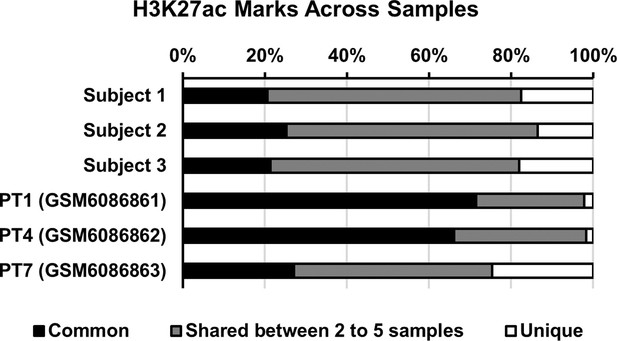
Assessment of the histone mark-based epigenomic landscape in human myometrium at term pregnancy
Figures
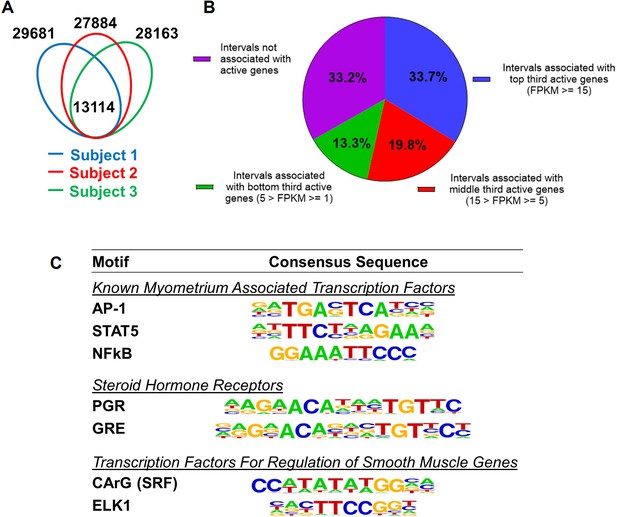
Putative enhancers in term pregnant human myometrial tissues.
(A) Distinct and common putative enhancers in term pregnant myometrial biopsies from three subjects. Genomic regions with H3K27ac and H3K4me1 double positive histone marks are defined as putative active enhancers. (B) Association of commonly shared putative enhancers with active genes. The association between an interval and an active gene is defined by locating within 100 kb vicinity of each other. (C) Over-Represented transcription factor binding motifs in putative enhancers. A subset of enriched motifs that are relevant to myometrial homeostasis in the 13,090 H3K4me1/H3K27ac-positive putative enhancer regions is displayed.
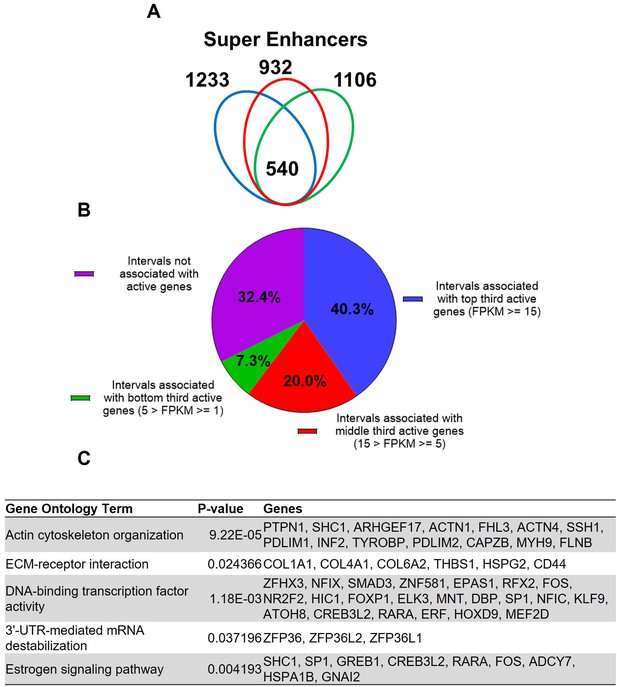
Putative super enhancers in term pregnant human myometrial tissues.
(A) Number of super enhancers mapped in tissues of each individual human subject. (B) Association of commonly shared super enhancers with active genes in human myometrium. (C) Selected enriched gene ontology terms in the 346 active genes that are associated with super enhancers.
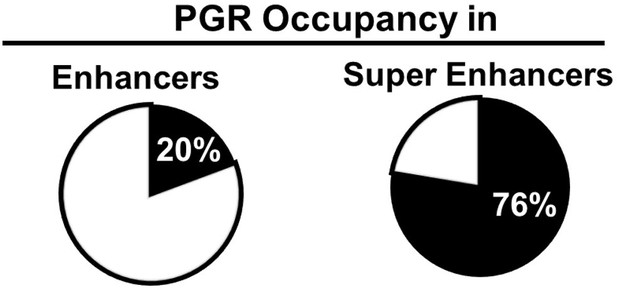
PGR occupancy in myometrial enhancers.
Percentages of enhancers and super enhancers that manifest PGR occupancy. PGR genome occupancy data was previously published in NCBI GEO accession numbers GSM4081683 and GSM4081684.
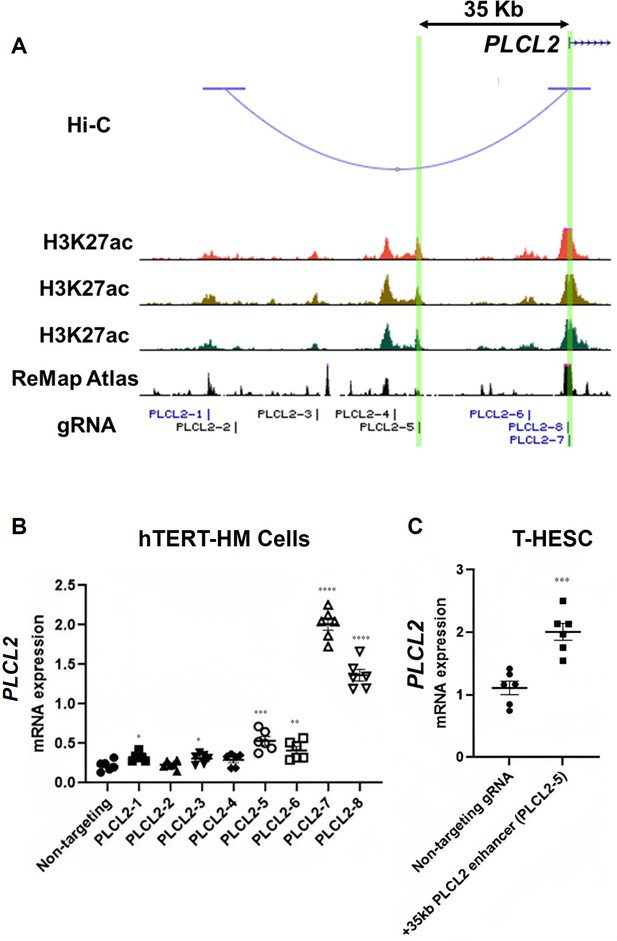
Identification of enhancers for the PLCL2 gene.
(A) UCSC Genome Browser track view of the human PLCL2 locus marked with gRNA targeting locations. (B, C) Relative PLCL2 mRNA levels measured by qRT-PCR in hTERT-HM cells (B) or T-HESC cells (C) that express denoted gRNAs with the CRISPR activator (N=3 with technical duplicates). Statistical significance was determined using unpaired t-test for comparisons between two groups, or one-way ANOVA for comparisons between >2 groups. Significance levels are denoted as follows: ****, p<0.0001; ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05. Error bars are shown as mean with SEM.
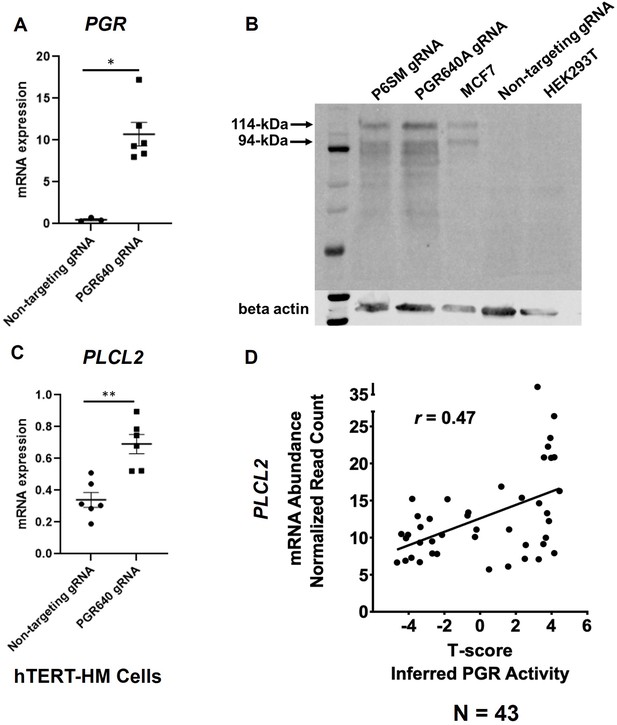
PGR regulation of PLCL2 expression.
(A) PGR mRNA abundance in hTERT-HM cells with the PGR-promoter targeting (PGR640) or non-targeting gRNAs under the CRISPR activation system. (N=3 with technical qPCR duplicates). (B) Protein abundance in hTERT-HM cells with the PGR-promoter targeting (PGR640 and P6SM) or non-targeting gRNAs under the CRISPR activation system. Protein extracts from unmanipulated MCF7 and HEK293T cells serve as positive and negative control for the PGR presence. (C) PLCL2 mRNA abundance in hTERT-HM cells with the PGR-promoter targeting (PGR640) or non-targeting gRNAs under the CRISPR activation system. (N=3 with technical qPCR duplicates). (D) Pearson correlation between PLCL2 mRNA levels and inferred PGR activities (T-Scores) in 43 human myometrial specimens. **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05 by Mann-Whitney test (A) and unpaired t-test (C). Error bars are shown as mean with SEM.
-
Figure 4—source data 1
Western blot analysis of GAPDH and PGR.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-fig4-data1-v1.zip
-
Figure 4—source data 2
Western blot analysis of GAPDH and PGR, labelled.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-fig4-data2-v1.zip
Tables
Epigenome and transcriptome profile of the individual myometrium biopsy.
Active genes are defined as FPKM ≥1. N.D., not determined.
| Subject | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of H3K27ac intervals | 47,223 | 39,465 | 46,026 |
| Number of H3K4me1 intervals | 72,091 | 74,511 | 76,374 |
| Number of active genes | 12,809 | 11,761 | 11,902 |
| Number of chromatin loops | 10,321 | N.D. | 16,841 |
Candidate upstream regulators that mediate PLCL2-5 enhancer’s regulatory effect on PLCL2 expression.
| Candidate Activators | Description |
|---|---|
| PGR | Steroid Hormone Receptor |
| ESR1 | |
| FOS, JUN | AP-1 Transcription Factor Subunit, bZIP Transcription Factor |
| JUN | |
| JUNB | |
| JUND | |
| MAF | bZIP Transcription Factor |
| BHLHE40 | bHLH Transcription Factor, Involved in CLOCK gene regulation |
| TCF21 | bHLH Transcription Factor |
| MAX | bHLHZ Transcription Factor |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box Transcription Factor |
| MRTFB | Myocardin Family, SRF Transcriptional Co-Activator |
| STAT3 | Transcriptional Regulator |
| ERG | ETS Transcriptional Regulator |
| Candidate Repressors | Description |
| ARID1a | SWI/SNF Family of Epigenetic Modifiers |
| BRD2 | Epigenetic Modifier, Chromatin Reader |
| BRD4 | |
| KMT2A | Component of MLL Epigenetic Modification Complex |
| SMARCb1 | Component of BAF Epigenetic Modification Complex |
| ZMYM3 | Component of Epigenetic Modification Complex |
| CREB1 | bZip Transcription Factor. Interacts with Epigenetic Modifiers |
| CREBP | CREB Binding Protein, Epigenetic Modifier |
| HCAC2 | Histone Deacetylase, Epigenetic Modifier |
| HDAC3 | |
| CLOCK | bHLH Transcription Factor Family, Rhythmic Epigenetic Modifier |
| MED1 | Mediator Complex Subunit |
| RELB | NF-KB Transcription Factor Subunit |
| CHD4 | Component of NuRD Epigenetic Modification Complex |
| RAD21 | Cohesin Complex Member |
| SMC2 | |
| REST | KLF Silencing Transcription Factor |
| TCF4 | bHLH Transcription Factor |
| ZNF687 | Zinc Finger Protein, Transcriptional Regulator |
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Summary table of sequencing datasets.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp1-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 2
Summary table of Hi-C quality control metrics.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp2-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 3
H3K27ac and H3K4me1 double positive enhancers in term pregnant not in labor human myometrial specimens.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp3-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 4
Enrichment of known transcription factor binding motifs in putative myometrial enhancers.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp4-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 5
Super enhancers in term pregnant not in labor human myometrial specimens.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp5-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 6
Active genes associated with super enhancers in the term nonlabor myometrium.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp6-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 7
Cell counts per gRNA and protospacer call frequencies per cell for Perturb-seq analysis.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp7-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 8
CRISPRa-dependent gene expression patterns in hTERT-HM cells and gRNA information.
DEG, differentially expressed genes between denoted gRNAs.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp8-v1.xlsx
-
Supplementary file 9
Normalized gene expression counts across the 43 human myometrial specimens and the PGR T-Scores of individual specimens.
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-supp9-v1.xlsx
-
MDAR checklist
- https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/95897/elife-95897-mdarchecklist1-v1.pdf