Sugar is an endogenous cue for juvenile-to-adult phase transition in plants
Figures
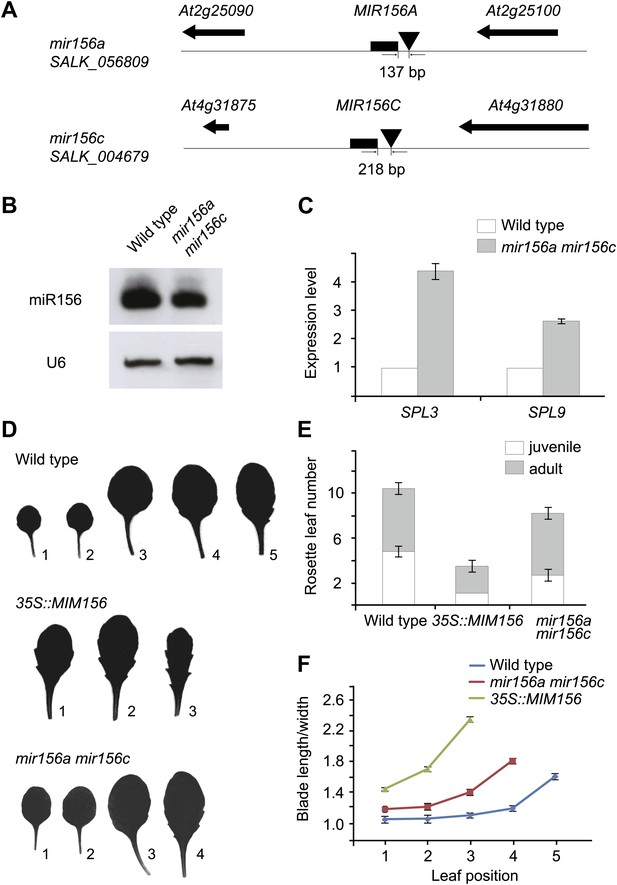
Phenotypic analyses of the mir156a mir156c double mutant.
(A) MIR156A and MIR156C genomic regions. Arrowheads mark T-DNA insertion sites. T-DNAs are inserted 137 bp and 218 bp upstream of the stem-loops of MIR156A and MIR156C, respectively. (B) Expression of miR156 in the wild type and the mir156a mir156c double mutant. U6 was monitored as loading control. (C) Expression of SPL3 and SPL9 in the wild type and the mir156a mir156c double mutant. The expression level in the wild type was set to 1.0. (D) Leaf morphology of wild type, mir156a mir156c, and 35S::MIM156 plants. The leaves were detached and scanned. The numbers indicate leaf positions. (E) The number of juvenile and adult leaves. n=12. (F) The length-to-width ratio of the blade. Fully expanded leaves were detached and scanned. The length and width of blades were measured. n=12. Error bars indicate SE.
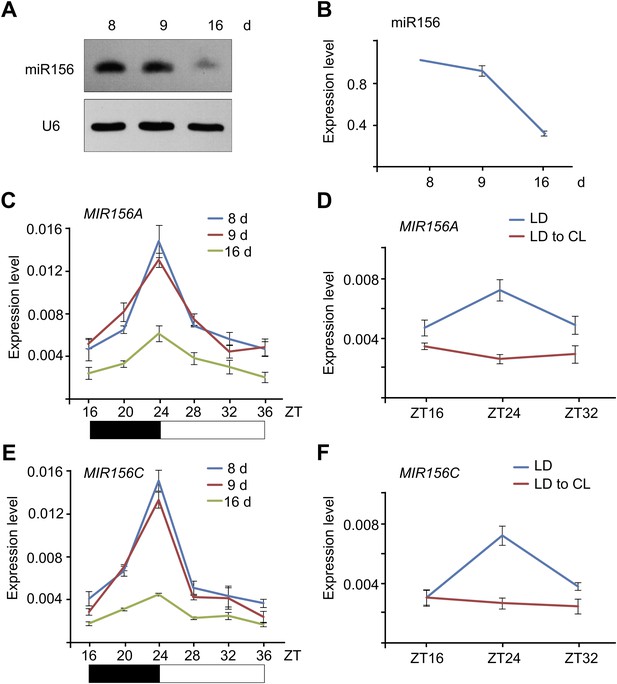
Expression of miR156.
(A and B) Accumulation of miR156 in 8-, 9-, and 16-day-old long day plants. Expression of miR156 was analyzed by small RNA blot (A) and qRT-PCR (B). The plants were collected at Zeitgeber time (ZT) 24. The expression level of miR156 in 8-day-old seedlings was set to 1. (C and E) Expression of pri-MIR156A (C) and pri-MIR156C (E). The plants were collected every 4 hr and subjected to qRT-PCR analyses. Black and white boxes indicate dark and light conditions, respectively. (D and F) Expression of pri-MIR156A (D) and pri-MIR156C (F) during the shift from long day (LD) to constant light (CL) conditions. Five-day-old wild type seedlings were shifted from long day to constant light conditions. The seedlings were collected at ZT 16, 24, and 32.
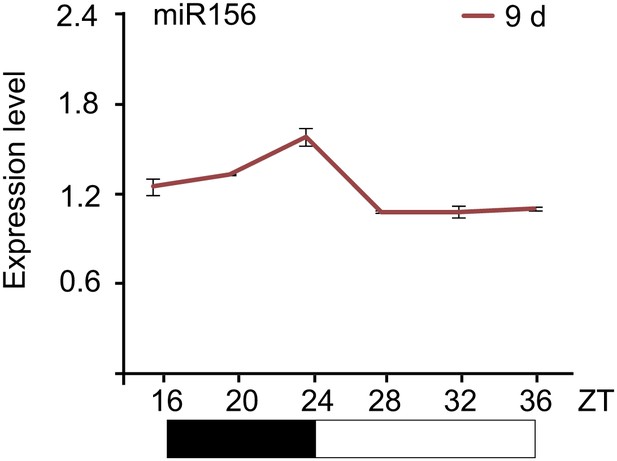
Expression pattern of miR156.
Expression of miR156. The plants were collected every 4 hr and subjected to qRT-PCR analyses. ZT: Zeitgeber time.
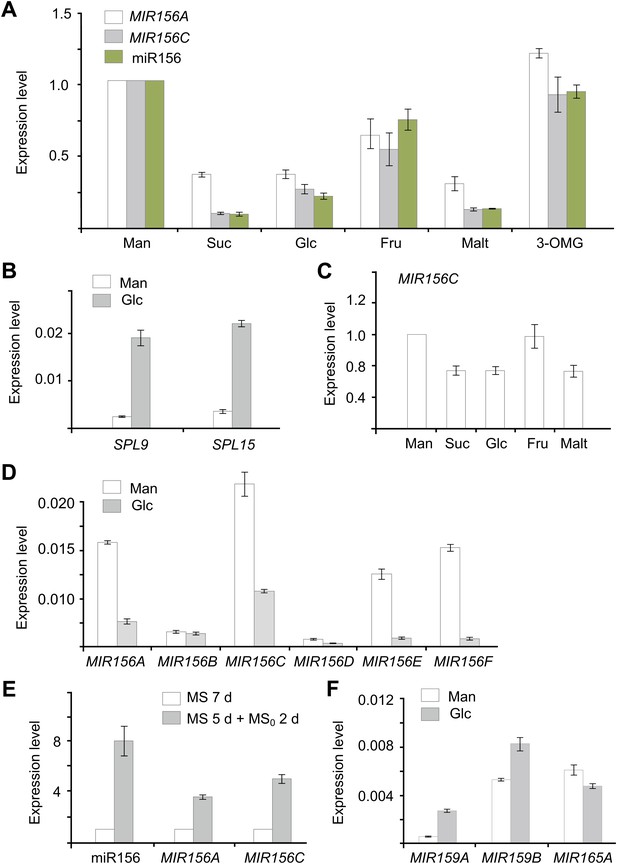
Sugar represses miR156.
(A) Expression of miR156, pri-MIR156A, and pri-MIR156C in response to sugar. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog (MS) liquid media were treated with 50 mM sucrose (Suc), glucose (Glc), fructose (Fru), maltose (Malt), or mannitol (Man) for 1 day. (B) Expression of SPL9 and SPL15 in response to sugar treatment. Five-day-old wild type seedlings were treated with 50 mM Man or Glc for 1 day. (C) pri-MIR156C quickly responds to sugar. Five-day-old wild type seedlings were treated with sugar for 30 min. The expression level in the mannitol-treated samples was set to 1. (D) Expression of pri-MIR156 transcripts. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media were treated with 50 mM glucose or mannitol for 1 day. (E) Expression of miR156 and pri-MIR156C during sugar starvation. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media supplemented with 50 mM sucrose were transferred to 1/2 MS media without sucrose (MS0). The seedlings were grown for another 2 days and then subjected to expression analyses. Seven-day-old seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media supplemented with 50 mM sucrose were used as control. (F) Expression of other pri-MIRNA transcripts. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media were treated with 50 mM glucose or mannitol for 1 day. The expression levels of pri-MIR156 and miR156 were normalized to those of TUBULIN (TUB). In the sugar treatment assays, 50 mM sugars were added at Zeitgeber time 12.
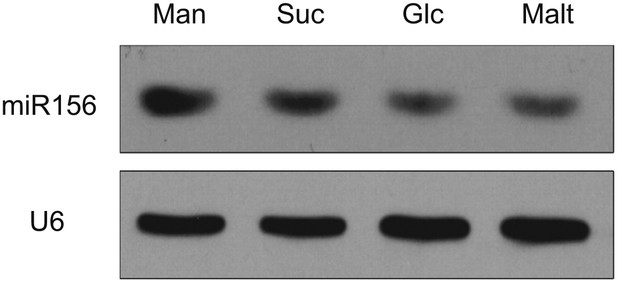
Sugar represses miR156.
Accumulation of miR156 in response to sugar. Five-day-old wild type seedlings were treated with sugar for 1 day and subjected to RNA blot analyses. U6 was monitored as an internal control. Sugar treatment started at Zeitgeber time 12. Man: mannitol; Suc: sucrose; Glc: glucose; Malt: maltose.
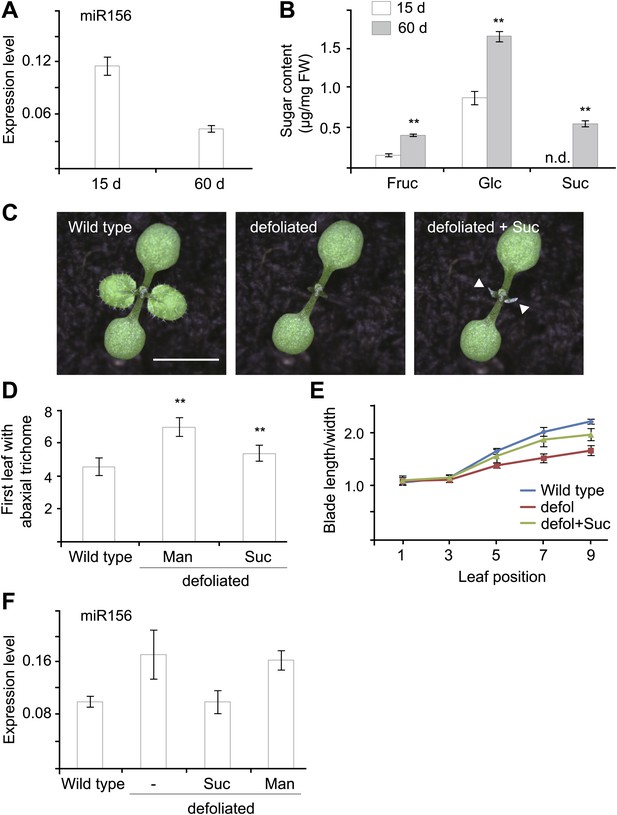
Sugar as a mobile signal to trigger vegetative phase transition.
(A) Expression of miR156 in 15-day-old and 60-day-old wild type plants grown under short day conditions. (B) Sugar measurement. Fifteen-day-old and 60-day-old short day plants were collected at Zeitgeber time 16. The fructose (Fru), glucose (Glc), and sucrose (Suc) content was analyzed by GC-MS and quantified. **Significant difference from 15-day-old wild type plants, Student t-test, p<0.001. Error bars indicate SD. n.d.: undetected; FW: fresh weight. (C) Seven-day-old wild type Arabidopsis seedlings before and after defoliation. Arrows indicate where the lanolin-sucrose (Suc) paste was applied. Scale bar indicates 0.5 cm. (D and E) Seven-day-old wild type seedlings before and after defoliation. Appearance of the first abaxial trichome (D) and the length-to-width ratios of blades (E) were measured. n=10. **Significant difference from wild type, Student t-test, p<0.001. Error bars indicate SE. defol: defoliated; Suc: sucrose. (F) Expression of miR156. Seven-day-old wild type seedlings were defoliated and sucrose (Suc) or mannitol (Man) was applied to the defoliated petioles. The shoot apices were collected for expression analyses 2 days after defoliation.
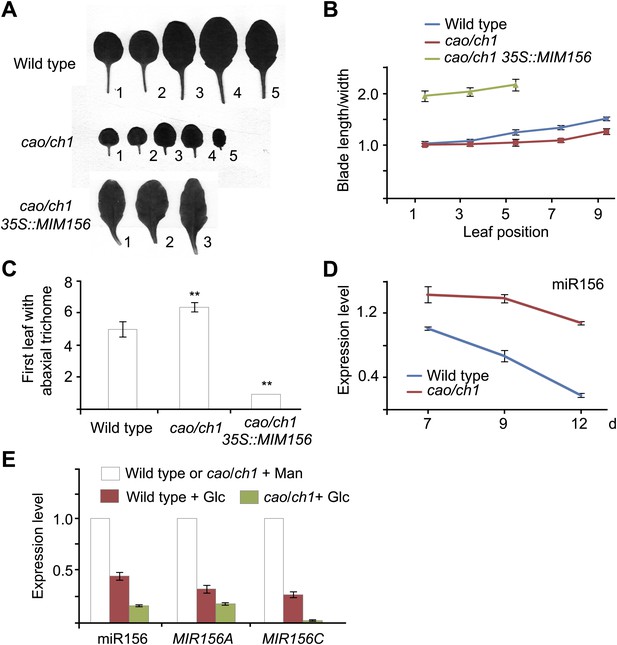
cao/ch1 mutant impairs vegetative phase transition.
(A) Leaf morphology of wild type, cao/ch1, and 35S::MIM156 cao/ch1 plants under long day conditions. The leaves from 15-day-old plants were detached and scanned. The numbers indicate leaf positions. (B and C) The length-to-width ratio of the blade (B) and the appearance of the first abaxial trichome (C). n=12. (D) Expression of miR156 during development. Wild type plants and cao/ch1 mutants were collected at 7, 9, or 12 days after germination under long day conditions. (E) Expression of miR156, pri-MIR156A, and pri-MIR156C. Five-day-old wild type and cao/ch1 mutants in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog (MS) liquid media were treated with 50 mM glucose or mannitol for 1 day. The expression levels in the mannitol-treated wild type or cao/ch1 were set to 1. The treatment was started at Zeitgeber time 12. **Significant difference from wild type, Student t-test, p<0.001. Error bars indicate SE.
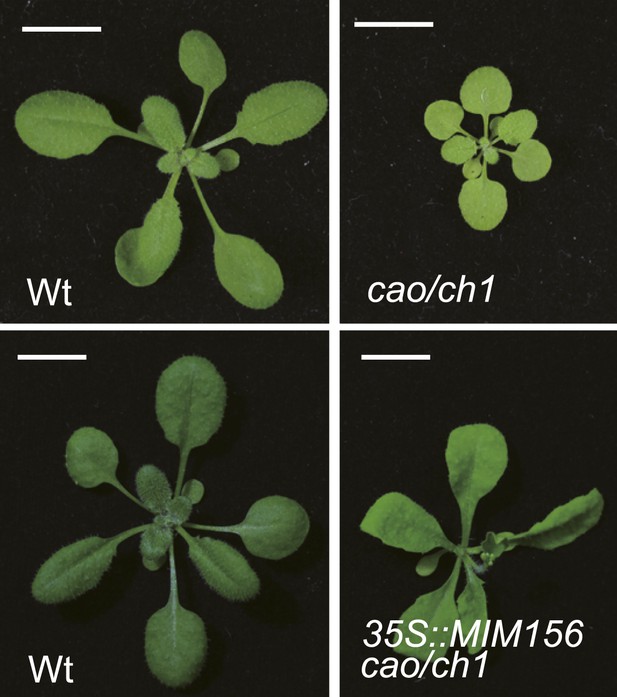

Phenotype of cao mutant.
Plant morphology of wild type (wt), cao/ch1, and 35S::MIM156 cao/ch1. Scale bar indicates 1.0 cm.
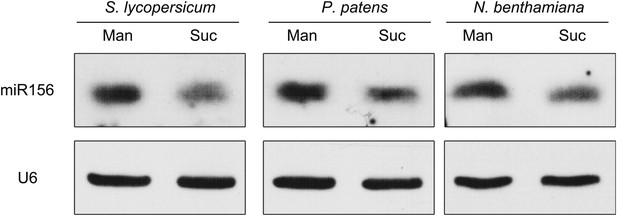
Repression of miR156 by sugar is evolutionarily conserved.
Expression of miR156 in Physcomitrella patens, Solanum lycopersicum, and Nicotiana benthamiana. The plants were treated with 50 mM sucrose (Suc) or mannitol (Man) for 2 days. U6 was monitored as the loading control. Treatment was started at Zeitgeber time 12.
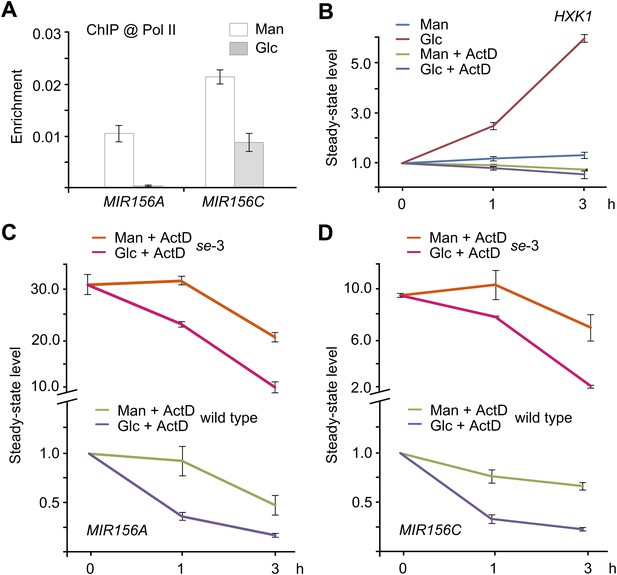
Sugar promotes the degradation of miR156 primary transcripts.
(A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses. Five-day-old wild type seedlings were treated with 50 mM glucose (Glc) or mannitol (Man) for 1 day. Anti-Pol II was used for ChIP analyses. The genomic fragments near the MIR156A or MIR156C TATA box were amplified. Relative enrichment was calculated by the ratio of bound DNAs after ChIP to input DNAs. (B) Expression of HXK1 in response to glucose. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog (MS) liquid media were pre-treated with or without actinomycin (ActD) for 12 hr. The seedlings were harvested at 0, 1, and 3 hr after 50 mM glucose or mannitol was added. The expression level at 0 hr was set to 1. (C and D) Expression of pri-MIR156A (C) and pri-MIR156C (D) in the wild type and se-3 mutant. Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media were pre-treated with ActD for 12 hr. The seedlings were then treated with 50 mM glucose or mannitol. The expression levels of pri-MIR156A and pri-MIR156C in the wild type at 0 hr were set to 1. Sugar treatment was started at Zeitgeber time 12.
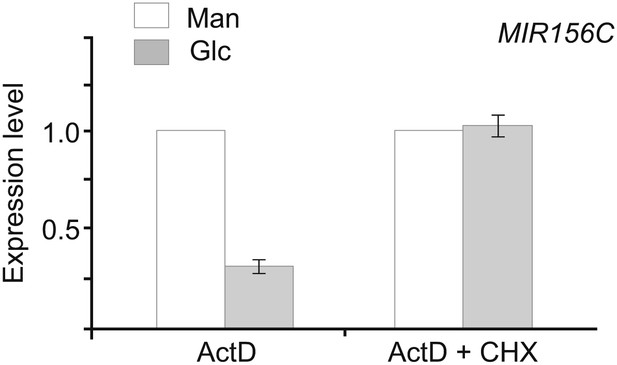
Effect of CHX on sugar-induced pri-MIR156C degradation.
Five-day-old wild type seedlings in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog liquid media were pre-treated with actinomycin-D (ActD) for 12 hr. Glucose was added 1 h after 100 µM cycloheximide (CHX). The levels in the mannitol-treated samples (mock) were set to 1. Glucose (50 mM) was added at Zeitgeber time 12.
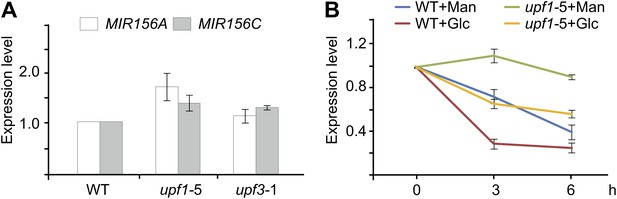
Expression analyses of pri-MIR156A and pri-MIR156C in upf mutants.
(A) Expression of pri-MIR156A and pri-MIR156C in upf1-5 and upf3-1 mutants. Seven-day-old wild type (WT), upf1-5, and upf3-1 seedlings were used for expression analyses. (B) Glucose response in upf mutants. Five-day-old wild type and upf1-5 seedlings in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog liquid media were pre-treated with actinomycin-D (ActD) for 12 h. The transcript level of pri-MIR156C was monitored at 0, 3, and 6 hr after glucose (Glc) or mannitol (Man) treatment. Glucose (50 mM) was added at Zeitgeber time 12.
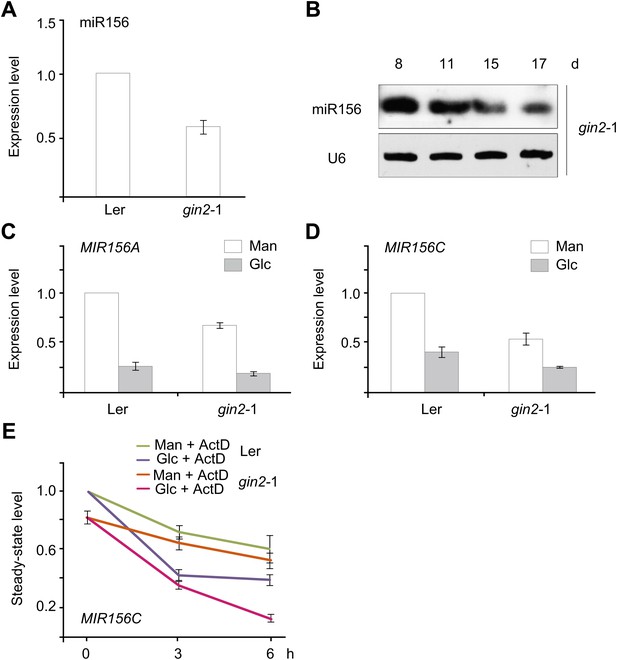
The role of HXK1 in sugar-induced miR156 repression.
(A) Expression of miR156 in the 5-day-old wild type (ecotype Ler) and gin2-1 mutant. The expression level of miR156 in Ler was set to 1. (B) Time course analyses of miR156 in the gin2-1 mutant. (C and D) Expression of pri-MIR156A (C) and pri-MIR156C (D) in response to glucose in the wild type (ecotype Ler) and gin2-1 mutant. Five-day-old seedlings in 1/2 Murashige and Skoog (MS) liquid media were treated with 50 mM glucose (Glc) or mannitol (Man) for 6 hr. The expression level in Ler at 0 h was set to 1. (E) Expression of pri-MIR156C in Ler and gin2-1. Five-day-old seedlings in 1/2 MS liquid media were pre-treated with actinomycin-D (ActD) for 12 hr and then treated with 50 mM glucose or mannitol. The expression level of pri-MIR156C in Ler at 0 hr was set to 1. Sugar treatment was started at Zeitgeber time 12.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
(A) MIR156 T-DNA insertion mutants. (B) Oligonucleotide primer sequences.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00269.016





