Clinical phenotypes in acute and chronic infarction explained through human ventricular electromechanical modelling and simulations
Figures
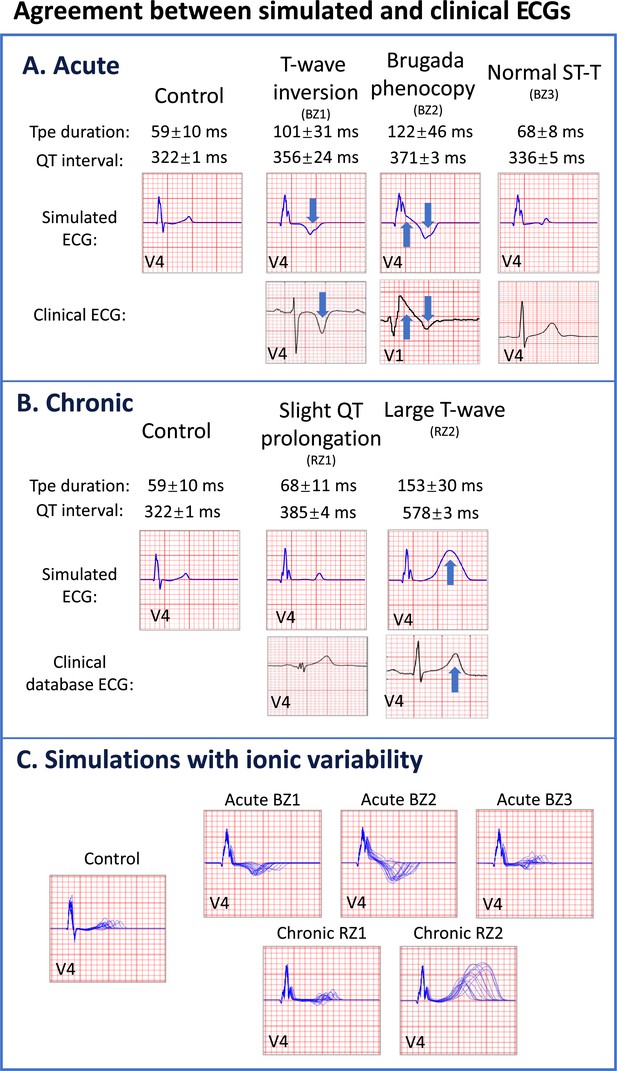
Agreement between simulated and clinical ECGs demonstrating variability in clinical phenotypes in acute and chronic post-myocardial infarction (post-MI).
(A) In acute MI, simulated ECGs show T-wave inversion (border zone model 1 (BZ1)), Brugada phenocopy (BZ2), and normal phenotypes (BZ3), in accordance with phenotypes found in clinical databases. (B) In chronic MI, simulated ECGs show prolonged QT and upright T-waves with a range of amplitude and duration (remote zone model 1 and 2 (RZ1, RZ2)) comparable to those observed in clinical databases. (C) ECG simulations of control, and acute and chronic post-MI considering ionic current variability of the baseline ToR-ORd model. T wave morphologies for acute and chronic post-MI are mostly preserved across ionic variability.
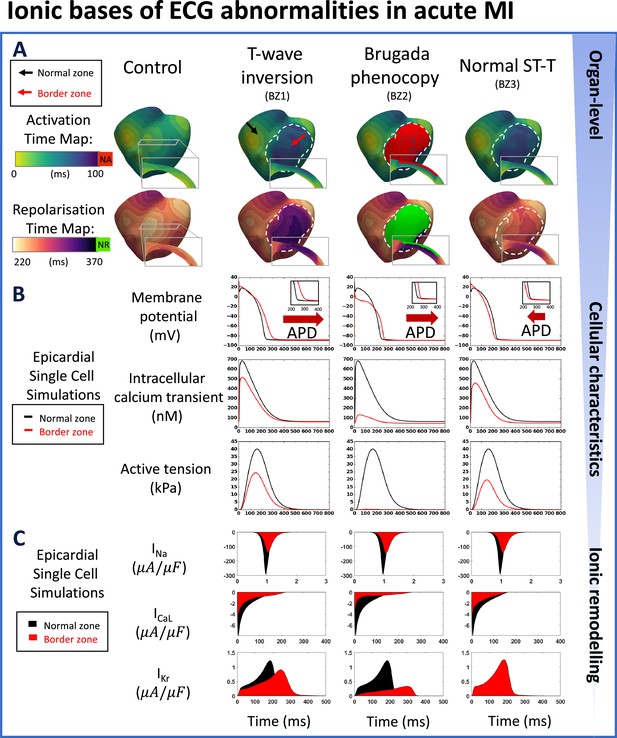
Multiscale explanation of ST and T-wave phenotypes in acute MI.
(A) Activation time maps reveal conduction delay in acute border zone in T-wave inversion and normal ST-T phenotypes, and conduction block in Brugada phenocopy, as well as large repolarisation dispersion and altered transmural repolarisation gradient in T-wave inversion and Brugada phenocopy. Red in activation map show regions of no activation (NA), green in repolarisation map highlights regions of no repolarisation (NR). (B) Action potential duration (APD) prolongation is present in T-wave inversion and Brugada phenocopy cellular phenotypes, while slight APD shortening is present in normal ST-T (red arrows). Decreased calcium amplitude occurs in all phenotypes, with a corresponding decrease in active tension generation. (C) INa, ICaL, and IKr remodelling underpin reduced conduction, reduced calcium amplitude, and alterations in action potential duration, respectively, in all acute phenotypes.
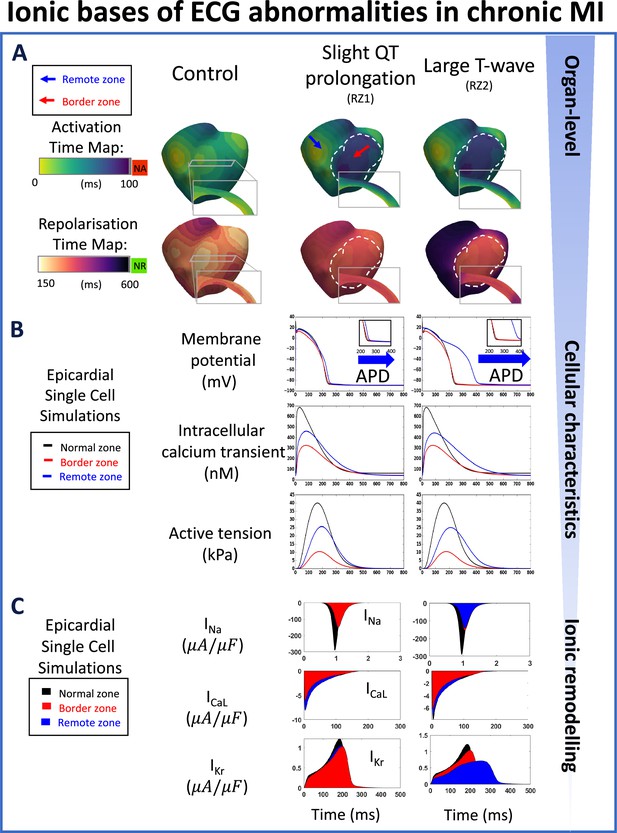
Multiscale explanation of QT and T-wave phenotypes in chronic MI.
(A) Conduction delay in chronic border zone occurs in slight QT prolongation and large T-wave phenotypes, while large repolarisation dispersion exists only in large T-wave. Red in activation map show regions of no activation (NA), green in repolarisation map show regions of no repolarisation (NR). (B) Varying degrees of action potential duration (ADP) prolongation in the remote zone (RZ) corresponding to extent of QT prolongation (blue arrows), with decreased calcium amplitude in remote and border zone of both phenotypes, and corresponding decrease in active tension generation. (C) As in acute MI, INa, ICaL, and IKr remodelling underpin reduced conduction, reduced calcium amplitude, and degree of prolongation in action potential duration, respectively, in both chronic phenotypes.
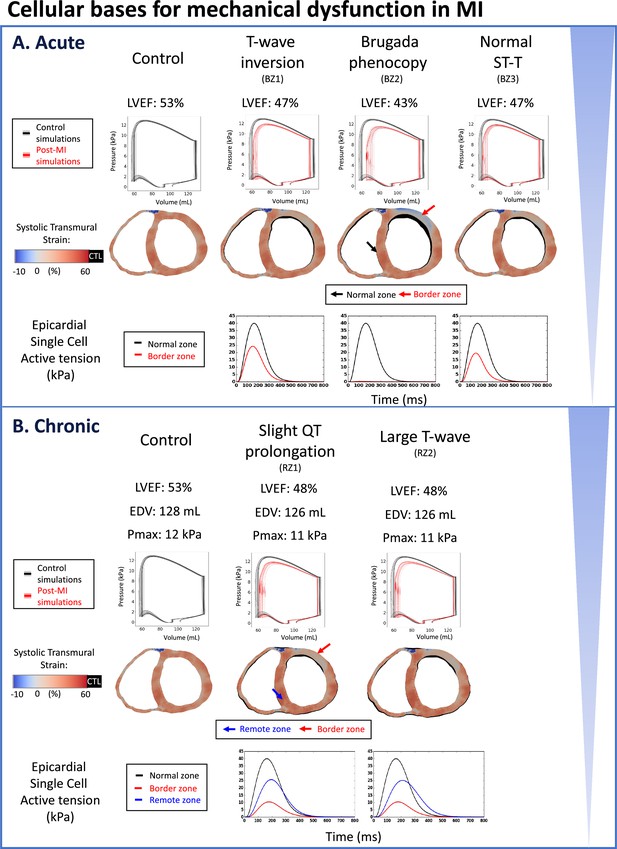
Reduced LVEF and heterogeneous systolic deformation caused by ionic current remodelling in both acute and chronic post-myocardial infarction.
Pressure-volume loops are shown in black (control) or red (post-MI) traces for the baseline model, and in gray (control) or pink (post-MI) traces for the population of models. (A) Reduced LVEF in all acute phenotypes due to reduced active tension amplitude in the border zone (BZ1~3). Brugada phenocopy shows the lowest LVEF due to activation block and loss of contractile function in part of the border zone in addition to reduced active tension amplitude in the activated border zone due to ionic current remodelling. Reduced contractile function in infarct and border zone results in infarct thinning and bulging in systole. Systolic cross section of control simulation shown in black (CTL) with post-MI cross-sections superimposed. (B) Reduced LVEF in both chronic phenotypes due to reduced active tension amplitude in remote zone (RZ) and border zones, independent of the extent of QT prolongation (RZ1, RZ2). Scar stiffening helped to reduce infarct bulging. Systolic cross-section of control simulation shown in black (CTL) with post-MI cross-sections superimposed.
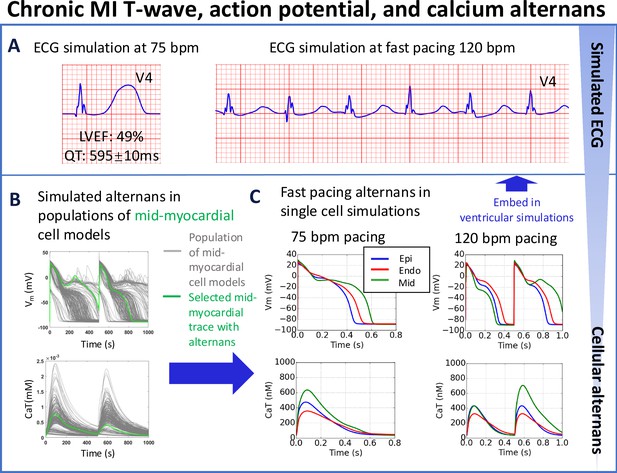
T-wave alternans in simulations underpinned by APD and calcium alternans at fast pacing (120 bpm), albeit with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF = 49%) at rest (75 bpm) for the chronic MI phenotype (A).
(B) Simulated APD and calcium traces in midmyocardial population of models with remote zone 2 (RZ2) remodelling. (C) Large action potential and calcium transient alternans were caused by EADs in simulations at 120 bpm with midmyocardial cells affected by RZ2 ionic current remodelling (green traces, representative example at 75 vs 120 bpm). A single cell model (in green) was selected from the population of models (in grey) for embedding into the remote region for ventricular simulations.
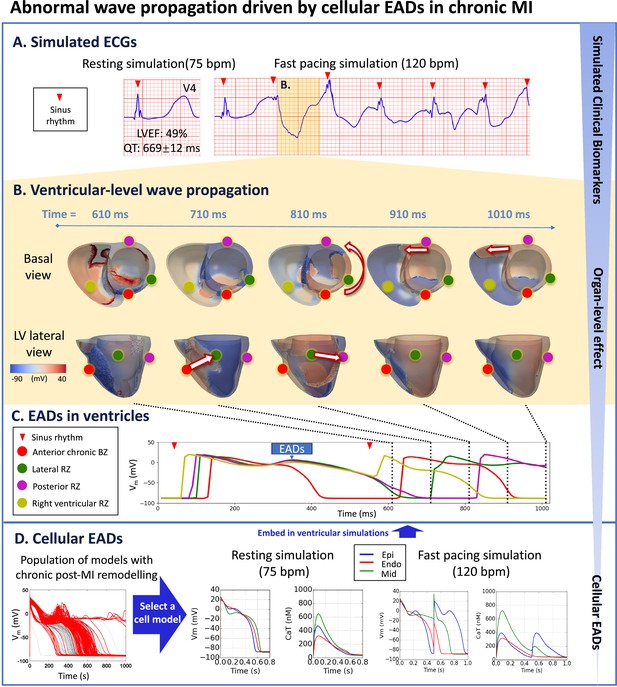
Prolonged QT and preserved LVEF at rest can manifest as severely abnormal ECG at fast heart rates in chronic MI with RZ2.
(A), due to electrotonically-triggered EADs across the border zone (B). In (B), membrane potential changes for the first 1010ms of fast pacing simulation, showing ectopic wave generation driven by electrotonic gradient at 710ms (arrow from red dot to green dot in lateral view), and anticlockwise propagation of ectopic wave starting at 810ms (anticlockwise arrow in basal view, and arrow from green dot to purple dot in lateral view). Ectopic wave propagates towards the right ventricle via the posterior side at 910ms (arrow in basal view) and at 1010ms (arrow in basal view). (C) Local action potential at anterior (red), lateral (green), posterior (purple), and right ventricular (yellow) sites. (D) A population of models demonstrating chronic remote zone 2 (RZ2) remodelling in promoting EADs. A representative example was selected from the population of models that showed EAD and was embedded in ventricular simulations.
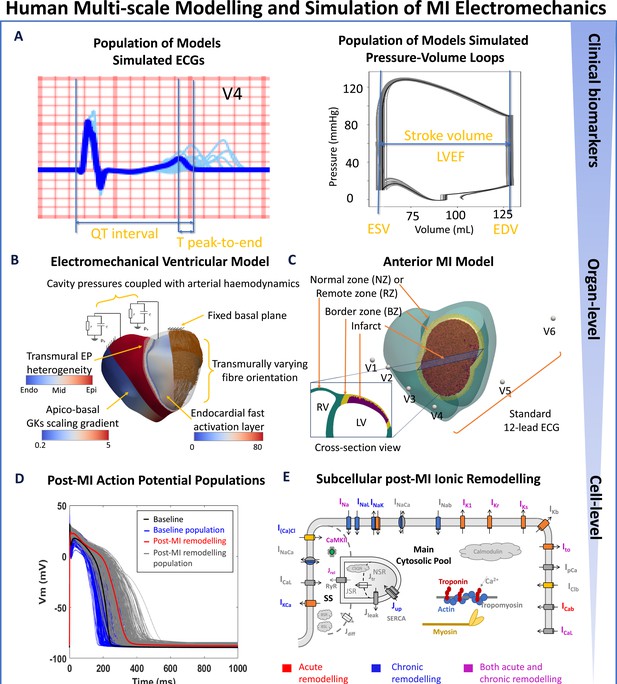
Human-based multi-scale modelling and simulation in acute and chronic myocardial infarction.
(A) Simulations using a population of ventricular models (n=17) to produce ECGs (light blue traces) and pressure-volume (PV) loops (grey traces) superimposed with the baseline ventricular model (ECG in blue and PV in black). Biomarkers are calculated from the baseline simulation of ECG and PV, as illustrated. (B) Ventricular electrophysiology is simulated using a fast endocardial activation layer to approximate Purkinje-myocardial junction, experimentally-informed transmural and apico-basal heterogeneities in action potential duration, and transmurally varying myocyte orientation. Mechanical pumping behaviour is modelled by coupling the intraventricular pressures with a two-element Windkessel model of arterial haemodynamics with a fixed basal plane. (C) An anterior 75% transmural infarction is modelled with acute and chronic ionic current remodelling embedded in the border zone and remote zones. Standard 12-lead ECG was evaluated at standard body-surface locations. (D) Simulated action potentials using populations of human ventricular models in healthy (baseline) and acute and chronic post-MI conditions with different degrees of ionic current remodelling. (E) Schematic representation of ionic fluxes, calcium dynamics and actin/myosin contraction mechanisms in the human ventricular electromechanically-coupled cellular model.
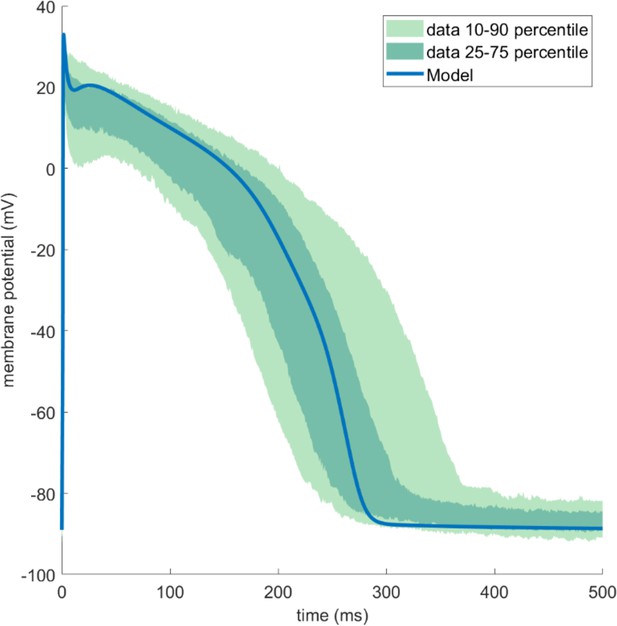
The ToR-ORd-SK model produced similar action potential (AP) traces as published human experimental data (O’Hara et al., 2011).
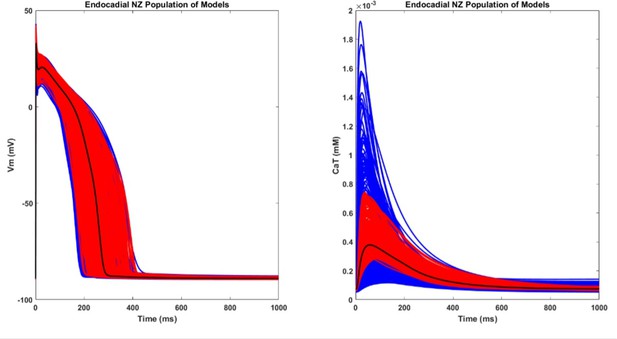
The AP and CaT traces of the population of NZ population of models.
The blue and red traces are the initial and the accepted population, respectively. The black trace is the baseline endocardial model.
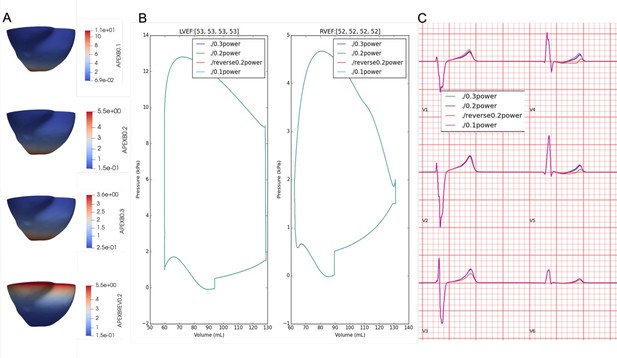
Effects of apex-to-base gradient (A) on pressure-volume, LVEF (B), and ECG morphology (C).
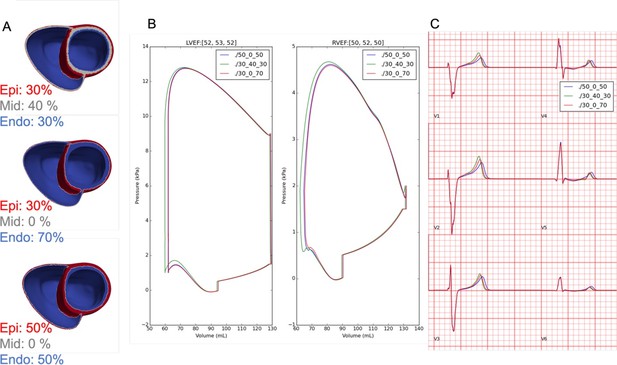
Effects of transmural electrophysiological heterogeneity (A) on pressure-volume, LVEF (B), and ECG morphology (C).
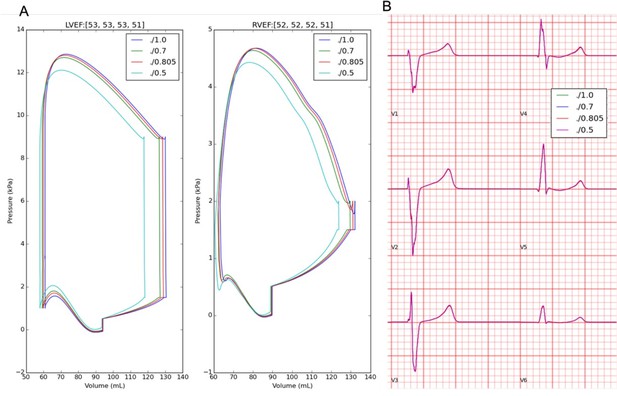
Effects of troponin calcium sensitivity on pressure-volume, LVEF (A), and ECG morphology (B).
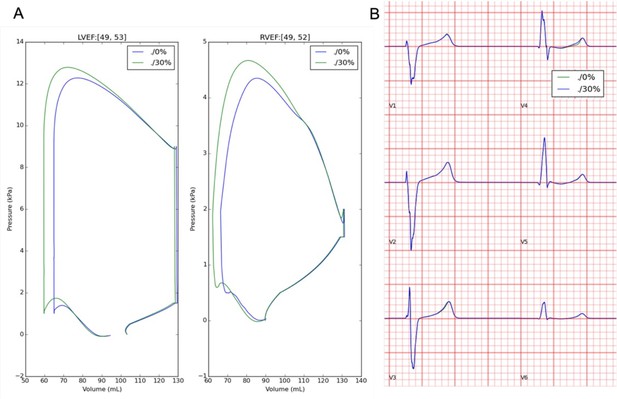
Effects of sheet activation percentage on pressure-volume, LVEF (A), and ECG morphology (B).
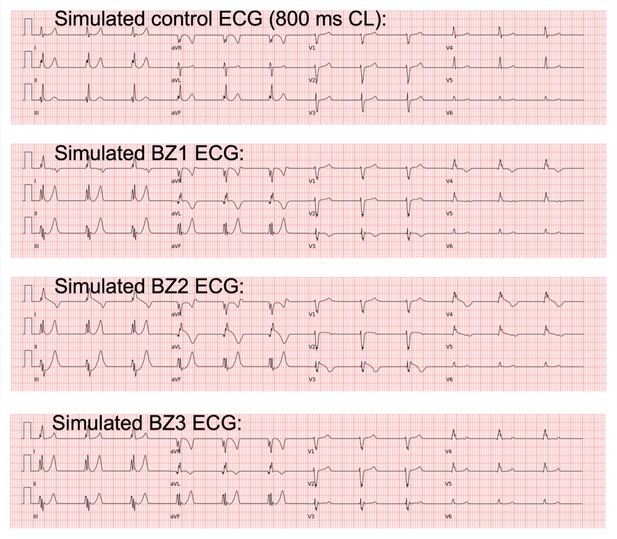
Simulated acute stage 12-lead ECGs for Acute BZ1-3.
Acute BZ1 caused T wave inversion in precordial leads of V3 and V4, where the QT prolongation was more significant. Acute BZ2 caused Brugada phenocopy in leads V3-V5, while Acute BZ3 produced similar ECG morphology as the control case.
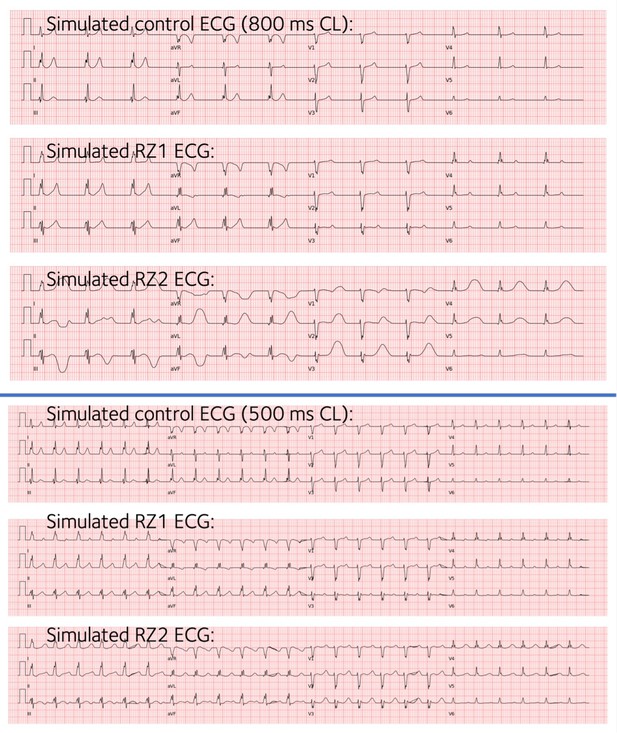
Simulated chronic stage 12-lead ECGs for Chronic RZ1 and Chronic RZ2, both combined with Chronic BZ.
Both produced normal ECG morphology, and T waves are wider and taller in the anterior leads (V2–V4) of Chronic RZ2.
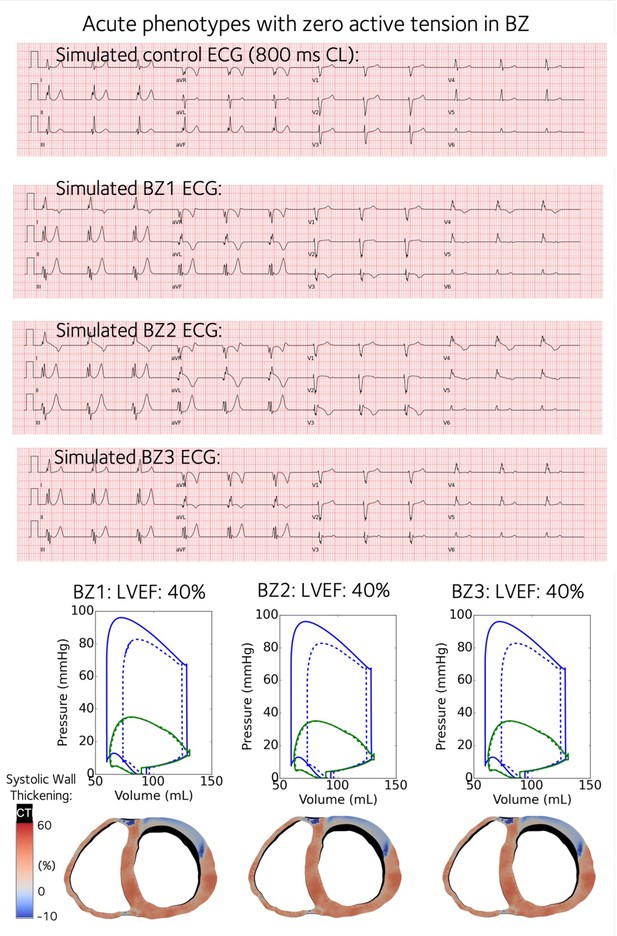
Simulated acute stage 12-lead ECGs for Acute BZ1-3 with contractility turned off in the BZs.
Acute BZ1 caused T wave inversion in precordial leads of V3 and V4, where the QT prolongation was more significant. Acute BZ2 caused Brugada phenocopy in leads V3-V5, while Acute BZ3 produced similar ECG morphology as the control case.
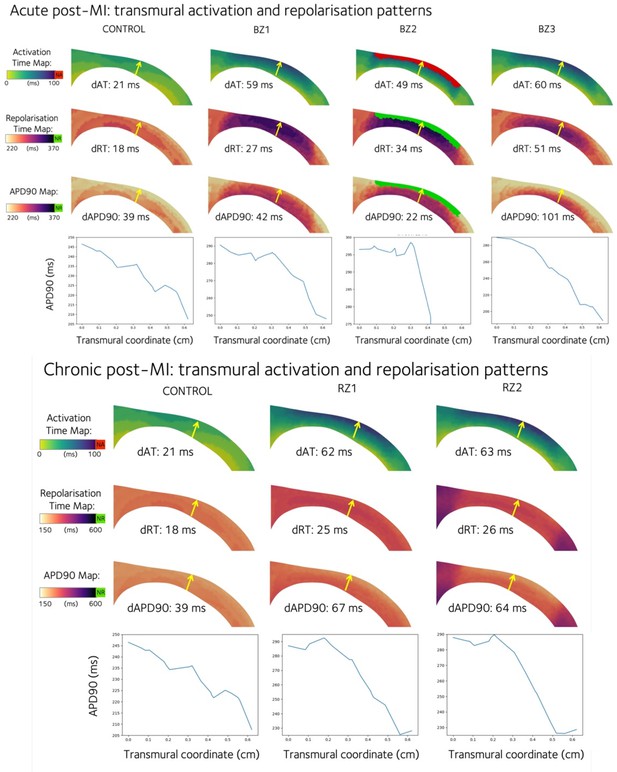
Transmural activation time (AT), repolarisation time (RT), and action potential duration at 90% repolarisation (APD90) are shown for the acute (top panel) and chronic (bottom panel) phenotypes.
A mid-ventricular anterior transmural slice is taken from the left ventricle that shows the cross-section of the anterior infarction and border zones. The transmural gradient is evaluated as the quantity of interest at the epicardium minus that at the endocardium, and is given as dAT, dRT, and dAPD90 values for each cross-section, evaluated at the beginning and end of the yellow arrows. APD90 is plotted across a transmural line as indicated by the yellow arrow.
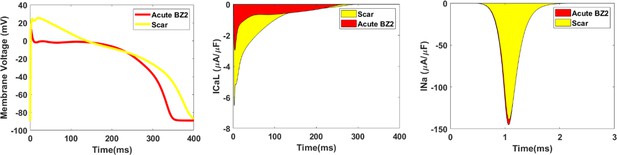
Single cell simulations of the action potential (left), L-type calcium ionic current (middle) and sodium ionic current (right) compared between the scar region and the acute BZ2 help to explain the activation pattern in BZ2.
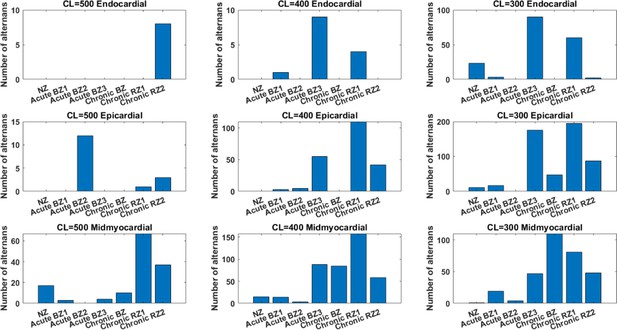
The effects of the BZ and RZ remodelling of the acute and chronic stages on alternans generation in the population of 245 population of models at CL = 500ms, 400ms and 300ms.
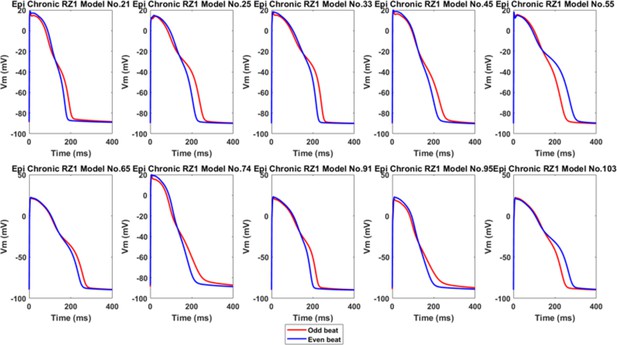
Ten representative alternans in the epicardial population of Chronic RZ1, showing calcium-driven repolarization alternans without EADs.
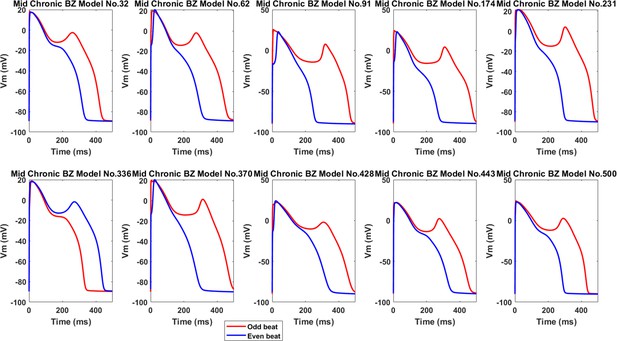
Ten representative alternans in the midmyocardial population of Chronic BZ, showing EAD as a major cause of big alternans.
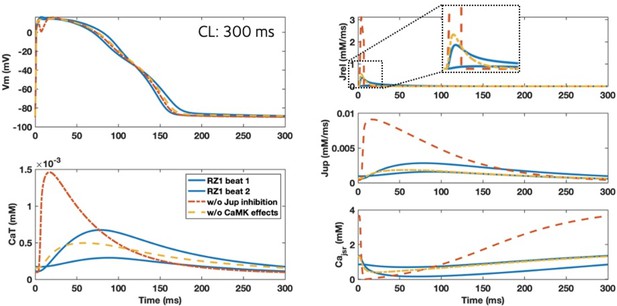
Inhibition of Jup and slower calcium release (Jrel) caused by enhanced CaMKII activity promoted alternans.
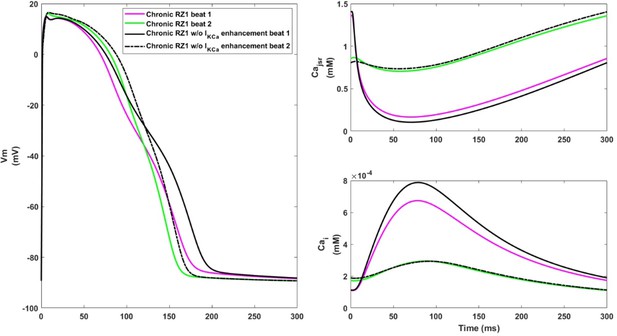
Effects of IKCa enhancement on alternans generation in the chronic stage.
Left: switching IKCa activity back to normal (black traces) caused AP prolongation and bigger alternans. Weaker IKCa also led to stronger CaT (bottom right, black solid line) and larger calcium release in the longer beat (black solid line) that was more difficult for calcium level to recover in JSR (upper right, black solid line).
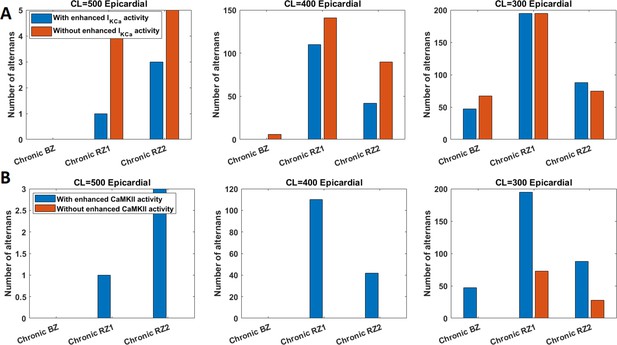
CaMKII and IKCa had opposite roles on alternans inducibility in chronic ionic current remodelling.
Enhanced IKCa tended to inhibit alternans generation (A), whereas augmented CaMKII promoted alternans (B).
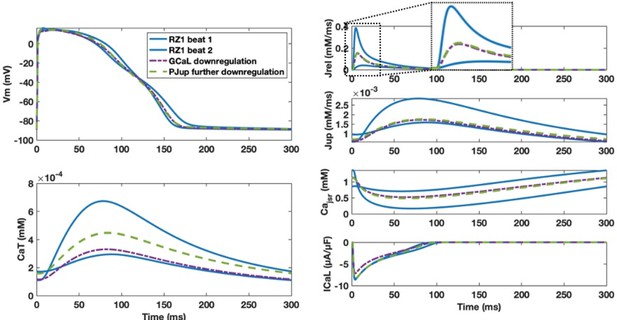
With chronic post-MI ionic current remodelling, alternans models needed stronger GCaL and more preserved PJup to enable alternans generation.
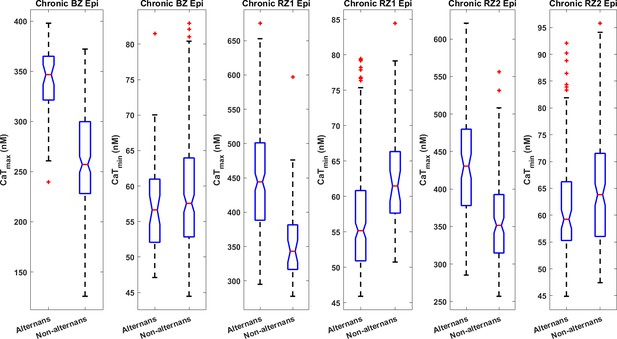
Alternans models had bigger CaTmax than the non-alternating models in the epicardial populations with chronic post-MI remodelling (all with P<0.001).
In addition, alternans models tended to have smaller CaTmin in epicardial populations of Chronic RZ1 (P<0.001) and RZ2 (P<0.05), while the difference was not statistically significant for Chronic BZ.
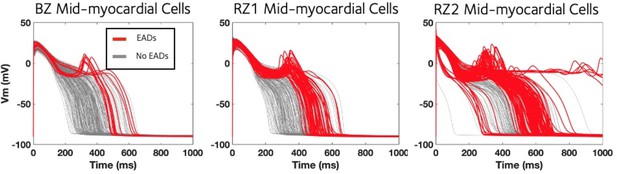
Midmyocardium was most prone for the development of EAD under chronic post-MI remodelling.
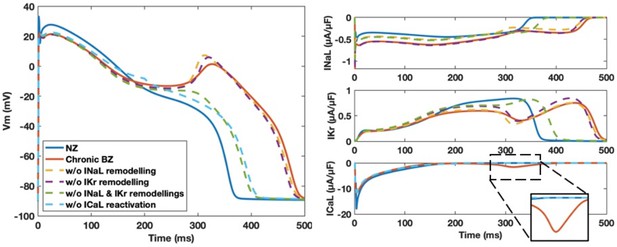
Chronic ionic current remodelling promotes EAD generation through the enhanced INaL and suppressed IKr, which facilitate ICaL reactivation.
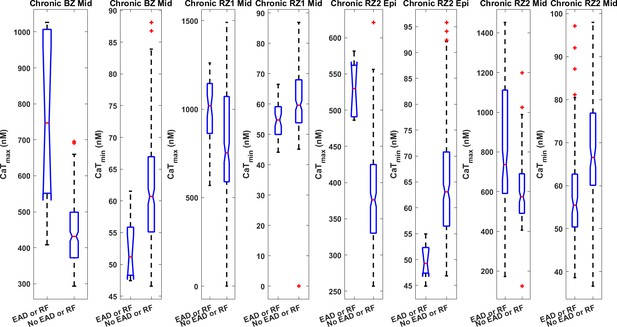
EAD models tended to have stronger CaTmax and weaker CaTmin in the population of Chronic BZ, RZ1 and RZ2 models (all with P<0.001).
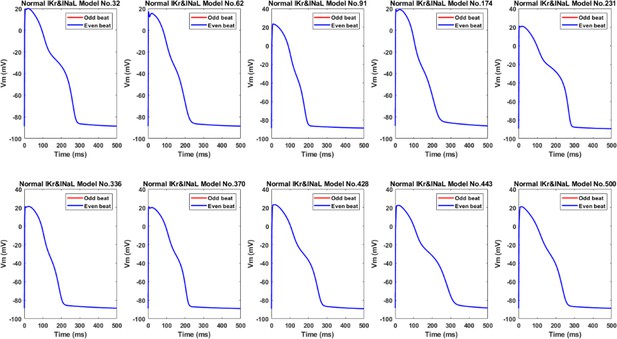
Chronic BZ remodelling induced EAD alternans in the ten representative midmyocardial models, but when these models were simulated without IKr and INaL remodelling, neither EAD nor alternans occurred.
Tables
Linking clinical ECG and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) phenotypes to tissue heterogeneities and subcellular ionic current remodelling in acute and chronic post-myocardial infarction.
| Clinical Phenotypes | Tissue or Cell Level phenomena | Corresponding Post Infarction Ionic Current Remodelling |
|---|---|---|
| Acute MI T-wave inversion in ECG | Reversed transmural repolarisation gradient due to delayed activation and repolarisation in the epicardial border zone | Inhibition of potassium currents in the border zone as well as the slower transmural conduction velocity |
| Acute MI Brugada phenocopy in ECG | Delayed repolarisation, as well as a small region of activation failure in the epicardial border zone | Strong inhibitions of sodium, calcium and potassium ionic currents in the border zone |
| Chronic MI upright tall T-waves in ECG | Large repolarisation time gradient between remote and border zones caused by more severe delay of repolarisation in the remote zone | More severe potassium channel suppression in the remote zone |
| Chronic MI T-wave alternans | Cellular repolarisation alternans or early afterdepolarisation | Suppressed SERCA and augmented CaMKII activity for alternans; Enhanced late sodium current and suppressed hERG current for early afterdepolarisation |
| Acute MI reduction in LVEF | Reduced calcium amplitude and/or regional conduction block | Inhibitions of calcium and sodium currents |
| Chronic MI reduction in LVEF | Reduced calcium amplitude | Decreased SERCA activity |
Experimental ranges of AP and calcium transient (CaT) biomarkers used to calibrate the normal zone (NZ) endocardial population of models at a pacing cycle length (CL) of 1000ms based on human cardiomyocyte experiments (Coppini et al., 2013; Britton et al., 2017).
| Biomakers at 1 Hz | minimum | maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Vmax (mV) | 7 | 55 |
| RMP (mV) | –95 | –80 |
| dvdtmax (mV/ms) | 100 | 1000 |
| APD90 (ms) | 180 | 440 |
| APD50 (ms) | 350 | |
| APD40 (ms) | 85 | 320 |
| APD90-APD40 (ms) | 50 | 150 |
| CaTD90 (ms) | 220 | 750 |
| CaTD90 (ms) | 120 | 420 |
| CaTamp (mM) | 2e-4 | 6e-4 |
| CaTmax(mM) | 2e-4 | 10e-4 |
| CaTmin (mM) | 0 | 4e-4 |
Calibrated electromechanical parameters for healthy baseline model, and modified parameters for post myocardial infarction models.
| Name | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy baseline electromechanical parameters | |||
| diffusivity in fibre, sheet and sheet normal directions | df | 0.00335 | cm/mS |
| ds | 0.000723 | cm/mS | |
| dn | 0.000153 | cm/mS | |
| active mechanics: scaling parameter for active tension | Tscale | 12 | |
| bulk modulus | K | 12185000 | Ba |
| passive mechanics: exponential term in isotropic matrix, fibre, sheet and normal direction | a | 20000 | Ba |
| b | 9.242 | ||
| af | 30000 | Ba | |
| bf | 15.972 | ||
| as | 20000 | Ba | |
| bs | 10.446 | ||
| afs | 10000 | Ba | |
| bfs | 11.602 | ||
| Scar and border zone diffusion parameters | |||
| diffusivity in fibre, sheet and sheet normal directions | df | 0.0012 | cm/mS |
| ds | 0.00023 | cm/mS | |
| dn | 0.000003 | cm/mS | |
| Scar mechanical parameters | |||
| active mechanics: scaling parameter for active tension | Tscale | 0 | |
| bulk modulus | K | 12185000 | Ba |
| passive mechanics: exponential term in isotropic matrix, fibre, sheet and normal direction | a | 200000 | Ba |
| b | 9.242 | ||
| af | 300000 | Ba | |
| bf | 15.972 | ||
| as | 200000 | Ba | |
| bs | 10.446 | ||
| afs | 100000 | Ba | |
| bfs | 11.602 | ||
Parameters for boundary conditions and phase control at resting heart rate and fast pacing (in brackets).
| Name | Parameter | LV | RV | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pericardial stiffness | Kepi | 10000 | Ba cm–1 | |
| Time to initial pressure | t0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | s |
| Initial pressure | P0 | 5000 | 5000 | Ba |
| Duration of passive diastolic filling | tdiastole | 0.08 (0.03) | 0.08 (0.03) | s |
| Pressure at end of diastole | Pendd | 15000 | 15000 | Ba |
| Arterial compliance | C | 0.00055908 | 0.00055908 | cm3 Ba−1 |
| Arterial resistance | R | 250 | 100 | Ba s cm−3 |
| Aortic pressure | Part0 | 90000 | 20000 | Ba |
| Pressure at end of isovolumetric relaxation | Ppost | 10000 | 10000 | Ba |
| Penalty parameters for isovolumetric contraction | Cv | 1 | 1 | cm3 s–1 Ba–1 |
| Penalty parameters for isovolumetric relaxation | Cv | 0.2 | 0.2 | cm3 s–1 Ba–1 |
| Penalty parameters for passive filling | Cp, Cv | 0.1,0.3 | 0.1,0.3 | cm3 Ba–1, cm3 s–1 Ba–1 |
Ionic current remodelling for the acute and chronic stage BZ and RZs.
Comparison of the simulated AP, CaT and active tension (Ta) biomarkers with post myocardial infarction (MI) acute stage canine experimental data and chronic stage human experimental data.
| Biomarkers | Experimental values | Simulated values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Post-MI Stage | Canine epi NZ APD (ms) (mean ± SD) | 295±34 Lue and Boyden, 1992 210±15 Gardner et al., 1985 219±39 Spear et al., 1983 Overall: [180, 329] | 227 |
| Canine epi BZ APD (ms) (mean ± SD) | 346±60 Lue and Boyden, 1992 170±15 Gardner et al., 1985 220±26 Spear et al., 1983 Overall: [194, 406] | BZ1: 284, BZ2: 256, BZ3: 208 | |
| Canine epi BZ Systolic Cai EBZ/NZ (%) | 74% Licata et al., 1997 | NZ: 686, BZ1: 517 (75%), BZ2: 133 (20%), BZ3: 457 (67%), | |
| Canine epi BZ Voltage Clamp Cai at 0 mV EBZ/NZ | 53% Pu et al., 2000 | ||
| Canine Cell shortening EBZ/NZ % | 12% Licata et al., 1997 | NZ systolic Ta: 40, BZ1: 24 (60%), BZ2: 0.37 (1%), BZ3: 20 (50%) | |
| Chronic Post-MI Stage | Human Mid Systolic Cai Failing/Non-Failing (%) | 49% Piacentino et al., 2003 | NZ (800 ms CL):1219, RZ1: 744 (60%), RZ2: 608 (50%) |
| Human Mid Systolic Cai MI/normal (%) 1 Hz | 37.5% Høydal et al., 2018 | ||
| Human Mid Diastolic Cai Failing/Non-Failing (%) | 96% Piacentino et al., 2003 | NZ (800 ms CL): 80, RZ1: 37 (46%), RZ2: 39 (49%) NZ (500 ms CL): 86, RZ1: 52 (61%), RZ2: 62 (72%) | |
| Human Mid Diastolic Cai MI/normal (%) 1 Hz | 115% Høydal et al., 2018 | ||
| Human Mid Cell shortening MI/normal (%) 1 Hz | 33% Høydal et al., 2018 | NZ systolic Ta (800 ms CL): 65, RZ1: 58 (89%), RZ2: 45 (70%) |
Simulated AP, CaT and Ta biomarkers from baseline NZ, BZ and RZ epi-, mid-, and endocardial single cell models.
For the acute stage, the Acute BZ1 and BZ2 induced significant APD prolongation, while the BZ3 led to mild APD shortening. The Acute BZ1 and BZ3 had similar degree of reduction in systolic Ca and Ta, whereas the Acute BZ2 had more severe loss of contractility. For the chronic stage, the Chronic RZ1 and RZ2 had similar decrease in systolic Ca and Ta than control, but the RZ2 had more severe APD prolongation than the Chronic RZ1.
| Type | APD90 (ms) | CaTD90 (ms) | Diastolic Ca (nM) | Systolic Ca (nM) | Diastolic Ta (kPa) | Systolic Ta (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (800ms) | epi: 227, mid: 336, endo: 263 | epi: 298, mid: 333, endo: 336 | epi: 62.32, mid: 79.74, endo: 70.70 | epi: 686.27, mid: 1218.83, endo: 477.71 | epi: 0.06, mid: 0.10, endo: 0.07 | epi: 40.00, mid: 65.47, endo: 23.87 |
| Acute BZ1 | epi: 284, mid: 391, endo: 315 | epi: 289, mid: 339, endo: 325 | epi: 59.63, mid: 63.52, endo: 65.62 | epi: 517.13, mid: 691.30, endo: 342.98 | epi: 0.05, mid: 0.06, endo: 0.06 | epi: 24.33, mid: 44.78, endo: 10.46 |
| Acute BZ2 | epi: 256, mid: 373, endo: 341 | epi: 266, mid: 342, endo: 334 | epi: 45.11, mid: 57.08, endo: 57.98 | epi: 133.09, mid: 326.57, endo: 184.93 | epi: 0.03, mid: 0.05, endo: 0.05 | epi: 0.37, mid: 8.97, endo: 1.48 |
| Acute BZ3 | epi: 208, mid: 316, endo: 247 | epi: 256, mid: 295, endo: 288 | epi: 49.05, mid: 60.49, endo: 59.79 | epi: 457.49, mid: 834.58, endo: 352.71 | epi: 0.03, mid: 0.05, endo: 0.05 | epi: 19.66, mid: 52.08, endo: 11.18 |
| Chronic BZ | epi: 235, mid: 362, endo: 293 | epi: 419, mid: 444, endo: 474 | epi: 41.90, mid: 40.80, endo: 50.59 | epi: 324.87, mid: 499.97, endo: 285.67 | epi: 0.03, mid: 0.03, endo: 0.04 | epi: 10.44, mid: 31.40, endo: 7.76 |
| Chronic RZ1 | epi: 247, mid: 411, endo: 313 | epi: 426, mid: 462, endo: 478 | epi: 39.64, mid: 37.47, endo: 49.34 | epi: 459.72, mid: 744.07, endo: 387.91 | epi: 0.03, mid: 0.05, endo: 0.04 | epi: 25.67, mid: 57.56, endo: 18.40 |
| Chronic RZ2 | epi: 392, mid: 591, endo: 467 | epi: 498, mid: 569, endo: 557 | epi: 39.77, mid: 38.61, endo: 49.51 | epi: 444.67, mid: 607.59, endo: 361.11 | epi: 0.03, mid: 0.09, endo: 0.05 | epi: 25.14, mid: 44.80, endo: 16.17 |
| Acute and (chronic) scar | epi: 250, mid: 366, endo: 295 | epi: 261, mid: 304, endo: 296 | epi: 49.17, mid: 62.49, endo: 59.70 | epi: 502.85, mid: 883.02, endo: 375.70 | epi: 0.03 (0), mid: 0.06 (0), endo: 0.05 (0) | epi: 24.23 (0), mid: 53.21 (0), endo: 13.28 (0) |
| Control (500ms) | epi: 210, mid: 306, endo: 240 | epi: 265, mid: 276, endo: 298 | epi: 58.61, mid: 85.60, endo: 67.91 | epi: 760.33, mid: 1740.38, endo: 531.49 | epi: 0.38, mid: 1.81, endo: 0.33 | epi: 42.77, mid: 68.04, endo: 27.54 |
| RZ1 (500ms) | epi: 226, mid: 296, endo: 271 | epi: 370, mid: 384, endo: 396 | epi: 47.10, mid: 52.52, endo: 65.07 | epi: 470.50, mid: 712.75, endo: 385.73 | epi: 0.50, mid: 2.04, endo: 0.51 | epi: 25.84, mid: 51.69, endo: 17.28 |
| RZ2 (500ms) | epi: 316, mid: 395, endo: 366 | epi: 389, mid: 401, endo: 410 | epi: 50.88, mid: 61.53, endo: 65.99 | epi: 425.66, mid: 605.85, endo: 337.64 | epi: 0.52, mid: 1.94, endo: 0.46 | epi: 21.20, mid: 41.79, endo: 12.23 |
Comparison of the ECG and mechanical biomarkers from biventricular electromechanical simulations against literature values at resting heart rate.
QTc was calculated using Bazett’s formula from the simulated QT intervals. Post-MI RVEF values were from ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients whose culprit and chronic total occlusion were not in the right coronary artery. VA: ventricular arrhythmia; VT: ventricular tachycardia; SDB: sleep disordered breathing. Our simulated ECG and mechanical biomarker values are mostly consistent with the clinically reported biomarker ranges.
| Biomarkers | Control | Acute Stage Post-MI | Chronic Stage Post-MI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrophysiological Biomarkers | Literature | Simulation | Literature | Simulation | Literature | Simulation |
| QRS duration (ms) | 96 ± 9 in men, 85 ± 6 in women Carlsson et al., 2006 | 79 ± 2 | 88 ± 35 Yerra et al., 2006 | 91±5, 95±9, 92±6 | Max 127 ± 16 without VT Min 81 ± 15 without VT Perkiömäki et al., 1995 Max 137 ± 25 with VT Min 89 ± 20 with VT Perkiömäki et al., 1995 | 94 ± 6, 93 ± 5 |
| QTc interval (Bazett formula) (ms) | 350–440 Johnson and Ackerman, 2009 | 360 ± 1 | 423 ± 50 without VA Ahnve, 1985 460±40 with VA Ahnve, 1985 | 398 ± 27, 415 ± 4, 376 ± 5 | Max 448 ± 39 without VT Min 383 ± 20 without VT Perkiömäki et al., 1995 Max 493 ± 51 with VT Min 388 ± 30 with VT ve stiffness parameters were calibrated based on Perkiömäki et al., 1995 | 430 ± 4, 578 ± 3 |
| Mechanical Biomarkers | Literature | Simulation | Literature | Simulation | Literature | Simulation |
| LVEDV (mL) | 142 ± 21 (SSFP-CMR) Maceira et al., 2006a | 129 | 116 ± 15 Uslu et al., 2013 | 124–125 | 106 ± 12 Uslu et al., 2013 | 126 |
| RVEDV (mL) | 144 ± 23 (SSFP-CMR) Maceira et al., 2006b | 131 | 129 ± 28 with SDB Buchner et al., 2015 132 ± 28 without SDB Buchner et al., 2015 | 131 | 143 ± 29 with SDB Buchner et al., 2015 132 ± 31 without SDB Buchner et al., 2015 | 133 |
| LVESV (mL) | 47 ± 10 (SSFP-CMR) Maceira et al., 2006a | 60 | 61 ± 12 Uslu et al., 2013 | 65~72 | 52 ± 10 Uslu et al., 2013 | 65 |
| RVESV (mL) | 50±14 (SSFP-CMR) Maceira et al., 2006b | 63 | 56 21 with SDB Buchner et al., 2015 53 ± 16 without SDB Buchner et al., 2015 | 64 | 58 ± 21 with SDB Buchner et al., 2015 51 ± 15 without SDB Buchner et al., 2015 | 64 |
| LVEF (%) | 67 ± 4.6 (SSFP-CMR) Maceira et al., 2006a, 62±7 (RNV) Nemerovski et al., 1982 | 53 | 48 ± 8 Uslu et al., 2013 | 43~47 | 52 ± 7 Uslu et al., 2013 | 48 |
| RVEF (%) | 48 ± 5 (RNV) Nemerovski et al., 1982 | 52 | 53.0 ± 7.1 van Veelen et al., 2022 | 51 | 55.9 ± 5.4 van Veelen et al., 2022 | 52 |
Simulated ECG biomarkers from biventricular electromechanical simulations for the acute and the chronic post-MI stages.
For the acute stage, Acute BZ1 and BZ2 caused significant QT prolongation, longer T peak to T end, whereas the Acute BZ3 induced milder effects. For the chronic stage, both Chronic RZ1 and RZ2 led to QT prolongation, with RZ2 also generating longer T wave duration, T peak to T end, and T start to T peak than control and RZ1 at CL = 800ms. At fast pacing of CL = 500ms, both Chronic RZ1 and RZ2 caused longer QT, T wave and T start to T peak durations. For both stages, the QT dispersions did not reflect the repolarization dispersion very well.
| ECG biomarkers | Control | Acute BZ1 | Acute BZ2 | Acute BZ3 | Chronic RZ1 | Chronic RZ2 | Control CL = 500ms | Chronic RZ1 CL = 500ms | Chronic RZ2 CL = 500ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QRS duration (ms) | 79±2 | 91±5 | 95±9 | 92±6 | 94±6 | 93±5 | 86±7 | 86±7 | 86±7 |
| T duration (ms) | 96±17 | 163±40 | - | 113±18 | 122±42 | 291±20 | 97±19 | 100±15 | 140±37 |
| T peak to T end (ms) | 59±10 | 101±31 | 122±46 | 68±8 | 68±11 | 153±30 | 57±8 | 55±12 | 82±17 |
| T start to T peak (ms) | 38±8 | 61±30 | - | 45±10 | 54±32 | 138±12 | 40±11 | 45±6 | 58±22 |
| QT interval (ms) | 322±1 | 356±24 | 371±3 | 336±5 | 385±4 | 578±3 | 305±2 | 344±4 | 419±4 |
| QT dispersion (precordial) (ms) | 3 | 55 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 5 |
Simulated pressure-volume mechanical biomarkers for each heart beat from biventricular electromechanical simulations for acute and chronic stages post-MI: left and right end diastolic volumes (EDVL, EDVR), left and right stroke volumes (SVL, SVR), left and right ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF, RVEF).
For the acute stage, Acute BZ1 and Acute BZ3 generated the same degree of reduction in SVL and LVEF, whereas the Acute BZ2 induced the smallest SVL and LVEF. For the chronic stage, both Chronic RZ1 and Chronic RZ2 produced the same SVL and LVEF at both pacing rates despite their difference in the degree of repolarization heterogeneity.
| Pressure-volume Biomarkers | Control | Acute BZ1 | Acute BZ2 | Acute BZ3 | Chronic RZ1 | Chronic RZ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 ms CL | EDVL (mL) | 129, 129, 129 | 124,124,124 | 124,125,125 | 124,124,124 | 127, 126, 126 | 127, 126, 126 |
| EDVR (mL) | 130,131,131 | 130,131,131 | 130,131,131 | 130,131,131 | 132,133,133 | 132,133,133 | |
| SVL (mL) | 68, 69, 69 | 59,59,59 | 53,53,53 | 59,59,59 | 62, 61, 61 | 62, 61, 61 | |
| SVR (mL) | 68,68,68 | 67,67,67 | 67,67,67 | 67,67,67 | 69,69,69 | 69,69,69 | |
| LVEF (%) | 53,53,53 | 47,47,47 | 43,43,43 | 47,47,47 | 49, 48, 48 | 49, 48, 48 | |
| RVEF (%) | 52,52,52 | 51,51,51 | 51,51,51 | 51,51,51 | 52,52,52 | 52,52,52 | |
| Peak left systolic pressure (kPa) | 12,12,12 | 11,11,11 | 11,11,11 | 11,11,11 | 11, 11, 11 | 11, 11, 11 | |
| Peak right systolic pressure (kPa) | 4,4,4 | 4,4,4 | 4,4,4 | 4,4,4 | 4,4,4 | 4,4,4 | |
| 500 ms CL | EDVL (mL) | 111,112,113, 113,113,113 | NA | 114,107,111, 108,110,108 | 116,108,111, 109,110,109 | ||
| EDVR (mL) | 123,122,123, 123,123,123 | 125,117,122, 119,121,119 | 126,119,123, 120,121,120 | ||||
| SVL (mL) | 53,53,54, 54,54,54 | 50,43,47, 44,45,44 | 51,43,46, 44,45,44 | ||||
| SVR (mL) | 61,61,61, 61,61,61 | 64,56,62, 56,60,57 | 65,57,62, 59,60,59 | ||||
| LVEF (%) | 47,47,47, 47,47,47 | 44,39,42, 40,41,40 | 44,39,41, 40,41,40 | ||||
| RVEF (%) | 49,49,49, 49,49,49 | 51,47,50, 47,50,48 | 51,48,50, 49,49,49 | ||||
| Peak left systolic pressure (kPa) | 11,11,11, 11,11,11 | 10,10,10, 10,10,10 | 10,10,10, 10,10,10 | ||||
| Peak right systolic pressure (kPa) | 4,4,4, 4,4,4 | 4,4,4, 4,4,4 | 4,4,4, 4,4,4 | ||||
Number of alternans induced by three chronic remodelling at CL = 500, 400 and 300ms in endocardial, midmyocardial and epicardial population of models.
| Population of models (n=245) | No. of alternans at CL = 300ms | No. of alternans at CL = 400ms | No. of alternans at CL = 500ms | Key parameters for alternans |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic BZ | Mid (110)>Epi (47) | Mid only (84) | Mid only (10) | ↑GCaL, ↑GKr, ↑PJup |
| Chronic RZ1 | Epi (195)>Mid (81)>Endo (60) | Mid (158)>Epi (110)>Endo (4) | Mid (67)>Epi (1) | ↑GCaL, ↑PJup |
| Chronic RZ2 | Epi (88)>Mid (48)>Endo (2) | Mid (58)>Epi (42) | Mid (37)>Endo (8)>Epi (3) | ↑GCaL, ↑GKr, ↓GNCX, ↑PJup, ↑PJrel |
Number of EADs and RFs induced by three chronic remodelling in endocardial, midmyocardial and epicardial population of models.
| Population of models (n=245) | No. of EADs and RFs at CL = 1000ms | Key parameters for EADs and RFs |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic BZ | Mid only (11) | ↑GCaL, ↓GKr, ↑GNCX |
| Chronic RZ1 | Mid only (52) | ↑GCaL, ↓GKr, ↑GNCX |
| Chronic RZ2 | Mid (118)>Epi (9)>Endo (1) | ↑GCaL, ↓GKr, ↑GNCX, ↑PJup |