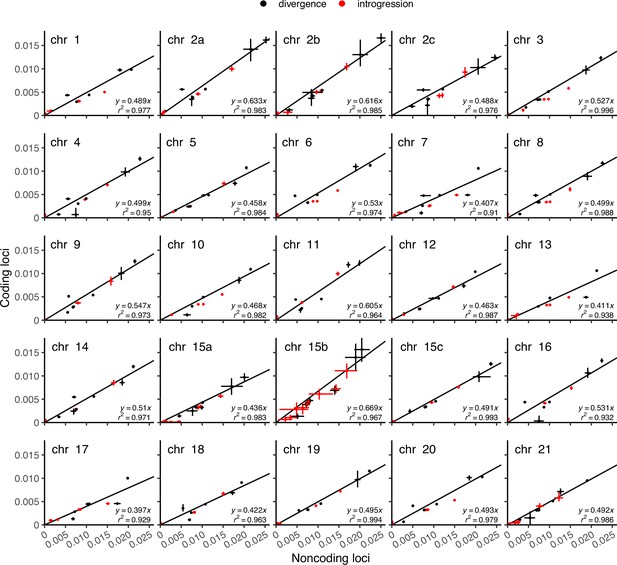
Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals of species divergence and introgression times (τ) obtained from coding loci (y-axis) versus noncoding loci (x-axis) under the multispecies coalescent with introgression (MSC-I) models of Figure 2B (for chromosomal regions other than 15b) and of (D) (for 15b).
We used the divergence times (black points) only to fit a regression line y = c x. For the number of loci used, see Supplementary file 1l or Figure 2—figure supplement 4.

Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals of migration rates (M), divergence times (τ), and population sizes (θ) under the multispecies coalescent with migration (MSC-M) model in three species obtained using bpp.
(A) Pardalinus-hecale clade: ((Par, Ele), Hec). (B) Pardalinus-elevatus clade: (Par, Ele), assuming all three populations have the same size θ. (C) Cydno-melpomene clade: ((Tim, Cyd), Mel). Full results for these three models are given in Supplementary file 1s–u.
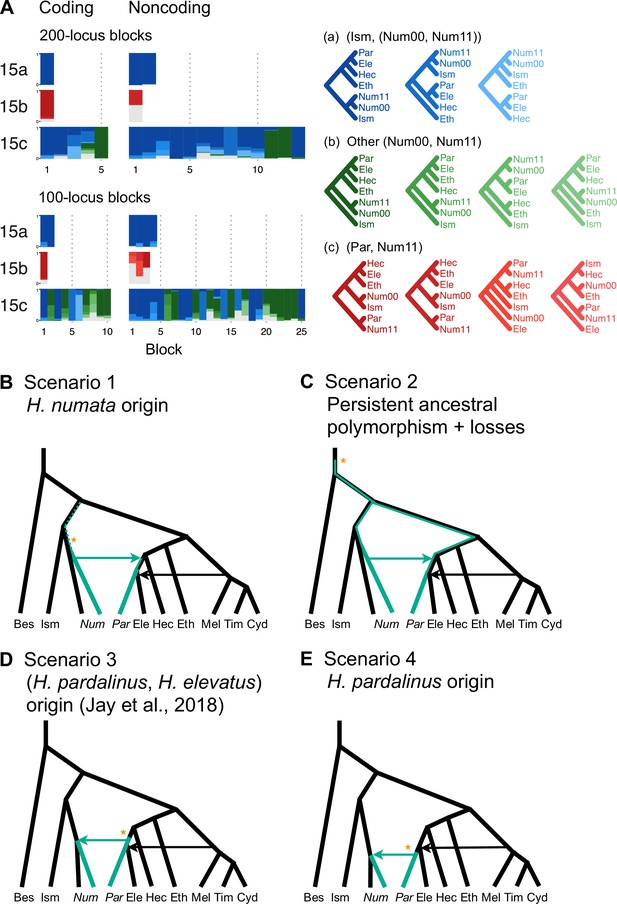
Introgression history of the chromosome 15 inversion region (15b).
(A) Blockwise estimates of species trees for the inversion (15b) and the remnant flanking regions (15a and 15c) of chromosome 15. Trees were inferred from 200-locus blocks and 100-locus blocks under the multispecies coalescent (MSC) model without gene flow using bpp (Supplementary file 1v). Tree legends are grouped by whether H. numata clusters with H. ismenius (blue), or H. numata with P1 inversion (Num11) clusters with H. pardalinus (red), or other relationships (green). (B–E) Four possible scenarios of the origin and introgression route of the P1 inversion. Star indicates the origin of the P1 inversion. Green lineages have the inversion, and green arrows indicates introgression of the inversion. Ism: H. ismenius; Num00: H. numata homozygous uninverted 15b (H. n. laura and H. n. silvana); Num11: H. numata homozygous for inversion P1 (H. n. bicoloratus); Eth: H. ethilla. See Figure 2 legend for codes for other species. For the direction of melpomene-cydno clade→H. elevatus, see Figure 3—figure supplement 3.
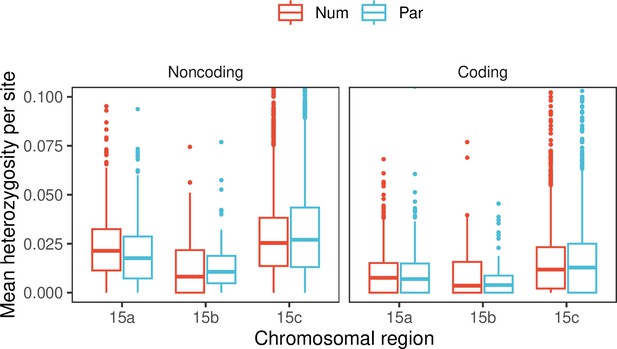
Mean heterozygosity per site of the 15b inversion region and flanking regions (15a and 15c) of H. numata (Num) and H. pardalinus (Par) individuals.
Both individuals are homozygotes for the P1 inversion.
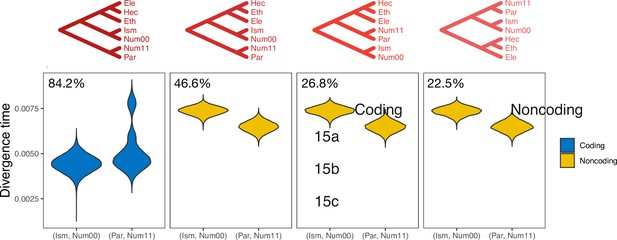
Posterior estimates of divergence time for (Ism, Num00) and (Par, Num11) in the 15b region.
Only estimates from trees with posterior probabilities >0.1 are shown. Trees are in order of decreasing frequency among coding or noncoding data. See legend to Figure 3 for full species names.
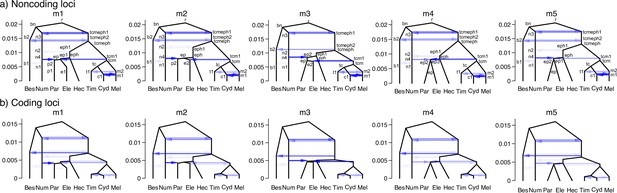
Estimated introgression history under five introgression models (m1–m5) of the 15b region.
Posterior estimates of all parameters under each model are in Supplementary file 1w.
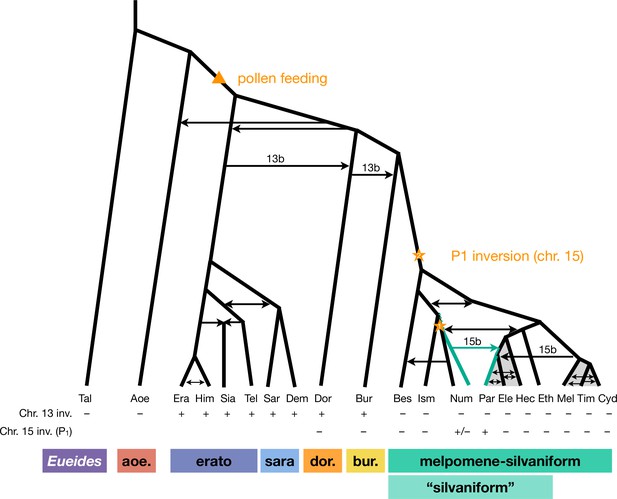
Revised phylogeny and introgression history of Heliconius.
Phylogeny of the erato-sara clade was previously estimated using a similar approach (Thawornwattana et al., 2022). Arrows represent introgression events. Introgression of chromosomal inversions are region-specific, indicated by a label (13b or 15b) above the arrow. Status of inversions 13b and 15b in each species is indicated in the two rows at the bottom, with + indicating inversion, – indicating standard orientation, and +/– inversion polymorphism. Gray shading represents a period of continuous gene flow. Triangle represents the origin of pollen feeding near the base of Heliconius. Star indicates a possible origin of the P1 inversion on chromosome 15, and green branches indicate lineages with the inversion (polymorphic in Num, fixed in Par). Him: H. himera; Sia: H. hecalesia; Tel: H. telesiphe; Dem: H. demeter; see Figures 1—3 legends for other species codes.
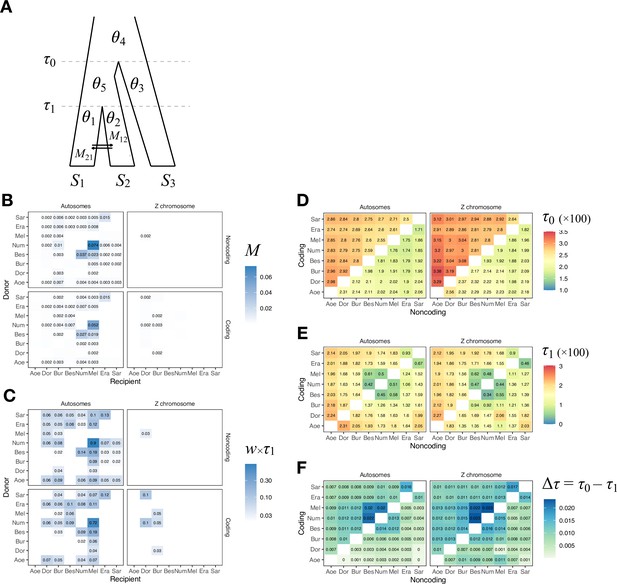
Isolation-with-migration (IM) analysis of the 'etales-9spp' dataset using 3s.
(A) Model specification in 3s. There are three types of parameters: divergence times (τ1, τ0), effective population sizes (θ1, θ2, θ4, and θ5) and migration rates (M12, M21). (B) Maximum-likelihood estimates (MLEs) of the pairwise migration rates (M12, M21), with donor species on the y-axis and recipient species on the x-axis. We used Eueides tales as the outgroup (S3 in A). Top and bottom quadrants are results from noncoding and coding loci, respectively. Left quadrants show results from all autosomal loci. Right quadrants show results from all Z chromosome loci (21a + 21b + 21c). For the number of loci, see Supplementary file 1c (H. erato reference, minDP (d) = 12). For pairs without displayed numbers, the likelihood ratio test (LRT) was not significant at 0.1%, thereby failing to reject a null model of zero gene flow. (C) Mutation-scaled migration rates (w12 = 4M12/θ2 and w21 = 4M21/θ1) as a measure of expected admixture fraction in the recipient genome. (D) Root age (τ0). Estimates from coding loci are shown in the upper triangle while estimates from noncoding loci are in the lower triangle. (E) Divergence time of the ingroup species pair (τ1). (F) Internal branch length (Δτ = τ0 – τ1). Full results are in Supplementary file 1k and Figure 1—figure supplement 7.
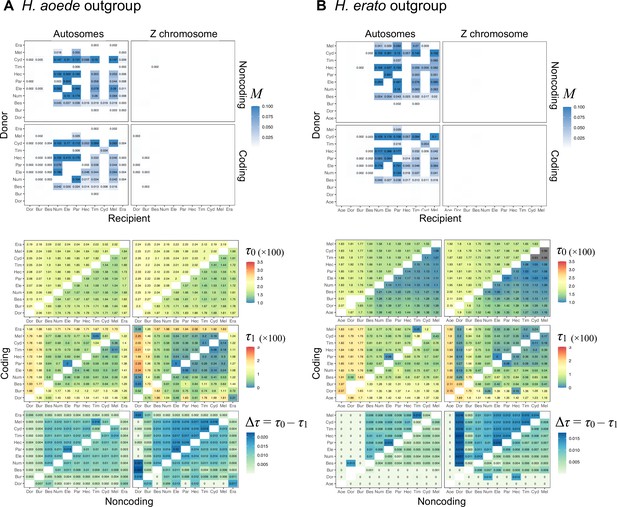
Maximum likelihood estimates (MLEs) of migration rates (M), divergence times (τ0, τ1), and the internal branch length (Δτ = τ0 – τ1) from 3s analysis of the 'hmelv25-all' dataset, using (A) H. aoede or (B) H. erato as an outgroup.
See legend to Appendix 1—figure 1.
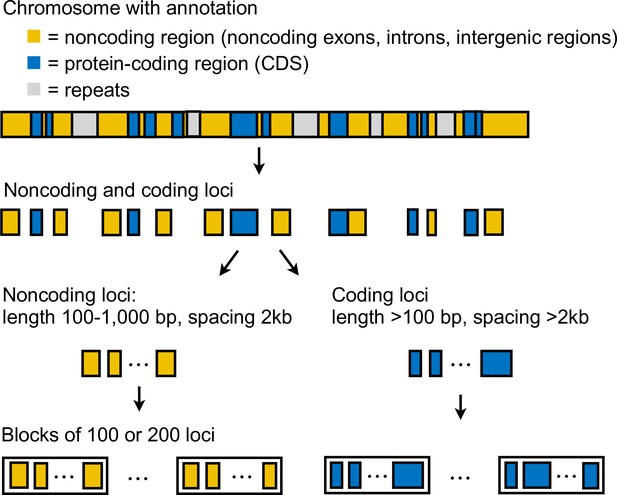
Generation of multilocus data.
Coordinates of coding and noncoding loci were obtained from a reference genome with an annotation of coding sequences (CDS).
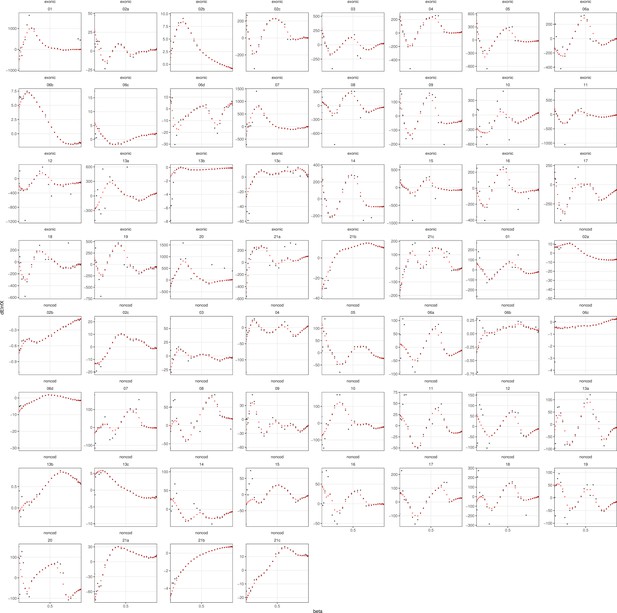
Raw (black) and adjusted (red) estimates of the difference in the mean log likelihood from the two models (y-axis).
Raw and adjusted estimates of the Bayes factor are in Supplementary file 1h.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Supplementary tables.
(a) Sample information. (b) Coordinates of chromosome inversion regions considered in this study. (c) Number of coding and noncoding loci by chromosomal region in four versions of the 'etales-9spp' dataset. (d) Proportions of posterior species tree estimates (maximum a posteriori [MAP] trees) from bpp multispecies coalescent (MSC) analysis without gene flow of all four versions of the 'etales-9spp' dataset in blocks of 200 loci, with BNM clade (H. besckei, H. numata, H. melpomene) collapsed into a single tip, summarized into major regions: auto (all autosomes excluding inversion regions), the Z chromosome (chr 21, excluding the inversion region), and individual inversion regions (2b, 6b, 6c, 13b, and 21b). n = number of blocks. Tree indices correspond to those in Figure 1—figure supplement 2. A full list of MAP trees for each chromosomal region is provided in (e). Full results without BNM lumping are provided in (f and g). (e) Proportions of MAP trees from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow of all four versions of the 'etales-9spp' dataset in blocks of 200 loci, with BNM clade collapsed into a single tip, summarized by chromosomal region. Genome-wide summaries are given in (d). (f) Full results from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow of the 'etales-9spp' dataset, summarized into major regions of the genome. See also legend to (d). Trees are in a decreasing order of the total frequencies across all four versions of the dataset. Tree indices correspond to those in Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (g) Full results from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow of the 'etales-9spp' dataset, summarized by chromosomal region. See legend to (f). (h) Bayes factor B = M1E/M1D for comparing the two MSC-I models in Figure 1D (M1E; scenario 1) and Figure 1E (M1D; scenario 2), calculated for coding and noncoding loci for each chromosomal region using thermodynamic integration with 32 Gaussian quadrature points. M1E (scenario 2) is preferred if B>100, M1D (scenario 1) is preferred if B < 0.01, and the test is not significant (n.s.) otherwise (i.e. 100 < B < 0.01). The last three columns are adjusted values of Bayes factor to account for numerical instability of the thermodynamic integration estimates (see ‘Methods’ and Appendix 1—figure 4). (i) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters from the bpp MSC-I model in Figure 1D (scenario 1) using noncoding and coding loci for each chromosomal region of 'etales-8spp' dataset (see a). Multiple posterior peaks, if present, are reported, for example there are two peaks, denoted chr1 and chr1-alt, from the coding loci in chromosome 1. Plots of these estimates with 95% HPD intervals are provided in Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Plots of species tree with estimated divergence times, introgression times, and introgression probabilities are provided in Figure 1—figure supplement 5. (j) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters from the bpp MSC-I model in Figure 1E (scenario 2) using noncoding and coding loci for each chromosomal region. Multiple posterior peaks, if present, are reported, for example, there are two peaks, denoted chr1 and chr1-alt, from the coding loci in chromosome 1. Plots of these estimates with 95% HPD intervals are provided in Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Plots of the species tree with estimated divergence times, introgression times, and introgression probabilities are in Figure 1—figure supplement 6. (k) Maximum likelihood estimates (MLEs) of parameters under the isolation-with-migration (IM) model obtained from 3s for each of the 28 pairs of species in the 'etales-9spp' dataset (H. erato reference, minDP12), using Eueides tales (Tal) as an outgroup. We used the likelihood ratio test (LRT) statistic to test if the model with gene flow (M2) was preferred to the model without gene flow (M0) using the p-value threshold of 1%. The ‘auto’ dataset used all autosomal loci excluding the inversion regions (see c for the number of loci). Plots of migration rate and divergence time estimates are provided in Appendix 1—figure 1. Plots of all parameter estimates with confidence intervals are provided in Figure 1—figure supplement 7. (l) Number of coding and noncoding loci in each chromosomal region in the ‘hmelv25-res' dataset used in bpp analysis and the ‘hmelv25-all' dataset use in 3s analysis. (m) Proportions of MAP trees, with minimum, median, and maximum posterior probabilities shown in parentheses, from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow of the 'hmelv25-res' dataset in blocks of 200 loci, summarized into four major regions: auto (all autosomes excluding 2b and 15b), 2b and 15b inversion regions, and chromosome 21 (Z chromosome). Trees are in a decreasing order of combined frequency across all chromosomes. Tree indices correspond to those in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. (n) Proportions of MAP trees, with minimum, median, and maximum posterior probabilities shown in parentheses from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow in blocks of 200 loci, summarized by chromosomal region. See legend to (m). (o) MLEs of parameters under the MSC-M model obtained from 3s for each of the 55 pairs of species in the 'hmelv25-all' dataset using H. aoede as an outgroup. We used the LRT statistic to test if the model with gene flow (M2) was preferred to the model without gene flow (M0) using the p-value threshold of 1%. See Figure 2—figure supplement 2A for plots of these estimates. The ‘auto’ setting used all autosomal loci excluding the inversion regions. See l for the number of loci. (p) MLEs of parameters under the MSC-M model obtained from 3s for each of the 55 pairs of species in the 'hmelv25-all' dataset using H. erato as an outgroup. See legend to (o). See Figure 2—figure supplement 2 for plots of these estimates. (q) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters obtained from the bpp MSC-I model of Figure 2B using noncoding loci from each non-15b chromosomal region, and under the MSC-I model m1 of Figure 3—figure supplement 3 for the chromosome 15b inversion region. Plots of the estimates are provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 4. 'n/a' means the parameter does not exist in the model. (r) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters from bpp MSC-I models are provided in Figure 2B and Figure 3—figure supplement 3 (model m1) using coding loci. See legend to (q). (s) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters from bpp MSC-M models for the pardalinus-hecale clade: ((Par, Ele), Hec), with six continuous migration rates (M = Nm) among the three species, two species divergence times (τ) and five population sizes (θ). Plot of the estimates is provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 6A. (t) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters obtained from bpp MSC-M models for the pardalinus-elevatus clade: (Par, Ele), with two continuous migration rates (M = Nm). All populations were assumed to have the same population size (θ). Plot of the estimates is provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 6B. (u) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters from bpp MSC-M models for the cydno-melpomene clade: ((Tim, Cyd), Mel), with six continuous migration rates (M = Nm) among the three species, two species divergence times (τ), and five population sizes (θ). Plot of the estimates is provided in Figure 2—figure supplement 6C. (v) Proportions of MAP trees, with minimum, median, and maximum posterior probabilities shown in parentheses, from bpp MSC analysis without gene flow of the ‘silv-chr15' dataset in blocks of 200 loci or 100 loci, summarized by three regions: the inversion region (15b) and flanking regions (15a and 15c). Trees are in decreasing order of combined frequency across all chromosomal regions and from both options of block size. (w) Posterior means and 95% HPD intervals (in parentheses) of parameters obtained from five bpp MSC-I models in Figure 3—figure supplement 3.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90656/elife-90656-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90656/elife-90656-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





