CoCoNuTs are a diverse subclass of Type IV restriction systems predicted to target RNA
Figures
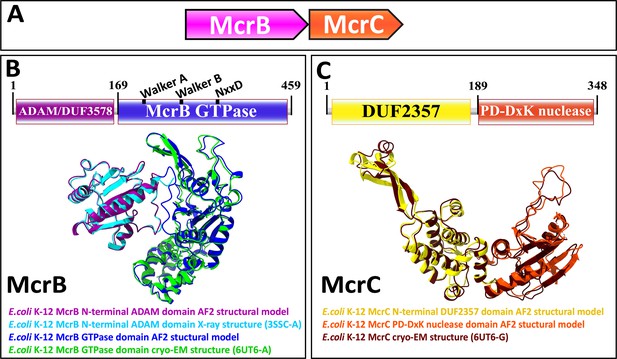
Genetic organization, signature sequence motifs, structural models, and phyletic distribution of McrB GTPases detected in this work.
(A) McrBC is a two-component restriction system with each component typically (except for extremely rare gene fusions) encoded by a separate gene expressed as a single operon, depicted here and in subsequent figures as arrows pointing in the direction of transcription. In most cases, McrB is the upstream gene in the operon. (B) In the prototypical E. coli K-12 McrBC system, McrB contains an N-terminal methylcytosine-binding domain, ADAM/DUF3578, fused to a GTPase of the AAA+ATPase clade (Sukackaite et al., 2012). This GTPase contains the Walker A and Walker B motifs that are conserved in P-loop NTPases as well as a signature NxxD motif, all of which are required for GTP hydrolysis (Nirwan et al., 2019; Niu et al., 2020; Pieper et al., 1999). An AlphaFold2 structural model of E. coli K-12 ADAM-McrB GTPase fusion protein monomer and separate X-ray diffraction and cryo-EM structures of the ADAM and GTPase domains (Niu et al., 2020; Sukackaite et al., 2012) show a high degree of similarity. (C) McrC consists of a PD-DxK nuclease and an N-terminal DUF2357 domain, which comprises a helical bundle with a stalk-like extension that interacts with and activates individual McrB GTPases while they are assembled into hexamers (Niu et al., 2020; Nirwan et al., 2019). An AlphaFold2 structural model and cryo-EM structure of E. coli K-12 McrC monomer with DUF2357-PD-DxK architecture (Niu et al., 2020) show a high degree of similarity. The structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
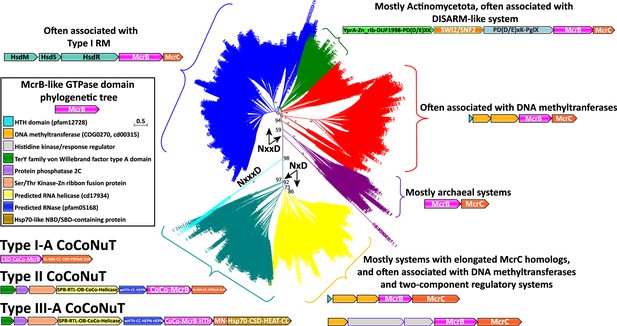
Phylogenetic tree of the McrB-like GTPases.
The major clades in the phylogenetic tree of the McrB-like GTPases are distinguished by the distinct versions of the Nx(xx)D signature motif. The teal and yellow groups, with bootstrap support of 97%, have an NxD motif, whereas the blue, green, red, and purple groups, with variable bootstrap support, have an NxxD motif, indicated by the arrows; the sequences in the smaller, cyan clade, with 98% bootstrap support, have an NxxxD motif. Each of the differently colored groups is characterized by distinct conserved genomic associations that are abundant within but not completely confined to the respective groups. This tree was built from the representatives of 90% identity clusters of all validated homologs. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; CoCo/CC, coiled-coil; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; OB, OB-fold domain; iPD-(D/E)xK, inactivated PD-(D/E)xK fold; Hsp70, Hsp70-like NBD/SBD; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats; YprA, YprA-like helicase domain; DUF1998, DUF1998 is often found in or associated with helicases and contains four conserved, putatively metal ion-binding cysteine residues; SWI2/SNF2, SWI2/SNF2-family ATPase; PglX, PglX-like DNA methyltransferase; HsdR/M/S, Type I RM system restriction, methylation, and specificity factors.
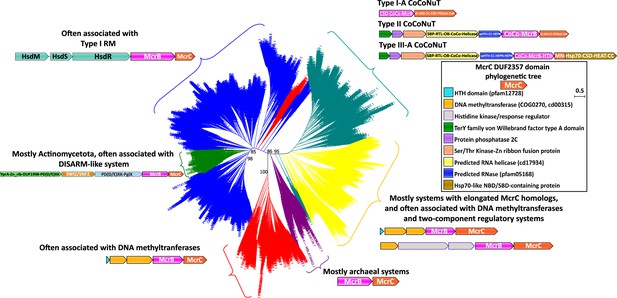
Phylogenetic tree of the McrC DUF2357 domain.
The phylogenetic tree of the McrC N-terminal DUF2357 domains is generally topologically concordant with the McrB family GTPase tree. Each of the differently colored groups is characterized by distinct conserved genomic associations that are abundant within but not completely confined to the respective groups. This tree was built from the representatives of 90% identity clusters of all validated homologs. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; CoCo/CC, coiled-coil; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; IG, immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; OB, OB-fold domain; iPD-(D/E)xK, inactivated PD-(D/E)xK fold; Hsp70, Hsp70-like NBD/SBD; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats; YprA, YprA-like helicase domain; DUF1998, DUF1998 is often found in or associated with helicases and contains four conserved, putatively metal ion-binding cysteine residues; SWI2/SNF2, SWI2/SNF2-family ATPase; PglX, PglX-like DNA methyltransferase; HsdR/M/S, Type I RM system restriction, methylation, and specificity factors.
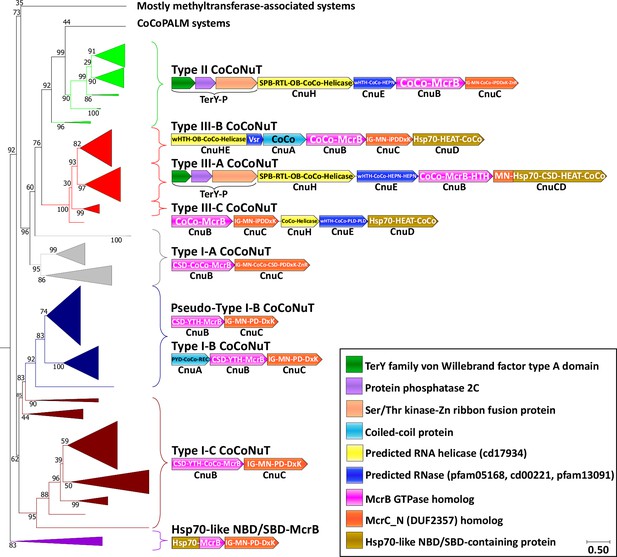
Coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) system phylogeny and classification.
The figure shows the detailed phylogeny of McrB-like GTPases from CoCoNuT systems and their close relatives. All these GTPases possess an NxD GTPase motif rather than NxxD. This tree was built from the representatives of 90% clustering of all validated homologs. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; Hsp70, Hsp70-like NBD/SBD; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; PYD, pyrin/CARD-like domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; OB, OB-fold domain; iPD-(D/E)xK, inactivated PD-(D/E)xK fold; REC, phosphoacceptor receiver-like domain; PLD, phospholipase D-like nuclease domain; Vsr, very-short-patch-repair PD-(D/E)xK nuclease-like domain. Underneath each gene is a proposed protein name, with Cnu as an abbreviation for CoCoNuT.
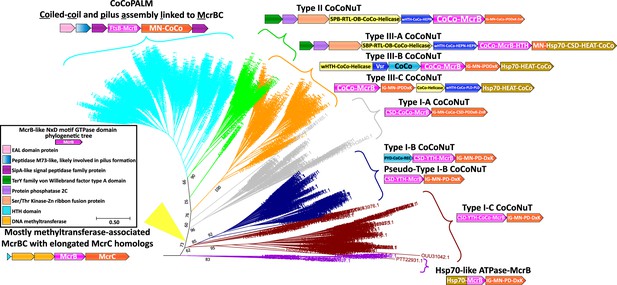
Phylogenetic tree of McrB family GTPases containing the NxD motif.
The phylogenetic tree of McrB-like GTPases with an NxD variant of the signature motif contains the coiled-coil nuclease tandems (CoCoNuTs), coiled-coil and pilus assembly linked to McrBC (CoCoPALMs), and systems associated with methyltransferases with additional domains fused to the McrC homologs. Each of the differently colored branches is characterized by distinct conserved genomic associations and domain compositions, which we used to define three CoCoNuT types and seven subtypes. These types are not generally found in other branches of the tree, except some CoCoPALMs, which can be found in the Type II CoCoNuT branch. This tree was built from the representatives of 90% identity clusters of all validated homologs. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; CoCo/CC, coiled-coil; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; IG, Immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; Hsp70, Hsp70-like NBD/SBD; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; PYD, pyrin/CARD-like domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; OB, OB-fold domain; wHTH, winged helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain; iPD-DxK, inactivated PD-(D/E)xK fold; FtsB, FtsB-like TM helix and coiled-coil; REC, phosphoacceptor receiver-like domain; PLD, phospholipase D-like nuclease domain; Vsr, very-short-patch-repair nuclease-like domain.

Pseudo-Type I-B coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) genomic context in Bacillus.
Pseudo-Type I-B CoCoNuTs in Bacillus are associated with various factors with potential involvement in overcrowding-induced stress. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain.
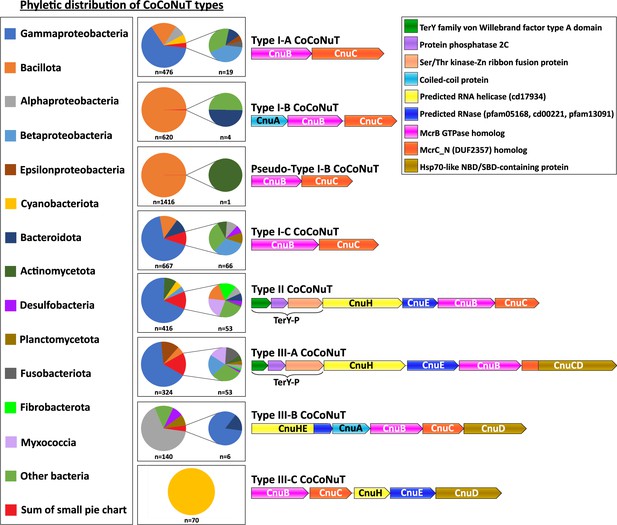
Phyletic distribution of coiled-coil nuclease tandems (CoCoNuTs).
The phyletic distribution of CnuB/McrB-like GTPases in CoCoNuT systems found in genomic islands with distinct domain compositions. Most CoCoNuTs are found in either Bacillota or Pseudomonadota, with particular abundance in Gammaproteobacteria. Type I-B and the related Pseudo-Type I-B CoCoNuTs are restricted mainly to Bacillota. In contrast, the other types are more common in Pseudomonadota, but can be found in a wide variety of bacteria. Types III-B and III-C are primarily found in Alphaproteobacteria and Cyanobacteriota, respectively.
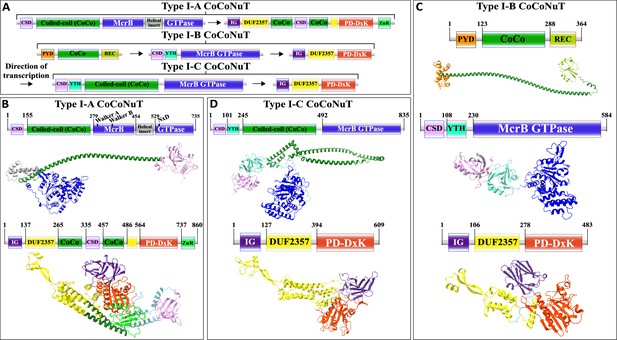
Domain composition, operon organization, and AlphaFold2 structural predictions of components of the Type I coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) systems.
(A) Type I CoCoNuT domain composition and operon organization. The arrows indicate the direction of transcription. (B–D) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] > 80), representative AlphaFold2 structural predictions for protein monomers in (B) Type I-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom), (C) Type I-B CoCoNuT systems (CnuA, CnuB, and CnuC, from top to bottom), and (D) Type I-C CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom). Models were generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): ROR86958.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuB), APL73566.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuC), TKH01449.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuA), GED20858.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuB), GED20857.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuC), GFD85286.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuB), and MBV0932851.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; PYD, pyrin/CARD-like domain; REC, phosphoacceptor receiver-like domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
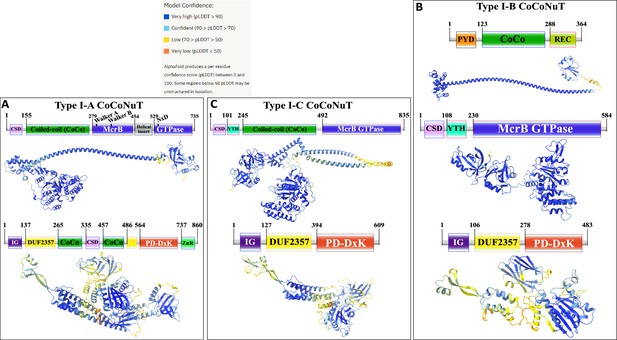
Domain composition and AlphaFold2 structural predictions of components of the Type I coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) systems colored by pLDDT.
(A–C) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] > 80), representative AlphaFold2 structural predictions for proteins in (A) Type I-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom), (B) Type I-B CoCoNuT systems (CnuA, CnuB, and CnuC, from top to bottom), and (C) Type I-C CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom). Models were generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): ROR86958.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuB), APL73566.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuC), TKH01449.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuA), GED20858.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuB), GED20857.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuC), GFD85286.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuB), and MBV0932851.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; PYD, pyrin/CARD-like domain; REC, phosphoacceptor receiver-like domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
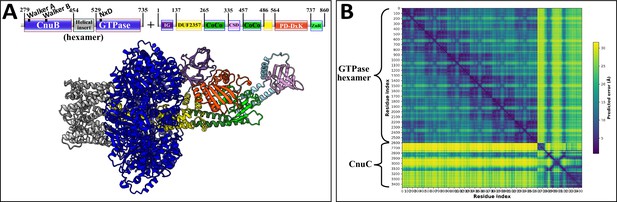
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type I-A coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuB GTPase hexamer and CnuC monomer complex.
(A) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 82.5, ipTM + pTM = 0.7392) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction for the CnuB GTPase hexamer (without the N-terminal domains) and CnuC monomer complex in a Type I-A CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): APL73567.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuB) and APL73566.1 (Type I-A CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
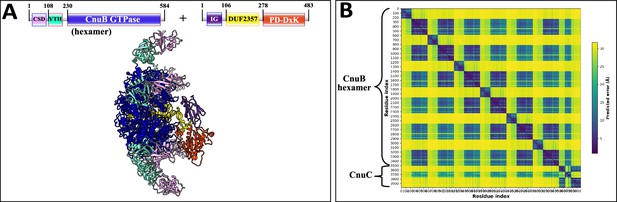
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type I-B coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuB hexamer and CnuC monomer complex.
(A) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 77.3, ipTM + pTM = 0.6308) for the full-length CnuB hexamer and CnuC monomer complex in a Type I-B CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): GED20858.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuB) and GED20857.1 (Type I-B CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; YTH, YTH-like domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
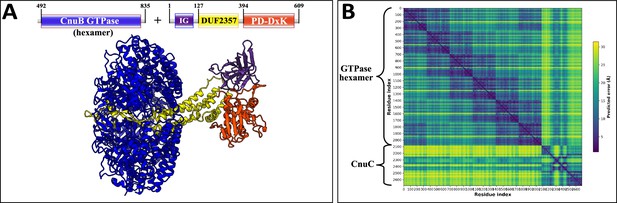
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type I-C coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuB GTPase hexamer and CnuC monomer complex.
(A) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 80.0, ipTM + pTM = 0.7271) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction for the CnuB GTPase hexamer (without the N-terminal domains) and CnuC monomer complex in a Type I-C CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): MBV0932852.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuB) and MBV0932851.1 (Type I-C CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
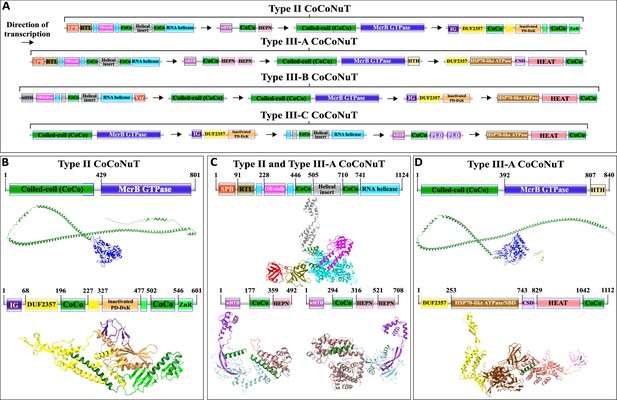
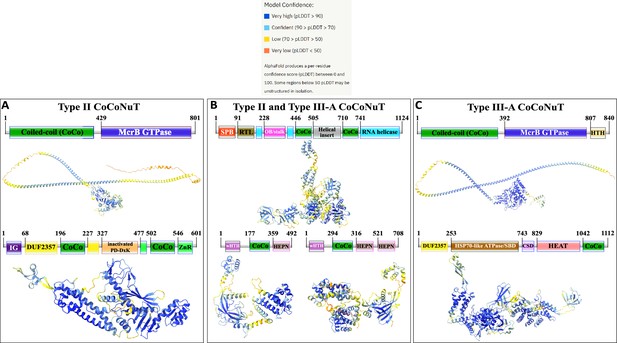
Domain composition, operon organization, and AlphaFold2 structural predictions for core protein components of Type II and III coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) systems.
(A) Type II and III CoCoNuT domain composition and operon organization. The arrows indicate the direction of transcription. Type II and III-A CoCoNuT systems very frequently contain TerY-P systems as well, but not invariably, and these are never found in Type III-B or III-C, thus, we do not consider them core components. (B–D) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] > 80), representative AlphaFold2 structural predictions for protein monomers in (B) Type II CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom), (C) Type II and III-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuH at the top, Type II CnuE on the bottom left, Type III-A CnuE on the bottom right), and (D) Type III-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom). Models were generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): AMO81401.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuB), AVE71177.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuC), AMO81399.1 (Type II and III-A CoCoNuT CnuH), AVE71179.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuE), ATV59464.1 (Type III-A CnuE), PNG83940.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuB), and NMY00740.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; OB/stalk, OB-fold domain attached to a helical stalk-like extension of ATPase; Vsr, very-short-patch-repair PD-(D/E)xK nuclease-like domain; PLD, phospholipase D family nuclease domain; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
Domain composition and AlphaFold2 structural predictions for core protein components of Type II and III-A coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) systems colored by predicted local distance difference test (pLDDT).
(A–C) High-quality (average pLDDT > 80), representative AlphaFold2 structural predictions for proteins in (A) Type II CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom), (B) Type II and III-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuH at the top, Type II CoCoNuT CnuE on the bottom left, Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuE on the bottom right), and (C) Type III-A CoCoNuT systems (CnuB and CnuC, from top to bottom). Models were generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): AMO81401.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuB), AVE71177.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuC), AMO81399.1 (Type II and III-A CoCoNuT CnuH), AVE71179.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuE), ATV59464.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuE), PNG83940.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuB), and NMY00740.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CSD, cold shock domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain; OB/stalk, OB-fold domain attached to a helical stalk-like extension of ATPase; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
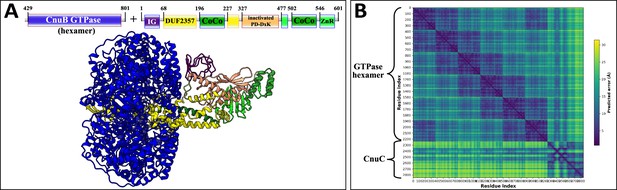
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type II coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuB GTPase hexamer and CnuC monomer complex.
(A) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 85.7, ipTM + pTM = 0.7933) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction for the CnuB GTPase hexamer (without the N-terminal coiled-coil domain) and CnuC monomer complex in a Type II CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): MBV0932852.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuB) and MBV0932851.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: CoCo, coiled-coil; IG, immunoglobulin (IG)-like beta-sandwich domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
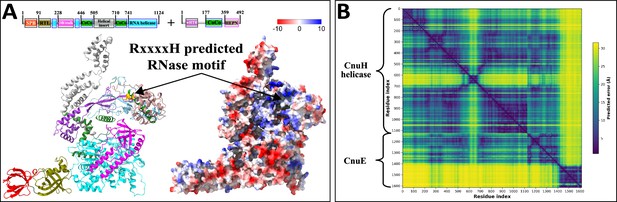
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type II coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuH helicase and CnuE effector complex.
(A) High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 80.5, ipTM + pTM = 0.7108) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction for the CnuH helicase and CnuE wHTH-HEPN effector in a Type II CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The helical insert found in the helicase and HEPN domain in the effector show a higher degree of error, but as we predicted them to be novel RNA-binding domains, this is not unexpected. The predicted surface charge distribution shows both domains forming, in conjunction with the OB/stalk domain, a positively charged (blue) groove, with the RxxxxH predicted RNase motif (orange) at its center, that might bind and cleave RNA. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): AMO81399.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuH) and AMO81400.1 (Type II CoCoNuT CnuE). Abbreviations of domains: CoCo, coiled-coil; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; OB/stalk, OB-fold domain attached to a helical stalk-like extension of ATPase; wHTH, winged helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
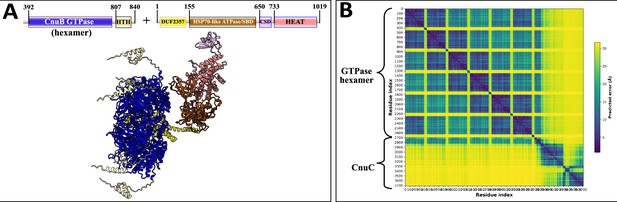
AlphaFold2 prediction of Type III-A coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) CnuB GTPase hexamer and CnuC monomer complex.
(A) AlphaFold2 multimer structural prediction (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] = 76.6, ipTM + pTM = 0.6472) for the CnuB GTPase hexamer (without the N-terminal coiled-coil domain) and CnuC monomer complex in a Type III-A CoCoNuT system. (B) Predicted aligned error (PAE) plot for the predicted complex. The model was generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): PNG83940.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuB) and PNG83939.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT CnuC). Abbreviations of domains: HTH, helix-turn-helix domain; CSD, cold shock domain; CoCo, coiled-coil; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats. These structures were visualized with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2021).
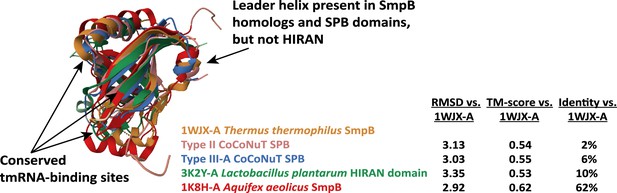
Comparisons of Type II and Type III-A coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) N-terminal SPB domains, SmpB, and prokaryotic HIRAN domains.
High-quality (average predicted local distance difference test [pLDDT] > 80) AlphaFold2 representative structural predictions for the N-terminal SPB domains in Type II and III-A CoCoNuT CnuH helicases and experimentally solved structures for SmpB and a prokaryotic HIRAN domain. Models were generated from representative sequences with the following GenBank accessions (see Supplementary file 3 for sequences and locus tags): AMO81399.1 (Type II CoCoNuT SPB) and PJX13386.1 (Type III-A CoCoNuT SPB). Structures were visualized and compared using the pairwise alignment tool on the RCSB PDB website (Berman et al., 2000).
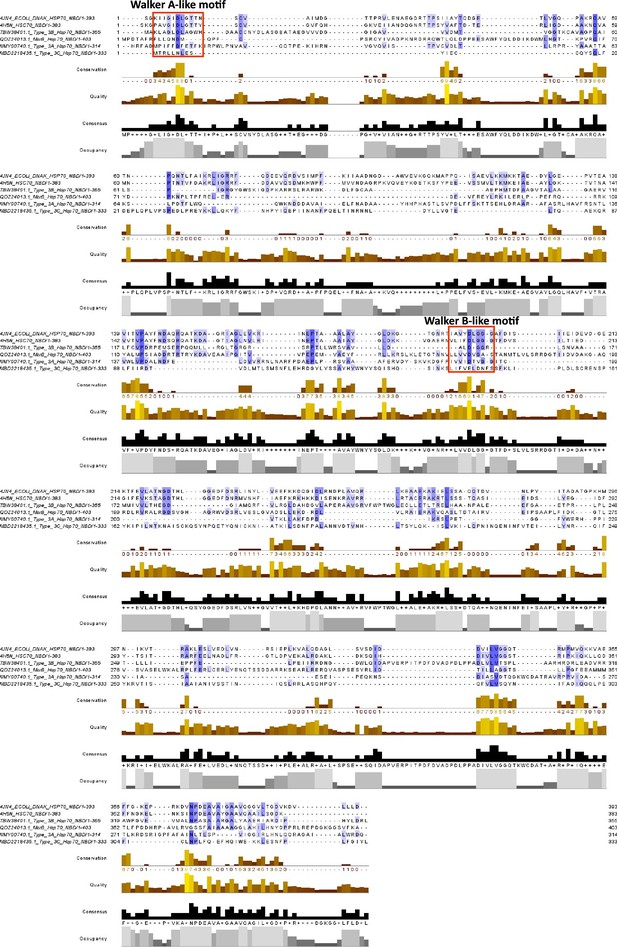
Alignment of Hsp70-like nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) from Type III coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) and related McrB homolog with E. coli Hsp70 (DnaK) and mammalian Hsp70 cognate protein H. sapiens HSC70.
Alignment of representatives of Hsp70 NBD homologs found in Type III CoCoNuT systems and fused to a closely related NxD motif McrB GTPase with characterized bacterial and mammalian Hsp70 NBD homologs. The alignment was initially performed with PROMALS3D (Pei et al., 2008) and then adjusted manually. The alignment was displayed with Jalview (Waterhouse et al., 2009). The blue shading corresponds to sequence conservation, and the red boxes indicate the Walker A-like and Walker B-like motifs. These motifs are identified on the CDD website in the entry for Hsp70_NBD (cd10170) (Lu et al., 2020).
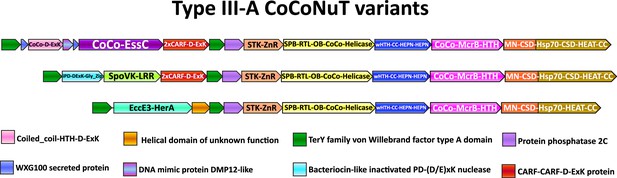
Compound Type III-A coiled-coil nuclease tandem (CoCoNuT) operons with 5′ extensions.
Additional genes that may be present in Type III-A CoCoNuT operons. Abbreviations of domains: McrB, McrB-like GTPase domain; CoCo/CC, coiled-coil; STK, serine/threonine kinase; 2xCARF, 2 CARF domains; D-ExK, D-ExK nuclease motif; MN, McrC N-terminal domain (DUF2357); CSD, cold shock domain; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; SPB, SmpB-like domain; RTL, RNase toxin-like domain; OB, OB-fold domain attached to helical stalk-like extension of ATPase; HEPN, HEPN family nuclease domain; Hsp70, Hsp70-like NBD/SBD; HEAT, HEAT-like helical repeats; LRR, leucine-rich repeat; Gly_zip, glycine zipper domain; SpoVK, EssC, EccE3-HerA – see text.
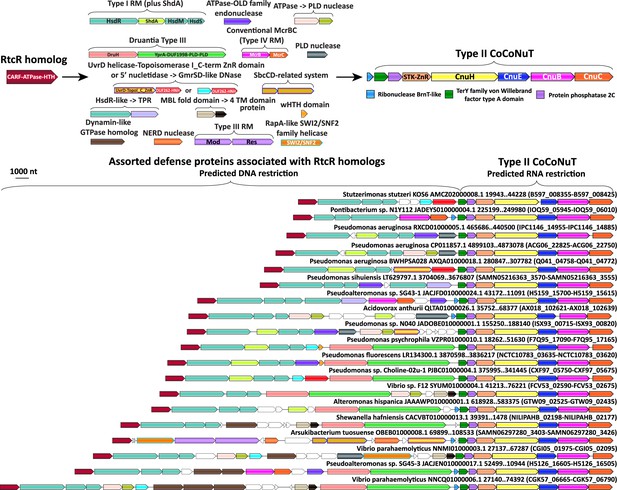
Complex operonic associations of Type II coiled-coil nuclease tandems (CoCoNuTs).
Type II CoCoNuTs are frequently associated with RtcR homologs, and in many cases, ancillary defense genes are located between the RtcR gene and the CoCoNuT, almost always oriented in the same direction in an apparent superoperon. Abbreviations of domains: STK, serine/threonine kinase; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain; YprA, YprA-like helicase domain; DUF1998, DUF1998 is often found in or associated with helicases and contains four conserved, putatively metal ion-binding cysteine residues; PLD, phospholipase D family nuclease domain; SWI2/SNF2, SWI2/SNF2-family ATPase; HsdR/M/S, Type I RM system restriction, methylation, and specificity factors; ShdA, shield system core component ShdA; TPR, tetratricopeptide repeat protein; MBL fold, metallo-beta-lactamase fold; 4 TM domain, protein with four predicted transmembrane helices; Mod/Res, Type III RM modification and restriction factors.

Type II coiled-coil nuclease tandems (CoCoNuTs) are associated with RtcR homologs in a variety of species.
About 30% of Type II CoCoNuT systems detected in this study are associated with RtcR homologs. This contextual connection is conserved in many species of Pseudomonadota. Abbreviations of domains: STK, serine/threonine kinase; ZnR, zinc ribbon domain.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Protein structure prediction and analysis for CoCoNuT systems components.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94800/elife-94800-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
List of AlphaFold 2 models for CoCoNuT protein components and their complexes, with modelarchive accession numbers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94800/elife-94800-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
GenBank accession numbers and protein sequences for protein components of the CoCoNuT systems.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94800/elife-94800-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94800/elife-94800-mdarchecklist1-v1.docx





