SCC3 is an axial element essential for homologous chromosome pairing and synapsis
Figures
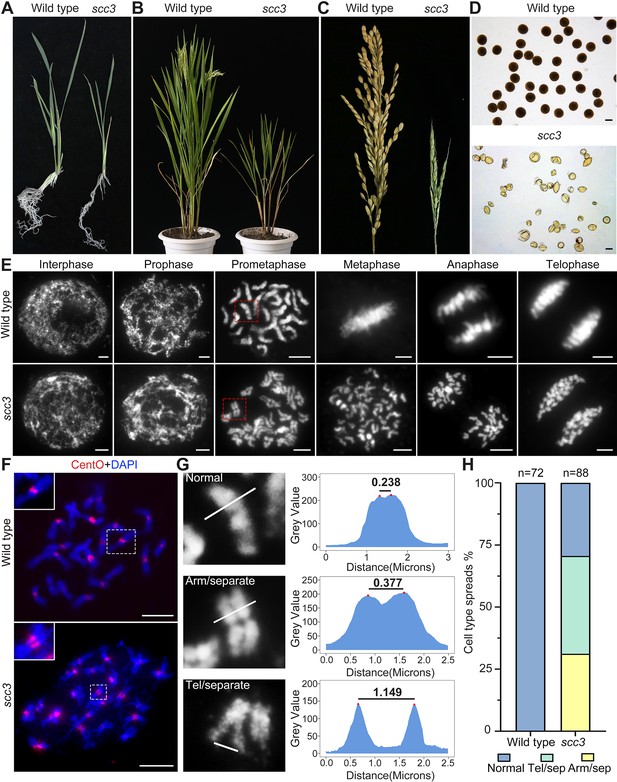
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) is required for sister chromatid cohesion during mitosis.
(A) Morphology of seedlings and root tips in wild-type and scc3. (B) Morphology of plants in wild-type and scc3. (C) Morphology of panicles in wild-type and scc3. (D) Pollen grains stained in 1% I2-KI solution in wild-type and scc3. Bars, 50 μm. (E) The chromosome behaviors of root tip cells in wild-type and scc3, stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Individual chromosomes are marked by red boxes. The distance between the sister chromatids increased significantly at prometaphase, and the sister chromatids separated in advance at metaphase in scc3. Bars, 5 μm. (F) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis of mitotic cells with centromere-specific probes in the wild-type and scc3. The distance between centromeres increased significantly in scc3. CentO (red) signals indicate centromeres. Chromosomes were stained with DAPI (blue). Bars, 5 μm. (G) The distance between sister chromatids in different mitotic chromosomes. In normal condition, two sister chromatids form tight stick. In scc3, the distance between chromosome arms and telomeres were increased significantly. Curve diagrams show the distance between the arms and the telomeres, respectively, as measured by IMAGEJ. Bars, 1 μm. (H) Graphical representation of the frequency of each type of chromosome morphology. The classification was assigned when >50% chromosomes in a spread showed the indicated morphology.
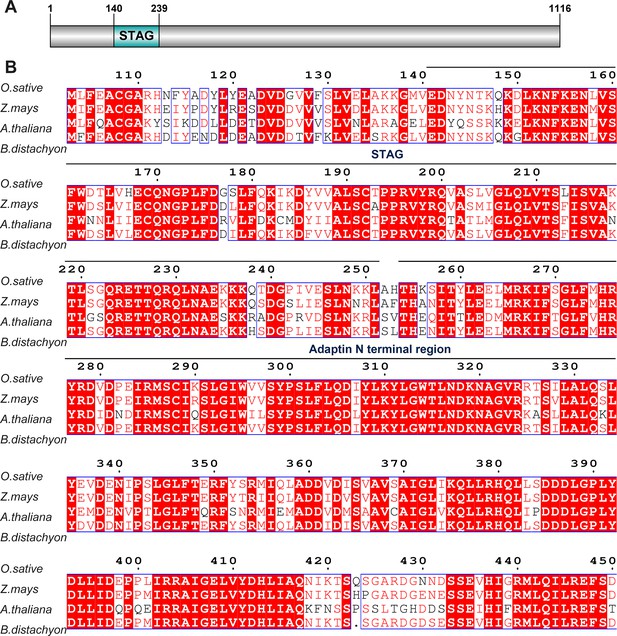
Multiple sequence alignment of sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) with its homologs from three different species.
(A) SCC3 contains a conserved STAG domain. (B) STAG domains are conserved in both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.

Protein structure and phylogenetic tree analysis of sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3).
(A) The full-length (1–1,116 aa) SCC3 protein among different species shows high structural similarity. The arrow indicates similarity in SCC3 subunits. (B) Phylogenetic tree derived from full-length SCC3 amino acid sequences and homologous sequences from other plant species. The right panel indicates the conserved domains of SCC3 proteins in different species.

Multiple sequence alignment of sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) with its homologs from different species analyzed in an evolutionary tree.
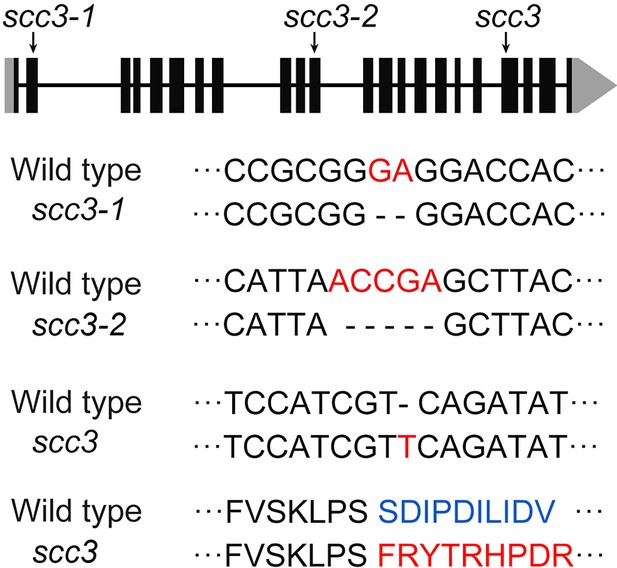
Schematic representation of sister chromatid cohesion 3s (SCC3’s) mutation site.
Schematic representation of the SCC3 gene and its mutation site. Coding regions are shown as black boxes and untranslated regions are shown as gray boxes.
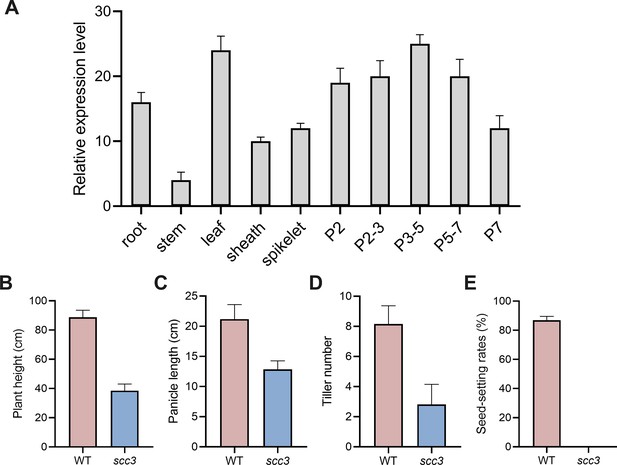
The expression pattern of sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) and plant phenotypic statistics of wild-type and scc3 mutants.
(A) The expression pattern of SCC3. P2, 2 cm long panicles; P2-3, 2–3 cm long panicles; P3-5, 3–5 cm long panicles; P5-7, 5–7 cm long panicles; P7, 7 cm long panicles. Expression values represent means ± SD of three biological replicates. (B) Statistics of plant height in wild-type and scc3. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (C) Statistics of panicle length in wild-type and scc3. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (D) Statistics of tiller number in wild-type and scc3. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. (E) Statistics of seed-setting rates in wild-type and scc3. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates.
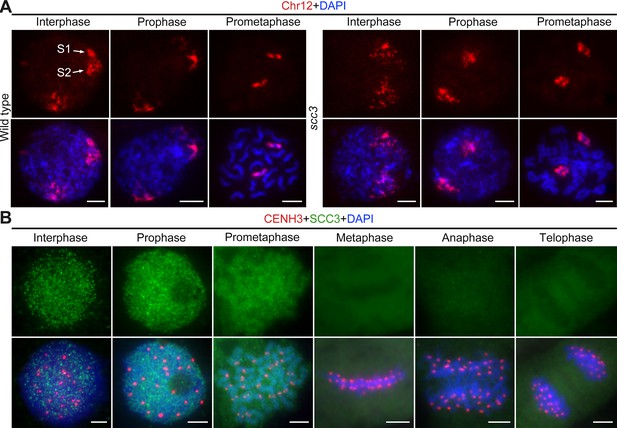
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) alters the structure of sister chromatids during mitosis.
(A) The dynamic process of chromosome structure in early mitosis as revealed by pooled oligos specific to chromosome 12 (red). In the wild-type, S1 and S2 indicate the replicated sister chromatids. However, in scc3 sister chromatids exhibited the variation of structure from interphase to prophase. Mitotic chromosomes in wild-type and scc3 were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Bars, 5 μm. (B) The loading pattern of SCC3 (green, from mouse) and CENH3 (red, from rabbit) in wild-type root tip cells. Chromosomes were stained with DAPI (blue). Bars, 5 μm.
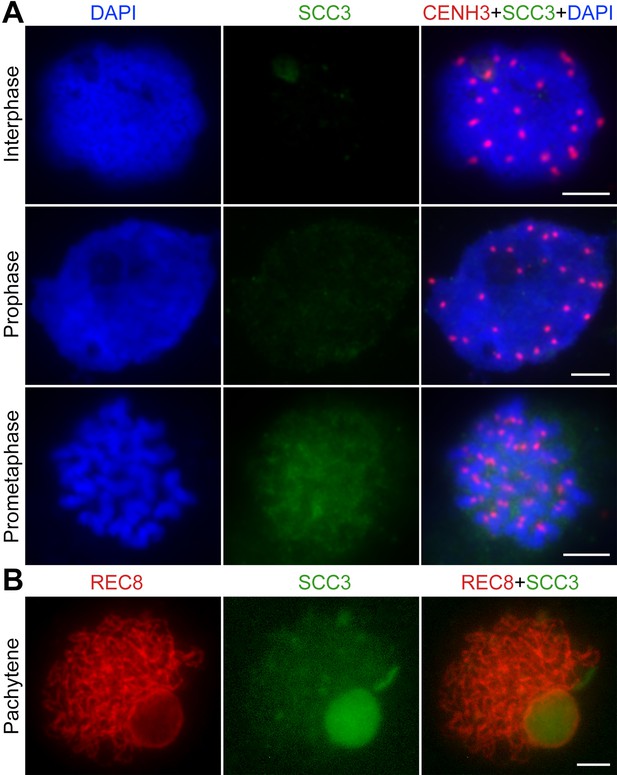
Immunolocalization of sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) in scc3 mitosis and mitosis.
(A) Immunolocalization of CENH3 (red, from rabbit) and SCC3 (green, from mouse) in scc3 root tip cells during mitosis. Chromosomes were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Bar, 5 μm. (B) Immunolocalization of REC8 (red, from rabbit) and SCC3 (green, from mouse) in scc3 meiocytes during meiosis. Bar, 5 μm.
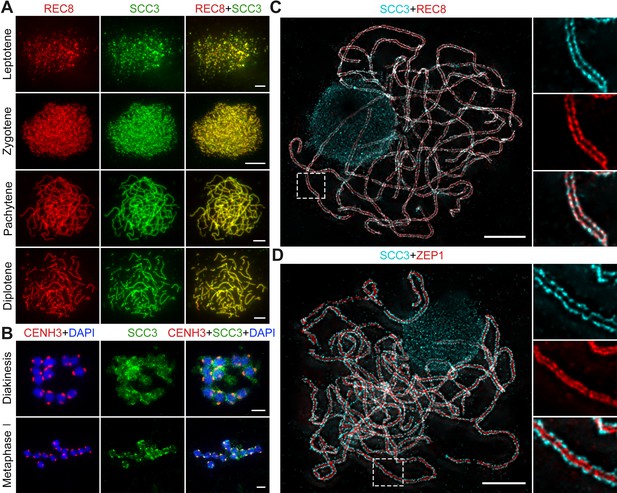
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) is an axial element during meiosis.
(A) In meiosis, SCC3 (green, from mouse) colocalizes with REC8 (red, from rabbit) from the leptotene to diplotene. Bars, 5 μm. (B) During diakinesis and metaphase I, SCC3 (green, from mouse) gradually dispersed and finally retained in the centromeres indicated by CENH3 (red, from rabbit). Chromosomes were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Bars, 5 μm. (C) Immunostaining of SCC3 (cyan, from mouse) and REC8 (red, from rabbit) in wild-type meiocytes at pachytene. Two parallel linear SCC3 signals colocalize with the REC8 linear signals, indicating chromosomal axial elements. Magnified images of the blocked regions are shown on the right. Bars, 5 μm. (D) Immunostaining of SCC3 (cyan, from mouse) and ZEP1 (red, from rabbit) in wild-type meiocytes at pachytene. Two linear SCC3 signals wrap the ZEP1 signals, indicating central elements of SC are wrapped by axial elements. Magnified images of the blocked regions are shown on the right. Bars, 5 μm.

Immunolocalization of CENH3 and REC8 in wild-type from diakinesis to metaphase I.
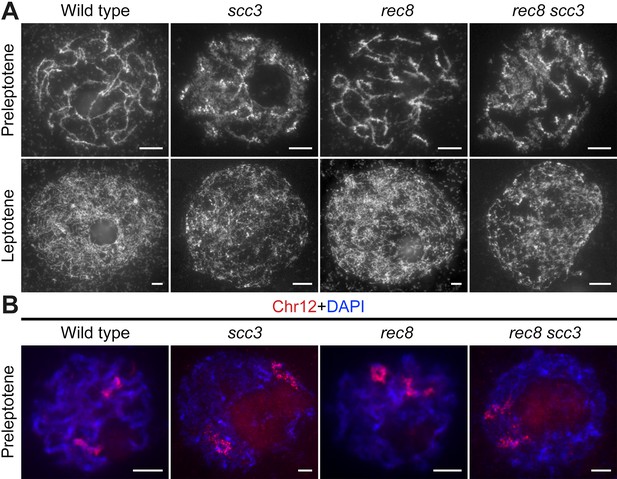
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) is required for sister chromatid cohesion in early meiosis.
(A) Meiocyte chromosome morphology at the preleptotene and leptotene in wild-type, scc3, rec8, and rec8 scc3. Chromosomes at preleptotene exhibited a hairy rodlike appearance and formed thin threads at leptotene in wild-type. However, chromosomes in scc3 were dispersed with blurred outlines and failed to form thin threads at leptotene. Bars, 5 μm. (B) The dynamic process of chromosome structure in preleptotene was revealed by pooled oligos specific to chromosome 12 (red). Preleptotene chromosomes in wild-type, scc3, rec8, and rec8 scc3. Chromosomes were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (blue). Bars, 5 μm.
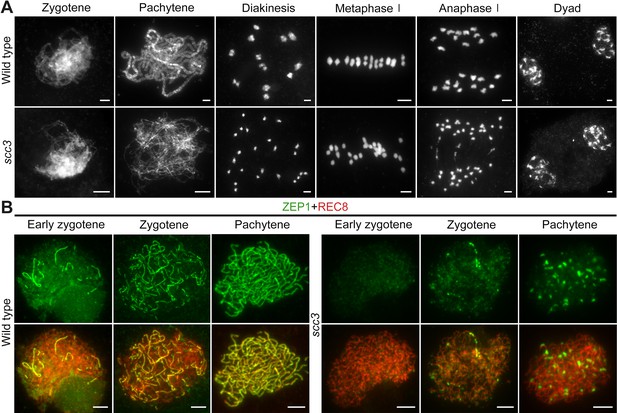
Homologous pairing and synapsis are disturbed in sister chromatid cohesion 3 (scc3).
(A) Meiotic chromosome behavior in wild-type and scc3. Bars, 5 μm. (B) Immunolocalization of ZEP1 (green, from mouse) and REC8 (red, from rabbit) in wild-type and scc3 meiocytes. ZEP1 was severely suppressed from early zygotene to pachytene in scc3. Bars, 5 μm.
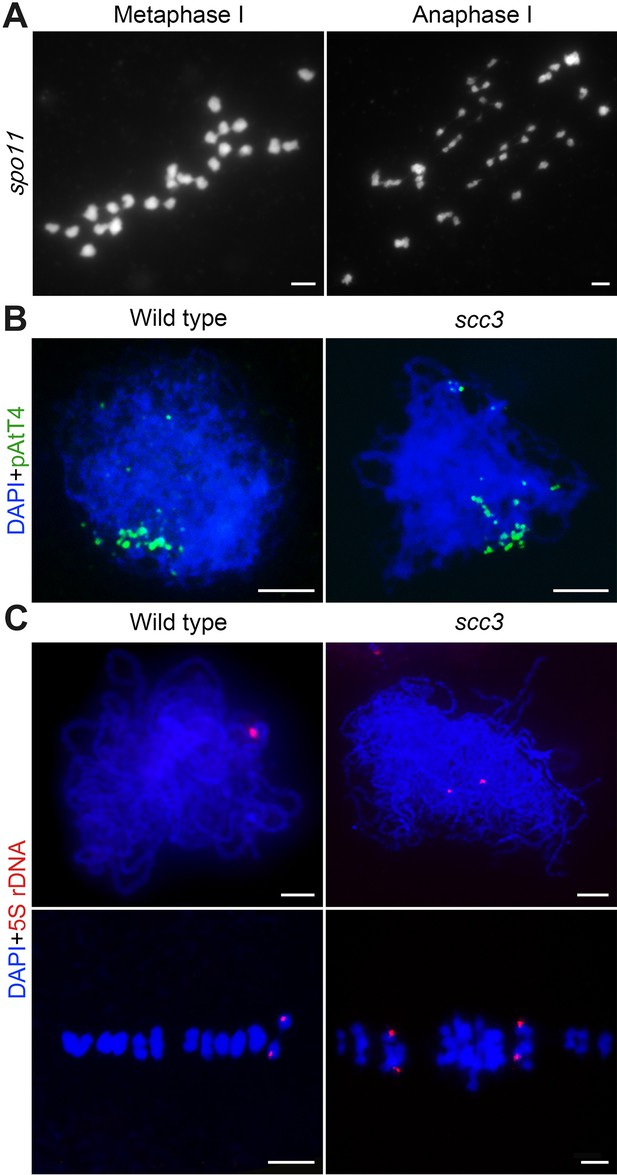
Chromosome behaviors of spo11 and cytogenetic analysis of homologous pairing in wild-type and sister chromatid cohesion 3 (scc3).
(A) Chromosome behavior of spo11 in metaphase I and anaphase I. Bars, 5 μm. (B) Telomere bouquets were detected in both wild-type and scc3 with the telomere-specific probe (pAtT4, green) by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assays. Chromosomes were stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Bars, 5 μm. (C) The pairing status of chromosomes revealed by 5 S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) in wild-type. Chromosomes were stained with DAPI. Bars, 5 μm.

Immunolocalization of ZEP1, PAIR2, and PAIR3 in sister chromatid cohesion 3 (scc3) at zygotene.
Bar, 5 μm.
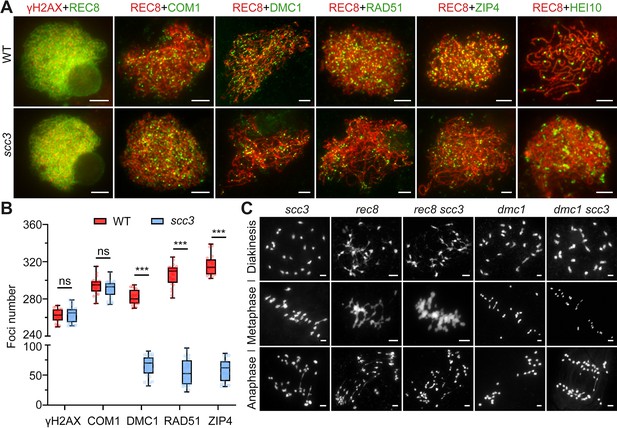
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) affects recombination progress and crossover (CO) formation.
(A) Immunolocalization of histone γH2AX (red), COM1 (green, from mouse), DMC1 (green, from mouse), RAD51 (green, from rabbit), ZIP4 (green, from mouse), and HEI10 (green, from mouse) in wild-type and scc3. REC8 (red, from mouse and rabbit) signals were used to visualize chromosome axes. Bars, 5 μm. (B) Box scatter plot of histone γH2AX phosphorylation, COM1, DMC1, RAD51, and ZIP4 in wild-type and scc3. No difference of histone γH2AX and COM1 were shown between the wild-type and scc3. DMC1, RAD51, and ZIP4 foci were significantly decreased in scc3 compared with wild-type. Values are means ± SD. *** represents p<0.001, two-tailed Student’s t-tests was performed. (C) Chromosome behaviors in scc3, rec8, rec8 scc3, dmc1, and dmc1 scc3 from diakinesis to anaphase I. Bars, 5 μm.
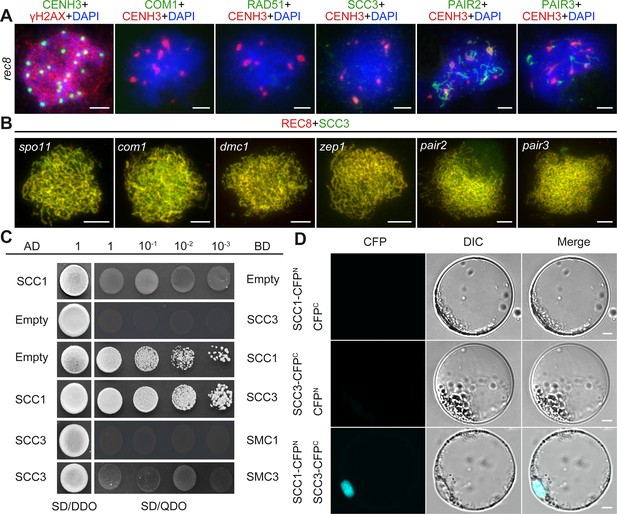
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) loading onto meiotic chromosomes depends on REC8.
(A) Immunolocalization of γH2AX (red, from rabbit), COM1 (green, from mouse), RAD51 (green, from rabbit), SCC3 (green, from mouse), PAIR2 (green, from rabbit), and PAIR3 (green, from rabbit) in rec8 meiocytes at zygotene. CENH3 (red and green, from rabbit and mouse) was used to indicate the centromeres. Bars, 5 μm. (B) Immunolocalization of REC8 (red, from rabbit) and SCC3 (green, from mouse) in spo11, com1, dmc1, zep1, pair2, and pair3 meiocytes at zygotene. Bars, 5 μm. (C) SCC3 interacts with RAD21.1 in yeast-two-hybrid assays. Interactions between bait and prey were examined on SD/DDO (SD-Leu-Trp) control media and SD/QDO (SD-Ade-His-Leu-Trp) selective media. AD, prey vector; BD, bait vector. (D) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays show the interactions between SCC3 and RAD21.1 in rice protoplasts. Bars, 5 μm.

Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) does not interact with REC8, SMC1, or SMC3.
(A) SCC3 does not interact with REC8, SMC1, and SMC3 in yeast-two-hybrid assays. (B) SCC3 does not interact with REC8, SMC1, and SMC3 in bimolecular fluorescence complementation assays in rice protoplast. Bars, 5 μm.
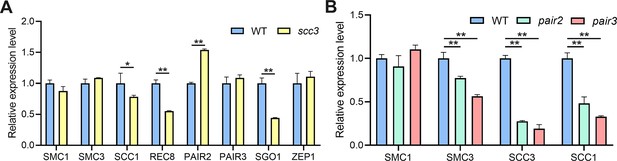
The expression levels of cohesin-related genes in wild-type and other mutants.
(A) The expression levels of SMC1, SMC3, SCC1, REC8, PAIR2, PAIR3, SGO1 and ZEP1 in sister chromatid cohesion 3 (scc3) and wild-type. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. * represents p<0.05, ** represents p<0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-tests was performed. (B) The expression levels of SMC1, SMC3, SCC3, and SCC1 in pair2, pair3, and wild-type. Values are shown as mean ± SD of three biological replicates. ** represents p<0.01, two-tailed Student’s t-tests was performed.
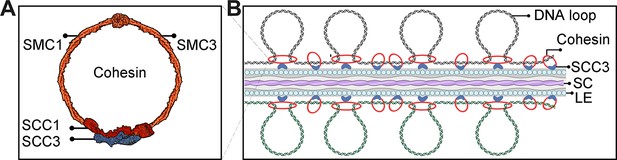
Sister chromatid cohesion 3 (SCC3) acts as the cohesin and promotes homologous pairing and synapsis.
(A) Structure model of the cohesin complex. The SCC3 subunit is associated with the middle region of SCC1. (B) During meiosis, SCC3’s localization pattern probably changes to the root of DNA loop with lateral elements (LEs), which wraps synaptonemal complex (SC). This indicates SCC3 is a meiotic LE essential for homologous chromosome pairing and synapsis, also affects recombination progress and crossover (CO formation).
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of primers used in this study.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94180/elife-94180-supp1-v1.docx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94180/elife-94180-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf





