A tethered delivery mechanism explains the catalytic action of a microtubule polymerase
Figures
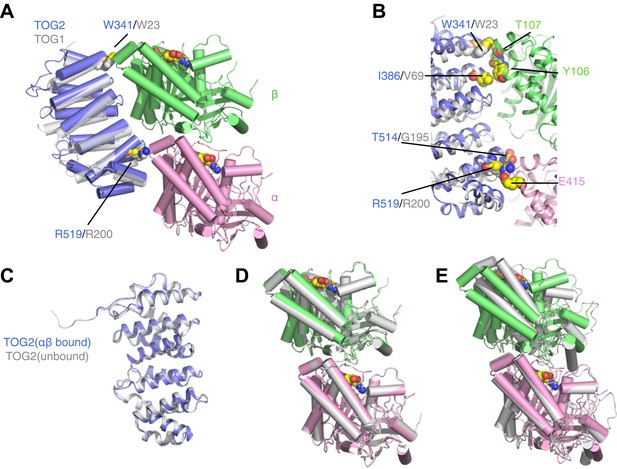
TOG2 binds to curved αβ-tubulin analogously to TOG1.
(A) Structure of the TOG2:αβ-tubulin complex (TOG2: slate, α-tubulin: pink, β-tubulin: green), with the important binding residues W341 and R519 represented as spheres. The semi-transparent gray cartoon shows the previously observed binding mode of TOG1, with its binding residues W23 and R200 depicted as spheres. (B) Close-up of the TOG2:αβ-tubulin interface, colored as in A, and showing in spheres important interacting residues based on an earlier study. (C) Structural superposition of αβ-tubulin-bound (slate) and unbound (gray) TOG2 (PDB 2QK1). The two structures of TOG2 show only small local deviations, arguing against any significant conformational change associated with αβ-tubulin binding. (D) Structural superposition of the αβ-tubulin conformations in the TOG2 (colored) and TOG1 (gray) complexes. In both complexes αβ-tubulin adopts very similar curved conformations. (E) Structural superposition of TOG2-bound αβ-tubulin (colored) and the straight conformation of αβ-tubulin (PDB 1JFF, gray), showing the ∼13° rotation of β-tubulin relative to α-tubulin that is characteristic of the curved conformation.
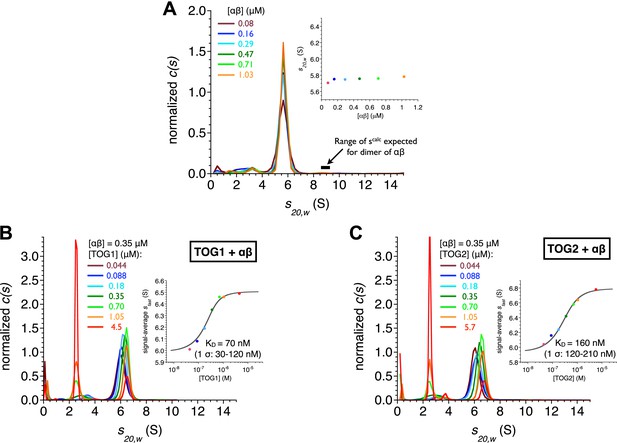
TOG1 and TOG2 bind αβ-tubulin with comparable affinity.
(A) Sedimentation velocity analytical ultracentrifugation of polymerization competent yeast αβ-tubulin does not show signs of self-association between 80 nM and 1 μM concentration. The main plot shows c(s) distributions for a range of αβ-tubulin concentration. The inset shows that the s20,w is not increasing with αβ-tubulin concentration. Data points are color coded to match the c(s) distribution for that concentration. c(s), signal population as a function of s; s20,w, sedimentation coefficient standardized to pure water and 20°C. (B) Analysis of TOG1:αβ-tubulin interactions by sedimentation velocity. The main plot shows c(s) distributions (color coded by concentration) for seven concentrations of TOG1 (44 nM–4.5 μM) titrated into 0.35 μM αβ-tubulin. The inset shows the fit (gray line) of a 1:1 binding isotherm to the signal average sfast (dots colored to match the c(s) distribution for that concentration of TOG1) resulting in a dissociation constant of 70 nM. (C) Analysis of TOG2:αβ-tubulin interactions by sedimentation velocity. Plots are as described in (B). The fitted dissociation constant is 160 nM.
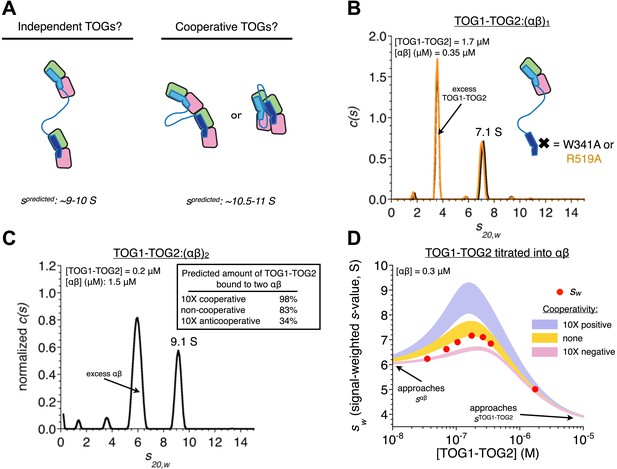
In TOG1-TOG2, the two TOG domains bind two αβ-tubulins without positive cooperativity.
(A) Cartoons illustrating three different possible arrangements of a TOG1-TOG2:(αβ)2 complex: independent (left) denotes that an αβ-tubulin:αβ-tubulin interface does not provide additional stability to the complex, cooperative (right) denotes that an αβ-tubulin:αβ-tubulin interface (either longitudinal or lateral) provides additional stability to the complex. Predicted sedimentation coefficients (calculated using HYDROPRO [García De La Torre et al., 2000]) are indicated. αβ-tubulin is represented in pink and green, TOG1-TOG2 in shades of blue. (B) Sedimentation behavior of a TOG1-TOG2:(αβ)1 complex by sedimentation velocity AUC using two different mutations (W314A and R519A) that impair TOG2:αβ-tubulin interactions. The ‘one tubulin’ complex sediments at 7.1 S. (C) Placing limits on the sedimentation behavior of a TOG1-TOG2:(αβ)2 complex by sedimentation velocity AUC. At ∼5 molar equivalents of αβ-tubulin to TOG1-TOG2, the resulting complex sediments at 9.1 S. The inset shows the predicted fraction of TOG1-TOG2 engaged in ‘two αβ-tubulin complex’ under different assumptions about cooperativity. (D) Concentration dependence of TOG1-TOG2:αβ-tubulin interactions. Seven concentrations of TOG1-TOG2 were mixed with 0.3 μM αβ-tubulin and analyzed by sedimentation velocity AUC. Red dots indicate the signal-weighted sw values for the seven runs. The blue and pink swaths show the predicted behavior for TOG1 and TOG2 binding αβ-tubulin with 10-fold positive or negative cooperativity, respectively, and assuming the sedimentation coefficient of TOG1-TOG2:(αβ)2 falls in the range 9.1–10.9 S (see text). The gold swath shows the predicted behavior for noncooperatively binding TOGs using the same range of sedimentation coefficient for TOG1-TOG2:(αβ)2. The data are not consistent with cooperative binding of TOG1-TOG2 to two αβ-tubulins. Instead, they are much better described by independently binding TOG domains.
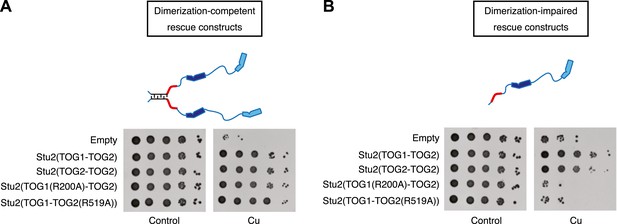
Two TOG domains are required for Stu2 function, but they do not have to be different.
(A) Yeast carrying plasmid-based rescue constructs coding for dimerization-competent variants of Stu2p were plated at serial dilutions on media that was unmodified (control) or that contained 500 μM CuSO4 (to deplete endogenous Stu2p; see text). All constructs, including those with debilitated TOG1 or TOG2 domains, showed full rescue. TOG domains are shown in blue, and the basic region in red. The coiled-coil is cartooned as a zipper. (B) As in A but using rescue constructs that are dimerization-impaired because the coiled-coil dimerization domain was deleted. In this more stringent background insults to either TOG domain abolished rescue activity. Replacing TOG1 with a second copy of TOG2 does not have adverse effects.
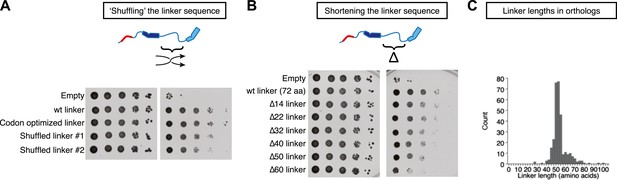
Stu2p function tolerates variation in the primary sequence and in the length of the TOG1-TOG2 linker.
Rescue assays were performed as in Figure 4, using dimerization-impaired rescue constructs. (A) Stu2p variants with ‘shuffled’ (randomized) linker sequences rescue the depletion of endogenous Stu2p comparably to those with the natural linker. (B) Stu2p function is substantially abolished when the TOG1-TOG2 linker is truncated by 60 amino acids. Smaller truncations only show slightly compromised rescue activity. (C) Histogram illustrating the distribution of TOG1-TOG2 linker lengths in ∼300 orthologs. The distribution shows that the linker length can vary but has a minimum tolerable length of ∼40 amino acids.
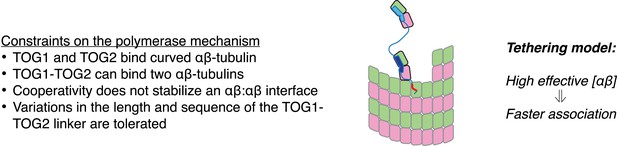
A tethering model for the polymerase function that incorporates our structural and biochemical observations.
The model posits that MT plus-end recognition occurs through TOG-mediated recognition of curved (black outline, ‘kinked’ αβ-tubulin cartoon), not straight (gray outlines), αβ-tubulin on the MT end, and that the linked TOG domains (blue; the basic region is indicated in red) serve to ‘tether’ an unpolymerized αβ-tubulin to the MT end. Polymerase activity is predicted to arise because increasing the effective concentration of αβ-tubulin near the MT end should also increase the rate of αβ-tubulin:MT encounters.
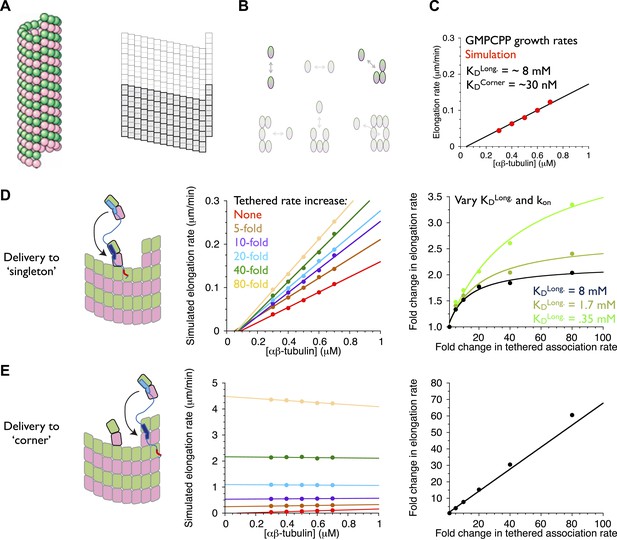
An implicit model can recapitulate the catalytic nature of polymerase activity.
We developed a kinetic model for microtubule elongation and altered it to explore models for the polymerase. (A) Cartoon of the cylindrical microtubule (left; pink and green spheres represent α- and β-tubulin, respectively) alongside a two-dimensional representation of the MT lattice (gray boxes, right; the darker boxes represent the microtubule ‘seed’ used to template elongation in our simulations). (B) The model parameterizes all six possible neighbor states for αβ-tubulin in the lattice, but the two that dominate the elongation behavior are the longitudinal (top left) and corner (top right) interactions. (C) A grid search identified parameters capable of recapitulating the concentration dependence of microtubule elongation rates in the presence of GMPCPP. The black line summarizes the trend from experimental observations (Brouhard et al., 2008; Gardner et al., 2011); red dots represent the results from our simulations. Using a kon of 4 × 106 M−1s−1, we obtained a good match to observed growth rates from KDlong = 8 mM and KDcorner = 33 nM. (D) (left) Cartoon illustrating the tethering model, with the polymerase (TOG domains in blue, basic region in red) localized to a curved αβ-tubulin bound at the MT end by pure longitudinal association, (middle) simulated growth rates obtained at increasing association rates for the tethered αβ-tubulin. Enhanced trapping of longitudinally-associated αβ-tubulin through the tethering effect shows catalyst-like activity: growth rates and apparent on-rate constant (slope) both change significantly but the apparent equilibrium for growth (x-intercept) does not. (right) Plot of fold increase in growth rate vs the fold increase in tethered αβ-tubulin association rate, using values at 0.5 μM αβ-tubulin concentration as a reference (black dots; the black line shows the fit of a hyperbolic curve to the growth rates). The model for the polymerase gives a relatively modest change in growth rates compared to the fold-increase in tethered association rate. Simulations with progressively stronger (dark green: 1.7 mM; light green, 0.35 mM) longitudinal interactions show higher maximal polymerase activity. The polymerase activity is related to the population of longitudinally-associated αβ-tubulin at the MT end. (E) Examining an alternative tethering model in which the polymerase promotes incorporation at a ‘corner’ site. This model yields much greater stimulation of elongation (middle) because there is always at least one corner site at the microtubule end. The predicted response also does not appear to saturate with increased tethering effect (right, linear fit). This alternative model does not describe the polymerase action because it fails to produce catalyst-like output.
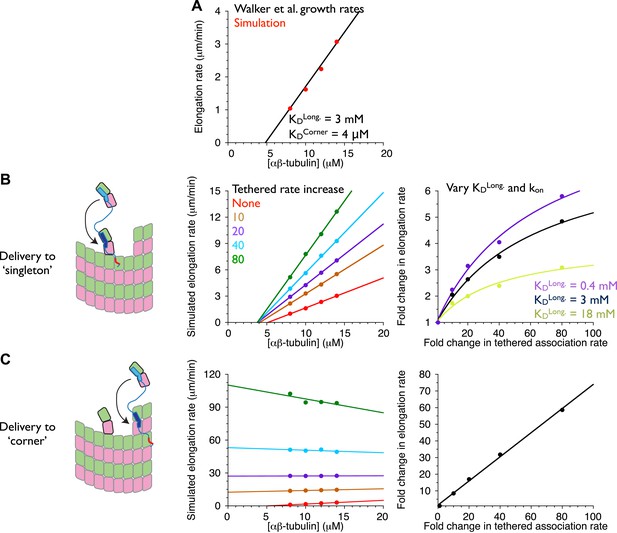
An implicit model as in Figure 7 but trained against different measured growth rates.
(A) A grid search identified parameters capable of recapitulating the concentration dependence of microtubule elongation rates measured by Walker et al. (1988). The black line summarizes the trend from experimental observations; red dots represent the results from our simulations. Using a kon of 4 × 106 M−1s−1, we obtained a good match to observed growth rates from KDlong = 3 mM and KDcorner = 4 μM. These parameters are similar to those obtained by Odde and Cassimeris using a similar model trained on the same data (VanBuren et al., 2005). Using kon of 2 × 106 M−1s−1 or 6 × 106 M−1s−1 yielded longitudinal affinities of 0.4 and 18 mM, respectively. (B) (left) Cartoon illustrating the tethering model, with the polymerase (TOG domains in blue, basic region in red) localized to a curved αβ-tubulin bound at the MT end by pure longitudinal association, (middle) simulated growth rates obtained at increasing association rates for the tethered αβ-tubulin. Enhanced trapping of longitudinally-associated αβ-tubulin through the tethering effect shows catalyst-like activity: growth rates and apparent on-rate constant (slope) both change significantly but the apparent equilibrium for growth (x-intercept) does not. (right) Plot of fold increase in growth rate vs the fold increase in tethered αβ-tubulin association rate, using values at 10 μM αβ-tubulin concentration as a reference (black dots; the black line shows the fit of a hyperbolic curve to the growth rates). The model for the polymerase gives a relatively modest change in growth rates compared to the fold-increase in tethered association rate. Simulations with stronger (purple: 0.4 mM) or weaker (light green, 18 mM) longitudinal interactions show higher or lower maximal polymerase activity. Thus, the polymerase activity is related to the population of longitudinally-associated αβ-tubulin at the MT end. (C) Examining an alternative tethering model in which the polymerase promotes incorporation at a ‘corner’ site. This model yields much greater stimulation of elongation (middle) because there is always at least one corner site at the microtubule end. The predicted response also does not appear to saturate with increased tethering effect (right, linear fit). This alternative model does not describe the polymerase action because it fails to produce catalyst-like output.
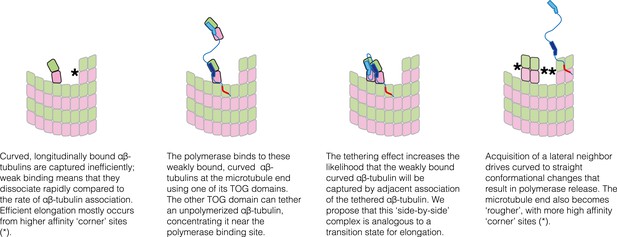
Schematic cartoons illustrating the origin of catalytic action.
The microtubule end has multiple sites where αβ-tubulin can associate, but elongation is largely dominated by additions into the few, high-affinity ‘corner’ sites (left panel) because pure longitudinal associations are weak. By preferentially recognizing curved αβ-tubulin with one of its TOG domains, the polymerase (TOG domains in blue, basic region in red) can selectively localize to these ‘unproductive’ binding sites (second from left). The tethering action greatly enhances the rate at which these weakly bound subunits are trapped by neighboring association of another αβ-tubulin (middle two panels). Polymerization-induced straightening of αβ-tubulin releases the polymerase for another round of catalysis (right).
Tables
Data collection and refinement statistics
| Data collection | |
| Space group | C2 |
| Cell dimensions | |
| a, b, c (Å) | 111.91, 89.57, 135.51 |
| β (°) | 112.31 |
| Resolution (Å) | 50.0–2.81 (2.92–2.81)* |
| Rsym | 0.143 (0.924) |
| <I>/<σI> | 9.6 (1.1) |
| Wilson B-value (Å) | 48.9 |
| Anisotropy (Å) relative to best direction (001) | |
| ΔB in (100) direction, ΔB in (010) direction | +29.95, +8.38 |
| CC1/2 in high resolution shell | 0.542 |
| Completeness (%) | 98.2 (91.3) |
| Redundancy | 4.1 (3.2) |
| Refinement | |
| Resolution (Å) | 2.81 |
| No. reflections | 26,235 |
| Completeness(%) | 86.5† (35.3) |
| Rwork/ Rfree (%) | 21.8/25.9 (33.0/41.3) |
| Maximum likelihood estimated coordinate error (Å) | 0.42 |
| No. atoms | 8524 |
| Protein (non-hydrogen) | 8437 |
| Ligand/ion | 66 |
| Water | 21 |
| B-factors | |
| Protein | 44.7 |
| Ligand/ion | 52.0 |
| Water | 27.3 |
| Rms deviations | |
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.003 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.66 |
| Ramanchandran plot | |
| Favored (%) | 95.0 |
| Allowed (%) | 4.25 |
| Disallowed (%) | 0.75 |
| Rotamer outliers (%) | 3.2 |
| Molprobity clash score | 1.5 |
-
*
Highest resolution shell is shown in parenthesis.
-
†
The data were corrected for anisotropy in HKL2000. This treatment eliminated weak reflections and reduced the completeness of the data used for refinement compared to the completeness reported for data collection.





