The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM23 regulates adipocyte differentiation via stabilization of the adipogenic activator PPARγ
Figures
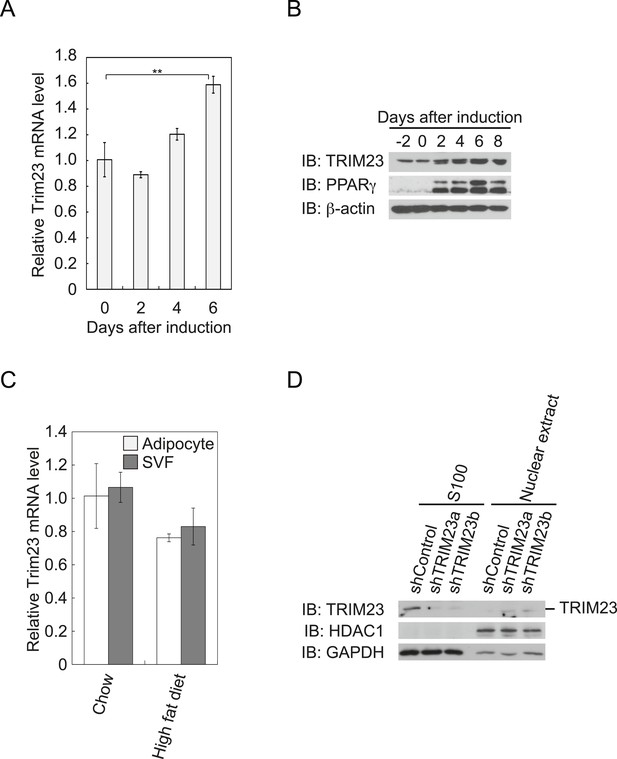
TRIM23 is expressed during adipocyte differentiation.
(A) Real-time PCR analysis of mRNA expression of Trim23 during 3T3-L1 differentiation. Total RNA was isolated from 3T3-L1 cells on the indicated days. Trim23 mRNA was normalized to that of Gtf2b. (B) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM23 and PPARγ protein during 3T3-L1 cell differentiation. (C) Real-time PCR analysis of mRNA expression of Trim23 in mouse adipose tissue. Trim23 mRNA was normalized to that of Gtf2b. (D) Subcellular localization of TRIM23. Nuclear extracts and cytoplasmic S100 fraction were prepared from 3T3-L1 cells, and immunoblot analysis of TRIM23, HDAC1, and GAPDH was performed.
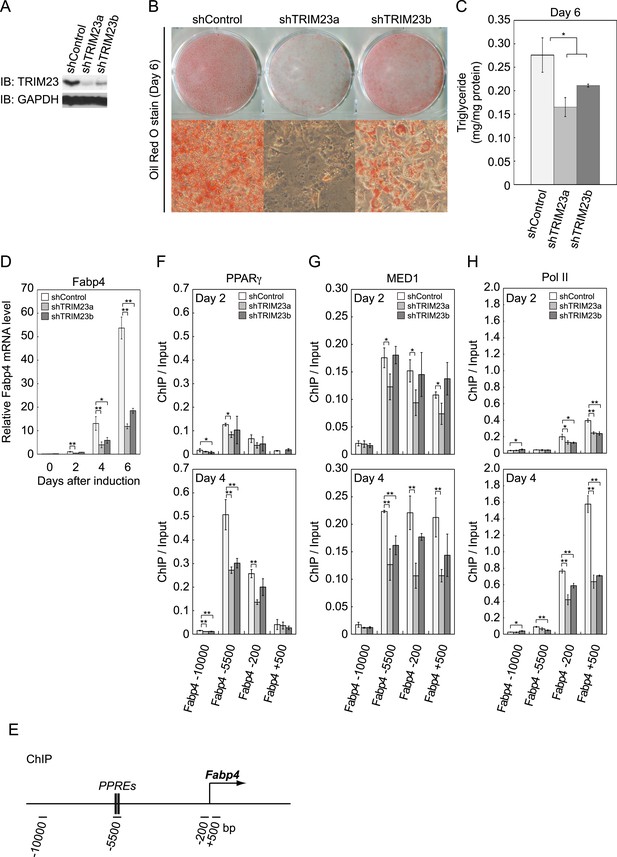
TRIM23 is required for 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM23 knockdown before induction of adipogenesis is shown. (B) Cells were stained with Oil Red O to visualize the accumulation of lipid droplets at day 6. (C) The amounts of intracellular triacylglyceride (TG) were quantified at day 6. (D) RNA levels of Gtf2b and Fabp4 were determined by real-time PCR at days 0, 2, 4 and 6. Expression level of each gene was normalized to that of the Gtf2b. (E) Schematic representation of the Fabp4 gene. The locations of the sequences amplified in the ChIP are shown at the bottom in base pairs relative to the Fabp4 transcriptional start site. (F, G and H) ChIP analysis of PPARγ (F), MED1 (G), and Pol II (H) on the Fabp4 gene during adipocyte differentiation. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. All data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined by Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
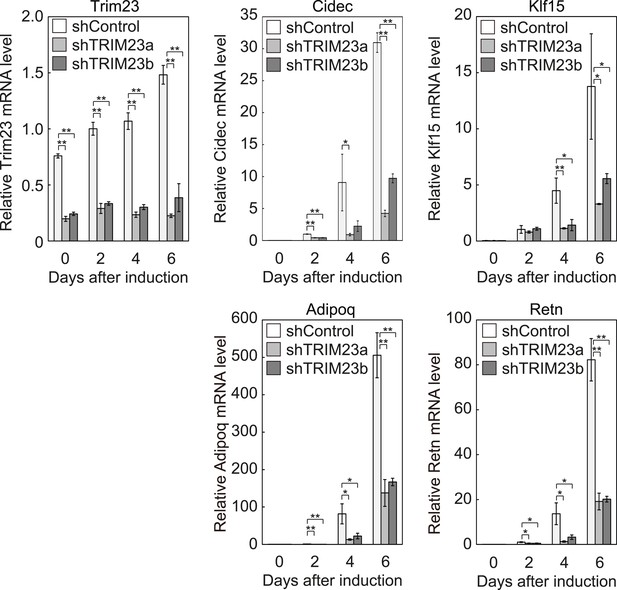
Quantitative analysis of Trim23, Cidec, Klf15, Adipoq and Retn mRNA during 3T3-L1 differentiation.
mRNA levels of Trim23, Cidec, Klf15, Adipoq and Retn were determined by real-time PCR at days 0, 2, 4, and 6. Expression level of each gene was normalized to the level of Gtf2b.
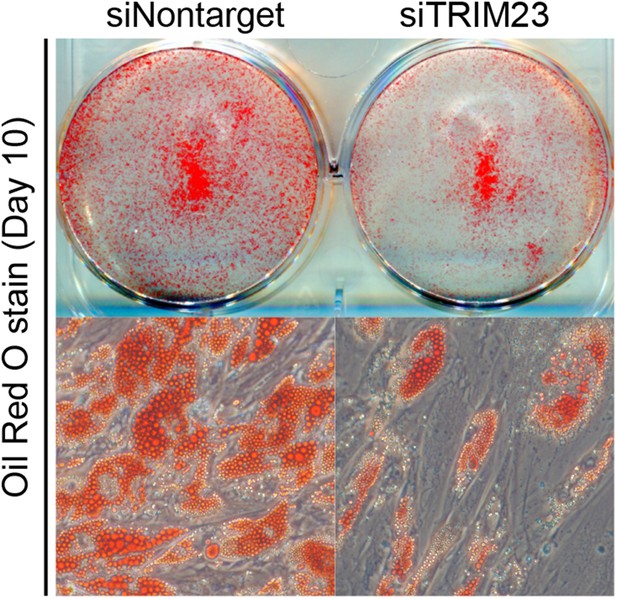
TRIM23 is required for human visceral preadipocyte differentiation.
Short interfering RNAs targeting TRIM23 (siTRIM23) and a non-targeting control siRNA (siControl) were introduced into human primary visceral preadipocytes, and the preadipocytes were differentiated to mature adipocytes. Adipocytes were stained with Oil Red O to visualize the accumulation of lipid droplets at day 10.
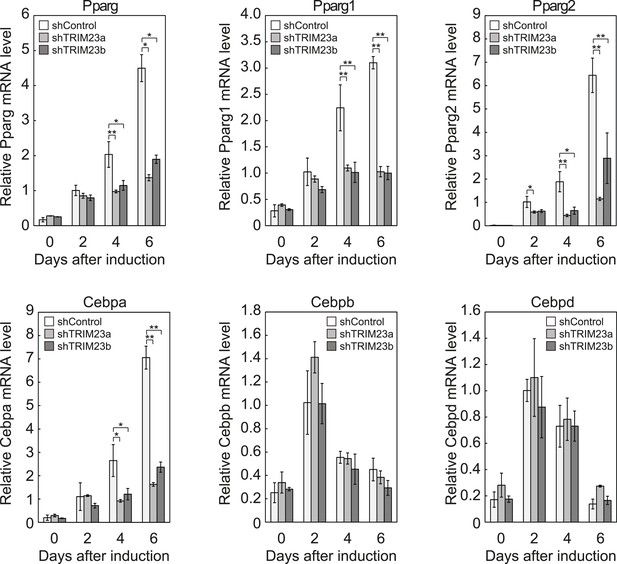
TRIM23 is required for induction of Pparg1, Pparg2 and Cebpa but not for induction of Cebpb and Cebpd during adipogenesis.
RNA levels of Pparg, Cebpa, Cebpb and Cebpd were determined by real-time PCR at days 0, 2, 4 and 6. Expression level of each gene was normalized to that of the Gtf2b. The data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined using Student's t-test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
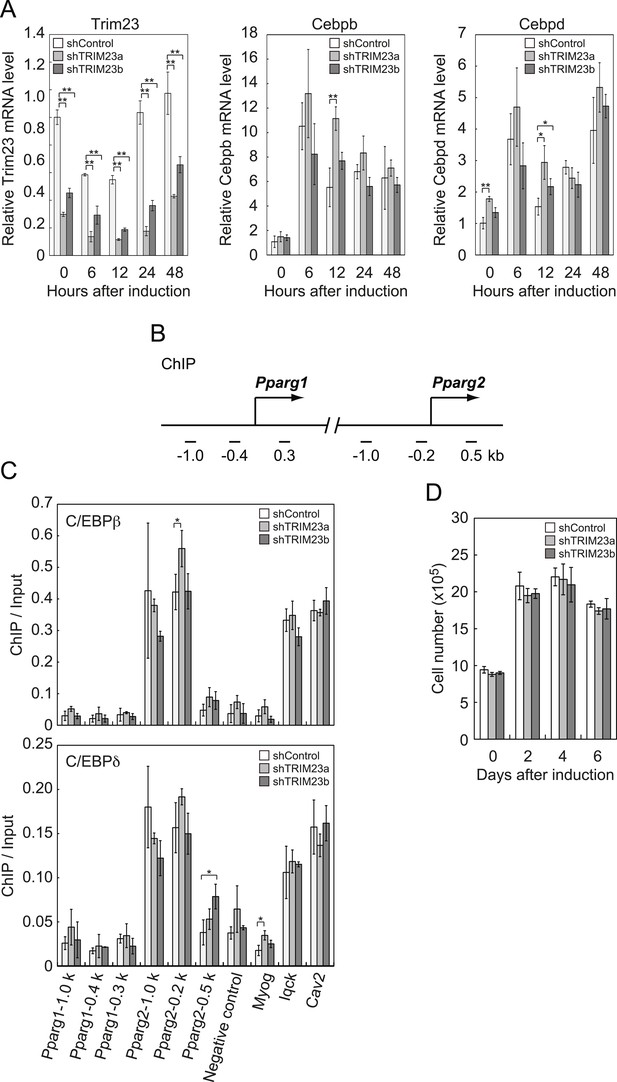
TRIM23 knockdown does not affect the induction and occupancy of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ at the Pparg promoter during adipogenesis.
(A) RNA levels of Trim23, Cebpb and Cebpd were determined by real-time PCR at 0, 6, 12, 24 and 48 hr. Expression level of each gene was normalized to that of Gtf2b. (B) Schematic representation of the Pparg promoters. The locations of the sequences amplified in the ChIP are shown at the bottom in base pairs relative to the Pparg1 and Pparg2 transcriptional start sites. (C) Occupancy of C/EBPβ and C/EBPδ on a subset of target genes at 4 hr. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. (D) Cell proliferation analysis of 3T3-L1 cells during adipocyte differentiation. 3T3-L1 cells were counted at each time point. The data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined by Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
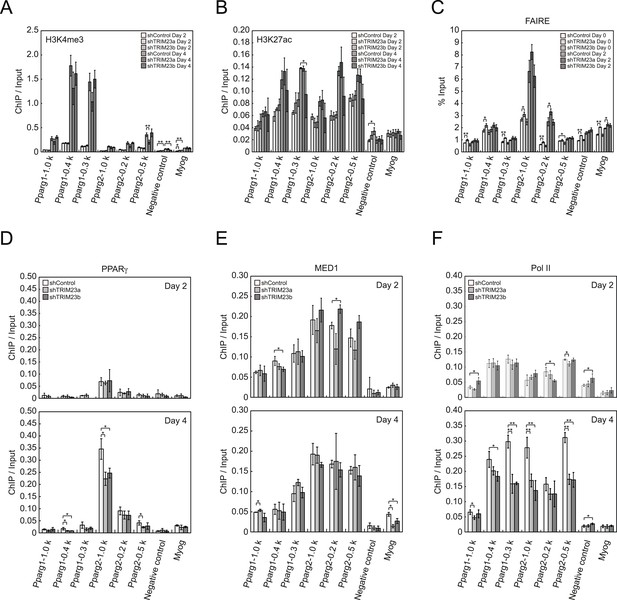
TRIM23 knockdown does not affect the epigenetic marks for activated genes and chromatin opening but decreases the occupancy of Pol II at the Pparg promoters.
(A and B) ChIP analysis of H3K4me3 (A) and H3K27ac (B) at the Pparg promoters during adipocyte differentiation. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. (C) Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) analysis during adipocyte differentiation. The enrichment of fragmented genomic DNA in the FAIRE samples was analyzed and normalized to that of input. (D, E and F) ChIP analysis of PPARγ (D), MED1 (E), and Pol II (F) at the Pparg promoter during adipocyte differentiation. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. All data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined by Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
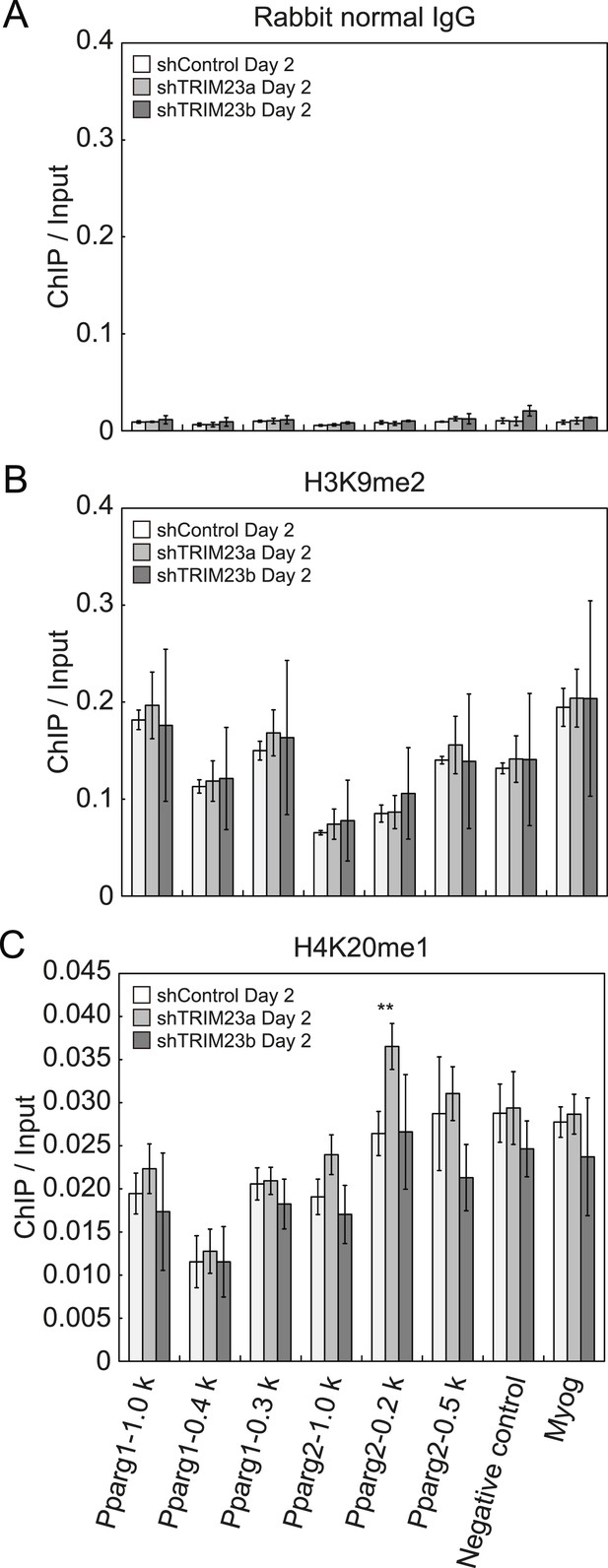
Depletion of TRIM23 does not affect H3K9me2 and H4K20me1 marks at the Pparg promoter.
(A) Control IgG ChIP does not occupy a subset of gene promoters during adipogenesis. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. (B and C) ChIP analysis of H3K9me2 (B) and H4K20me1 (C) at the Pparg promoter during adipocyte differentiation. Ct values of each ChIP were normalized to that of input. All data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined by Student's t test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
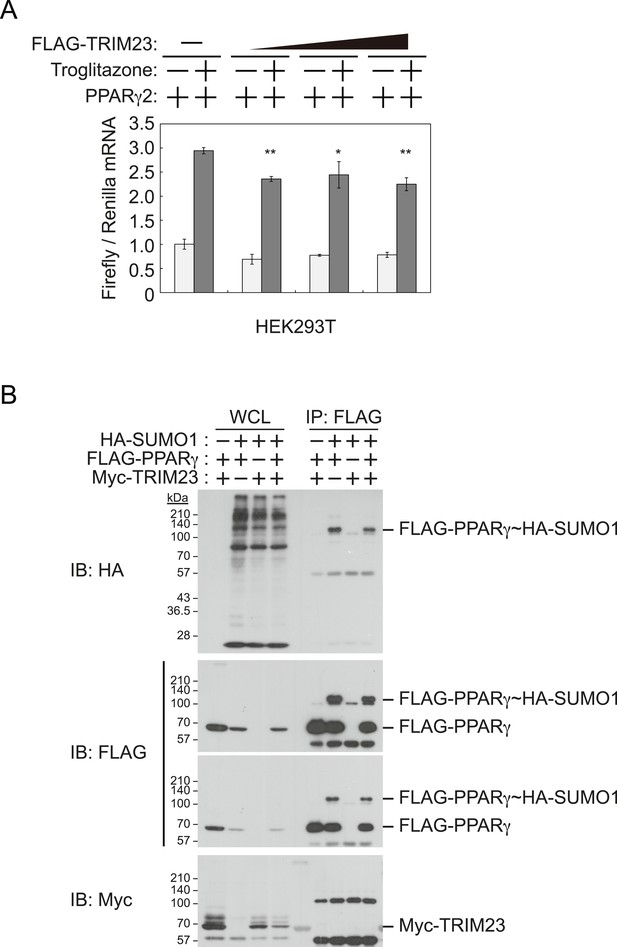
TRIM23 does not affect PPARγ2 transcriptional activity.
(A) TRIM23 does not affect PPARγ-mediated transcriptional activity in HEK293T cells. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor response element firefly luciferase reporter vector (PPRE–Luc), pGL4.74 renilla luciferase reporter plasmid, and expression vectors encoding TRIM23 and Pparg were transfected into HEK293T cells and the cells were incubated in culture medium containing 10% charcoal-treated fetal bovine serum for 24 hr. Cells were incubated with or without troglitazone (2 μM) for 24 hr, harvested, and quantified firefly luciferase and renilla luciferase mRNA with real-time PCR. The data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. (B) TRIM23 does not promote SUMOylation of PPARγ2. An in vivo assay for SUMOylation of PPARγ2 by TRIM23 was performed. Expression vectors encoding FLAG-PPARγ2, Myc-TRIM23, and HA-SUMO1 were transfected into HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblot analysis was performed to detect modifications of PPARγ2.
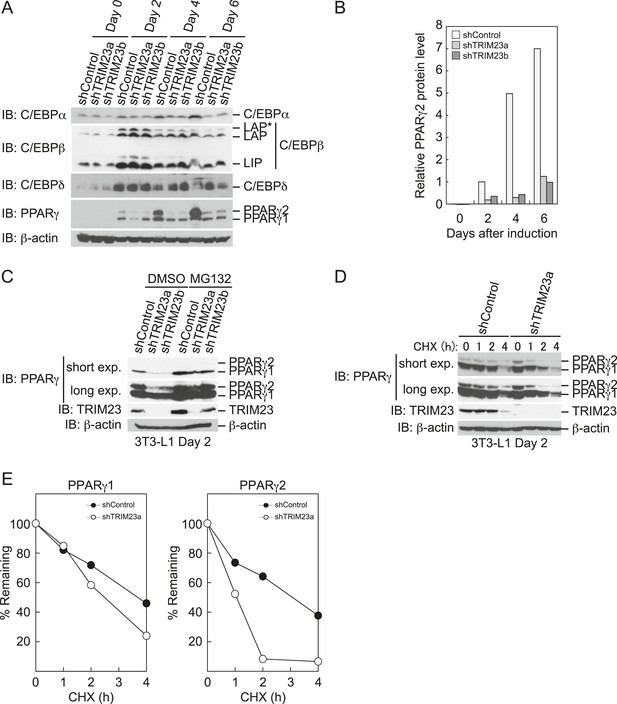
TRIM23 stabilizes PPARγ2.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ and PPARγ proteins during 3T3-L1 cell differentiation. (B) The intensity of the immunoreactive bands of PPARγ2 obtained by immunoblot analysis with anti-PPARγ antibody was determined relative to that obtained with anti-β-actin antibody. (C) Immunoblot analysis of PPARγ protein in the absence and presence of MG132. 3T3-L1 cells with stable knockdown of TRIM23 or the corresponding control cells were differentiated by the differentiation cocktail for 48 hr and subsequently treated with 10 μM of MG132 for 6 hr (D) 3T3-L1 cells with stable knockdown of TRIM23 or the corresponding control cells were differentiated by the differentiation cocktail for 48 hr and subsequently treated with 10 μM of MG132 for 6 hr, followed by cycloheximide (CHX) treatment (5 μM) for 0, 1, 2 or 4 hr. The cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with an anti-PPARγ, anti-TRIM23 or anti-β-actin antibody. β-actin is shown as a loading control. The result is representative of two independent experiments. (E) The intensity of the PPARγ1 and PPARγ2 bands was normalized to that of the corresponding β-actin bands shown in (D) and is indicated as a percentage of the normalized value at 0 hr.
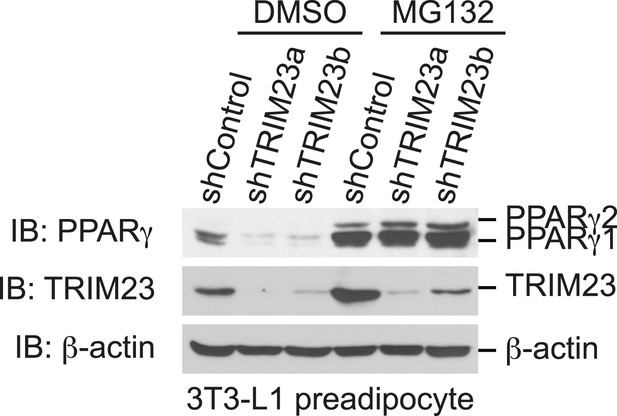
The presence of TRIM23 is sufficient to inhibit basal degradation of PPARγ.
Immunoblot analysis of PPARγ protein in the absence and presence of MG132. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes with stable knockdown of TRIM23 or the corresponding control cells were treated with MG132 (10 mM) for 6 hr.
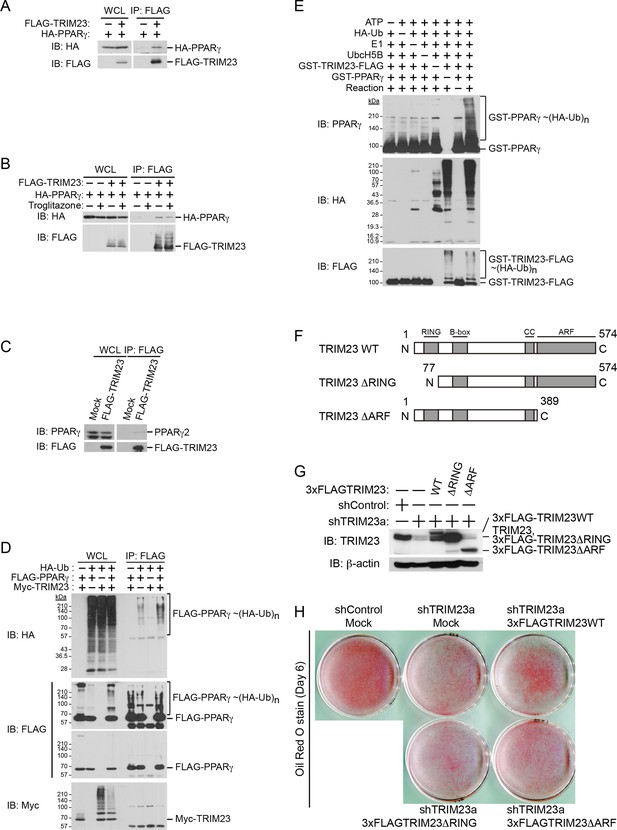
TRIM23 interacts with PPARγ2 and promotes ubiquitination of PPARγ2.
(A) In vivo assay for interaction between TRIM23 and PPARγ2. FLAG-TRIM23 and HA-PPARγ2 were transfected into HEK293T cells. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and immunoblotted with anti-FLAG and anti-HA antibodies. (B) In vivo assay for interaction between TRIM23 and PPARγ2 with or without troglitazone (1 μM). FLAG-TRIM23 and HA-PPARγ2 were transfected into HEK293T cells. Coimmunoprecipitation assays were performed using the cell extract from these cells with anti-FLAG antibody in the presence or absence of 1 μM troglitazone. (C) In vivo assay for interaction between TRIM23 and PPARγ2. 3T3-L1 cells stably expressing FLAG-TRIM23 were generated, differentiated, and harvested at day 6. Whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblot analysis was performed with anti-FLAG and anti-PPARγ antibodies. (D) In vivo assay for ubiquitination of PPARγ2 by TRIM23. FLAG-PPARγ2, Myc-TRIM23, and HA-ubiquitin (HA-Ub) were transfected into HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and then immunoblot analysis was performed to detect ubiquitination of PPARγ2. (E) Promotion of in vitro PPARγ2 polyubiquitination by TRIM23. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated combinations of ATP, HA-Ub, His6-E1, His6-E2 (UbcH5B), His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG, and GST-PPARγ2. Reaction mixtures were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-PPARγ (top), anti-HA (middle) or anti-FLAG (bottom). The positions of GST-PPARγ2 or His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG modified by various numbers of HA-Ub moieties are indicated. (F) Schematic representation of TRIM23 deletion mutants is shown. Protein motifs are indicated. RING, ring-finger domain; B-box, B-box domain; CC, coiled-coil domain; ARF, ADP ribosylation factor domain. (G) Immunoblot analysis of ectopic expression of TRIM23 deletion mutants in TRIM23-knockdown 3T3-L1 cells before induction of adipogenesis. (H) Cells were stained with Oil Red O to visualize the accumulation of lipid droplets at day 6.
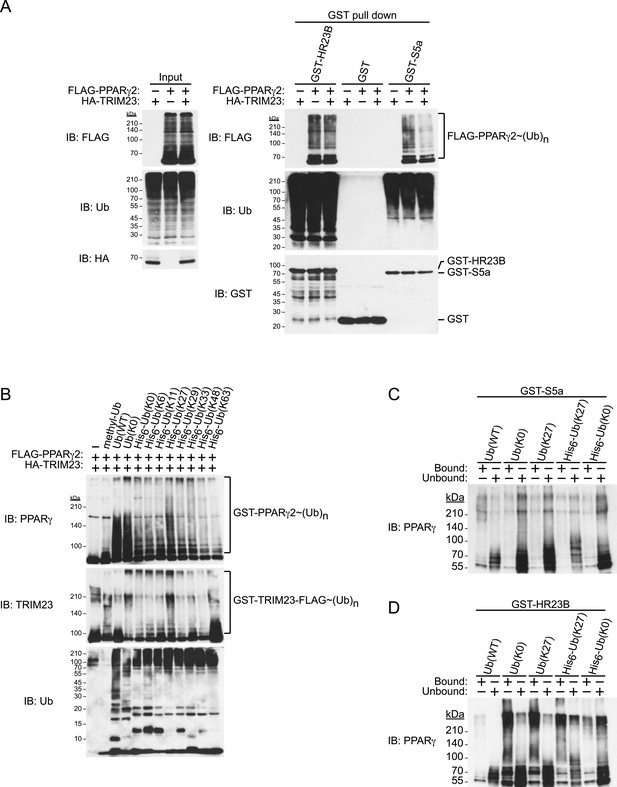
TRIM23 mediates atypical polyubiquitin conjugation of PPARγ2, leading to reduced recognition of ubiquitinated PPARγ2 by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a.
(A) PPARγ2 polyubiquitination by TRIM23 leads to reduced recognition by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a. HEK293T cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-PPARγ2 and/or HA-TRIM23 were lysed. GST, GST-HR23B, and GST-S5a were resuspended with cell lysates, followed by pull-down with glutathione Sepharose beads. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (B) In vitro PPARγ2 polyubiquitination by TRIM23. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated combinations of ATP, various ubiquitin mutants, His6-E1, E2 (UbcH5C), His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG, and GST-PPARγ2. Reaction mixtures were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-PPARγ (top), anti-TRIM23 (middle) or anti-Ub (bottom) antibodies. The positions of GST-PPARγ2 or His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG modified by various numbers of ubiquitin moieties are indicated. (C and D) Conjugation of PPARγ2 with M1- and/or K27-linked polyubiquitin chains leads to reduced recognition by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated combinations of ATP, ubiquitin mutants, His6-E1, E2 (UbcH5C), TRIM23-FLAG, and PPARγ2. Reaction mixtures were subjected to GST pull-down assay. PPARγ2-ubiquitin conjugates were incubated with GST-S5a (C) or GST-HR23B (D) prebound to glutathione Sepharose beads. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using a PPARγ antibody. Equivalent amounts of bound and unbound fractions were loaded in each lane.
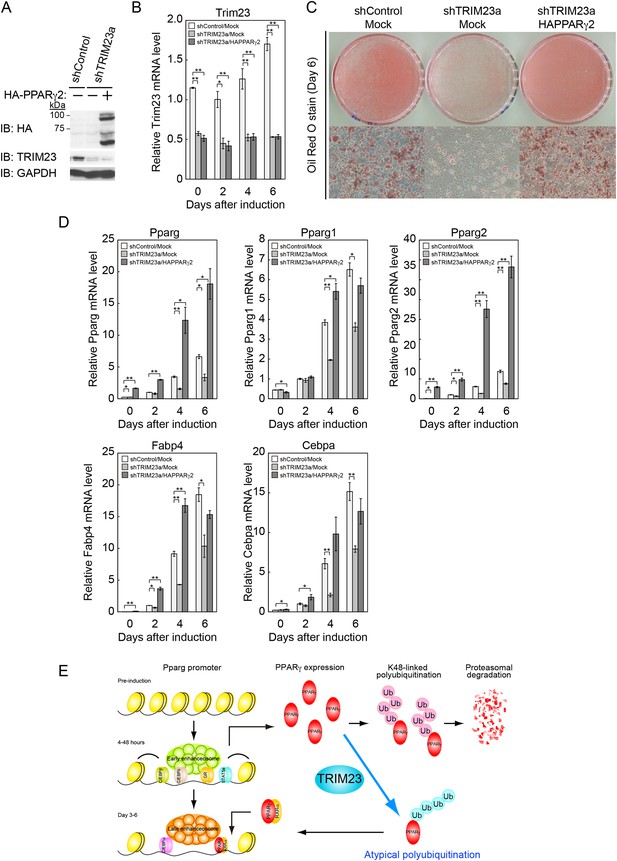
PPARγ2 expression rescues the adipogenesis defect in TRIM23-knockdown 3T3-L1 cells.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of ectopic PPARγ2 expression before induction of adipogenesis is shown. (B) Changes in Trim23 mRNA during adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Total RNA was isolated from 3T3-L1 cells on the indicated days of differentiation. Trim23 mRNA was determined by real-time PCR and normalized to that of Gtf2b. (C) Cells were stained with Oil Red O to visualize the accumulation of lipid droplets at day 6. (D) RNA levels of Fabp4, Cebpa, and Pparg were determined by real-time PCR at days 0, 2, 4 and 6 of differentiation. Expression level of each gene was normalized to the level of Gtf2b. The data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined using Student's t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). (E) Model for TRIM23 function in PPARγ abundance during adipocyte maturation. Several adipogenic stimuli activate early adipogenic activators such as C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ, glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a (STAT5a). These activators then induce late adipogenic activators including PPARγ and C/EBPα. TRIM23 mediates atypical polyubiquitin conjugation to PPARγ and may stabilize the PPARγ protein. TRIM23 plays a critical role in the switching from early to late adipogenic enhanceosomes by regulating the abundance of PPARγ.
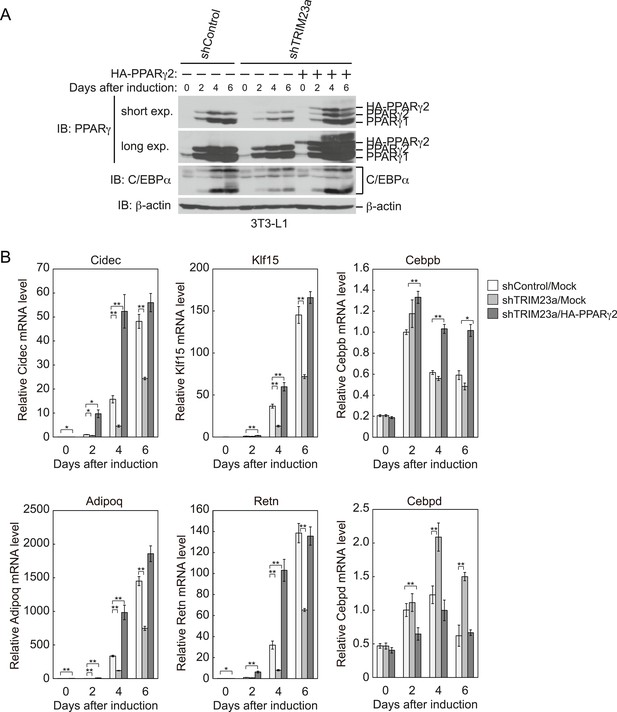
PPARγ2 expression rescues the adipogenesis defect that occurred in TRIM23-knockdown 3T3-L1 cells.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of PPARγ and C/EBPα protein during 3T3-L1 differentiation. (B) RNA levels of Cidec, Klf15, Cebpb, Adipoq, Retn and Cebpd, were determined by real-time PCR at days 0, 2, 4, and 6. Expression level of each gene was normalized to that of Gtf2b. The data represent means ± s.d. from three independent experiments. The p values for the indicated comparisons were determined using Student's t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
Tables
List of SYBR Green primers for real-time PCR
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PCR primers for cloning of cDNA | ||
| Trim23 | AGGATGGCTACCCTGGTTGTAAAC | AAATCAAGCAACATCCAATACTCC |
| Pparg2 | GTTATGGGTGAAACTCTGGGA | CTGCTAATACAAGTCCTTGTA |
| Oligonucleotides for shRNA | ||
| shTRIM23a | GATCCCCGAAGAAATGGCTCTAAGTGTTCAAGAGACACTTAGAGCCATTTCTTCTTTTTA | AGCTTAAAAAGAAGAAATGGCTCTAAGTGTCTCTTGAACACTTAGAGCCATTTCTTCGGG |
| shTRIM23b | GATCCCCGGTAGATGTTAAATCGCATTTCAAGAGAATGCGATTTAACATCTACCTTTTTA | AGCTTAAAAAGGTAGATGTTAAATCGCATTCTCTTGAAATGCGATTTAACATCTACCGGG |
| qRT-PCR primers for gene expression | ||
| Adipoq | GCACTGGCAAGTTCTACTGCAA | GTAGGTGAAGAGAACGGCCTTGT |
| Cebpa | TGCGCAAGAGCCGAGATAA | CGGTCATTGTCACTGGTCAACT |
| Cebpb | CAAGCTGAGCGACGAGTACA | AGCTGCTCCACCTTCTTCTG |
| Cebpd | ATCGACTTCAGCGCCTACAT | GCTTTGTGGTTGCTGTTGAA |
| Cidec | AGCTAGCCCTTTCCCAGAAG | TCAGGCAGCCAATAAAGTCC |
| Fabp4 | CATCAGCGTAAATGGGGATT | GTCGTCTGCGGTGATTTCAT |
| Klf15 | CCCAATGCCGCCAAACCTAT | GAGGTGGCTGCTCTTGGTGTACATC |
| Pparg1 +2 | TGCAGGAGCAGAGCAAAGAG | CGGCTTCTACGGATCGAAAC |
| Pparg1 | TGAAAGAAGCGGTGAACCACTG | TGGCATCTCTGTGTCAACCATG |
| Pparg2 | TGGCATCTCTGTGTCAACCATG | GCATGGTGCCTTCGCTGA |
| Retn | TTTTCTTCCTTGTCCCTGAACTG | GATCTTCTTGTCGATGGCTTCAT |
| Gtf2b | GTTCTGCTCCAACTTTTGCCT | TGTGTAGCTGCCATCTGCACTT |
| Trim23 | TTGGAATGGCTCACACAGAAC | ACATGGGCATCAACAACAC |
| qPCR primers for ChIP | ||
| Pparg1 −1.0 kb | CTGTCTATCATGTGGGCTTCAG | ACCTTACACATAGGGTGGAGA |
| Pparg1 −0.4 kb | ACAAACTTCTCCATGACAGACA | CGCCTTGCTCCTCACAG |
| Pparg1 +0.3 kb | CTGCGTAACTGACAGCCTAAC | ACTTGGTCACTCTCCGTCCT |
| Pparg2 −1.0 kb | GATACACTGCCCTGTGTAAGG | GAGCAGCCCTTGTCACATAA |
| Pparg2 −0.2 kb | GAACAGTGAATGTGTGGGTCA | CTGACTGAGAGCCAGTTGTGA |
| Pparg2 +0.5 kb | GTGAGCATTTCAGAACACTTGG | GCCTGAAGAAGAACAGAAATTCTAC |
| Negative control | TGGTAGCCTCAGGAGCTTGC | ATCCAAGATGGGACCAAGCTG |
| Myog | GGGTCTCTTCCTCTTACCCGAT | ACCTTGCTGGCCATGGAC |
| Iqck | GAAACAAAGCCTTCCCATCC | TCCTTTCTTGCTGTGGCTTC |
| Cav2 | CTCAGAAAAGGCAGGGAAAG | CCCAGTCATGACAACACCAA |
| Fabp4 -10,000 bp | CCATGAGGAAATTCGCTACAC | CCTTCCACCCTTATCTCACAC |
| Fabp4 −5500 bp | GAGAGCAAATGGAGTTCCCAGA | TTGGGCTGTGACACTTCCAC |
| Fabp4 −200 bp | CATTGCCAGGGAGAACCAA | TCCTTCATGACCAGACCCTGT |
| Fabp4 +500 bp | CAGGTGAACCCGCAAGAAAG | GCTTGGCAAAGAAGGCCAC |





