Identification of NPC1 as the target of U18666A, an inhibitor of lysosomal cholesterol export and Ebola infection
Figures
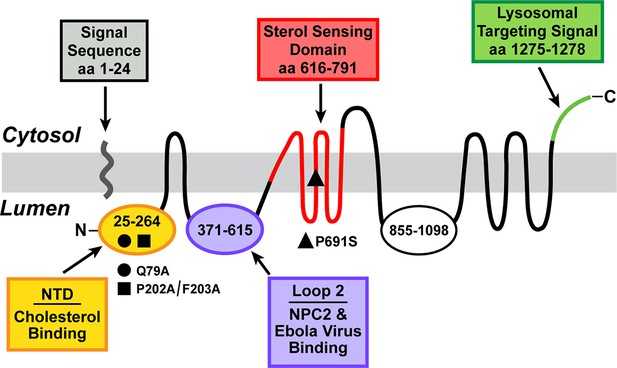
Domain structure of human Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1).
The predicted topology of the polytopic protein is based on the data of Davies and Ioannou (2000). Each of the five known functional domains of the protein are shown in a different color. The locations of three loss-of-function mutations referred to in the manuscript are indicated. aa, amino acid; NTD, N-terminal domain.
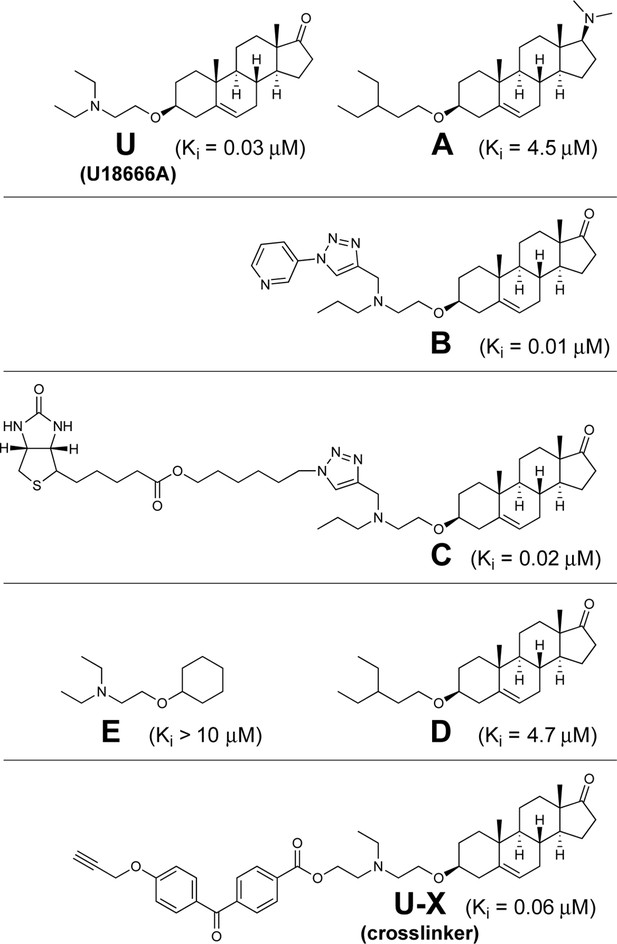
Chemical structures of U18666A and derivatives used in this study.
Inhibitory constant (Ki) values denote the concentration at which each compound inhibited the incorporation of [14C]oleate into cholesteryl [14C]oleate by 50% in monolayers of intact Chinese Hamster Ovary 7 (CHO-7) cells that were incubated with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) (mean of 3–14 experiments for each compound). Assays were carried out under conditions identical to those described in Figure 3A.
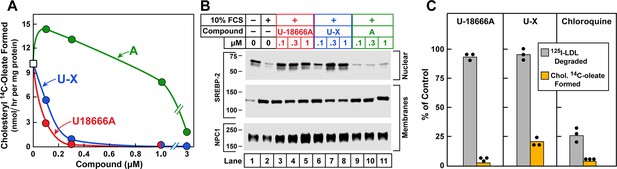
Cholesterol esterification, sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) 2 processing, and 125I-LDL (low density lipoprotein) degradation in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) 7 cells.
On day 0, CHO-7 cells were set up for experiments in medium A with 5% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LPDS) at a density of 2.5 x 105 cells/60-mm dish. On day 2, the medium was switched to fresh medium containing 5 µM sodium compactin and 50 µM sodium mevalonate. On day 3, the medium was switched to medium B containing either 10% LPDS or 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 50 µM compactin, 50 µM mevalonate, and various concentrations of the indicated compound and then incubated for either 7 hr (A) or 6 hr (B) as described below. (A) Cholesterol esterification. After a 5 hr incubation with the above medium with 10% FCS and the indicated compounds, each cell monolayer was labeled for 2 hr with 0.2 mM sodium [14C]oleate (8133 dpm/nmol). The cells were then harvested for measurement of their content of cholesteryl [14C]oleate and [14C]triglycerides. Each value is the average of duplicate incubations. Values for [14C]triglyceride content in cells treated with 1 µM of U18666A, compound A, and U-X were 117, 116, and 106 nmol/hr/ mg protein, respectively. (B) SREBP-2 processing. After a 5 hr incubation with the above medium containing either 10% LPDS (lane 1) or 10% FCS (lanes 2–11), each monolayer received a direct addition of 20 µg/ml of N-acetyl-leu-leu-norleucinal (A.G. Scientific, San Diego, CA). After 1 hr, cells were harvested and fractionated into a nuclear extract and 105g membrane fraction (Sakai et al., 1996). Aliquots (30 and 10 μg protein for SREBP-2 and Niemann-Pick C1 [NPC1], respectively) were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Immunoblot analysis and image scanning were carried out with monoclonal antibodies directed against SREBP-2 or NPC1 as described in Materials and methods. (C) 125I-LDL degradation. On day 3, the medium was switched to medium B containing 5% human LPDS, 20 µg protein/ml of either 125I-LDL (for 125I-LDL degradation) or unlabeled LDL (for cholesterol esterification), 10 µM compactin, and 50 µM mevalonate in the presence of one of the following compounds: none, 0.3 µM U18666A, 0.3 µM U-X, and 50 µM chloroquine. For the 125I-LDL degradation assay, cells were incubated for 6 hr with 125I-LDL (48 cpm/ng protein), after which the medium from each monolayer was removed and its content of 125I-monoiodotyrosine was measured as previously described (Goldstein, 1983). The 100% control value for 125I-LDL degradation in the absence of any compound (none) was 4.1 µg/6 hr/mg of protein. The cholesterol esterification assay was carried out as in A except that the cells were pulse-labeled with 0.1 mM [14C]oleate (6515 dpm/nmol). The 100% control value for cholesteryl [14C]oleate formed was 5.9 nmol/hr/mg protein. The content of [14C]triglycerides in cells receiving the various compounds were not significantly different: 50, 57, 55, and 81 nmol/hr/mg protein, respectively, for no addition, U18666A, U-X, and chloroquine. All values are the mean of triplicate incubations with individual values shown.
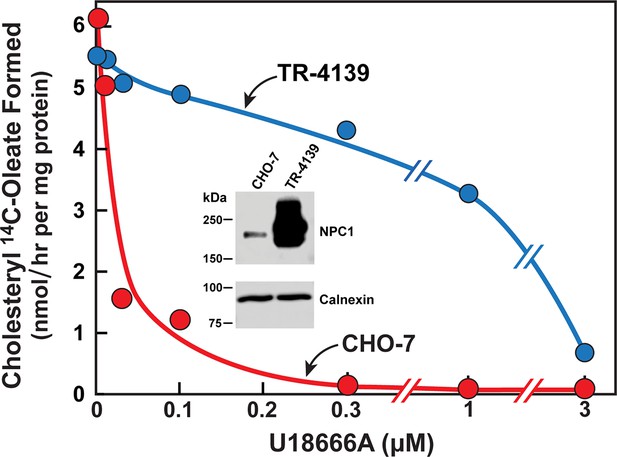
Cholesterol esterification in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) 7 and TR-4139 cells that overexpress Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1).
CHO-7 cells and TR-4139 cells were set up for experiments in medium A with 5% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LPDS) as described in the legend to Figure 3. On day 2, the medium was switched to fresh medium containing 5 µM sodium compactin, 50 µM sodium mevalonate, and the indicated concentration of U18666A. After incubation for 4 hr, each cell monolayer was labeled for 2 hr with 0.2 mM sodium [14C]oleate (11,662 dpm/nmol). The cells were then harvested for measurement of their content of cholesteryl [14C]oleate and [14C]triglycerides. Each value is the average of duplicate incubations. The cellular content of [14C]triglycerides in CHO-7 and TR-4139 cells was 38 and 40 nmol/hr/mg protein, respectively. Inset shows immunoblots of sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels of whole cell extracts (30 µg) from the indicated cell line incubated with 0.5 µg/ml anti-NPC1 or 1 µg/ml anti-calnexin as described in Materials and methods.
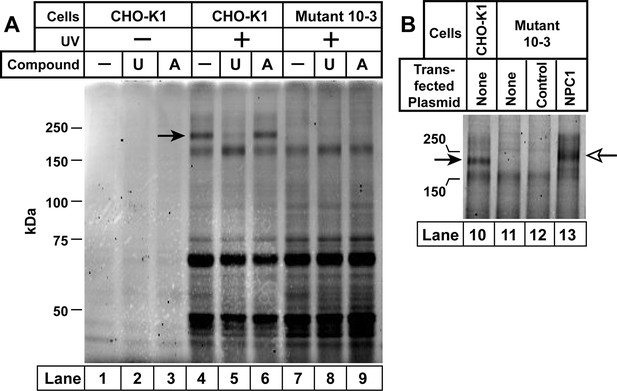
Ultraviolet (UV) crosslinking of U-X to Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO)-K1 cells, but not in mutant 10–3 cells.
On day 0, CHO-K1 cells and 10–3 cells (mutant derivative of CHO-K1 cells that lack NPC1) were set up in a six-well plate in medium A with 5% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LPDS) (2 ml/35-mm well). (A) In-gel fluorescence of U-X binding proteins in parental CHO-K1 cells and mutant 10–3 cells that lack NPC1. On day 3, each well of cells received a direct addition of ethanol (final concentration, 0.2%) containing 0.3 µM of U-X crosslinker (lanes 1–9) and one of the following compounds: none (lanes 1, 4, 7); 6 µM U18666A (lanes 2, 5, 8); or 6 µM compound A (lanes 3, 6, 9). After incubation for 1 hr at 37°C, cells in lanes 4–9 were exposed to UV light as described in Materials and methods. Cell extracts were prepared, and the crosslinked U-X was fluorescently tagged using click chemistry. Proteins were then subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) followed by in-gel fluorescence scanning. Arrow denotes a 190-kDa protein crosslinked to U-X and competed by U18666A, but not compound A. (B) Fluorescent labeling of 190-kDa protein in wild-type (WT) CHO-K1 cells, but not in 10–3 cells lacking NPC1: restoration by expression of NPC1. On day 1, mutant 10–3 cells were transfected with 1 µg/well of either control plasmid (pcDNA3.1; lane 12) or plasmid encoding NPC1 (pCMV-NPC1-Flag-TEV-StrepTactin; lane 13). Nontransfected CHO-K1 and 10–3 cells were set up in parallel (lanes 10 and 11, respectively). On day 3, all cells were incubated with 0.3 µM U-X for 1 hr, after which they were exposed to UV light. Cell extracts were prepared, and the cross-linked U-X was fluorescently tagged using click chemistry, followed by SDS-PAGE and in-gel fluorescence as in Panel A. Closed arrow denotes a 190-kDa protein crosslinked to U-X; open arrow shows the appearance of a similar band in transfected 10–3 cells expressing epitope-tagged NPC1.
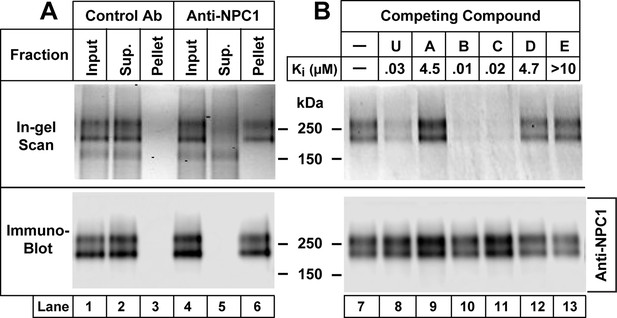
Immunoprecipitation of Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) crosslinked with U-X (A) and specificity of crosslinking reaction (B).
On day 0, Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) 7 cells were set up at 1.6 x 106/150-mm dish in 25 ml medium A with 5% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LPDS) per dish as described in Materials and methods. (A) Immunoprecipitation with anti-NPC1 antibody. On day 3, each monolayer received 25 µl of ethanol containing U-X (final concentration, 0.3 µM). After incubation for 1 hr at 37°C, cells were exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. Cell lysates from two dishes were pooled and incubated with 2 µg/ml control rabbit monoclonal antibody (lanes 1–3) or anti-NPC1 antibody (lanes 4–6). The solutions were applied to Protein A/G beads that were washed and eluted as described in Materials and methods. Aliquots of the input, supernatant (Sup.), and pellet fractions were obtained, and the crosslinked U-X was fluorescently tagged using click chemistry. The proteins were then subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and in-gel fluorescence scanning (upper lanes) or immunoblot analysis with 0.5 µg/ml anti-NPC1 (lower lanes) as described in Materials and methods. (B) Specificity of crosslinking of U-X to NPC1. On day 3, each monolayer received a direct addition of 25 µl of ethanol containing U-X crosslinker (final concentration, 0.3 µM) in the absence (lane 7) or presence (lanes 8–13) of 6 µM of one of the indicated compounds whose structures are shown in Figure 2. After incubation for 1 hr at 37°C, cells and homogenates were processed as described in Panel A. Proteins eluted from the Protein A/G beads were subjected to fluorescent labeling using click chemistry, followed by SDS-PAGE and in-gel fluorescence scanning (upper lanes) or immunoblot analysis with 0.5 µg/ml anti-NPC1 (lower lanes) as described in Materials and methods. The Ki values for the competing compounds denote the concentration at which each compound inhibited the incorporation of [14C]oleate into cholesteryl [14C]oleate by 50% in monolayers of CHO-7 cells that were incubated with 10% FCS (see Figure 2).
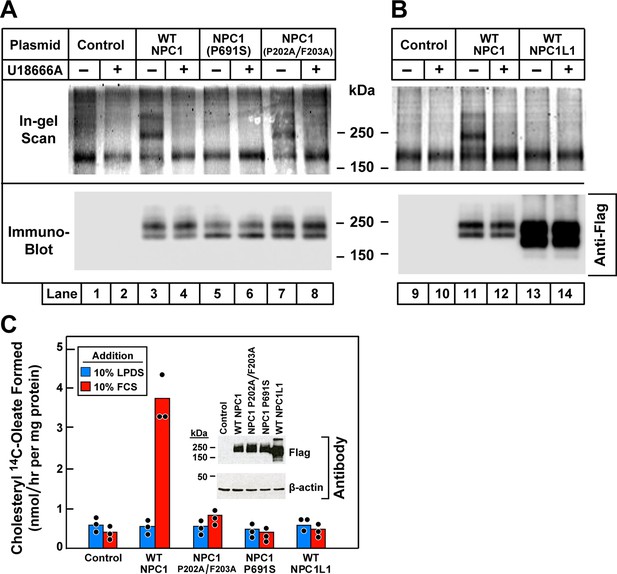
Ultraviolet (UV) crosslinking of U-X to transfected wild-type Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1), mutant versions of NPC1, and wild-type NPC1L1 in 10–3 cells that lack NPC1.
(A and B) Crosslinking, fluorescent labeling, and in-gel fluorescence. On day 0, 10–3 cells were set up in a six-well plate with 2 ml medium A with 5% lipoprotein-deficient serum (LPDS) per 35-mm well as described in Materials and methods. On day 1, cells were transfected by direct addition of 1 µg DNA per dish (FuGENE HD reagent) with one of the following plasmids: pcDNA3.1 control plasmid (lanes 1, 2, 9, 10); pCMV-NPC1-Flag-TEV-StrepTactin (lanes 3, 4, 11, 12); pCMV-NPC1(P691S)-Flag-TEV-StrepTactin (lanes 5, 6); pCMV-NPC1(P202A/F203A)-Flag-TEV-StrepTactin (lanes 7, 8); pCMV-NPC1L1-Flag-TEV-StrepTactin (lanes 13, 14). On day 3, all cells were incubated (without change of media) for 1 hr with 0.3 µM U-X crosslinker in the absence (–) or presence (+) of 6 µM U18666A, after which they were exposed to UV light. Cell extracts were prepared, and the crosslinked U-X was fluorescently tagged using click chemistry, followed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and in-gel fluorescence as in Figure 5. (C) Cholesterol esterification. On day 0, 10–3 cells were set up in medium A with 5% fetal calf serum (FCS) at 2.5 x 105 cells/60-mm dish. On day 1, monolayers were washed once with Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), switched to fresh medium A with 5% LPDS (devoid of penicillin and streptomycin sulfate), and then transfected with 2 µg DNA per dish with the indicated plasmids as described above. After incubation for 24 hr, cells were washed once with PBS and switched to medium A with 5% LPDS containing 10 µM sodium compactin and 50 µM sodium mevalonate. On day 3, the cells received fresh medium B containing compactin and mevalonate in the presence of either 10% LPDS or 10% FCS as indicated. After incubation for 3 hr at 37°C, each cell monolayer was pulse-labeled for 1 hr with 0.1 mM sodium [14C]oleate (5436 dpm/nmol). The cells were then harvested for measurement of their content of cholesteryl [14C]oleate and [14C]triglycerides. Each value is the mean of triplicate incubations with individual values shown. The cellular content of [14C]triglycerides in all transfected cell lines did not differ significantly in cells treated with LPDS (81–91 nmol/hr/mg) or FCS (88–105 nmol/hr/mg). Inset shows immunoblot analysis of whole cell extracts (6 µg) from the indicated transfection using a 1:1000 dilution of anti-Flag and anti-β-actin.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
Six schemes showing the synthesis of derivatives of U18666A.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12177.010





