Early moderate prenatal alcohol exposure and maternal diet impact offspring DNA methylation across species
Figures
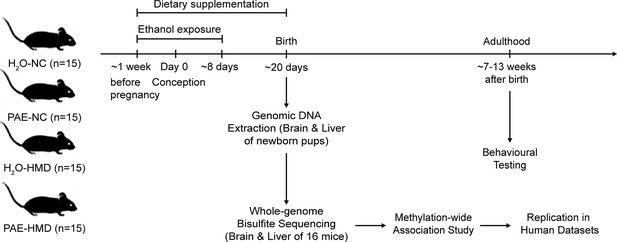
Overview of prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) model.
A schematic representation of the experiment design is shown in the figure. Fifteen dams were allocated to each treatment group. PAE mice were exposed to ethanol (10% vol/vol in non-acidified reverse osmosis drinking water ad libitum) from 1 week before pregnancy to gestational days 8–10 and the remaining mice received water (H2O). The PAE and H2O groups received either normal chow (NC) or a high methyl donor (HMD) diet (NC containing 20 mg/kg folate and 4970 mg/kg choline) from 1 week before pregnancy until birth.
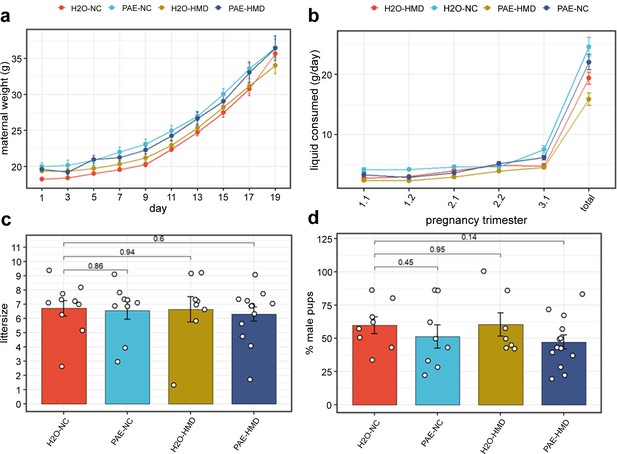
PAE and HMD effects on dam characteristics.
(a) Dam weight progression was significantly affected by HMD but not PAE by quadratic mixed effects model without interaction. (b) Trajectory of liquid consumption across pregnancy was affected by PAE and HMD by quadratic mixed effects model. PAE and HMD significantly interacted with trimester of pregnancy. (c) Litter size (N=40) and (d) pup sex ratios (N=36) were not significantly associated with PAE or HMD by unpaired t-test or ANOVA. All line and bar plots show mean and standard deviation. NC = normal chow, HMD = high methyl diet, PAE = prenatal alcohol exposure. Comparisons show p-value by unpaired t-test compared to the H2O-NC baseline treatment group.
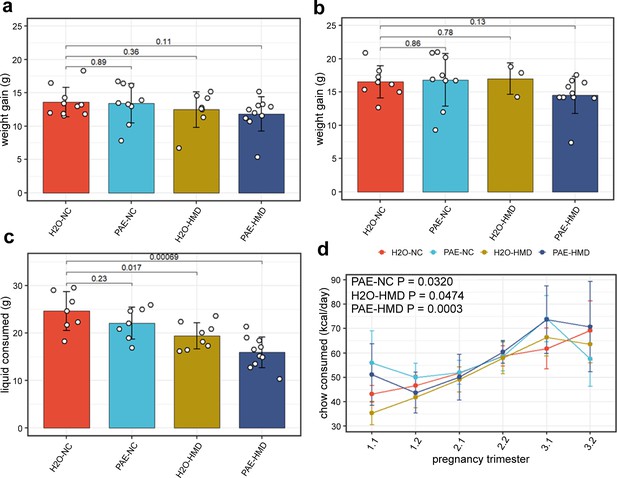
Prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) and high methyl donor (HMD) effects on dam characteristics.
There was no significant difference in the average gain of weight in dams between (a) days 1–17 and (b) days 1–19 by treatment group. Both timepoints were included due to some pregnancies ending by day 19. (c) Dams given supplemented chow consumed significantly lower total quantity of liquid across pregnancy. Bar plots show mean and standard deviation for each treatment group. Each point represents one dam. (d) The trajectory of chow consumed by dams across pregnancy significantly varied with the addition of treatments. Points show mean and standard deviation for each treatment group. Statistical analysis involved linear mixed effects regression comparing trajectories of treatment groups to H2O-NC baseline control group. N=36.
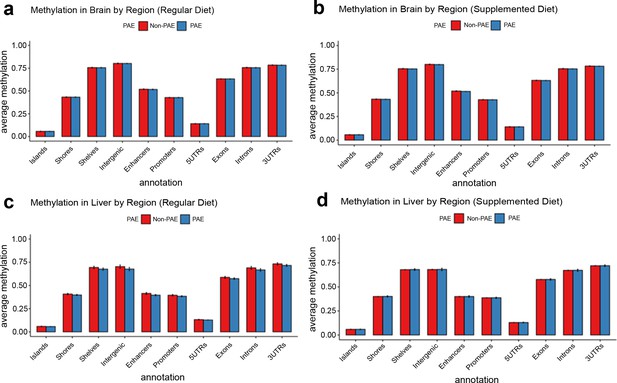
No evidence for global disruption of methylation by prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE).
The figure shows methylation levels averaged across cytosine-guanines (CpGs) in different regulatory genomic contexts. Neither brain tissue (a and b) nor liver tissue (c and d) were grossly affected by PAE exposure (blue bars). Bars represent means and standard deviation.
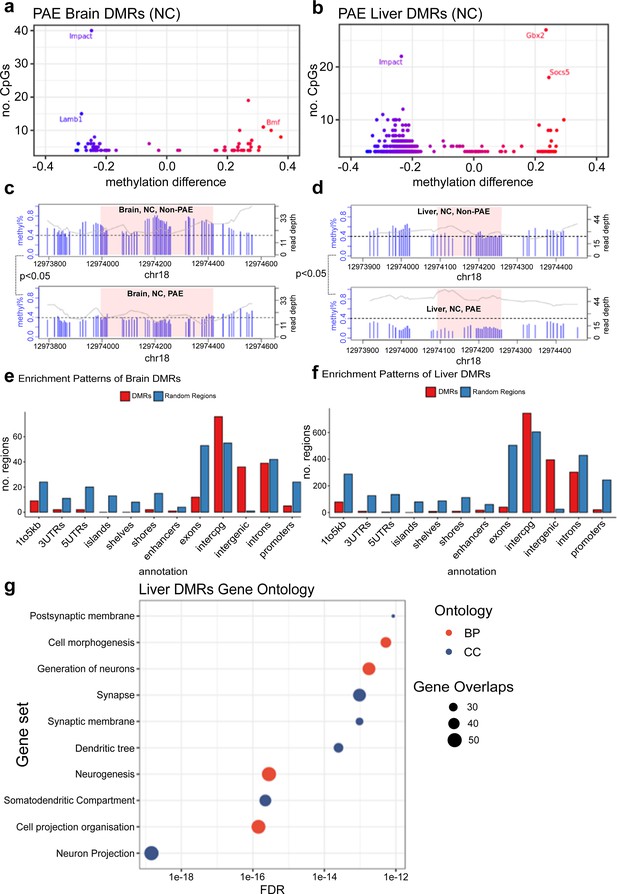
Prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) was associated with site-specific differences in offspring DNA methylation.
The majority of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) lost methylation with PAE in (a) brain and (b) liver of mice given normal chow (NC). Each point represents one DMR. Point colour indicates change in DNA methylation with PAE. PAE was also associated with lower methylation in the DMRs identified in the promoter of the Impact gene in (c) brain and (d) liver, within NC mice. Each plot represents a separate treatment group. Each blue vertical line indicates a cytosine-guanine (CpG) site, with the height and corresponding left y-axis indicating the methylation ratio. The grey line and corresponding right y-axis indicate coverage at each CpG site. The black horizontal dotted line indicates 40% methylation for comparison purposes. The x-axis indicates the base position on chromosome 18, with the pink shaded area highlighting the DMR. DMR plots include 200 base pair flanking regions on each side of the DMR. DMRs identified in (e) brain and (f) liver were enriched in intergenic and inter-CpG regions, whilst being underrepresented in CpG and gene regions. The bar plot compares the number of whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (WGBS) DMRs in red to a set of equivalent randomly generated regions in blue. (g) Gene ontology analysis of liver DMRs shows enrichment within neuronal cellular components and biological processes. BP/red point = biological process, CC/blue point = cellular component. X-axis of point indicates FDR of ontology. Size of point indicates number of overlapping genes with ontology. There were insufficient number of DMRs identified in the brain for a gene ontology analysis.
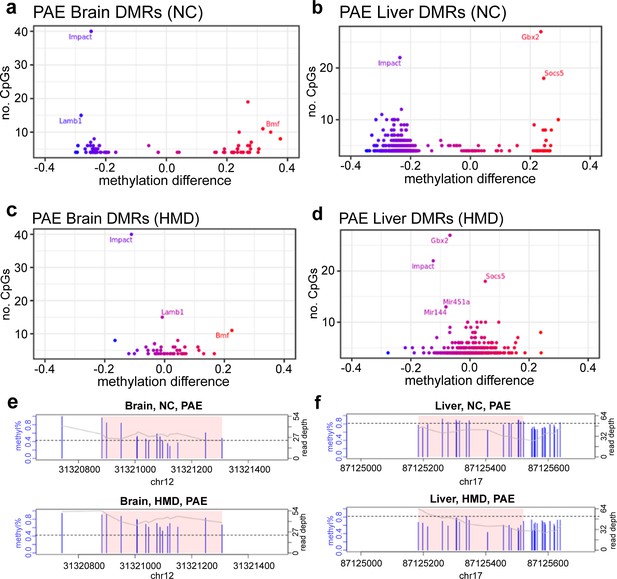
High methyl donor (HMD) partially mitigated effects of prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) on offspring DNA methylation.
Average DNA methylation effect sizes above 30% with PAE were observed in some (a) brain and (b) liver differentially methylated regions (DMRs) in normal chow (NC) mice. Mean absolute difference in methylation with PAE is reduced within the HMD mice in (c) brain and (d) liver. Each point represents one DMR. Point colour indicates change in DNA methylation with PAE. Points with a high number of cytosine-guanines (CpGs) and methylation difference are annotated with associated gene if located within a genic region. HMD was associated with (e) higher methylation in the DMR identified proximal to Lamb1 on chromosome 12 in brain and (f) lower methylation in the DMR identified proximal to Socs5 on chromosome 17 in liver. Each plot represents a separate treatment group. Each blue vertical line indicates a CpG site, with the height and corresponding left y-axis indicating the methylation ratio. The grey line and corresponding right y-axis indicate coverage at each CpG site. The black horizontal line indicates (e) 40% and (f) 80% methylation for comparison purposes. The x-axis indicates the base position on the chromosome, with the pink shaded area highlighting the DMR. DMR plots include 200 base pair flanking regions on each side of the DMR.
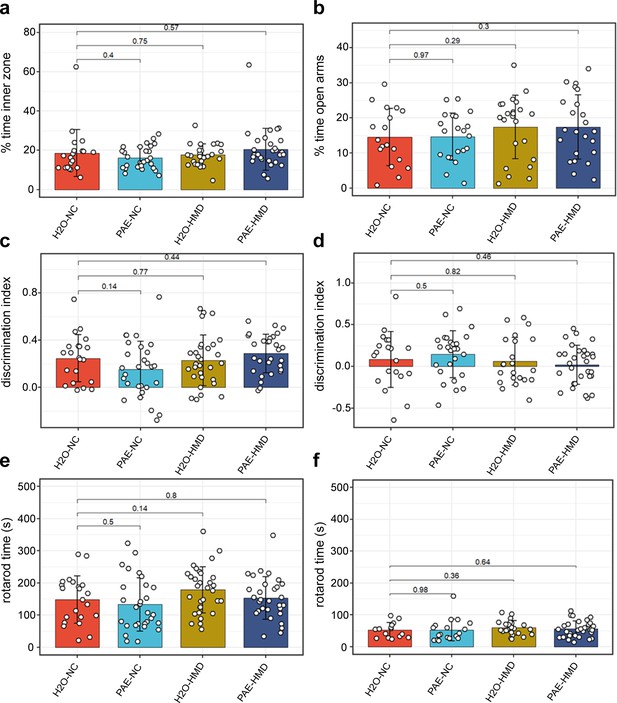
PAE had no significant effect on other assessed behavioural outcomes.
PAE and HMD had no significant effect on anxiety as evident by no significant difference by unpaired t-test in the (a) percent time in the inner zone in the open field test (N=104) and (b) percent time open arms in the elevated plus maze test (N=85). PAE and HMD had no significant effect on spatial recognition as evident by no significant difference by unpaired t-test in the discrimination index in (c) object recognition (N=108) and (d) object in place test (N=98). PAE and HMD had no significant effect on motor coordination and balance as evident by no significant difference by unpaired t-test in times in (e) first rotarod test (N=112) and (f) second rotarod test (N=87). Bars show mean and standard deviation. Each point represents one mouse. NC = normal chow, HMD = high methyl diet, PAE = prenatal alcohol exposure. Time interval for each mouse was (a–c) 300 s and (d) 180 s.
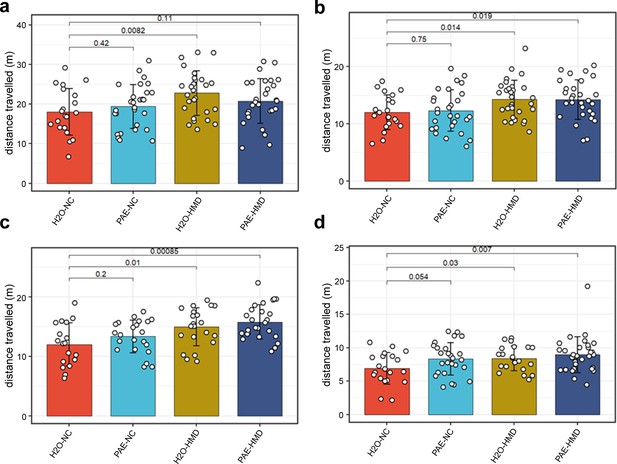
HMD was associated with increased locomotor activity.
HMD was associated with increased locomotor activity compared to NC, indicated by significantly greater total distance travelled in the (a) open field test (N=104), (b) object recognition test (N=108), (c) elevated plus maze test (N=88), and (d) object in place test (N=98) by unpaired t-test. Bars show mean and standard deviation. Each point represents one mouse. NC = normal chow, HMD = high methyl diet, PAE = prenatal alcohol exposure. Time interval for each mouse was (a–c) 300 s and (d) 180 s.
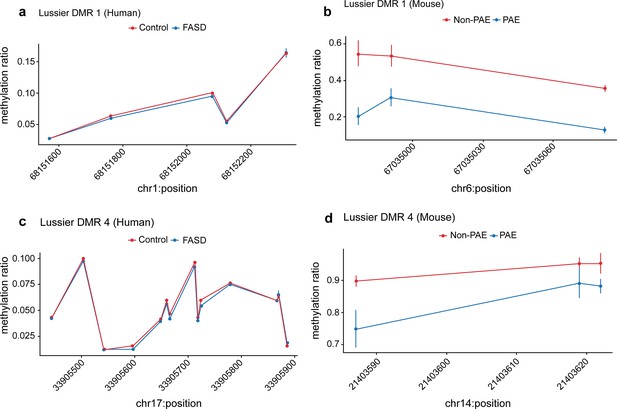
Seven prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) differentially methylated regions (DMRs) identified in the murine model were successfully replicated in the Lussier et al., 2018 human fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) cohort.
Examples of two PAE DMRs that had significantly lower DNA methylation with a clinical diagnosis of FASD in the Lussier et al., 2018 cohort (a and c), while their mouse liftover DMR also had significantly lower DNA methylation with PAE in the murine model experiment (b and d).
Tables
Table of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) identified in the intronic regions of genes that contained DMRs in both the brain and liver.
Δmeth indicates the percentage change in average methylation level within the DMR with prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) compared to non-PAE mice.
| Gene | Tissue | Intronic DMR | Width | No. CpGs | Δmeth | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auts2 | Brain | chr5:131510296–131510465 | 170 | 5 | –23.5% | <0.05 |
| Auts2 | Liver | chr5:131621828–131621999 | 172 | 4 | –22.5% | <0.05 |
| Adgb | Brain | chr10:10455557–10455883 | 327 | 4 | –25.0% | <0.05 |
| Adgb | Liver | chr10:10353338–10353613 | 276 | 4 | –25.9% | <0.05 |
| Rbfox1 | Brain | chr16:6813039–6813217 | 179 | 5 | –24.3% | <0.05 |
| Rbfox1 | Liver | chr16:6781985–6782330 | 346 | 5 | –22.6% | <0.05 |
Number and percentage of brain and liver differentially methylated regions (DMRs) that overlap with tissue-specific regulatory regions.
ATAC-seq, H3K4me1, and H3K27ac regions were obtained at 0 days postnatal from the ENCODE database. p-Values for permutation testing using a randomisation strategy.
| Assay type | Brain DMRs | Brain randomised regions | Liver DMRs | Liver randomised regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATAC-seq | 21/78 (26.92%), p=0.01 | 1/78 (1.28%), p=0.16 | 53/759 (6.98%) p=0.01 | 22/759 (2.90%) p=0.31 |
| H3K4me1 | 4/78 (5.13%) p=0.03 | 2/78 (2.56%) p=0.18 | 38/759 (5.01%) p=0.05 | 35/759 (4.61%) p=0.32 |
| H3K27ac | 9/78 (11.54%) p=0.01 | 2/78 (2.56%) p=0.74 | 48/759 (6.32%) p=0.01 | 19/759 (2.50%) p=0.26 |
Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) identified in the murine model that were validated in the Lussier et al., 2018 human case-control cohort for a clinical diagnosis of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD).
The upper section describes properties of Lussier et al., 2018 human DMRs. The lower section describes properties of the equivalent murine model DMRs.
| DMR | Organism | Tissue | Chr | Start | End | Width | No. CpGs | FDR | Meandiff | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Human | Buccal | 1 | 68151571 | 68152310 | 740 | 5 | 0.028636 | –0.00497 | GADD45A |
| 2 | Human | Buccal | 19 | 13000782 | 13002357 | 1576 | 11 | 0.000197 | –0.00203 | GCDH |
| 3 | Human | Buccal | 7 | 33148815 | 33149316 | 502 | 11 | 0.001149 | –0.00011 | RP9 |
| 4 | Human | Buccal | 17 | 33905444 | 33905888 | 445 | 14 | 0.000171 | –0.00359 | AP2B1, PEX12 |
| 5 | Human | Buccal | 17 | 27181503 | 27182342 | 840 | 11 | 0.018536 | –0.00246 | ERAL1, FAM222B |
| 6 | Human | Buccal | 19 | 12992181 | 12992479 | 299 | 9 | 0.037431 | –0.00179 | CTD-2265O21.7, DNASE2 |
| 7 | Human | Buccal | 19 | 11849531 | 11850013 | 483 | 9 | 0.022724 | –0.00244 | ZNF823 |
| 1 | Mouse | Liver | 6 | 67034885 | 67035082 | 197 | 4 | <0.05 | –0.220833 | E230016M11Rik |
| 2 | Mouse | Liver | 8 | 84901298 | 84901544 | 246 | 5 | <0.05 | –0.234457 | Klf1 |
| 3 | Mouse | Liver | 9 | 22453836 | 22453893 | 57 | 5 | <0.05 | –0.226427 | Rp9 |
| 4 | Mouse | Brain | 14 | 21403570 | 21403622 | 52 | 4 | <0.05 | –0.234193 | Adk |
| 5 | Mouse | Liver | 11 | 78069463 | 78070002 | 539 | 9 | <0.05 | –0.255864 | Mir144, Mir451a |
| 6 | Mouse | Liver | 11 | 78072079 | 78072313 | 234 | 4 | <0.05 | –0.215227 | Mir144, Mir451a |
| 7 | Mouse | Liver | 2 | 177091927 | 177092945 | 1018 | 5 | <0.05 | –0.224354 | Intergenic |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Statistical results from MWA studies.
(a) Table of brain differentially methylated regions (DMRs) identified by DSS and annotated with annotatr. (b) Table of liver DMRs identified by DSS and annotated with annotatr. (c) Table of gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) ontology results from genes associated with liver DMRs. (d) GSEA Ontology Gene/Gene Set Overlap Matrix for liver DMRs. (e) List of genes included in candidate gene analysis. (f) Table of regions assessed in candidate genes analysis. (g) Table of brain DMRs having differences to DNA methylation with prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) being rescued by dietary supplementation. (h) Table of liver DMRs having differences to DNA methylation with PAE being rescued by dietary supplementation. (i) Table of FDR-significant brain DMLs from candidate gene regions in regular diet mice. (j) Table of FDR-significant liver DMLs from candidate gene regions in regular diet mice. (k) Sequencing statistics and bioinformatic quality control.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92135/elife-92135-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/92135/elife-92135-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





