Txnip deletions and missense alleles prolong the survival of cones in a retinitis pigmentosa mouse model
Figures
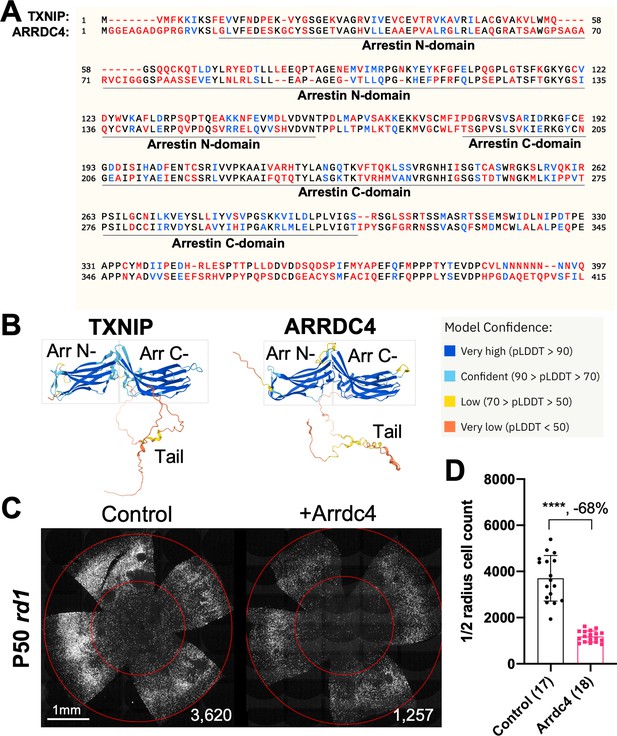
Effect of arrestin domain containing protein 4 (Arrdc4) on cone survival in retinitis pigmentosa mice.
(A) Amino acid sequences of mouse TXNIP and mouse ARRDC4. In the full-length alignment (421 amino acid), Identity: 172/421, 40.86%; Similarity: 246/421, 58.43%; Gaps: 28/421, 6.65%. Color code: identical, black; similar, blue; not similar, red. (B) Predicted 3D protein structures of mouse TXNIP and mouse ARRDC4 by artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm AlphaFold-2. Abbreviations: Arr N-, N-terminal arrestin domain; Arr C-, C-terminal arrestin domain. (C) Representative P50 rd1 flat-mounted retinas after P0 subretinal infection with AAV8-RO1.7-Arrdc4 (1×109 vg/eye), plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP (2.5×108 vg/eye), or control eyes infected with AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye alone. (D) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 rd1 retinas transduced with Arrdc4, and control (same as in C). The number in the round brackets ‘()’ indicates the number of retinas within each group. Error bar: standard deviation. Statistics: two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. **** p<or << 0.0001. RedO: red opsin promoter; RO1.7: a 1.7 kb version of red opsin promoter. AAV: adeno-associated virus.
-
Figure 1—source data 1
This file contains the source data of Figure 1D.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90749/elife-90749-fig1-data1-v1.xlsx
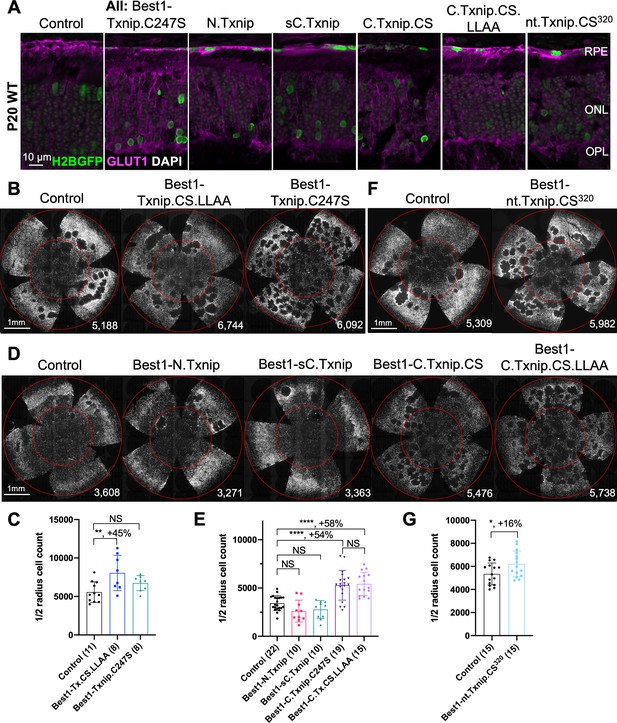
Txnip deletions expressed only within retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) cells: effects on GLUT1 removal and cone survival.
(A) Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) expression in P20 wild-type eyes infected with control (AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye), or a Txnip allele (2.5×108 vg/eye) plus RedO-H2BGFP (2.5×108 vg/eye), as indicated in each panel. Txnip deletions are detailed in Figure 4. GLUT1 intensity from basal RPE is quantified in Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Magenta: GLUT1; green: RedO-H2BGFP for infection tracing; gray: DAPI. (B, D, F) Representative P50 rd1 flat-mounted retinas after P0 infection with one of seven different Txnip alleles expressed only within the RPE, as indicated in the figure, or control eyes infected with AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye alone. (C, E, G) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 rd1 retinas transduced with indicated vectors, as shown in B, D, F. The number in the round brackets ‘()’ indicates the number of retinas within each group. Error bar: standard deviation. Statistics: ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for C and E; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test for G. C.Txnip.CS: C-terminal portion of Txnip.C247S; C.Txnip.CS.LLAA: C-terminal portion of Txnip.C247S.LL351 and 352AA; nt.Txnip.CS320: no tail Txnip (1-320aa). NS: not significant, p>0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<or << 0.0001. Best1: Best1 promoter.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
This file contains the source data of Figure 2C, E and G and Figure 2—figure supplement 1.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90749/elife-90749-fig2-data1-v1.xlsx
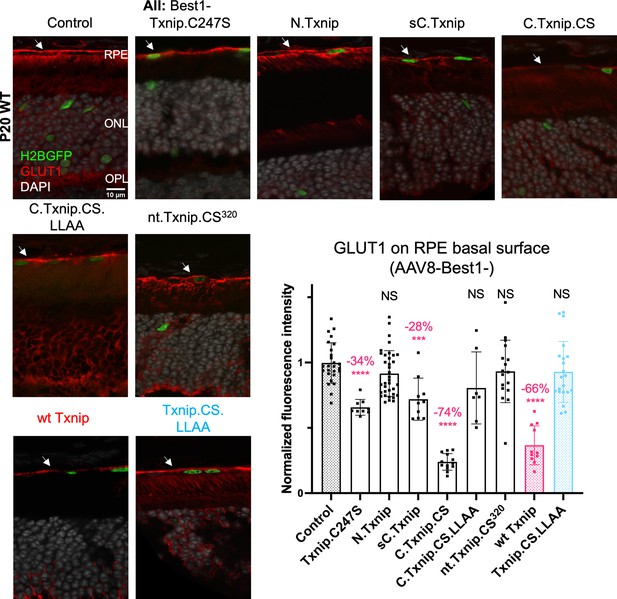
Txnip deletions expressed only within retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) cells: quantification of the Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) level within the basal surface of the RPE.
GLUT1 expression in P20 wild-type (wt) eyes infected with control (AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye), or a Txnip allele (2.5×108 vg/eye) plus RedO-H2BGFP (2.5×108 vg/eye), as indicated in each panel. Txnip deletions are detailed in Figure 4. Wt Txnip (red group) and Txnip.C247S.LLAA (blue group) were published previously (Xue et al., 2021), and are repeated here using the same conditions as in this study for comparison to the new alleles. Only regions that were infected, as indicated by the H2BGFP marker that was co-injected, were analyzed. GLUT1 intensity from regions of interest (ROIs) within the basal RPE was quantified. Red: GLUT1; green: RedO-H2BGFP for infection tracing; gray: DAPI. Arrows: RPE basal surface. Sample size: control, 26 ROIs from four eyes; Txnip.C247S, nine ROIs from three eyes; N.Txnip, 36 ROIs from six eyes; sC.Txnip, 10 ROIs from six eyes; C.Txnip.CS, 13 ROIs from three eyes, C.Txnip.CS.LLAA, seven ROIs from three eyes; nt.Txnip.CS320, 14 ROIs from four eyes; wt Txnip, 11 ROIs from four eyes; Txnip.CS.LLAA, 21 ROIs from four eyes. Error bar: standard deviation. Statistics: Mann-Whitney U Test compared to control with Bonferroni correction. NS: not significant, ***p<0.001, ****p<or << 0.0001.
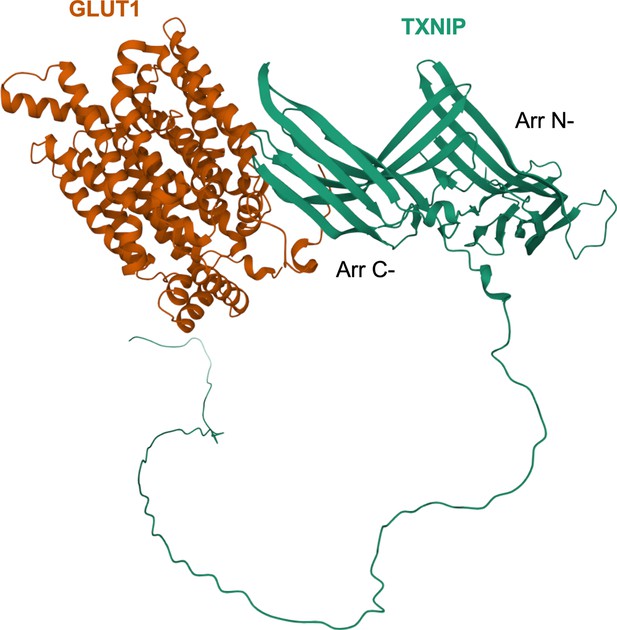
Predicted protein-protein interactions of TXNIP and Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) by an algorithm, ColabFold, based on AlphaFold-2.
Tests of Txnip alleles on cone survival.
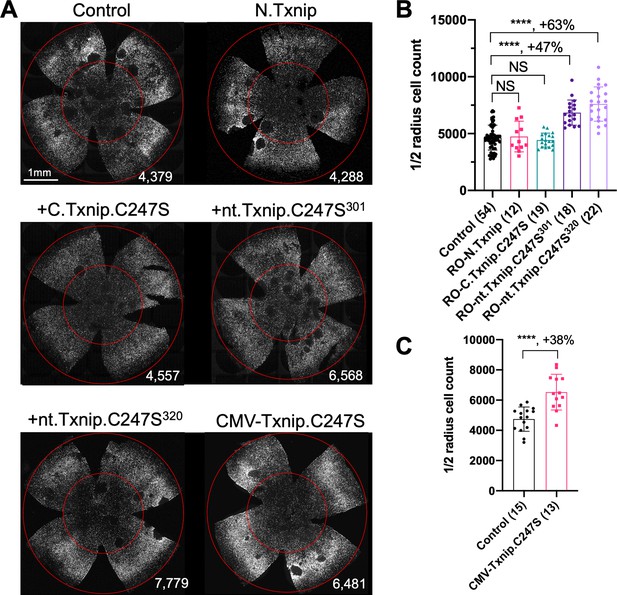
(A) Representative P50 rd1 flat-mounted retinas after P0 infection with 1 of 5 different Txnip alleles (AAV8-RedO- N.Txnip /C.Txnip.C247S/ nt.Txnip.C247S1-301/nt.Txnip.C247S1-320 or AAV8-CMV-Txnip.C247S, ≈1×109 vg/eye, plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye), or control eyes infected with AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye alone. (B, C) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 rd1 retinas transduced with AAV8-RedO- N.Txnip /C.Txnip.C247S/ nt.Txnip.C247S1-301/nt.Txnip.C247S1-320 or AAV8-CMV-Txnip.C247S, and control (same as in A). The number in the round brackets ‘()’ indicates the number of retinas within each group. Error bar: standard deviation. Statistics: ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for B; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test for C. NS: not significant, ****p<or << 0.0001.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
This file contains the source data of Figure 3B and C.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90749/elife-90749-fig3-data1-v1.xlsx

Summary of various alleles of Txnip in this and previous study (Xue et al., 2021).
‘Retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) Removal’ refers to the amount of GLUT1 immunohistochemical signal on the basal surface following expression in the RPE using the Best1 promoter. ‘Cone Rescue: Expression in RPE’ refers to cone rescue following expression only in the RPE using the Best1 promoter. ‘Cone Rescue: Expression in Cones’ is due to expression only in cone photoreceptors using the RedO promoter. Abbreviations: Y (x%): Yes with x% increase compared to AAV-H2BGFP control; N: No; NT: Not tested. N.TXNIP, N-terminal portion of TXNIP; C.TXNIP.C247S, C-terminal portion of TXNIP.C247S mutant allele; sC.TXNIP: a shorter version of C-terminal portion of TXNIP; nt.TXNIP.C247S, no tail version TXNIP.C247S mutant allele; Arrestin N-, N-terminal arrestin domain; Arrestin C-, C-terminal arrestin domain; PPxY, a motif where P is proline, x is any amino acid and Y is tyrosine.

Effect of knockdown of Hsp90ab1 in retinitis pigmentosa cones in vivo.
(A) AAV8-RO1.7-Hsp90ab1-FLAG (1×109 vg/eye) co-injected with shNC (non-targeting shRNA control, AAV8-RedO-shRNA, 1×109 vg/eye) or co-injected with Hsp90ab1 shRNAs #a, #b, #c (AAV8-RedO-shRNA, 1×109 vg/eye) in P20 wild-type (wt) retina, all also injected with AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP (2.5×108 vg/eye) to track the infection. Magenta: anti-FLAG; green: anti-GFP; gray: DAPI. Right panel: (B) The quantification of FLAG intensity from multiple fields of inner segment regions in A. The number in the square brackets ‘[]’ indicates the number of images taken from regions of interest of one retina, in each condition. (C) Representative P50 rd1 flat-mounted retinas injected with shNC, shHsp90ab1(#a), shHsp90ab1(#b), or shHsp90ab1(#c) (AAV8-RedO-shRNAs, 1×109 vg/eye, plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye). (D) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 rd1 retinas transduced with shNC, shHsp90ab1(#a, #b, #c) (same as in C). (E) Representative P50 rd1 flat-mounted retinas with H2BGFP (gray)-labeled cones transduced with Txnip.C247S or Txnip.C247S+shHsp90ab1 (AAV8-RedO-Txnip.C247S, 1×109 vg/eye; AAV8-RO1.7-shHsp90ab1(#a or #c), 1×109 vg/eye; plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye). (F) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 rd1 retinas transduced with Txnip.C247S or Txnip.C247S+shHsp90ab1 (same as in E). (G) Representative P50 Parp1-/- rd1 flat-mounted retinas with H2BGFP (gray)-labeled cones transduced with shNC (non-targeting shRNA control, AAV8-RedO-shRNA, 1×109 vg/eye; plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye) or shHsp90ab1 (AAV8-RedO-shRNA #a or #c, 1×109 vg/eye; plus AAV8-RedO-H2BGFP, 2.5×108 vg/eye). (H) Quantification of H2BGFP-positive cones within the center of P50 Parp1-/- rd1 retinas transduced with shNC or shHsp90ab1 (same as in G). Error bar: standard deviation. Statistics: ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for B and D; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test for F and H. NS: not significant, p>0.05, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 ****p<or << 0.0001.
-
Figure 5—source data 1
This file contains the source data of Figure 5B, D, F and H.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/90749/elife-90749-fig5-data1-v1.xlsx
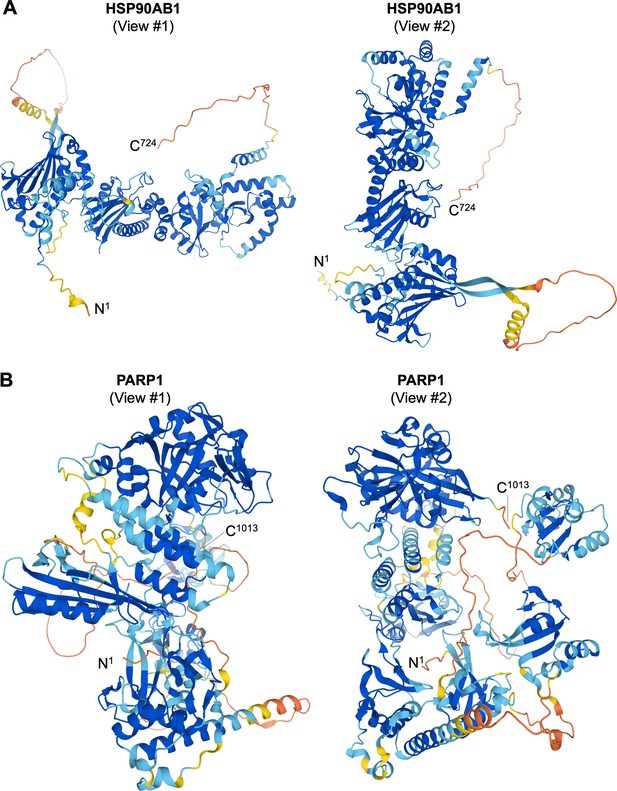
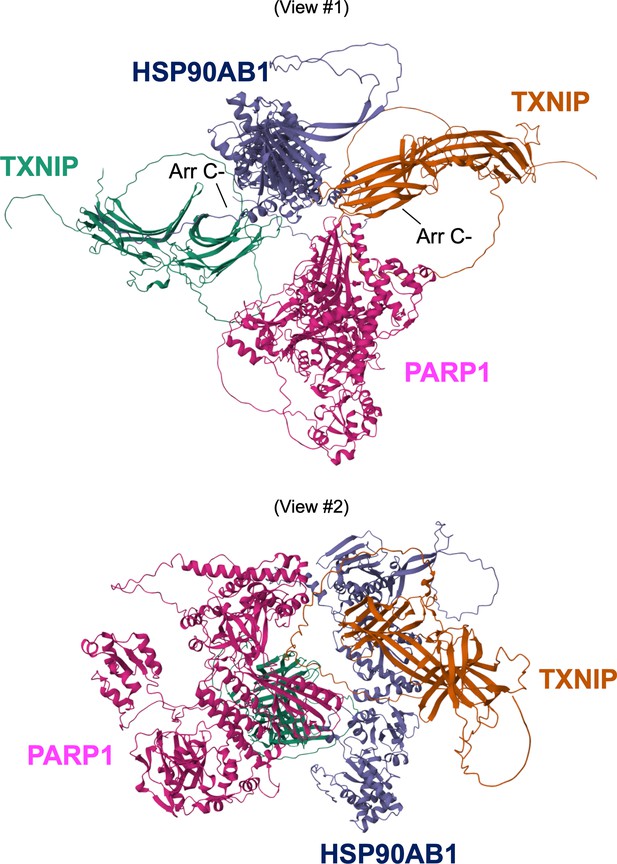
Predicted 3D protein structures of HSP90AB1 and PARP1.
(A) Predicted 3D protein structures of HSP90AB1 by AI algorithm AlphaFold-2 from two angles of view. (B) Predicted 3D protein structures of PARP1 by AI algorithm AlphaFold-2 from two angles of view.
Tables
| Reagent type (species) or resource | Designation | Source or reference | Identifiers | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | GLUT1 (rabbit monoclonal) | Abcam | ab115730 | IHC (1:500) |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Arrdc4 cDNA | GeneCopoeia | Cat. #: Mm26972 NCBI: NM_001042592.2 | |
| Genetic reagent (M. musculus) | Hsp90ab1 cDNA | GeneCopoeia | Cat. #: Mm03161 NCBI: NM_008302.3 | |
| Software, algorithm | Protein 3D structure prediction | AlphaFold-2 | TXNIP (M. musculus); ARRDC4 (M. musculus); HSP90AB1 (M. musculus); PARP1 (M. musculus) | Jumper et al., 2021; https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk |
| Software, algorithm | Protein 3D interaction prediction | ColabFold | AlphaFold2_mmseqs2 | Mirdita et al., 2022; Ovchinnikov, 2021; https://github.com/sokrypton/colabfold |
| Software, algorithm | Protein 3D interaction prediction | COSMIC2 | AlphaFold2 – Multimer | Evans et al., 2021; http://cosmic-cryoem.org/tools/alphafoldmultimer/ |
| Software, algorithm | Protein 3D structure viewer | RCSB PDB | Mol* 3D Viewer | To visualize the 3D structure of proteins in.pdb files https://www.rcsb.org/3d-view |