Structural determinants of nuclear export signal orientation in binding to exportin CRM1
Figures
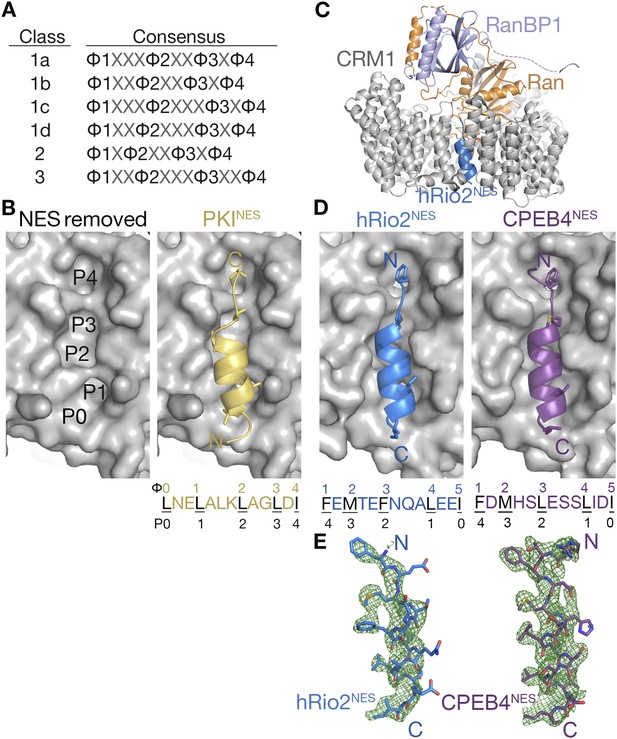
hRio2NES and CPEB4NES bind CRM1 in orientation opposite to the PKINES.
(A) Six nuclear export signal (NES) consensus patterns (Φ is Leu, Val, Ile, Phe or Met; X is any amino acid). (B) Structure of PKINES (yellow cartoon) bound to Chromosome Region of Maintenance (CRM1) (gray surface) (3NBY) on the right and PKINES was removed to show hydrophobic pockets P0–P4 in the CRM1 groove on the left panel. (C) Overall structure of the CRM1* (gray)-RanGppNHp (orange)-RanBP1 (light purple)-hRio2NES (blue) complex. (D) Structures of hRio2NES (blue) and CPEB4NES (purple) bound to the CRM1 groove (gray surfaces). All NES peptides are in cartoon and their hydrophobic Φ residues shown as sticks. Their Φ residues and the corresponding P0–P4 CRM1 pockets that they bind are shown below. (E) Kick OMIT map meshes contoured at the 3.0σ level overlaid on the final, refined coordinates for hRio2NES and CPEB4NES. Kicked OMIT maps were generated by PHENIX by omitting the NES peptides.
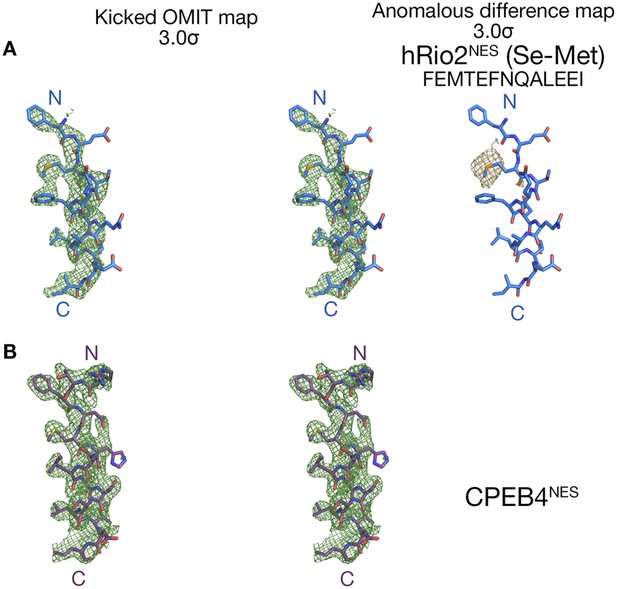
Electron densities of the wild-type NES peptides.
Stereo views of kicked OMIT map meshes contoured at the 3.0σ level, on the final, refined coordinates for (A) hRio2NES and (B) CPEB4NES as shown in sticks. Anomalous difference map for Se-met hRio2NESis calculated in PHENIX and contoured at the 3.0σ level in the leftmost panel in (A).
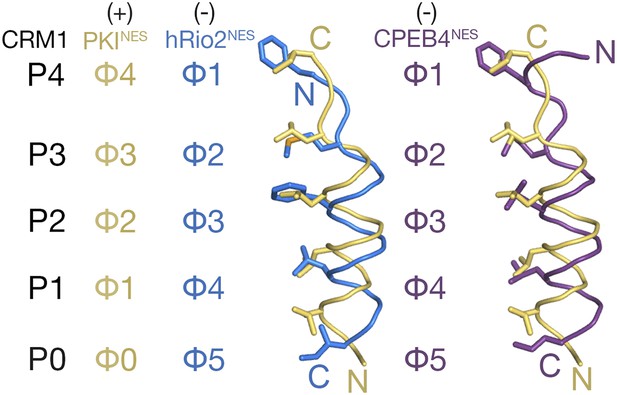
Comparison of plus and minus NESs.
Pairwise comparison of hRio2NES (blue) or CPEB4NES (purple) with PKINES (yellow; 3NBY) upon superposition of NES-bound CRM1 grooves. Hydrophobic NES residues (Φs) are shown as sticks and orientation of the CRM1 grooves is indicated by positions of the P0–P4 pockets.
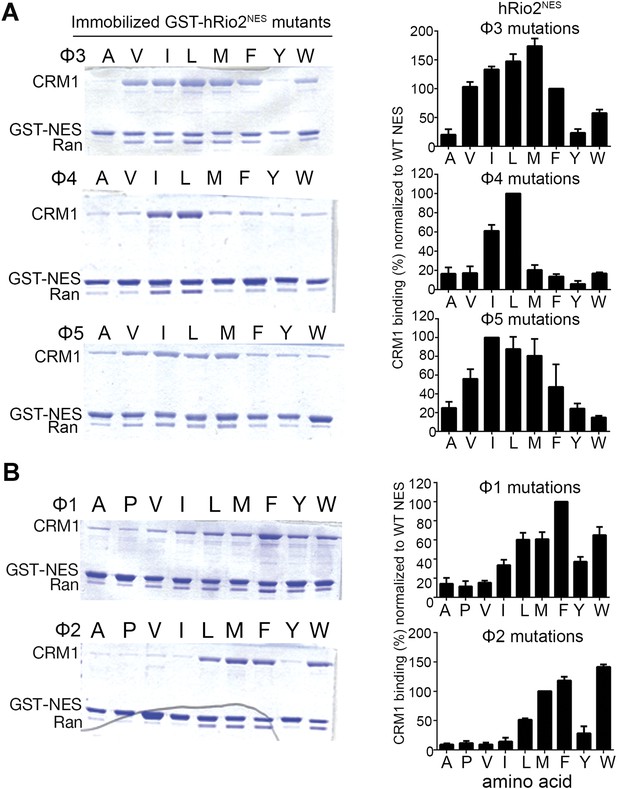
Hydrophobic side chain preferences for hRio2NES binding to CRM1.
In vitro pull-down assay (Coomassie-stained SDS/PAGE) of purified human CRM1 binding to immobilized GST-hRio2NES mutants (A) Φ3, Φ4, or Φ5 or (B) Φ1 or Φ2 position mutated in the presence of excess ScRanGTP. Relative band intensities of triplicate experiments are plotted in histograms.
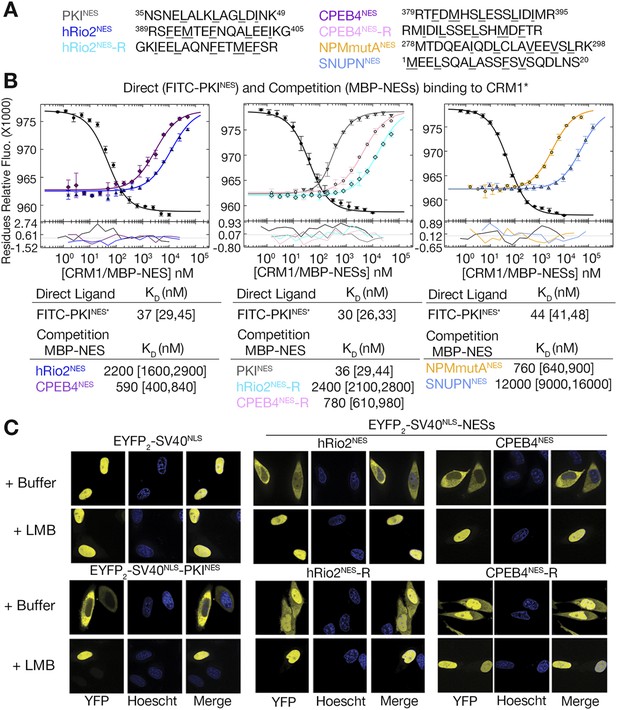
hRio2NES, CPEB4NES, and their reverse counterparts bind CRM1 with similar binding affinities.
(A) Sequences of NESs used. (B) Binding of FITC-PKINES and various MBP-NESs to CRM1 measured by differential bleaching, monitored by a microscale thermophoresis instrument. MBP-NESs compete with FITC-PKINES for CRM1 in competition titrations. Fitted binding curves are overlaid onto data points with error bars representing the mean and standard deviation of triplicate titrations. Dissociation constants (KDs) of the NESs are reported below the graphs with ranges in brackets representing the 68.3% confidence intervals. Binding of MBP-NPMmutANES (a moderate CRM1 binder) and MBP-SNUPNNES (a weak binder) is shown on the rightmost panel for reference. *Experiments performed on separate days were fitted with a new triplicate set of direct bind titrations. (C) Leptomycin B (LMB) sensitive nuclear export activity of EYFP-NLS-NES fusions in HeLa cells. YFP (pseudocolored in yellow), Hoechst (pseudocolored in blue), and merged images were captured using spinning disk confocal microscope (60×). Images are maximum intensity projection of five confocal Z stacks spaced 0.3 µm apart.

Binding affinities of shorter hRio2NES and CPEB4NES constructs.
(A) Sequences of shorter hRio2NES and CPEB4NES constructs. (B) Binding of these NESs to CRM1 measured by differential bleaching. Comparison of hRio2NES constructs in Figure 4 and in this supplement shows that the addition of a lysine and glycine residue C-terminal of the NES helix weakens binding. In contrast, comparison of CPEB4NES constructs shows that addition of methionine and arginine C-terminal of the CPEB4NES helix improved binding. One possible explanation is addition of these residues may have affected helical propensity of the NESs, and hence affect binding affinity.

Differential bleaching of fluorescence probe in a sigmoidal and binding-dependent manner.
Fluorogram of normalized fluorescence signal collected from the direct titration of CRM1 into fluorescent-labeled PKINES peptide in presence of excess ScRanGTP is plotted on the top panel. Traces are colored in rainbow, indicating increasing concentrations of CRM1. The shaded areas in blue and red represent the time frames where data collected represent pre-bleach and post-bleach fluorescence, respectively. Data points and the fitted curve are plotted in the panel below, with the data points colored according to their respective time-trace. Residuals are plotted on the bottom panel.
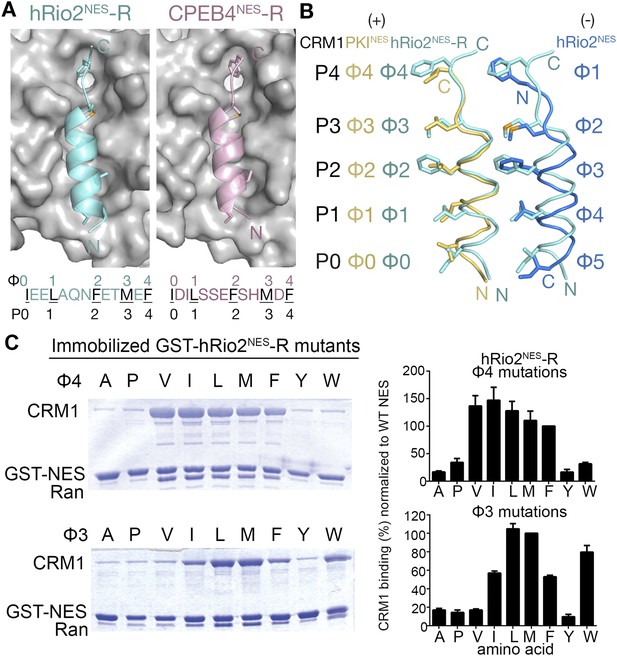
hRio2NES-R and CPEB4NES-R are plus NESs.
(A) Structures of hRio2NES-R (light blue) and CPEB4NES-R (light pink) bound to CRM1 (gray surfaces). (B) Pairwise comparisons of PKINES (yellow), hRio2NES-R (light blue), and hRio2NES (blue) when bound to CRM1. (C) In vitro pull-down assay of purified human CRM1 binding to immobilized GST-hRio2NES-R mutants (Φ3 or Φ4 mutated) in the presence of excess ScRanGTP. Relative band intensities of triplicate experiments are plotted in histograms.
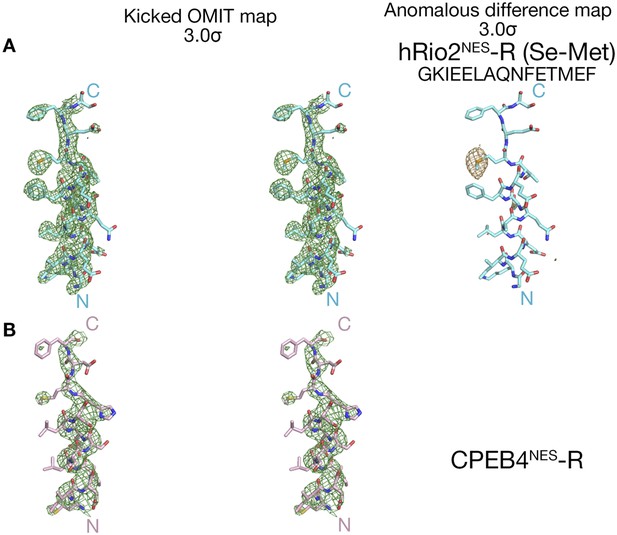
Electron densities of the reverse NES peptides.
Stereo views of kicked OMIT map meshes, on the final coordinates for (A) hRio2NES-R, (B) CPEB4NES-R and as shown in sticks. Anomalous difference map for Se-met hRio2NES-R is contoured at the 3.0σ level in the leftmost panel in (A).
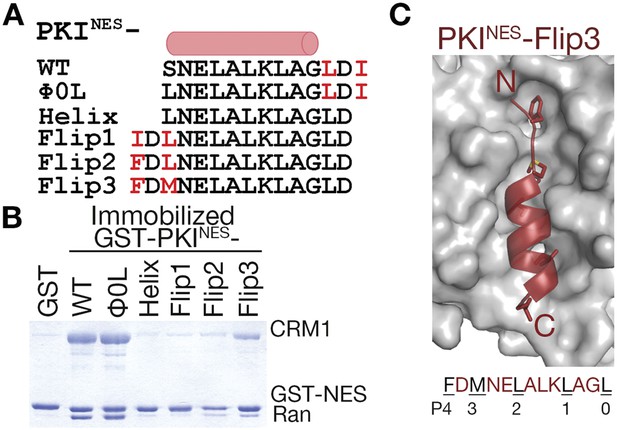
N-terminal ΦXΦ motif generates a minus orientation PKINES-Flip mutant.
(A) Sequence alignment of PKINES and PKINES-Flip peptides with their hydrophobic residues of ΦXΦ motifs in red and the NES helix shown as a cylinder. (B) Pull-down assay of immobilized GST-PKINES mutants, purified CRM1 and RanGTP (Coomassie-stained SDS/PAGE). (C) Structure of the PKINES-Flip3 peptide (red, in cartoon with Φ residues in sticks) bound to CRM1 (gray surface) with its sequence and CRM1 pockets for each Φ residue shown below.

Electron densities of the PKINES-Flip3 NES peptide.
Stereo views of kicked OMIT map meshes, on the final coordinates for PKINES-Flip3.
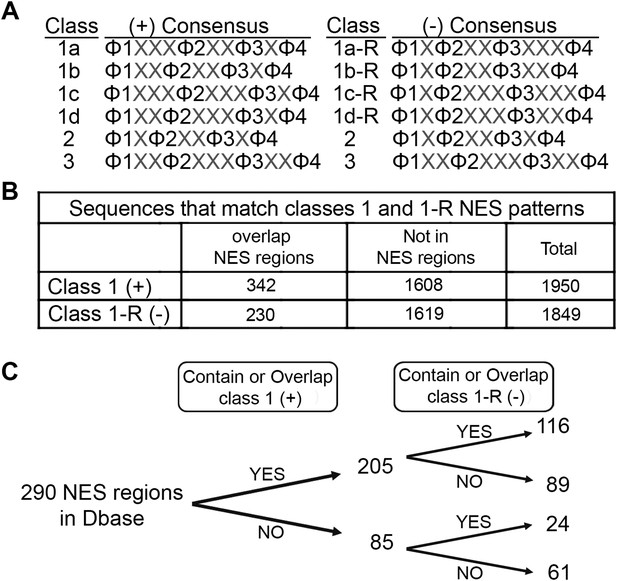
Prevalence of putative minus NESs in the Dbase data set.
(A) Consensus patterns for minus NESs in new NES classes 1a-R to 1d-R (reverse of class 1 patterns). (B) The number of sequences in the 246 proteins in Dbase that match the class 1 (+) and class 1-R (−) consensus patterns. NES regions are defined according to original literature that experimentally identified CRM1 cargos and their NES regions. (C) The numbers of NES regions in Dbase divided into four categories according to the consensus matches they overlap with.
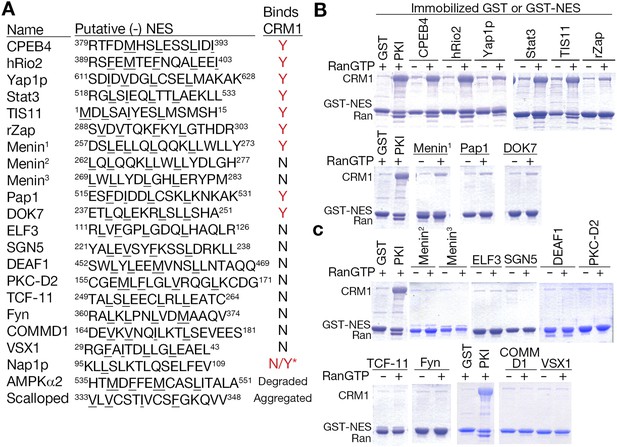
Putative minus NESs in the Dbase data set.
(A) Summary of putative minus NESs (in the Dbase data set that match class 1-R patterns exclusively) tested for CRM1 binding. Nap1p (*) was previously shown to direct nuclear export in cells even though no CRM1 binding was observed (Xu et al., 2015). (B) Putative minus NESs that bind CRM1 in pull-down assays with CRM1 and RanGTP. (C) Putative minus NESs that show no observable CRM1 binding.
Tables
Data collection and refinement statistics
| ScXPO1-RanGppNHp-Yrb1p bound to NES of: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selenomethione-hRio2 | CPEB4 | Selenomethione-hRio2-R | CPEB4-R | PKI-Flip3 | |
| Data collection | |||||
| Space group | P43212 | ||||
| Cell dimensions | |||||
| a, b, c (Å) | 106.48, 106.48, 303.73 | 105.96, 105.96, 304.00 | 106.69, 106.69, 304.50 | 106.48, 106.48, 303.73 | 105.96, 105.96, 304.00 |
| a, b, g (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) | 50.00–2.28 (2.32–2.28)* | 50.00–2.10 (2.14–2.10) | 50.00–2.28 (2.32–2.28) | 50.00–2.94 (3.00–2.94) | 50.00–2.55 (2.59–2.55) |
| Rpim | 2.9 (37.7) | 3.5 (43.4) | 3.5 (38.6) | 4.9 (40.6) | 4.1 (46.5) |
| I/sI | 24.3 (2.17) | 19.5 (1.70) | 22.5 (2.72) | 13.3 (1.87) | 19.0 (1.92) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.6 (99.8) | 99.5(100) | 98.0 (99.2) | 94.6 (96.0) | 99.6 (100) |
| Redundancy | 7.0 (5.9) | 6.0 (6.1) | 7.0 (7.0) | 6.2 (5.7) | 5.5 (5.5) |
| Refinement | |||||
| Resolution (Å) | 45.7–2.28 (2.32–2.28) | 40.2–2.09 (2.12–2.09) | 37.7–2.28 (2.31–2.28) | 47.5–2.94 (3.02–2.94) | 47.5–2.54 (2.60–2.54) |
| No. reflections | 77,245 (2833) | 98,659 (1793) | 79,492 (3267) | 34,265 (2013) | 56862 (3361) |
| Rwork/Rfree | 17.8 (25.8)/21.9 (27.3) | 17.0 (23.8)/20.8 (27.0) | 16.8 (24.7)/21.2 (27.6) | 18.1 (25.2)/24.0 (31.3) | 18.6 (25.0)/22.6 (30.6) |
| No. atoms | |||||
| Protein | 10,859 | 11,114 | 10,823 | 10,708 | 10797 |
| Ligand/ion | 60 | 76 | 59 | 51 | 51 |
| Water | 271 | 660 | 358 | 8 | 253 |
| NES Peptide/Φ | 111/46 | 122/43 | 130/46 | 112/43 | 105/43 |
| B-factors | |||||
| Protein | 42.0 | 39.3 | 43.9 | 53.8 | 46.5 |
| Ligand/ion | 44.3 | 51.7 | 46.9 | 41.8 | 41.6 |
| Water | 33.4 | 34.8 | 35.4 | 23.3 | 35.3 |
| NES peptide/Φ | 80.5/77.3 | 77.6/70.4 | 67.5/61.7 | 81.2/80.5 | 98.6/96.0 |
| R.m.s deviations | |||||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| Bond angles (°) | 0.617 | 0.689 | 0.835 | 0.578 | 0.673 |
| PDB code | 5DHF | 5DIF | 5DI9 | 5DHA | 5DH9 |
-
*
Highest resolution shell is shown in parenthesis.
-
One crystal was used for each structure.





