The Drosophila HNF4 nuclear receptor promotes glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and mitochondrial function in adults
Figures
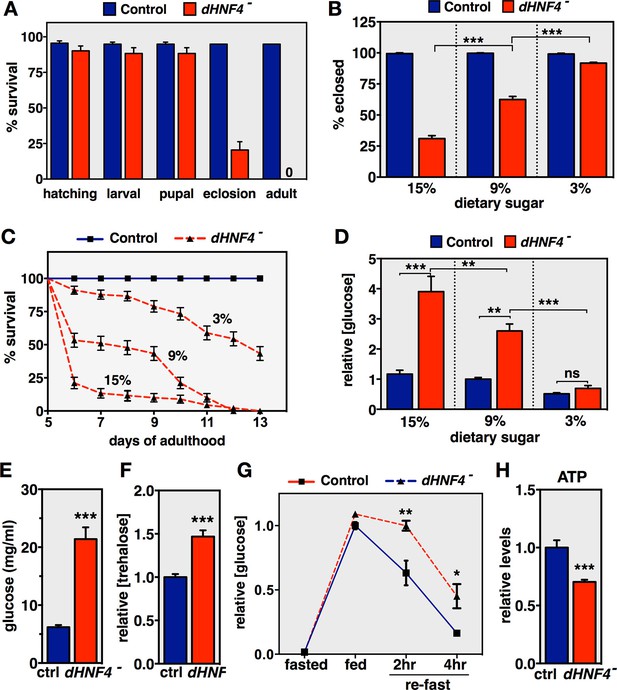
dHNF4 mutants are sugar intolerant and display hallmarks of diabetes.
(A) Percent survival of genetically-matched controls and dHNF4 mutants at each stage of development when raised on standard media. Adult viability represents survival past the first day of adulthood. (B) Percent of control and dHNF4 mutants that successfully eclose when reared on the 15%, 9%, or 3% sugar diet. (C) Controls and dHNF4 mutants were reared on the 3% sugar diet until 5 days of adulthood, transferred to the indicated diet, and scored for survival. (D) Free glucose levels measured from whole animal lysates of controls and dHNF4 mutants raised on the 3% sugar diet and transferred to the indicated diet for three days. (E) Circulating free glucose levels were measured from hemolymph extracted from control and dHNF4 mutant adults raised on the 3% sugar diet and transferred to the 15% sugar diet for 1 day prior to analysis. (F) Trehalose levels measured from whole animal lysates of controls and dHNF4 mutants raised on the 3% sugar diet and transferred to the 15% sugar diet for three days. (G) Oral-glucose tolerance test performed on adults raised on the 3% sugar diet, fasted overnight, fed on 15% glucose media for 1 hr, and then re-fasted for either 2 or 4 hr. Data represents relative free glucose levels from whole animal homogenates. (H) Relative ATP levels in control and dHNF4 mutant adults raised on the 3% sugar diet and transferred to sugar-only medium (10% sucrose) for 1 day prior to analysis. Data is plotted as the mean ± SEM. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05.
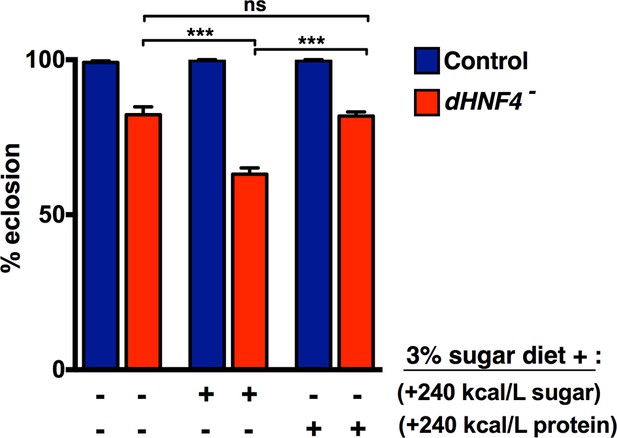
Dietary sugar, but not protein, correlates with reduced dHNF4 mutant survival.
Newly hatched first instar larvae were placed in vials (~60 larvae per vial) containing either the 3% sugar diet, the 3% sugar diet + 240 kcal/L extra sugar (2:1 glucose to sucrose, 9% final concentration), or the 3% sugar diet + 240 kcal/L of additional protein (peptone). All diets contained 8% yeast, 1% agar, 0.05% MgSO4, and 0.05% CaCl2,, as described in Materials and methods. Animals were reared at 25˚C and successful eclosion was scored as complete emergence from the pupal case. Data is plotted as the mean ± SEM. ***p≤0.001.
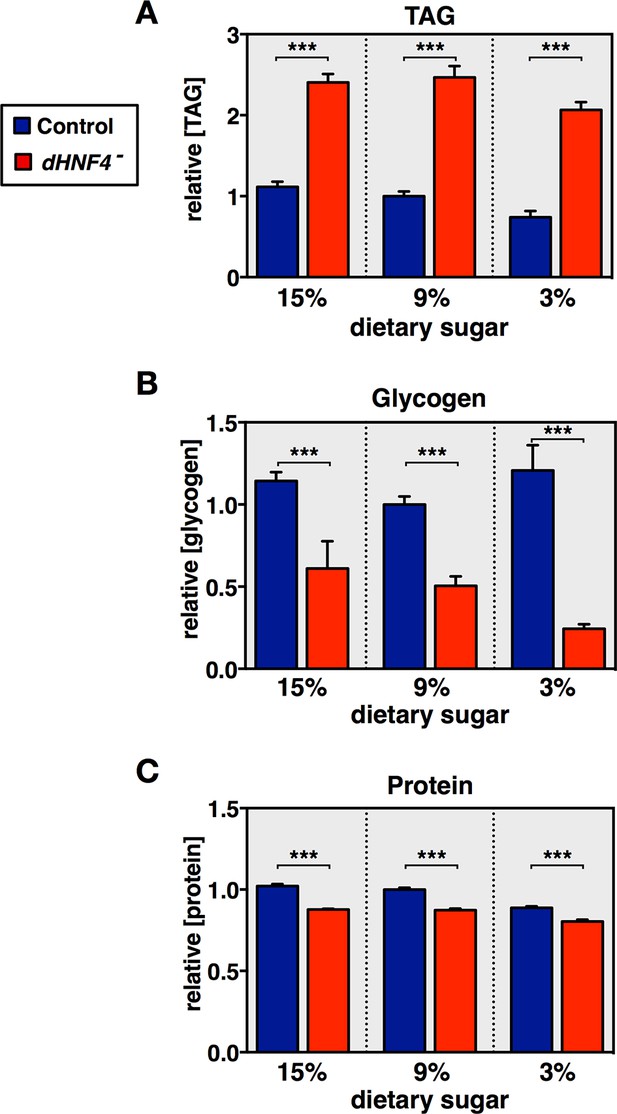
Profiling of major metabolites in dHNF4 mutant adults fed different levels of dietary sugar.
Controls and dHNF4 mutants were raised to adulthood on the 3% sugar diet under density-controlled conditions. Five days after eclosion, mature adult males were transferred to the 3%, 9%, or 15% sugar diets for three days prior to analysis. Whole-animal lysates were analyzed for concentrations of total triacylglycerol (TAG) (A), glycogen (B), or protein (C). All data was normalized to the level in controls on the 9% sugar diet. Data represents six biological replicates each with five animals, and results were consistent between at least three independent experiments. Data is plotted as the mean ± SEM. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05 Student’s t-test.
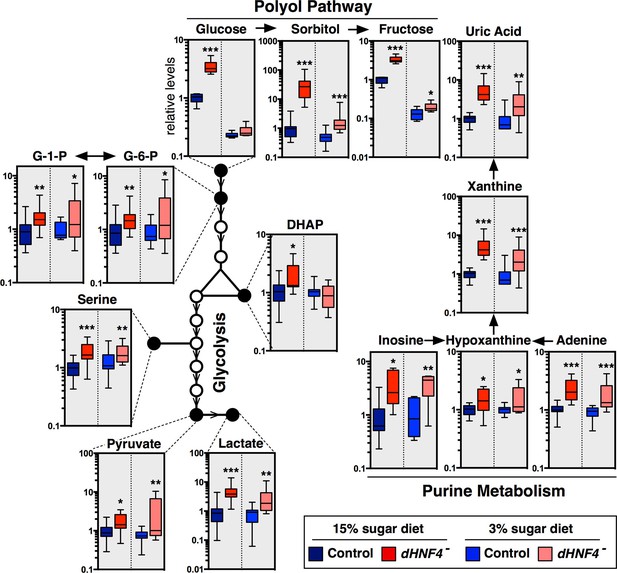
dHNF4 mutants display defects in glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolism.
GC/MS metabolomic profiling of controls and dHNF4 mutants raised to adulthood on the 3% sugar diet, transferred to the indicated diet for 3 days, and subjected to analysis. Data were obtained from three independent experiments consisting of 5–6 biological replicates per condition and values were normalized to control levels on the 15% sugar diet. Box plots are presented on a log scale, with the box representing the lower and upper quartiles, the horizontal line representing the median, and the error bars representing the minimum and maximum data points. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05.

dHNF4 mutants show broad defects in carbohydrate homeostasis.
GC/MS metabolomic profiling reveals that a range of sugars and sugar alcohols are increased in dHNF4 mutants compared to genetically matched controls, indicating that dHNF4 is required for proper carbohydrate metabolism. Animals were raised to adulthood on the 3% sugar diet prior to being transferred to the indicated diet for 3 days. Data was obtained from three independent experiments consisting of five to six biological replicates per condition and values were normalized to control levels on the 15% sugar diet. Data are graphically represented as a box plot, with the box representing the lower and upper quartiles, the horizontal line representing the median, and the error bars denoting the minimum and maximum data points. ***p≤0.001, **p≤ 0.01, *p≤0.05.
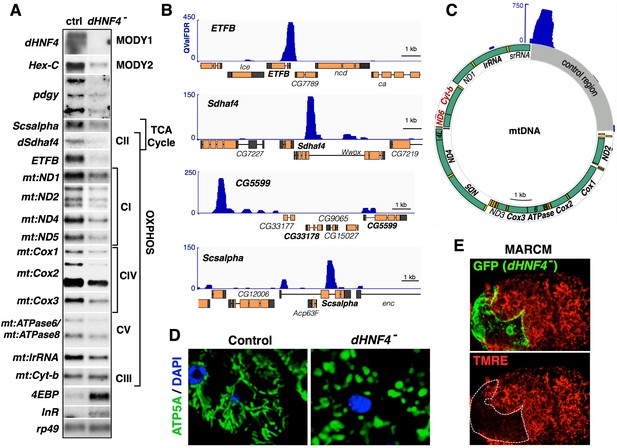
dHNF4 regulates nuclear and mitochondrial gene expression.
(A) Validation of RNA-seq data by northern blot using total RNA extracted from control and dHNF4 mutant adults. Affected transcripts include those involved in glucose homeostasis (Hex-C, pdgy), the electron transport chain (Sdhaf4, mt:ND1, mt:ND2, mt:ND4, mt:ND5, mt:CoxI, mt:Cox2, mt:Cox3, mt:ATPase6/8, mt:Cyt-b and mt:lrRNA), the TCA cycle (Scsalpha, dSdhaf4), and insulin signaling (4EBP, InR). rp49 is included as a control for loading and transfer. Mitochondrial-encoded transcripts are indicated by the prefix 'mt'. Depicted results were consistent across multiple experiments. (B–C) ChIP-seq analysis performed on adult flies for endogenous dHNF4 genomic binding shows direct association with both nuclear (B) and mitochondrial-encoded (C) genes involved in OXPHOS. Data tracks display q value FDR (QValFDR) significance values (y-axis) compared to input control, where QValFDR 50 corresponds to P=10–5 and 100 corresponds to P=10–10. Gene names in bold represent those expressed at reduced levels in dHNF4 mutants by RNA-seq and/or northern blot analysis. Gene names in red (ND6, Cyt-B) denote the mtDNA-encoded transcriptional unit confirmed to show no change in dHNF4 mutants. (D) Whole-mount immunostaining of adult fat body tissue for ATP5A (green) to detect mitochondria and DAPI (blue) to mark nuclei, showing fragmented mitochondrial morphology in dHNF4 mutants. (E) Analysis of dHNF4 mutant MARCM clones (GFP+) shows reduced mitochondrial membrane potential by TMRE staining of live fat body tissue from adult flies maintained on the 15% sugar diet.
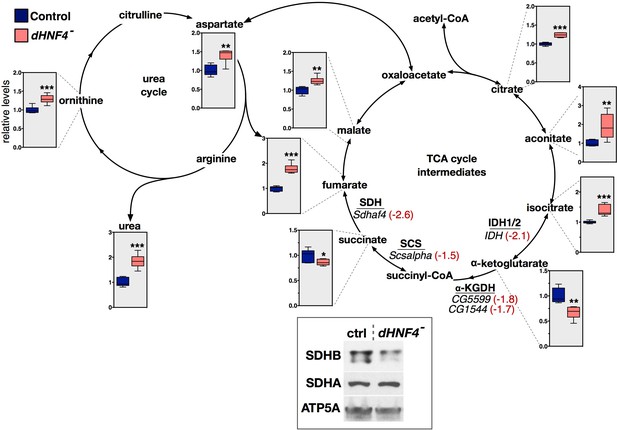
dHNF4 mutants display changes in TCA cycle intermediates that correlate with changes in gene expression.
GC/MS metabolomic profiling of adult flies fed a sugar only diet (10% sucrose + 1% agar) reveals defective TCA cycle metabolism in dHNF4 mutants. Intermediates of the TCA cycle are presented along with genes that are underexpressed in dHNF4 mutants (in italics). The mRNA abundance for each gene in dHNF4 mutants is indicated (red text) relative to matched controls from RNA-seq data. These genes are predicted to affect enzymatic complexes for isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH1/2), alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (α-KGDH), succinyl-CoA synthetase (SCS), or succinate dehydrogenase (SDH). Consistent with impaired IDH and SCS activity, levels of alpha-ketoglutarate and succinate are reduced, while upstream citrate, aconitate, and isocitrate accumulate. The modest effect on succinate abundance is possibly due to a combined effect of impaired succinate production balanced by decreased succinate oxidation resulting from impaired SDH activity. In addition, intermediates of the urea cycle are broadly accumulated in dHNF4 mutants including fumarate, which lies at the interface of these two pathways. This may contribute to the elevated levels of fumarate and downstream malate independent of impaired SDH activity. Metabolites lacking graphical data were not detected or could not be measured by GC/MS. Animals were reared on the 3% sugar diet until 5 days of adulthood and then transferred to medium containing 10% sucrose with 1% agar (sugar only) for 3 days prior to analysis. Data represents six biological replicates consisting of 20 males per replicate. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05. Inset - western blot analysis of whole animal lysates revealed reduced levels of SDHB protein, but no effect on SDHA, in dHNF4 mutants. ATP5A was detected as a control for loading and transfer.

dHNF4 mutants display mitochondrial defects.
(A) mtDNA abundance relative to nuclear DNA quantified by qPCR in control and dHNF4 mutant adult males on the 15% sugar diet. (B) Adult fat body tissue from control or dHNF4 mutants immunostained for ATP5A (green) to detect mitochondria, dHNF4 protein (red), and DAPI (blue) to mark nuclei. (C) Analysis of dHNF4 mutant MARCM clones (GFP+) shows reduced mitochondrial membrane potential by TMRE staining of live fat body tissue from adult flies maintained on the 15% sugar diet. (D) MARCM clonal analysis of adult dHNF4 mutant fat body cells (GFP+) for reactive oxygen species (ROS) by DHE staining shows no detectable difference in ROS levels in mutant cells.

Predicted functions of dHNF4 target genes.
Forty-seven genes identified as high confidence targets for direct regulation by dHNF4 are depicted. These genes fit the criteria of showing proximal dHNF4 binding along with reduced transcript abundance in mutant animals as determined by RNA-seq (≥1.5 fold change, 1% FDR) (Supplementary Tables 1,3).
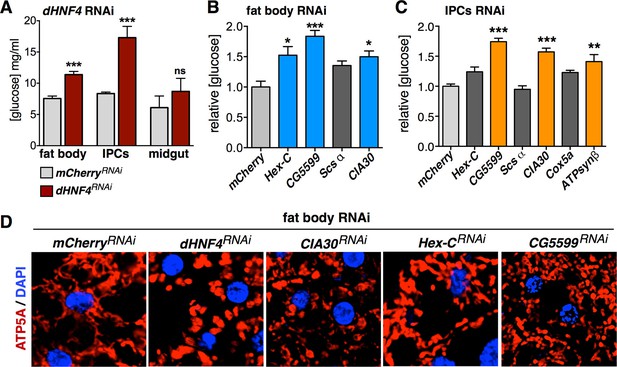
dHNF4 acts through multiple tissues and pathways to control glucose homeostasis.
(A) Circulating glucose levels in adult males expressing tissue-specific RNAi against mCherry (TRiP 35785, grey bars) or dHNF4 (TRiP 29375, dark red bars) in the fat body (r4-GAL4), IPCs (dilp2-GAL4), or midgut (mex-GAL4). (B–C) Relative free glucose levels in adult males on the 15% sugar diet expressing fat body (r4-GAL4, B) or IPC (dilp2-GAL4, C)-specific RNAi compared to mCherry RNAi controls (light grey bars). RNAi lines directed against Hex-C, CG5599, Scsα, CIA30, Cox5a, and ATPsynβ were obtained from the TRiP RNAi collection. Blue and orange bars depict significant changes in glucose levels. Dark grey bars are not significant. Data represents the mean ± SEM. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05. (D) Confocal imaging of mitochondrial morphology (marked by ATP5A immunostaining, red) in the adult fat body from animals expressing fat-body specific RNAi (r4-GAL4). The extended network of mitochondria seen in controls is disrupted and appears more punctate upon RNAi for dHNF4, CIA30, or CG5599, indicative of mitochondrial fragmentation. No effect is seen upon RNAi for Hex-C.
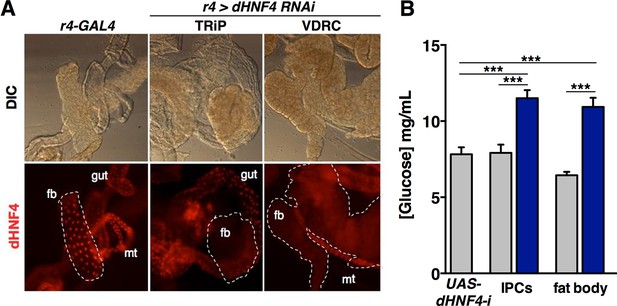
dHNF4 is required in the insulin-producing cells and fat body to maintain glucose homeostasis.
(A) Tissue-specific RNAi directed against dHNF4 effectively reduces steady-state levels of dHNF4 protein. Immunostaining was used to detect dHNF4 in organs dissected from third instar larvae that express either the r4-GAL4 driver alone as a control or fat body-specific RNAi for dHNF4 (r4>dHNF4RNAi) using UAS-RNAi constructs from either the TRiP or VDRC stock collections (fb = fat body, mt = Malpighian tubules). (B) dHNF4 function is required in both the IPCs and fat body for glucose homeostasis. This data reproduces that shown in Figure 4A using a distinct dHNF4 UAS-RNAi construct. Circulating glucose levels were measured in animals with tissue-specific RNAi against dHNF4 (VDRC) in the IPCs (dilp2-GAL4) or fat body (r4-GAL4) compared to GAL4 and UAS lines alone as controls. Controls are represented by grey bars while dHNF4 RNAi is represented by blue bars. Data represents the mean ± SEM, ***p≤0.001.

Fat body-specific disruption of the electron transport chain causes sugar intolerance.
Newly hatched first instar larvae were placed in vials (~60 per vial) containing the 3% or 15% sugar diet and scored for puparium formation when raised at either 25˚C (A) or 18˚C (B). Disruption of ETC complex IV (Cox5a RNAi) or complex V (ATPsynβ RNAi) in the fat body (r4-GAL4) results in sugar intolerance as seen by a pronounced developmental delay and reduced survival to puparium formation on the 15% sugar diet. These defects are partially suppressed when reared on the low sugar diet at either temperature; however, the 18˚C condition allows for more robust suppression of the sugar-dependent developmental delay (B).
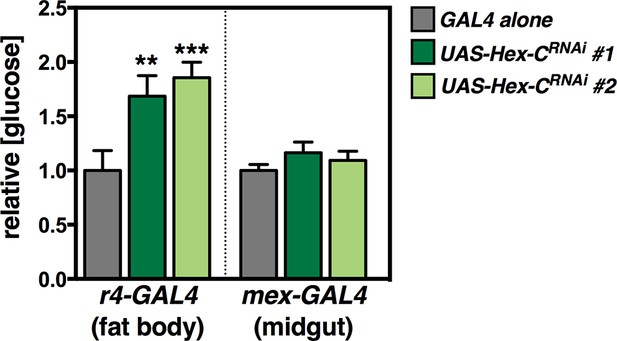
Additional RNAi lines confirming the importance of Hex-C in the fat body for glycemic control.
Tissue-specific RNAi directed against Hex-C in the fat body, but not midgut, results in elevated levels of free glucose. RNAi lines against Hex-C were obtained from the VDRC RNAi collection (UAS-Hex-C RNAi#1: VDRC 35337, and UAS-Hex-C RNAi#2: VDRC 35338). Grey bars represent the indicated GAL4 driver line crossed to w1118 as a negative control. These results are consistent with those in Figure 4B showing hyperglycemia upon fat body-specific RNAi for Hex-C using a line from the TRiP collection (Bloomington stock #57404).
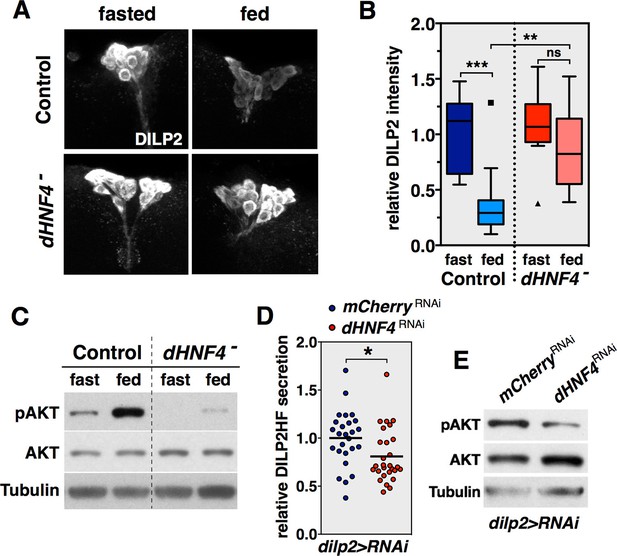
dHNF4 is required for glucose-stimulated DILP2 secretion by the insulin-producing cells.
(A) Whole-mount staining for DILP2 peptide in brains dissected from adult control and dHNF4 mutants that were either fasted overnight or re-fed glucose for two hours. (B) Quantification of relative DILP2 fluorescent intensity in the IPCs of fasted and glucose-fed controls and dHNF4 mutants. Data is plotted as a Tukey boxplot with outliers denoted as individual data points (n= 11 ± 3 brains per-condition). Results were consistent between three independent experiments. (C) Western blot analysis to detect phosphorylated AKT (pAKT), total AKT, and Tubulin in extracts from controls and dHNF4 mutants that were either fasted overnight or re-fed glucose for two hours. (D) Levels of circulating HA-FLAG-tagged DILP2 (DILP2HF) were assayed in animals with IPC-specific RNAi (TRiP) against either mCherry as a control (blue) or dHNF4 (red) using the dilp2-GAL4 driver (dilp2>RNAi). Data is combined from five independent experiments, each containing 5–6 biological replicates per genotype. The horizontal lines depict the mean value. (E) Western blot analysis to detect phosphorylated AKT (pAKT), total AKT, and Tubulin in extracts from ad libitum fed adult males with IPC-specific RNAi against either mCherry as a control or dHNF4 using the dilp2-GAL4 driver (dilp2>RNAi). ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05.

dHNF4 RNAi in the IPCs causes reduced levels of circulating DILP2-HF.
This data reproduces that shown in Figure 5D using a distinct dHNF4 UAS-RNAi construct (VDRC collection). Levels of circulating HA-FLAG-tagged DILP2 (DILP2HF) were assayed in ad libitum fed animals with IPC-specific RNAi against dHNF4 (VDRC 12692) using the dilp2-GAL4 driver compared to animals carrying the dilp2-GAL4 driver alone as a control. Dot plot depicts individual sample values from two independent experiments and the midline represents the mean (n=6 biological replicates per genotype per experiment). ***p≤0.001.
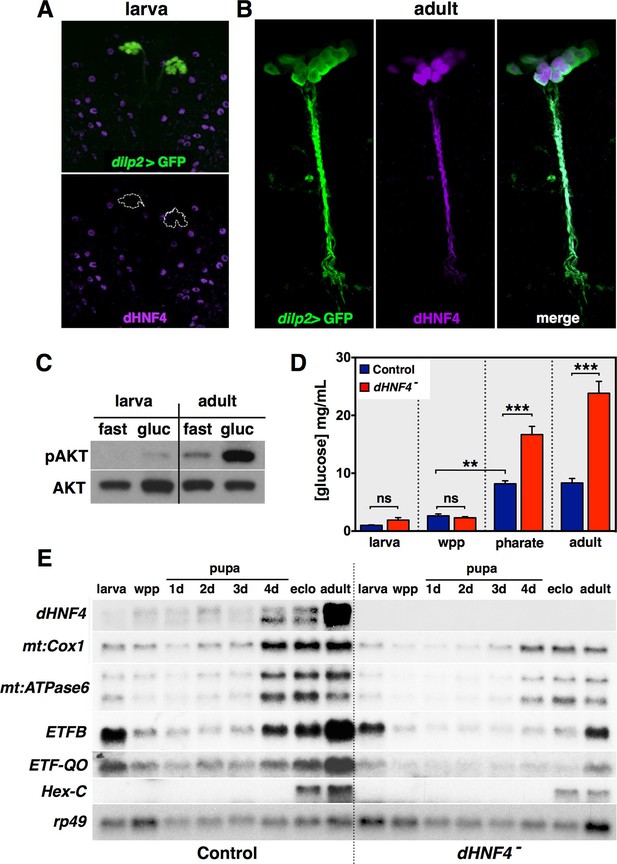
dHNF4 supports a developmental transition toward GSIS and OXPHOS in adult Drosophila.
(A–B) Whole-mount immunostaining of larval (A) or adult (B) brains to detect dHNF4 protein (magenta) or GFP, which marks the IPCs (dilp2>GFP, green). (C) Western blot analysis to detect phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) and total AKT in extracts from w1118 third-instar larvae or mature adults that were fasted overnight and re-fed 10% glucose for two hours. (D) Relative levels of free glucose in controls and dHNF4 mutants staged as either feeding third-instar larvae (larva), white prepupae (wpp), pharate adults (~4 day-old pupae), or mature adults. Data is plotted as the mean ± SEM. ***p≤0.001, **p≤0.01, *p≤0.05. (E) Northern blot analysis of RNA extracted from feeding third-instar larvae (larva), white prepupae (wpp), pupae at one-day intervals, mid-eclosion (eclo), and mature adults. rp49 is included as a control for loading and transfer.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
List of genes identified by RNA-seq that display differential abundance between dHNF4 mutant adult males and matched controls, meeting an FDR cutoff of 20 (1%) and Log2 ratio of ± 0.6 (>1.5 fold change).
Transcripts that show reduced abundance in dHNF4 mutants are marked in beige, while those with increased abundance are colored blue.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11183.019
-
Supplementary file 2
List of the gene ontology categories (determined using GOstat) represented in the top 500 down-regulated and 500 up-regulated genes in dHNF4 mutant adults.
The top 10-16 GO categories for each gene set are listed in order of significance along with the number of genes affected in that category, the total number of genes in that category (in parentheses), and the statistical significance of the match.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11183.020
-
Supplementary file 3
List of genes with transcription start sites (TSS) within 10 kb of dHNF4 enrichment peaks determined by ChIP-seq analysis, meeting an FDR 20 cutoff (1%).
The chromosomal region and coordinates are indicated for each enrichment peak with neighboring genes listed below each region. Genes are listed from proximal to distal, where the distance reported represents the number of base pairs from the TSS to the middle of the enrichment peak. Gene symbols and corresponding FlyBase gene ID numbers are reported, along with chromosomal location, gene start and stop sites, strand, and TSS position. Neighboring genes also identified by RNA-seq as being either up- or down-regulated in dHNF4 mutants are highlighted in blue and beige, respectively.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11183.021





