Chromatin is an ancient innovation conserved between Archaea and Eukarya
Figures
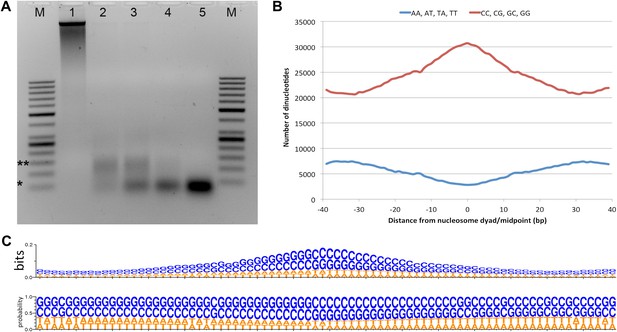
Micrococcal nuclease digestion produces nucleosomal fragments from crosslinked Hfx. volcanii chromatin.
(A) Formaldehyde cross-linked chromatin was subjected to MNase digestion with increasing amounts on microccocal nuclease (from 1 to 5 units). De-crosslinked DNAs were separated on a 3% agarose gel and ∼60 bp and ∼120 bp mono- and di-nucleosomes were observed. Markers (M) indicate *50 bp and **150 bp. (B) The counts of AA, AT, TA, TT or CC, CG, GC, GG dinucleotides are reported at each position showing an enrichment of G/C nucleotides and a depletion of A/T nucleotides at the dyad relative to the end points of the protected fragment. This differs from the observation of Bailey et al. (2000), where GC, AA and TA dinucleotides were repeated at ∼10-bp intervals in recombinant archaeal histone B from Methanothermus fervidus (rHMfB) (Bailey et al., 2000). (C) The sequence logo of a nucleosome-binding site in Hfx. volcanii centered at the nucleosome midpoint. There is a significant GC enrichment towards the nucleosome midpoint. This is exhibited using both bit score and probability measures.
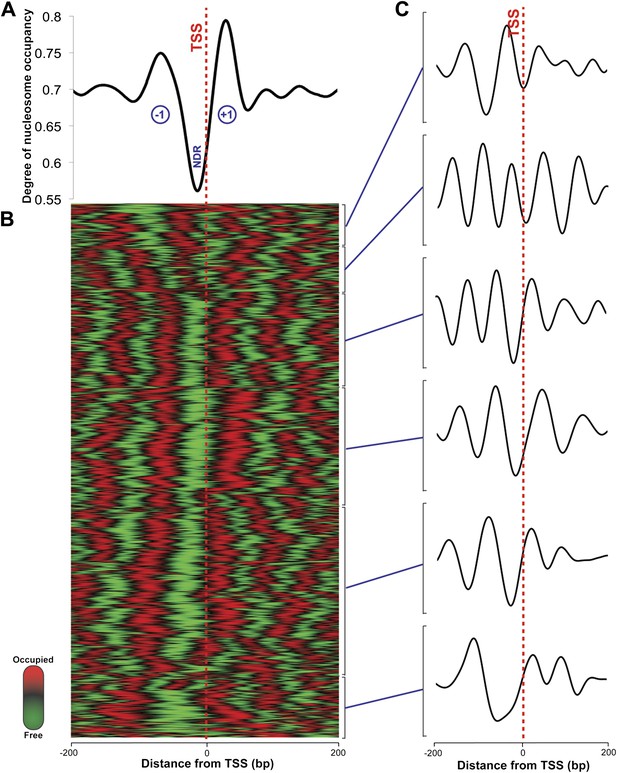
Nucleosome occupancy in Haloferax volcanii.
(A) Degree of normalized nucleosome occupancy in aggregate for the main chromosome. As observed in eukaryotes, there is a prominent nucleosome-depleted region (NDR) at the transcriptional start site (TSS) preceded by a −1 nucleosome and followed by a +1 nucleosome, demonstrating that promoter genome architecture is conserved between archaea and eukaryotes. (B) Hierarchical clustergram for the 2343 expressed transcripts on the main Haloferax chromosome. Green represents nucleosome-depleted regions and red represents occupied regions. (C) The clustered heatmap was subdivided into the largest six subclades, and differential density of nucleosomes can be observed with occupancy profile clusters containing between four to six nucleosomes.
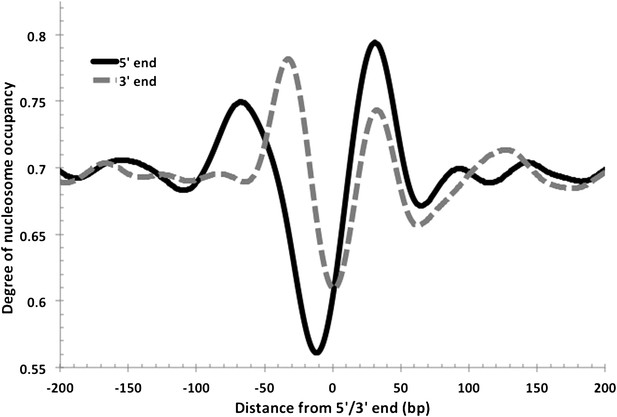
Nucleosome-depleted regions at the 5′ and 3′ ends of transcripts.
As observed in eukaryotes, NDRs are also found at the transcriptional termination sites in Hfx. volcanii. Both 5′ and 3′ end profiles are overlaid in this figure for comparison. The 5′ NDR is, on average, more depleted and longer.
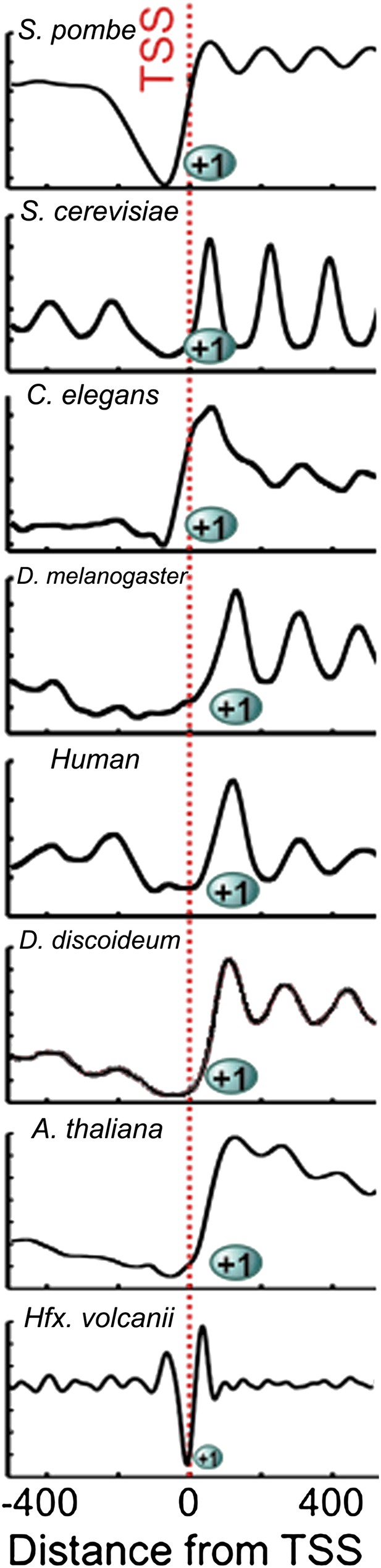
Chromatin architecture is conserved at the 5′ end of transcripts across eukaryotes and archaea.
Due to the smaller size of archaeal nucleosome DNA, the occupancy has a shorter periodicity. Figure adapted with permission from Chang et al. (2012).
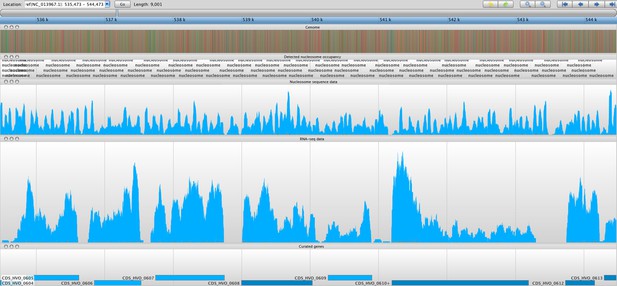
Sample screenshot of all data tracks loaded into the Savant genome browser (Fiume et al., 2010).
The nucleosome sequence data is displayed, and the periodicity reflects protected and unprotected fragments after MNase digestion (magnitude of peak is not considered). Peaks represent nucleosome midpoints, which were detected and marked. Below are the corresponding RNA-seq and curated gene tracks. In this screenshot, one can observe seven entire ORFs in line with their NDRs and –1 and +1 nucleosomes.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
A table describing the 32 novel transcripts identified in Hfx. volcanii.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00078.008





