Modulation of GABA and resting state functional connectivity by transcranial direct current stimulation
Figures
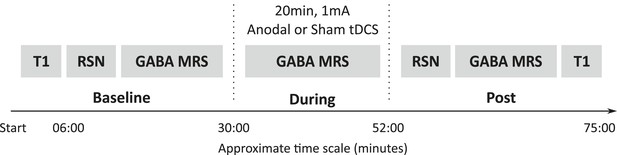
Experimental design.
All subjects participated in two testing sessions with either anodal or sham tDCS, the order of which was counterbalanced across the group. GABA was measured at three time points (baseline, during, post) and resting state connectivity was measured at two time points (baseline, post). Timeline shown is an estimate of the length of the scans in minutes.
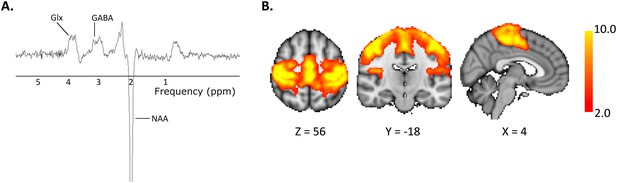
Representative (A) MR spectrum and (B) Group mean motor resting state network.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.08789.003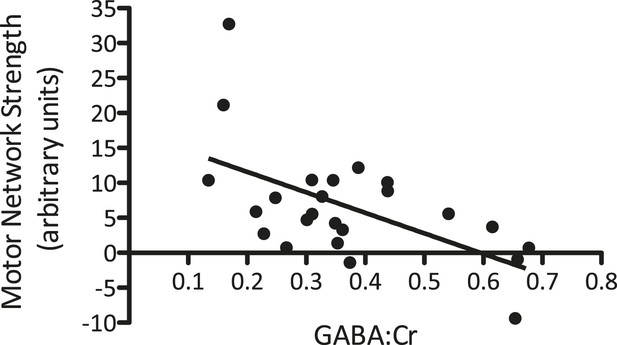
A significant relationship between M1-GABA and the strength of the motor network measured from the same region was identified at baseline (r = −0.62, p < 0.01).
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.08789.004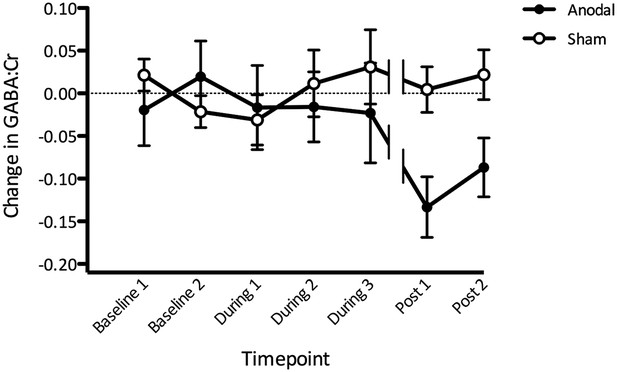
Change in GABA before, during, and after anodal tDCS relative to the sham condition.
(A) Gradual decrease in GABA levels was observed during anodal stimulation with the most prominent decrease approximately 10–15 min after stimulation has finished (Post1). Break in the lines indicate a time gap when approximately 7 min of resting state acquisition was performed immediately after tDCS stimulation. Timescale shows the approximate time from the beginning of the scan session. (Post 1: t(11) = −4.14, p < 0.01; Post 2: t(11) = −2.86, p = 0.02).
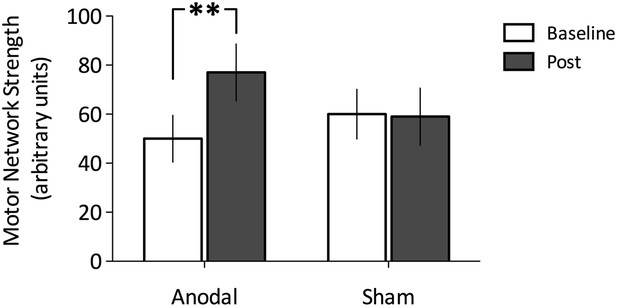
Change in functional connectivity before and after Anodal tDCS and the Sham condition.
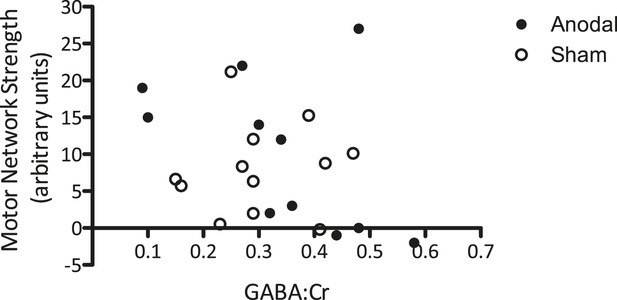
(A) Anodal tDCS applied to M1, significantly increased functional connectivity within M1 of the motor network (t (11) = −2.45, p = 0.03). (B) There were no differences in the sham condition (t(11) = 0.07, p = 0.95).