The Brm-HDAC3-Erm repressor complex suppresses dedifferentiation in Drosophila type II neuroblast lineages
Figures
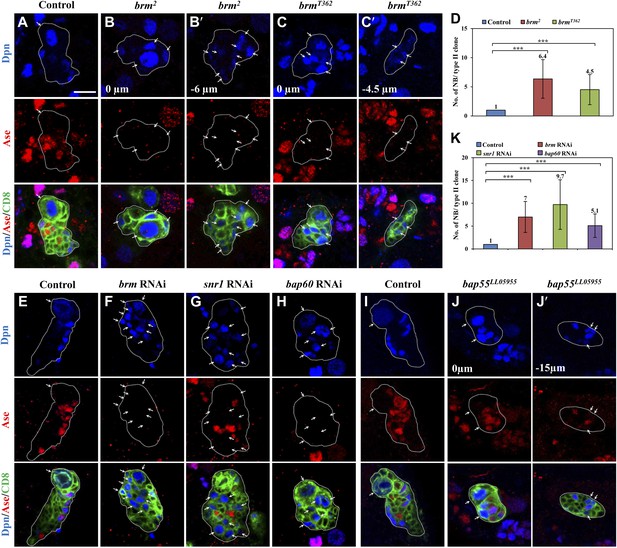
The Brm complex suppresses the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts.
(A–C) Type II MARCM clones of control (the MARCM driver; D), brm2 (B, B′) and brmT362 (C, C′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (D) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone for A–C. (E–H) Type II neuroblast lineage from control (‘the type II driver’: wor-Gal4 ase-Gal80; E), brm knockdown (F), snr1 knockdown (108599 KK; G), and bap60 knockdown (H) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (I–J′) type II MARCM clone of control (I) and bap55LL05955 (J, J′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (K) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II lineage for E–I. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Scale bars, 10 µm. *** indicates p<0.001.
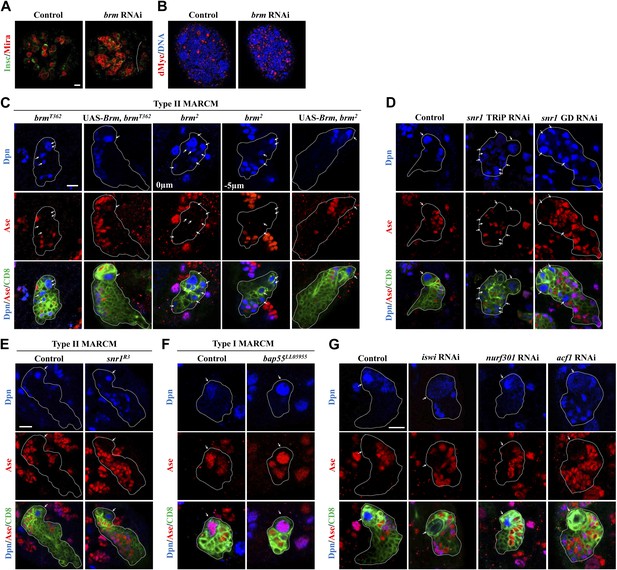
Analysis of chromatin remodelers in larval brains.
(A and B) Larval brains of control (elav-Gal4 driver) and brm knockdown under the control of elav-Gal4 driver were labeled with Insc and Mira (A) and dMyc (B). Central brain is to the left of white dotted line. (C) Type II MARCM clones of brmT362, brm2 with or without the expression of UAS-Brm were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (D) Type II driver control, snr1 TRiP RNAi (BDRC#32372), and snr1 VDRC RNAi (12645GD) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (E) Control (MARCM driver) and snr1R3 type II MARCM clones were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (F) Control (MARCM driver) and bap55LL5955 type I MARCM clones were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (G) Type II neuroblast lineages of control (type II driver), iswi knockdown, nurf301 knockdown and acf1 knockdown were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows, neuroblasts. Clone outline is indicated by white dotted line (C–G). Scale bars, 10 μm.
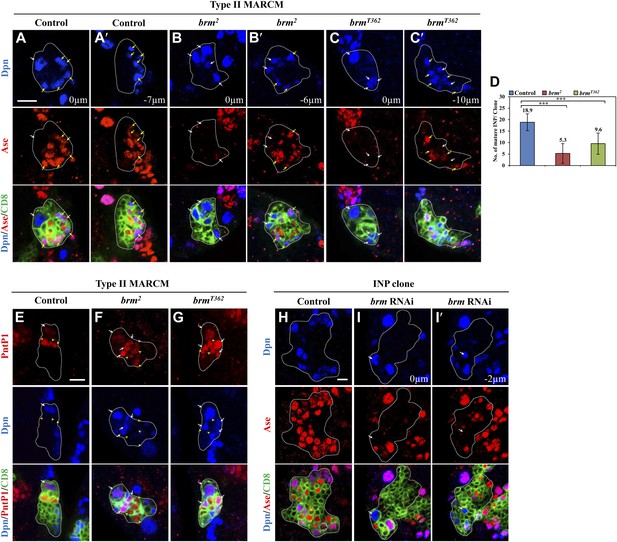
The Brm complex suppresses INP dedifferentiation into type II neuroblasts.
(A–C′) Type II MARCM clones of control (the MARCM driver; A, A′), brm2 (B, B′) and brmT362 (C, C′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (D) Quantifications of INP number per type II clone for A–C′. *** indicates p<0.001. (E–G) Type II MARCM clones of control (E), brm2 (F) and brmT362 (G) were labeled with Dpn (blue), PntP1 (red) and CD8::GFP (green). (H–I′) INP clones of a control (driver: erm-Gal4 [II]; erm-Gal4 [III]; (H) and brm RNAi under erm-Gal4 (II); erm-Gal4 (III) with UAS-Dcr2 UAS-CD8-GFP (I, I′) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). White arrows indicate neuroblasts, yellow arrows indicate Dpn+ Ase+ mature INPs and yellow arrowheads indicate Dpn− PntP1+ INPs. Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Scale bars, 10 µm (A–G) and 5 µm (H–I′).
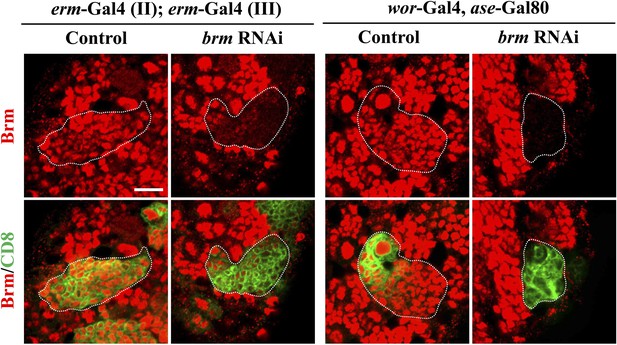
Partial knock down of brm in INP clones.
Left panels, INP clones of a control (driver: erm-Gal4 [II]; erm-Gal4 [III]) and brm RNAi under erm-Gal4 (II); erm-Gal4 (III) with UAS-Dcr2 UAS-CD8-GFP were labeled with Brm (red) and CD8 (green). Right panels, Brm is absent in type II neuroblast clones under the type II driver. Clones are indicated by white dotted line. Scale bars, 10 µm.
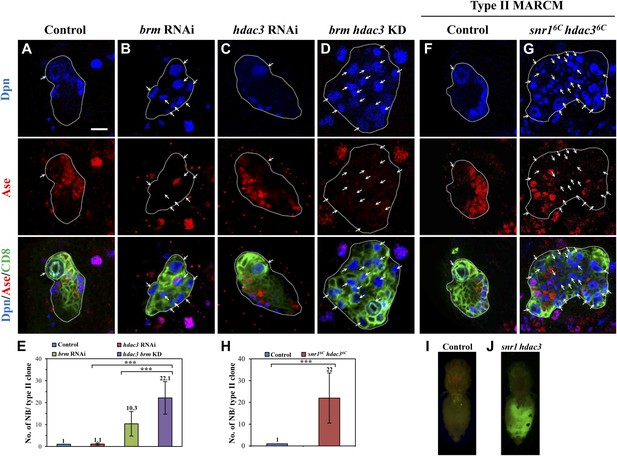
HDAC3 acts cooperatively with the Brm complex to suppress the formation of ectopic type II neuroblasts.
(A–D) The driver control (A), brm RNAi (B), hdac3 RNAi (C), brm hdac3 double knockdown (D) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn, Ase, and CD8. (E) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in A–D. (F–G) Type II MARCM clones from the driver control (F) and snr16c hdac36c (G) homozygous MARCM clones were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. (H) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone in F–G. *** indicates p<0.001. (I–J) Clones are marked by CD8::GFP and indicated by white dotted line. Larval brain tissues from the wild-type MARCM clones (I) and snr16c hdac36c MARCM clones (J) were implanted into the abdomen of wild-type hosts. Scale bar, 10 µm.
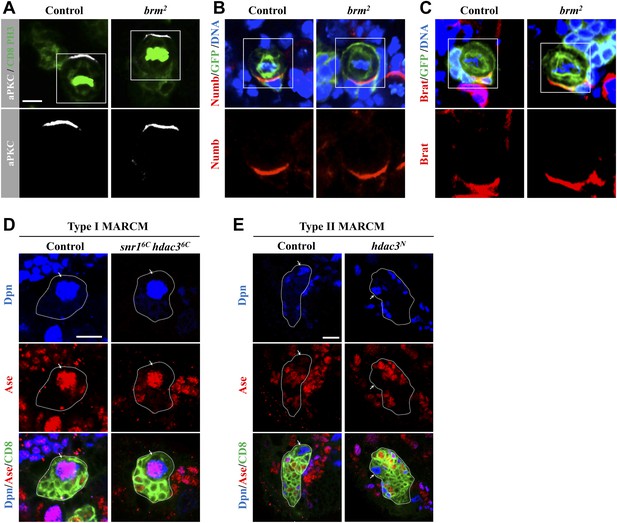
Brm is not important for the apical-basal polarity of neuroblasts.
(A–C) Neuroblast of control MARCM clones and brm2 MARCM clones were co-labeled with aPKC (white), CD8 (green) and Phospho-Histone H3 (PH3; green) (A) or Numb, GFP and DNA (B) or Brat, GFP and DNA (C). Lower panels are enlarged images of the boxed region. (D) Type I MARCM clones from control (MARCM driver) and snr16c hdac36c were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (E) Type II MARCM clones from control (driver) and hdac3N were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows, neuroblasts. Scale bars, 5 µm (A–C), 10 μm (D–E).
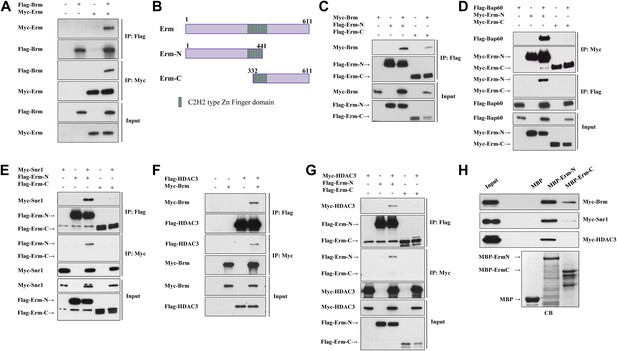
The Brm remodeling complex physically associates with Erm and HDAC3.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) between Flag-Brm and Myc-Erm. (B) An illustration of Erm domains and truncated constructs. (C) Co-IP between Myc-Brm and Flag-Erm-N or Flag-Erm-C. (D) Co-IP between Flag-Bap60 and Myc-Erm-N or Myc-Erm-C. (E) Co-IP between Myc-Snr1 and Flag-Erm-N or Flag-Erm-C. (F) Co-IP was Flag-HDAC3 and Myc-Brm. (G) Co-IP between Flag-HDAC3 and Myc-Erm-N or Myc-Erm-C. IP was performed using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies. Western blot was performed using anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. (H) Protein pull-down assay. MBP, MBP-Erm-N and MBP-ErmC bound beads were incubated with protein extracts from S2 cells expressing Myc-Brm, Myc-Snr1 or Myc-HDAC3. Western blot was performed using an anti-Myc antibody. Coomassie blue (CB) staining showed 10% input of various purified MBP or MBP fusion proteins.
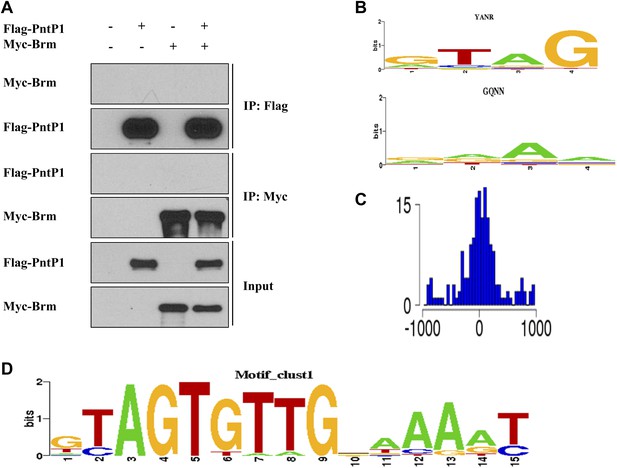
Brm and Erm may regulate gene expression of some common downstream targets.
(A) Co-IP was performed using S2 cells expressing Flag-PntP1 and Myc-Brm. IP was performed using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies. Western blot was performed using anti-Flag and anti-Myc antibodies. (B) The DNA binding preferences of the first zinc-finger ‘GTAG’ and the fourth zinc-finger ‘RAAA’. They are observed to be enriched in 270 Brm binding sites. (C) The distant distribution between the ChIP–chip peak and the occurrences of the motif in (D). (D) The de novo Erm-binding motif learned by SEME based on the 270 Brm binding sites.
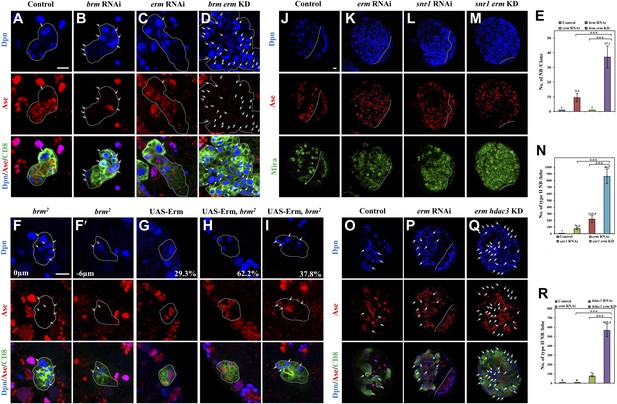
Brm genetically interacts with Erm to prevent dedifferentiation of INPs to neuroblasts.
(A–D) Type II clones of control (the type II driver; A), brm knockdown (B), erm knockdown (C) and brm erm double knockdown (D) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (E) Quantifications of neuroblast number per type II neuroblast lineage for A–D. (F–I) Type II MARCM clones of brm2 (F, F′), UAS-Erm (G) and UAS-Erm, brm2 (H–I) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (J–M) Larval brains of control (J, elav-Gal4 driver), erm knockdown (K), snr1 knockdown (L) and erm snr1 double knockdown (M) were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and Mira (green). (N) Quantifications of the number of type II neuroblasts per brain hemisphere in various genotypes in J–M. Control (elav-Gal4), 7 ± 0; erm RNAi, 76.6 ± 14.2; snr1 RNAi, 219.5 ± 52.2; erm snr1 double knockdown (KD), 862.0 ± 106.7. (O–Q) Larval brains of control (driver; O), erm knockdown (P) and erm hdac3 double knockdown (Q) under the type II driver were labeled with Dpn (blue), Ase (red) and CD8 (green). (R) Quantifications of neuroblast number per brain hemisphere in O–Q. Central brain is to the left of white dotted lines. Arrows indicate neuroblasts. Clones were indicated by white dotted lines. Scale bars, 10 µm. *** indicates p<0.001.
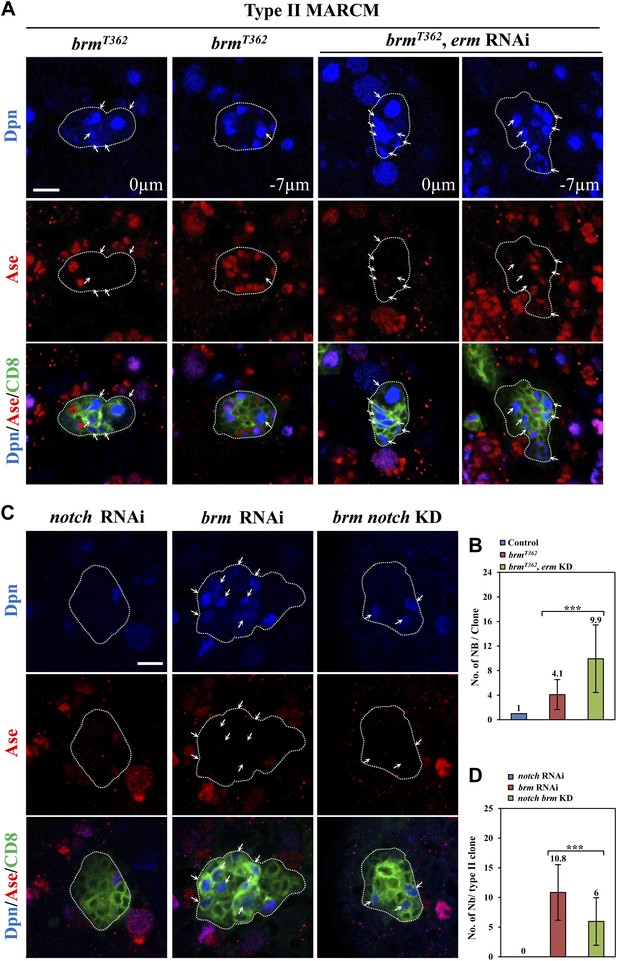
Knocking down of erm enhanced the neuroblast overgrowth observed in brm mutants.
(A) Type II MARCM clones of brmT362 and UAS-Dcr2; erm RNAi, brmT362 were labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. Arrows, neuroblasts. Clone outline is indicated by white dotted line. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Quantification of neuroblast number per type II MARCM clone. MARCM Control, 1.0 ± 0; brmT362, 4.1 ± 2.4; erm RNAi, brmT362, 9.9 ± 5.5. (C) Simultaneous knockdown of brm and notch in type II neuroblast lineages partially suppressed the ectopic neuroblast phenotype, compared with brm knockdown alone. Type II neuroblast lineages are labeled with Dpn, Ase and CD8. (D) Quantification of genotypes in C. brm notch double knockdown, 6.0 ± 4.7 neuroblasts/lineage, n = 76; brm knockdown, 10.8 ± 4 neuroblasts/lineage, n = 39. *** indicates p<0.001.
Tables
Histone modifiers and their RNAi lines
| S/No. | Gene name | Full name | CG # | Main function | VDRC RNAi lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | enok | Enoki mmushroom | CG11290 | HAT | KK108400, GD37527 |
| 2 | nej | Nejire/CBP | CG15319 | HAT | KK105115 |
| 3 | CG1894 | CG1894 | HAT | GD41575, GD41574 | |
| 4 | CG2051 | CG2051 | HAT | GD33458 | |
| 5 | Mof | Males absent on the first | CG3025 | HAT | KK105370 |
| 6 | Rpb4 | Rpb4 | CG33520 | HAT | GD21985, GD23308 |
| 7 | Pcaf | Gcn | CG4107 | HAT | KK108943, GD21786 |
| 8 | YL-1 | YL-1 | CG4621 | HAT | GD21903 |
| 9 | Chm | Chameau | CG5229 | HAT | KK105542 |
| 10 | Dik | Diskette | CG7098 | HAT | GD46320 |
| 11 | lid | Little imaginal discs | CG9088 | HAT | GD42203, KK103830 |
| 12 | Ada2b | CG9638 | HAT | GD24076 | |
| 13 | Sirt7 | CG11305 | HDAC | GD18043, GD18045 | |
| 14 | HDAC4 | CG1770 | HDAC | GD20522 | |
| 15 | HDAC3 | CG2128 | HDAC | KK107073 | |
| 16 | HDACX | CG31119 | HDAC | KK108098 | |
| 17 | Sirt4 | CG3187 | HDAC | GD40295, KK110639 | |
| 18 | Sirt2 | CG5085 | HDAC | KK103790 | |
| 19 | Sir2 | CG5216 | HDAC | GD23199, KK108241, KK105502 | |
| 20 | Bin1 | Bicoid interacting protein | CG6046 | HDAC | KK105352, GD15710 |
| 21 | Sirt6 | CG6284 | HDAC | GD22483 | |
| 22 | Gug | Grunge | CG6964 | HDAC | GD13687 |
| 23 | Rpd3 | HDAC1 | CG7471 | HDAC | GD46929, GD30600, GD46929 |
| 24 | Sin3a | CG8815 | HDAC | KK105852 | |
| 25 | Rtf1 | CG10955 | Methyl transferase | KK110392 | |
| 26 | Vig2 | CG11844 | Methyl transferase | KK107081, GD17245 | |
| 27 | egg | eggless | CG12196 | Methyl transferase | KK101677, GD33730 |
| 28 | esc | extra sexcombs | CG14941 | Methyl transferase | GD5690, GD5692 |
| 29 | set2 | CG1716 | Methyl transferase | GD30707 | |
| 30 | g9a | CG2995 | Methyl transferase | GD25474 | |
| 31 | pr-set7 | CG3307 | Methyl transferase | KK105422 | |
| 32 | trr | trithorax-related | CG3848 | Methyl transferase | GD10749, KK110276 |
| 33 | CG40351 | CG40351 | Methyl transferase | GD40683, GD10833, GD45267 | |
| 34 | CG4565 | CG4565 | Methyl transferase | GD5665 | |
| 35 | mes-4 | CG4976 | Methyl transferase | GD10836 | |
| 36 | Art4 | Arginine methyl transferase 4 | CG5358 | Methyl transferase | KK107009 |
| 37 | Su(var)3–9 | auppressor of variegation 3–9 | CG6476 | Methyl transferase | GD39377 |
| 38 | Art1 | Arginine methyl transferase 11 | CG6554 | Methyl transferase | GD40388, KK110391 |
| 39 | ash2 | absent, small or homeotic discs 2 | CG6677 | Methyl transferase | KK100718 |
| 40 | LKR | Lysine ketoglutarate reductase | CG7144 | Methyl transferase | GD51346 |
| 41 | Su(z)12 | Suppressor of Zeste 205 | CG8013 | Methyl transferase | GD42422, GD42423 |
| 42 | Su(var)205 | Suppressor of variegation 205 | CG8409 | Methyl transferase | KK107477 |
| 43 | Ash1 | Absent, small or homeotic discs 1 | CG8887 | Methyl transferase | GD28928 |
Predicted common target genes of Brm and Erm
| S/No. | CG name | Gene name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | CG10033 | for |
| 2 | CG10117 | ttv |
| 3 | CG10137 | CG10137 |
| 4 | CG10159 | BEAF-32 |
| 5 | CG10388 | Ubx |
| 6 | CG10610 | ECSIT |
| 7 | CG1071 | E2f2 |
| 8 | CG10844 | RyR |
| 9 | CG1100 | Rpn5 |
| 10 | CG11228 | hpo |
| 11 | CG11309 | CG11309 |
| 12 | CG11589 | VhaM9.7-c |
| 13 | CG12165 | Incenp |
| 14 | CG12321 | CG12321 |
| 15 | CG12333 | CG12333 |
| 16 | CG12387 | zetaTry |
| 17 | CG12797 | Ciao1 |
| 18 | CG12818 | CG12818 |
| 19 | CG12819 | sle |
| 20 | CG12855 | HPS1 |
| 21 | CG12994 | CG12994 |
| 22 | CG13004 | CG13004 |
| 23 | CG13016 | CG13016 |
| 24 | CG13018 | CG13018 |
| 25 | CG13117 | CG13117 |
| 26 | CG1322 | zfh1 |
| 27 | CG13316 | Mnt |
| 28 | CG13350 | Ctf4 |
| 29 | CG13366 | CG13366 |
| 30 | CG13432 | qsm |
| 31 | CG13472 | CG13472 |
| 32 | CG13688 | Ipk2 |
| 33 | CG13900 | CG13900 |
| 34 | CG13919 | CG13919 |
| 35 | CG14291 | CG14291 |
| 36 | CG14463 | CG14463 |
| 37 | CG1453 | Klp10A |
| 38 | CG14813 | deltaCOP |
| 39 | CG14814 | CG14814 |
| 40 | CG14938 | crol |
| 41 | CG14939 | CycY |
| 42 | CG15010 | ago |
| 43 | CG15027 | CG15027 |
| 44 | CG15120 | CG15120 |
| 45 | CG15387 | CG15387 |
| 46 | CG15701 | CG15701 |
| 47 | CG15706 | CG15706 |
| 48 | CG15845 | Adf1 |
| 49 | CG1600 | Drat |
| 50 | CG1616 | dpa |
| 51 | CG17033 | elgi |
| 52 | CG17035 | GXIVsPLA2 |
| 53 | CG17052 | obst-A |
| 54 | CG17233 | CG17233 |
| 55 | CG17249 | CG17249 |
| 56 | CG17259 | CG17259 |
| 57 | CG17260 | CG17260 |
| 58 | CG1765 | EcR |
| 59 | CG17803 | CG17803 |
| 60 | CG1785 | CG1785 |
| 61 | CG1817 | Ptp10D |
| 62 | CG18292 | CG18292 |
| 63 | CG1845 | Br140 |
| 64 | CG18660 | Nckx30C |
| 65 | CG18675 | CG18675 |
| 66 | CG2004 | CG2004 |
| 67 | CG2019 | disp |
| 68 | CG2051 | CG2051 |
| 69 | CG2146 | didum |
| 70 | CG2189 | Dfd |
| 71 | CG2446 | Amun |
| 72 | CG2698 | CG2698 |
| 73 | CG2720 | Hop |
| 74 | CG2813 | cold |
| 75 | CG2977 | Inx7 |
| 76 | CG3059 | NTPase |
| 77 | CG3127 | Pgk |
| 78 | CG31481 | pb |
| 79 | CG3157 | gammaTub23C |
| 80 | CG3165 | CG3165 |
| 81 | CG3166 | aop |
| 82 | CG31712 | CG31712 |
| 83 | CG31713 | Apf |
| 84 | CG3178 | Rrp1 |
| 85 | CG31794 | Pax |
| 86 | CG31852 | Tap42 |
| 87 | CG31855 | CG31855 |
| 88 | CG31911 | Ent2 |
| 89 | CG32022 | CG32022 |
| 90 | CG32556 | chas |
| 91 | CG32592 | hiw |
| 92 | CG33116 | CG33116 |
| 93 | CG33162 | SrpRbeta |
| 94 | CG3587 | CG3587 |
| 95 | CG3666 | Tsf3 |
| 96 | CG3842 | CG3842 |
| 97 | CG3857 | CG3857 |
| 98 | CG3920 | Reph |
| 99 | CG42254 | CG42254 |
| 100 | CG42311 | grh |
| 101 | CG42334 | comm3 |
| 102 | CG42362 | CG42362 |
| 103 | CG42363 | CG42363 |
| 104 | CG42365 | CG42365 |
| 105 | CG42379 | CG42379 |
| 106 | CG42380 | CG42380 |
| 107 | CG42381 | CG42381 |
| 108 | CG4400 | CG4400 |
| 109 | CG4590 | Inx2 |
| 110 | CG4619 | CG4619 |
| 111 | CG4645 | CG4645 |
| 112 | CG4798 | l(2)k01209 |
| 113 | CG4996 | CG4996 |
| 114 | CG5229 | chm |
| 115 | CG5393 | apt |
| 116 | CG5505 | scny |
| 117 | CG5548 | CG5548 |
| 118 | CG5588 | Mtl |
| 119 | CG5599 | CG5599 |
| 120 | CG5611 | CG5611 |
| 121 | CG5613 | CG5613 |
| 122 | CG5824 | l(3)07882 |
| 123 | CG5836 | SF1 |
| 124 | CG6022 | Cchl |
| 125 | CG6202 | Surf4 |
| 126 | CG6218 | CG6218 |
| 127 | CG6235 | tws |
| 128 | CG6241 | CG6241 |
| 129 | CG6272 | CG6272 |
| 130 | CG6322 | U4-U6-60K |
| 131 | CG6343 | ND42 |
| 132 | CG6401 | CG6401 |
| 133 | CG6511 | CG6511 |
| 134 | CG6556 | cnk |
| 135 | CG6565 | CG6565 |
| 136 | CG6604 | H15 |
| 137 | CG6634 | mid |
| 138 | CG6829 | Ark |
| 139 | CG6948 | Clc |
| 140 | CG6951 | CG6951 |
| 141 | CG6983 | CG6983 |
| 142 | CG7082 | papi |
| 143 | CG7085 | l(2)s5379 |
| 144 | CG7186 | SAK |
| 145 | CG7191 | CG7191 |
| 146 | CG7372 | CG7372 |
| 147 | CG7379 | CG7379 |
| 148 | CG7564 | CG7564 |
| 149 | CG7597 | Cdk12 |
| 150 | CG7632 | CG7632 |
| 151 | CG7685 | CG7685 |
| 152 | CG7734 | shn |
| 153 | CG7771 | sim |
| 154 | CG7828 | APP-BP1 |
| 155 | CG7845 | CG7845 |
| 156 | CG7849 | CG7849 |
| 157 | CG7957 | MED17 |
| 158 | CG7961 | alphaCop |
| 159 | CG8067 | CG8067 |
| 160 | CG8241 | pea |
| 161 | CG8287 | Rab8 |
| 162 | CG8360 | CG8360 |
| 163 | CG8372 | CG8372 |
| 164 | CG8396 | Ssb-c31a |
| 165 | CG8409 | Su(var)205 |
| 166 | CG8481 | CG8481 |
| 167 | CG8790 | Dic1 |
| 168 | CG8798 | Lon |
| 169 | CG8817 | lilli |
| 170 | CG9042 | Gpdh |
| 171 | CG9054 | Ddx1 |
| 172 | CG9063 | Rich |
| 173 | CG9065 | CG9065 |
| 174 | CG9243 | CG43345 |
| 175 | CG9243 | CG43346 |
| 176 | CG9244 | Acon |
| 177 | CG9249 | CG9249 |
| 178 | CG9250 | Mpp6 |
| 179 | CG9305 | CG9305 |
| 180 | CG9376 | CG9376 |
| 181 | CG9473 | MED6 |
| 182 | CG9596 | CG9596 |
| 183 | CG9635 | RhoGEF2 |
| 184 | CG9641 | CG9641 |
| 185 | CG9730 | mRpL21 |
| 186 | CG9750 | rept |
| 187 | CG9829 | poly |
| 188 | CG9865 | CG9865 |





