Scientists have revealed how common respiratory bugs that cause serious infections in people with cystic fibrosis interact together, according to a new study in eLife.
The results provide insights into how bacterial pathogens wrestle each other for territory that could open avenues for new antibacterial treatments.
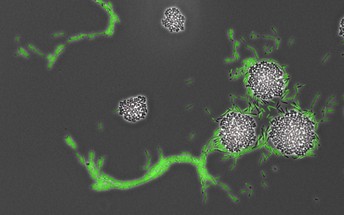
P. aeruginosa bacteria (shown here as green rods) respond to secreted interspecies factors and mount attack behaviours against S. aureus. Credit: Limoli et al. (CC BY 4.0)
Studies of microbes from mouths, intestines, chronic wounds and chronic respiratory infections show that interactions between bacteria in these communities influence survival of the bugs and progression of disease. For example, infection with two bacterial species called Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) in the airways of cystic fibrosis patients is linked to decreased lung function and a shorter lifespan.
“One strategy to improve outcomes for people with cystic fibrosis carrying multiple infections is to block harmful interspecies interactions before they begin,” explains lead author Dominique Limoli, Assistant Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Iowa, US. “We designed a system to visualise the early interactions between two microbes that cause infections in people with cystic fibrosis to follow their behaviour over time.”
Limoli and her team used a co-culture system to grow both microbes together and then studied them using time-lapse microscopy to create videos of the bacteria’s movements. They found that, on their own, P. aeruginosa cells multiply and form groups that appear like ‘rafts’ under a microscope. By contrast, when grown along with S. aureus, the P. aeruginosa cells move as single cells and accelerate their movement in the direction of the S. aureus colony. Studying the cells in more detail revealed that once the single P. aeruginosa cells reach the S. aureus cells, they enter the colony and dismantle it.
The researchers proposed that P. aeruginosa behaves in this way because S. aureus produces substances into the environment that trigger the change in movement of P. aeruginosa. To prove this, they took the liquid that S. aureus had been growing in and placed it in the bottom of a petri dish, before using it to grow P. aeruginosa. In this environment, P. aeruginosa was much more mobile – moving across a greater surface area than on the normal petri dish.
So, does this hold true for other types of bacteria? Of three pathogens commonly found in patients with cystic fibrosis, the team found one that enhanced the movement of P. aeruginosa. However, when they looked at a broader group of bacteria, including Salmonella, Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, they found a significant increase in the movement of P. aeruginosa in the presence of these communities.
“By acquiring a fundamental understanding of how bacteria sense and respond to life with each other, we move closer to learning how to rationally manipulate these behaviours during infection and in the environment,” says Limoli. “For cystic fibrosis patients, this may mean preventing P. aeruginosa and S. aureus physical interactions. In other instances, we might bring together bacterial species that synergise to produce a beneficial compound.”
Media contacts
Emily Packer
eLife
e.packer@elifesciences.org
+441223855373Jennifer Brown, PhD
University of Iowa Health Care
jennifer-l-brown@uiowa.edu
+13193847195
+13196215266
About
About eLife
eLife aims to help scientists accelerate discovery by operating a platform for research communication that encourages and recognises the most responsible behaviours in science. We publish important research in all areas of the life and biomedical sciences, including Microbiology and Infectious Disease, which is selected and evaluated by working scientists and made freely available online without delay. eLife also invests in innovation through open source tool development to accelerate research communication and discovery. Our work is guided by the communities we serve. eLife is supported by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, the Max Planck Society, the Wellcome Trust and the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation. Learn more at https://elifesciences.org.
To read the latest Microbiology and Infectious disease research published in eLife, visit https://elifesciences.org/subjects/microbiology-infectious-disease.
About the University of Iowa Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine
The University of Iowa Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine is part of University of Iowa Health Care – a fully integrated academic medical center, which also includes University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics, and University of Iowa Physicians, the largest multi-specialty group practice in Iowa. As Iowa’s only comprehensive academic medical center, UI Health Care is committed to world-class patient care, biomedical research, and medical education.




