Dbx1 precursor cells are a source of inspiratory XII premotoneurons
Figures
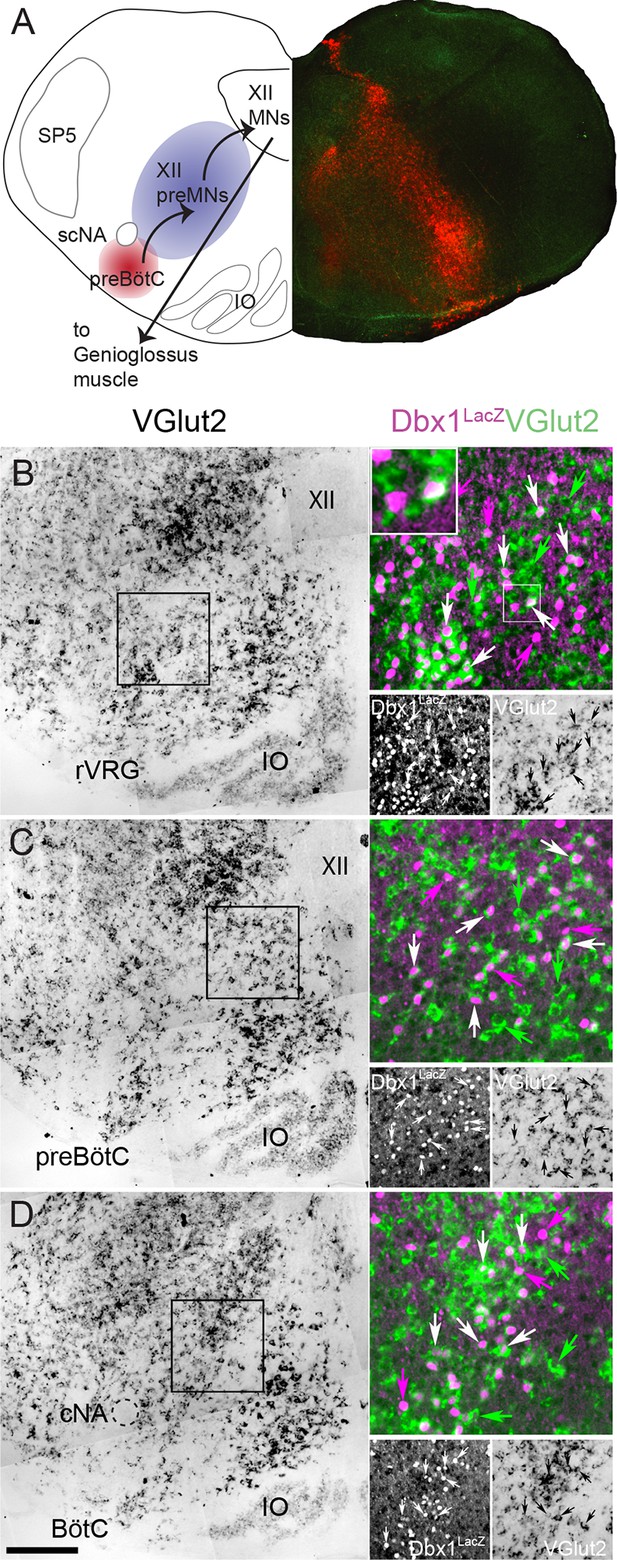
Fifty-seven percent of Dbx1 IRt neurons are glutamatergic.
(A) Composite diagram of a neonatal mouse medullary slice showing (left) a schematic of the multi-synaptic medullary circuit where inspiratory rhythm in vitro is generated within the preBötC (red), transmitted to inspiratory premotoneurons (preMNs) in the IRt (purple), and hypoglossal motoneurons (XII MNs) in the XII nucleus that innervate the genioglossus muscle of the tongue. Right, fluorescent image of a transverse confocal section showing localization of Dbx1-derived cells (red) extending from the preBötC through the IRt. (B-D) Mosaic images of bright field in situ hybridization for VGlut2 in the IRt and ventral medulla at the level of the rVRG (corresponding to the -0.55 mm plate of Fig S1 [Ruangkittisakul et al., 2014]) (B), the preBötC (corresponding to the -0.45 mm plate of Fig S1 [Ruangkittisakul et al., 2014]) (C), and the BötC (corresponding to the -0.30 mm plate of Fig S1 [Ruangkittisakul et al., 2014]) (D) from a P0 Dbx1lacz/+ brainstem. Insets expanded in the right sides of panels B-D show confocal expression of lacZ gene product β-galactosidase (pseudocolor magenta, lower left) and VGlut2 (pseudocolor green, lower right) within the reticular formation with examples of glutamatergic Dbx1 reticular neurons (white arrows). The inset expanded in the upper left of panel B highlights one cell that shows colocalized lacZ and VGlut2 expression. Green arrows indicate glutamatergic neurons lacking lacZ co-expression. Magenta arrows indicate lacZ-expressing cells lacking VGlut2 co-expression. Scale bar = 250 μm. SP5 – trigeminal nucleus, cNA – compact division of nucleus ambiguus, scNA – semi-compact division of nucleus ambiguus, preBötC - pre-Bötzinger Complex, BötC – Bötzinger Complex, IO – inferior olive, rVRG – rostral ventral respiratory group, XII – hypoglossal nucleus.
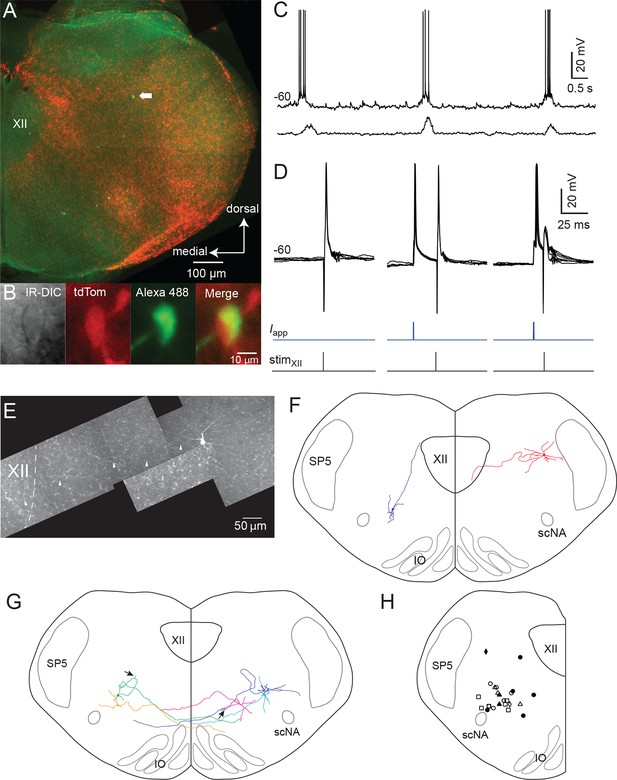
Inspiratory Dbx1 IRt neurons are ipsilaterally projecting, putative XII premotoneurons.
(A) Right half of the rhythmic slice preparation after PFA fixation and optical clearing using the Scale method. White arrow points to the soma of the inspiratory-modulated Dbx1 neuron, which is further characterized in panels B-E. (B) From left to right, IR-DIC image of the recorded neuron and epifluorescence images showing tdTomato, Alexa 488 dialyzed from the intracellular solution, and a composite of tdTomato and Alexa 488 labeling. (C) Whole cell recording of imaged neuron showing rhythmic inspiratory firing (top trace) and integrated inspiratory XII nerve output (bottom trace). (D) Membrane potential (upper black traces), whole cell stimulation (0.8 mA, 1 ms duration, middle blue traces), and XII stimulation time (0.3 mA, 0.2 ms duration, bottom black trace, stimulation time is at vertical line); Left panel: antidromic action potentials activated from XII nucleus stimulation, 5 traces overlaid; Middle: evoked orthodromic action potentials followed 46 ms later by XII nucleus stimulation, 4 traces overlaid; Right: evoked orthodromic action potential followed 16 ms later by XII stimulation resulted in the extinction of the antidromic action potential (i.e., a successful collision test, 7 traces overlaid). (E) Composite diagram showing biocytin-filled, FITC-labeled, reconstructed neuron; arrowheads point to the axon. Orientation is the same as the image in A (images adjusted for brightness and contrast). (F) Morphologic reconstruction of all neurons that only projected ipsilaterally, illustrating axon trajectory and dendritic tree organization (n = 2). (G) Morphologic reconstruction of all commissurally-projecting neurons illustrating axon trajectory and dendritic tree organization (n = 5). Reconstructed neurons on the left-hand side were also antidromically activated. Arrowhead indicates axon bifurcation. (H) Image showing location for 24 of 34 recorded inspiratory Dbx1 IRt neurons. Open squares: antidromic activation not tested; open circles: negative antidromic activation; filled circles: positive antidromic activation; open triangles: commissural projection, negative antidromic activation; filled triangles: commissural projection, positive antidromic activation; open diamonds: ipsilateral projection, negative antidromic activation; filled diamond: ipsilateral projection, positive antidromic activation. XII – hypoglossal nucleus, IO – inferior olive, SP5 – trigeminal nucleus, scNA – semicompact division of nucleus ambiguus.
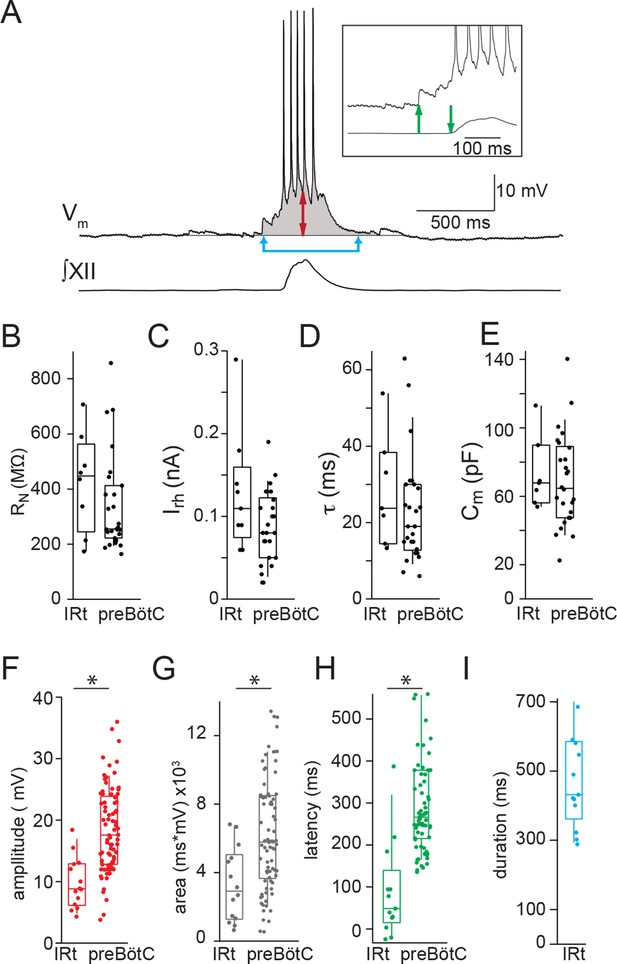
Electrophysiological characteristics of Dbx1 IRt neurons.
(A) Membrane potential recording (Vm) from an inspiratory Dbx1 IRt neuron and integrated XII nerve (∫XII) activity showing inspiratory burst characteristics. Inspiratory drive amplitude for neurons that generated action potentials during inspiratory bursts was estimated based on the shape of the underlying drive potential (double-ended red arrow). Inspiratory drive area was calculated as the integral of membrane potential over time (shaded area). Panel inset: inspiratory drive latency was defined as the delay between the onset of inspiratory depolarization (upward green arrow) and the onset of XII inspiratory nerve burst (downward green arrow). Inspiratory drive duration was measured as the length of time the membrane potential was above baseline (joined blue arrows). Membrane potential scale bar applies to inset as well. Group data (median, box: interquartile range, whiskers: 10th and 90th percentiles) and individual values (solid circles) measuring passive membrane properties and inspiratory drive characteristics in Dbx1 neurons of the IRt and preBötC: (B) neuronal input resistance, RN, n = 8 (IRt), n = 27 (preBötC); (C) rheobase, Irh, n = 9 (IRt), n = 26 (preBötC); (D) membrane time constant, τ, n = 7 (IRt), n = 26 (preBötC); (E) whole-cell capacitance, Cm, n = 7 (IRt), n = 26 (preBötC); (F) inspiratory drive amplitude, n = 14 (IRt), n = 82 (preBötC); (G) inspiratory drive area, n = 14 (IRt), n = 82 (preBötC); (H) inspiratory drive latency, n = 13 (IRt), n = 70 (preBötC); (I) inspiratory drive duration, n = 13 (IRt); All preBötC data from (Picardo et al., 2013). IRt – intermediate reticular formation. *, p < 0.05, unpaired t-test.
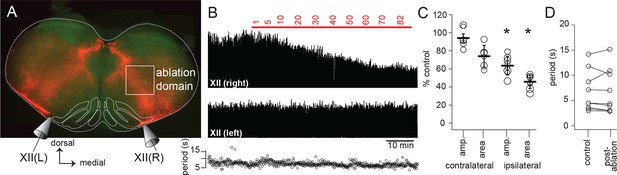
Dbx1 IRt neurons contribute significantly to XII inspiratory burst output.
(A) Confocal image of a rhythmic slice preparation after fixation and Scale clearing illustrating the region targeted for laser ablations within the white rectangle on the right-hand side. Bilateral XII output was recorded, XII(R) and XII(L). (B) Example bilateral XII output, corresponding to the slice in (A). Integrated XII output corresponds to the lesioned side [XII(right)] and the non-lesioned side [XII(left)] as a function of time and lesion number. The red bar indicates the start and duration of ablations and the numbers above show the confirmed ablation tally. (C) Group data (mean ± SEM) and individual values (open circles) for contralateral (i.e. unlesioned) XII amplitude and area, n = 6; and for ipsilateral (i.e. lesioned) XII amplitude and area, n = 8. *, p < 0.05, comparison of XII amplitude or area pre- and post-ablation, repeated measures ANOVA, Tukey post-hoc test, n = 5. (D) Individual values (open circles) pre- and post-ablation, linked by solid lines, of XII inspiratory burst period. IRt – intermediate reticular formation.





