Role of protein synthesis and DNA methylation in the consolidation and maintenance of long-term memory in Aplysia
Figures
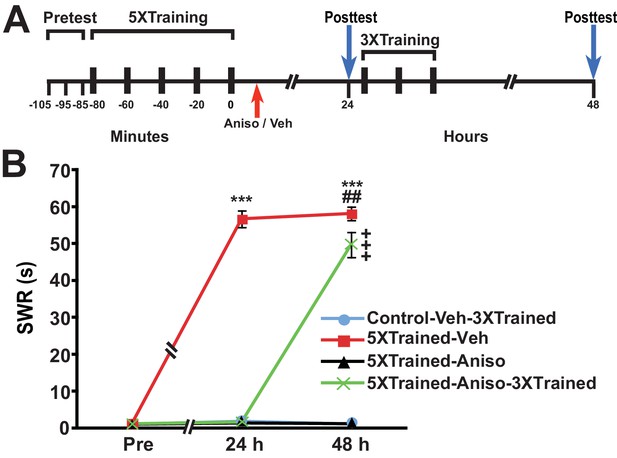
LTS can be established by truncated training following its disruption by posttraining PSI.
(A) Experimental protocols. The times of the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections are shown relative to the end of the fifth bout of sensitization training (time = 0). The time of the intrahemocoelic injection of anisomycin or vehicle is indicated by the red arrow. After the 24-h posttest, animals in the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained groups received truncated sensitization training (3 bouts of tail shocks). (B) The mean duration of the SWR measured at 24 h and 48 h for the Control-Veh-3XTrained (n = 7), 5XTrained-Veh (n = 6), 5XTrained-Aniso (n = 5), and 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained (n = 6) groups. A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that there was a significant group x time interaction (F[6,40] = 210.9, p < 0.0001). Subsequent planned comparisons indicated that the overall differences among the four groups were highly significant on all of the posttests (24 h, F[3,20] = 456.7, p < 0.0001; and 48 h, F[3,20] = 250.6, p < 0.0001). SNK posthoc tests revealed that the initial sensitization training produced significant LTS, as indicated by the increased mean duration of the SWR, in the 5XTrained-Veh group (56.7 ± 2.2 s) at 24 h compared with that in the Control-Veh-3XTrained (1.9 ± 0.9 s, p < 0.001). The mean duration of the SWR in the 5XTrained-Veh group at 24 h was also significantly longer than that in the 5XTrained-Aniso (1.4 ± 0.4 s, p < 0.001), and 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained groups (1.7 ± 0.7 s, p < 0.001). The differences among the Control-Veh-3XTrained, 5XTrained-Aniso and 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained groups were not significant at 24 h. The mean duration of the SWR in the 5XTrained-Veh group (58.2 ± 1.8 s) was still protracted at 48 h, and was significantly longer than that in the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (1.1 ± 0.2 s), as well as that in the 5XTrained-Aniso group (1.2 ± 0.2 s, p < 0.001 for both comparisons). LTS was induced in the 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained group by the three additional tail shocks applied after the 24-h posttest. The mean duration of the SWR in this group at 48 h was 49.7 ± 3.4 s, which was significantly longer than that for the Control-Veh-3XTrained group. In addition, the mean duration of the reflex in the 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained group was longer than that in 5XTrained-Aniso group, but still significantly shorter than that in the 5XTrained-Veh group at 48 h (p < 0.01). Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group, the 5XTrained-Aniso group, and 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained group at 24 h; and comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group and the 5XTrained-Aniso group at 48 h. Pound signs, comparison of the 5XTrained-Veh with the 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained group at 48 h. Plus signs, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Aniso-3XTrained group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-Aniso groups at 48 h. Here and in subsequent figures one symbol indicates p < 0.05; two symbols, p < 0.01; and three symbols, p < 0.001. Error bars in this and subsequent figures represent ± SEM.
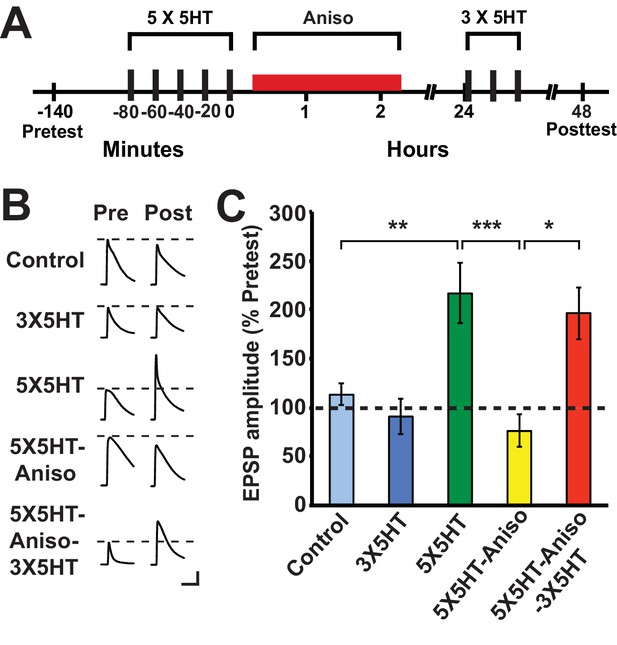
Partial training induces LTF following its disruption by PSI immediately after long-term training.
(A) Experimental protocols. The initial training consisted of five 5-min pulses of 100 µM 5HT (5X5HT) spaced at 15-min intervals. Cocultures in the 5X5HT-Aniso and 5X5HT-Aniso-3X5HT groups were treated with anisomycin (10 µM, red bar) for 2 h immediately after the 5X5HT training. Three 5-min pulses of 5HT (100 µM; 3X5HT training) were given to cocultures in the 5X5HT-Aniso-3X5HT group at 24 h after 5X5HT training, as well as to cocultures in the 3X5HT group at the equivalent experimental time. (B) Sample EPSPs. Each pair of traces shows EPSPs recorded from the same coculture on the pretest and posttest. Scale bars: 10 mV, 100 ms. (C) Graph presenting the mean normalized EPSPs, measured at 48 h, for the five experimental groups: Control (n = 13), 3X5HT (n = 12), 5X5HT (n = 16), 5X5HT-Aniso (n = 12), and 5X5HT-Aniso-3X5HT (n = 7). A one-way ANOVA indicated that the overall differences among the five groups were highly significant (F[4,55] = 7.9, p < 0.0001). SNK posthoc tests showed that the mean normalized EPSP in the 5X5HT group (216.6% ± 30.6%) at 48 h was significantly larger than that in the Control (113.1% ± 11.1%, p < 0.01), 3X5HT (90.8% ± 17.9%, p < 0.001), and 5X5HT-Aniso (76.1% ± 16.4%, p < 0.001) groups. The mean normalized EPSP in the 5X5HT-Aniso-3X5HT group (196.5% ± 26.8%) was also significantly larger than that in the Control (p < 0.05), 3X5HT (p < 0.05), and 5X5HT-Aniso (p < 0.05) groups. None of the other differences among the groups was significant.
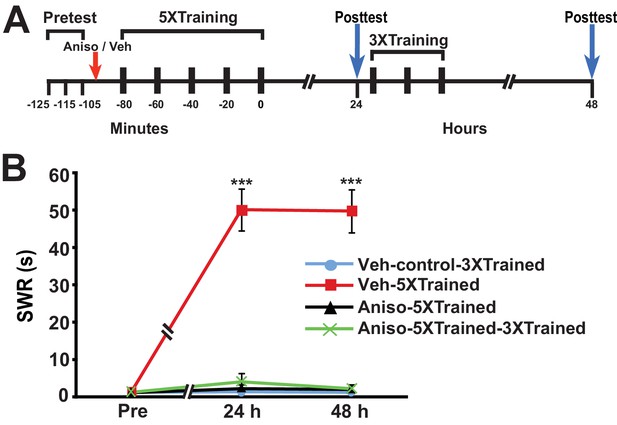
LTS cannot be induced by partial training when PSI occurs during the original (5X) sensitization training.
(A) Experimental protocols. The times at which the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections occurred are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The red arrow indicates when either anisomycin or vehicle was injected into the hemocoel. (B) The mean duration of the SWR measured at 24 h and 48 h for the Veh-Control-3XTrained (n = 5), Veh-5XTrained (n = 8), Aniso-5XTrained (n = 6), and Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained (n = 6) groups. A repeated-measures ANOVA showed a significant group x time interaction (F[6,42] = 40.9, p < 0.0001). Planned comparisons indicated that the group differences were highly significant for both 24-h (F[3,21] = 43.9, p < 0.0001) and 48-h (F[3,21] = 45.4, p < 0.0001) posttests. SNK posthoc tests revealed that the 5X training produced sensitization of the SWR in the Veh-5XTrained group (mean duration = 50.1 ± 5.6 s) at 24 h compared with the results for the Veh-Control-3XTrained group (mean duration of the SWR = 1.4 ± 0.4 s, p < 0.001). In addition, the SWR in the Veh-5XTrained group was significantly longer than that in the Aniso-5XTrained group (2.2 ± 1.2 s, p < 0.001) and the Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained group (4.0 ± 2.3 s, p < 0.001). The differences among the Veh-Control-3XTrained, Aniso-5XTrained, and Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained groups were not significant at 24 h. The SWR in the Veh-5XTrained group (mean duration = 49.8 ± 5.8 s) remained sensitized at 48 h, as indicated by the comparison with the reflex in the Veh-Control-3XTrained group (mean duration = 1.2 ± 0.2 s). The SWR was also significantly prolonged in the Veh-5XTrained group compared with that in the Aniso-5XTrained group (mean duration = 2.0 ± 1.0 s, p < 0.001 for both comparisons). The three tail shocks applied after the 24-h posttest did not establish LTS in the Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained group. The mean duration of the SWR in this group at 48 h was 2.2 ± 1.2 s, which was not significantly different from that in the Veh-Control-3XTrained and Aniso-5XTrained groups. The SWR of the Veh-5XTrained group at 48 h was significantly longer than that in the Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained group (p < 0.001). Asterisks, comparisons of the Veh-5XTrained group with the Veh-Control-3XTrained group, the Aniso-5XTrained group, and the Aniso-5XTrained-3XTrained group.
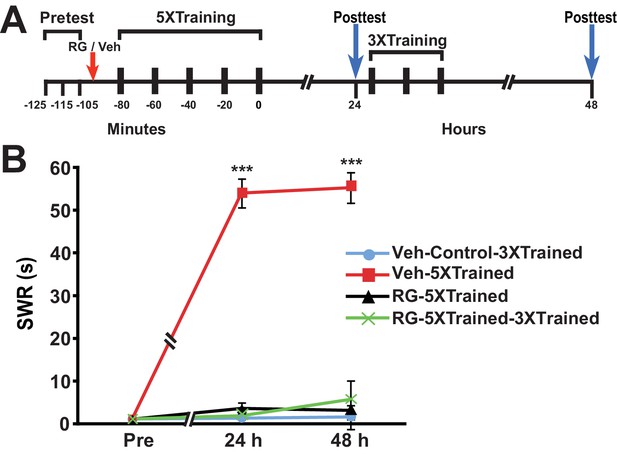
DNMT inhibition during the original (5X) sensitization training precludes the ability of subsequent partial training to induce LTS.
(A) Experimental protocol. The times of occurrence of the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections are shown relative to the end of the last training session. Either RG108 or vehicle was injected into the hemocoel at the time indicated by the red arrow. (B) The mean duration of the SWR measured at 24 h and 48 h for the Veh-Control-3XTrained (n = 7), Veh-5XTrained (n = 7), RG-5XTrained (n = 8), and RG-5XTrained-3XTrained (n = 7) groups. A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that there was a significant group x time interaction (F[6,50] = 73.6, p < 0.0001). Subsequent planned comparisons showed that the overall differences among the four groups for the 24-h and 48-h posttests were highly significant (24 h, F[3,25] = 197.9, p < 0.0001; and 48 h, F[3,25] = 82.8, p < 0.0001). As revealed by SNK posthoc tests, the SWR exhibited sensitization at 24 h in the Veh-5XTrained group (mean duration = 54.0 ± 3.4 s) compared with that in the Veh-Control-3XTrained group (mean duration = 1.3 ± 0.3 s, p < 0.001). The differences in duration of the SWR at 24 h among the Veh-Control-3XTrained, RG-5XTrained (3.6 ± 1.3 s), and RG-5XTrained-3XTrained (1.9 ± 0.6 s) groups were not significant. Sensitization of the SWR was maintained in the Veh-5XTrained group (mean duration of the reflex = 55.3 ± 3.6 s) at 48 h, as shown by the comparison with the Veh-Control-3XTrained group (mean duration of the reflex = 1.6 ± 0.6 s, p < 0.001). There were no significant differences among the Veh-Control-3XTrained, RG-5XTrained (mean duration of the SWR = 3.1 ± 1.2 s), and RG-5XTrained-3XTrained (mean duration of the SWR = 5.7 ± 4.4 s) groups at 48 h, indicating that the three additional bouts of tail shocks given to the latter group after the 24-h posttest failed to induce LTS. Asterisks, comparisons of the Veh-5XTrained group with the Veh-Control-3XTrained group, the RG-5XTrained group, and the RG-5XTrained-3XTrained group.
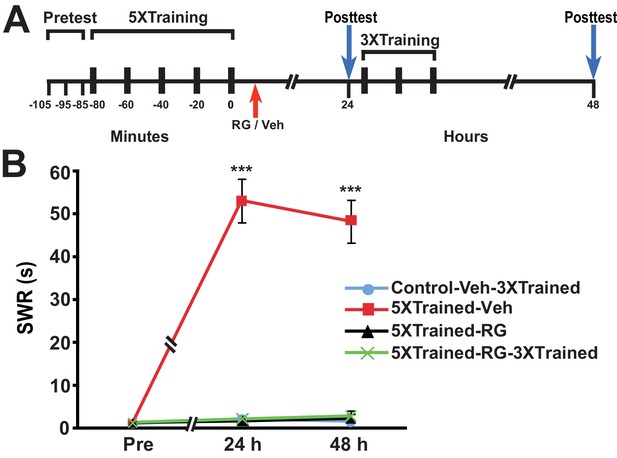
Posttraining inhibition of DNMT precludes later induction of LTS by partial training.
(A) Experimental protocol. The times at which the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections occurred are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The time of the intrahemocoelic injection of either RG108 or vehicle is indicated by the red arrow. After the 24-h posttest, animals in the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained groups received 3X sensitization training. (B) The mean duration of the SWR measured at 24 h and 48 h for the Control-Veh-3XTrained (n = 8), 5XTrained-Veh (n = 8), 5XTrained-RG (n = 7), and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained (n = 6) groups. A repeated-measures ANOVA showed that the group x time interaction was significant (F[6,50] = 64.7, p < 0.0001). The overall differences among the four groups for the 24-h and 48-h posttests were highly significant, as indicated by a one-way ANOVA (24 h, F[3,25] = 82.6, p < 0.0001; and 48 h, F[3,25] = 69.2, p < 0.0001). SNK posthoc tests revealed significantly greater sensitization in the 5XTrained-Veh group at 24 h (mean duration of the SWR = 53.1 ± 5.1 s) than in the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (mean duration of the SWR = 2.1 ± 0.9 s, p < 0.001). The differences among the 5XTrained-RG (mean duration of the SWR = 1.7 ± 0.7 s), 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained (mean duration of the SWR = 2.2 ± 0.7 s), and Control-Veh-3XTrained groups at 24 h were not significant. Sensitization persisted in the 5XTrained-Veh group at 48 h (mean duration of the SWR = 48.3 ± 5.0 s) compared with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (mean duration of the SWR = 1.6 ± 0.3 s, p < 0.001). The failure of the 3X training to induce sensitization in the 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained group was shown by the lack of significant differences between this group (mean duration of the SWR = 2.8 ± 1.2 s) and the Control-Veh-3XTrained group at 48 h. There was also no significant difference between the mean duration of the reflex in the 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained group and that in the 5XTrained-RG (2.3 ± 1.0 s) group at 48 h. Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group, the 5XTrained-RG group, and the 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained group.
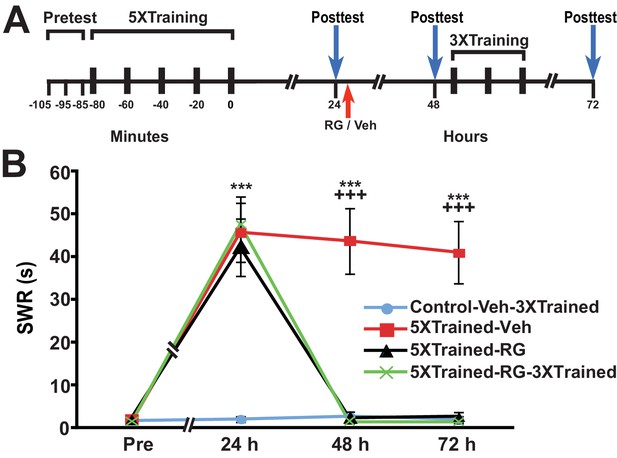
Inhibition of DNMT with RG108 eliminates established LTS in Aplysia.
(A) Experimental protocol. The occurrences of the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections are shown relative to the end of the last training session. Either RG108 or vehicle was injected into the animals at the time indicated by the red arrow. After the 48-h posttest, animals in the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained groups received 3 bouts of sensitization training. (B) RG108 treatment at 24 h after training abolished LTS. There were four experimental groups: Control-Veh-3XTrained group (n = 6), 5XTrained-Veh group (n = 6), 5XTrained-RG group (n = 6), and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained group (n = 6). A repeated-measures ANOVA disclosed a significant group x time interaction (F[9,60] = 22.9, p < 0.0001). Subsequent planned comparisons showed that the overall differences among the four groups for the 24-, 48- and 72-h posttests were highly significant (24 h, F[3,20] = 13.8, p < 0.0001; 48 h, F[3,20] = 28.6, p < 0.0001; and 72 h, F[3,20] = 27.9, p < 0.0001). Animals in all three groups trained with five bouts of tail shocks exhibited significant sensitization at 24 h, as indicated by SNK posthoc tests. Thus, the mean SWR was longer in the 5XTrained-Veh (45.7 ± 6.9 s), 5XTrained-RG (42.2 ± 6.7 s), and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained (47.5 ± 6.5 s) groups than that in the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (2.0 ± 0.7 s; p < 0.001 for each comparison). However, although the 5XTrained-Veh group exhibited significant sensitization on both the 48-h (mean SWR = 43.7 ± 7.6 s) and 72-h (mean SWR = 41.0 ± 7.3 s) posttests, sensitization was absent in both groups of RG108-treated animals after 24 h. Posthoc tests revealed no significant differences for any of the comparisons between the Control-Veh-3XTrained group and the 5XTrained-RG group, or the 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained group, on the posttests after 24 h. Therefore, inhibiting DNMT with RG108 24 h after training erased established LTS. There was no evidence of spontaneous recovery of sensitization over the 48-h period after RG108 injection; furthermore, three additional bouts of training failed to reinstate LTS. Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh, 5XTrained-RG, and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained groups with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group at 24 h; and comparison of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group at 48 h and 72 h. Plus signs, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the 5XTrained-RG and 5XTrained-RG-3XTrained groups at 48 h and 72 h.
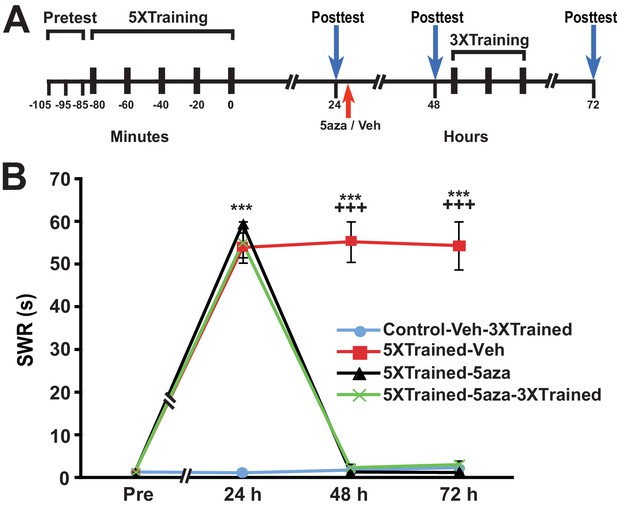
Inhibition of DNMT with 5-azadeoxycytidine (5-aza) also eliminates established LTS in Aplysia.
(A) Experimental protocol. The occurrences of the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The red arrow indicates the time at which either the drug or the vehicle was injected into animals. After the 48-h posttest, animals in the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups received 3 additional bouts of sensitization training. (B) 5-aza treatment at 24 h after training abolished LTS. There were four experimental groups: Control-Veh-3XTrained group (n = 11), 5XTrained-Veh group (n = 8), 5XTrained-5aza group (n = 8), and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained group (n = 10). A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that there was a significant group x time interaction (F[9,99] = 132.2, p < 0.0001). The overall differences among the four groups at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h were highly significant (24 h, F[3,33] = 145.9, p < 0.0001; 48 h, F[3,33] = 145.7, p < 0.0001;and 72 h, F[3,33] = 99.3, p < 0.0001), as revealed by a one-way ANOVA. SNK posthoc tests on the 24-h data showed that the mean SWR was significantly more prolonged in the 5XTrained-Veh (53.9 ± 3.5 s), 5XTrained-5aza (59.4 ± 0.6 s), and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained (55.0 ± 3.4 s) groups than that in the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (1.3 ± 0.3 s; p < 0.001 for each comparison). The 5XTrained-Veh group also exhibited significant sensitization at both 48 h (mean duration of the SWR = 55.3 ± 4.8 s) and 72 h (mean duration of the SWR = 54.4 ± 5.6 s; p < 0.001 for both comparisons with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group). However, sensitization was absent in the 5XTrained-5aza and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups at both 48 h and 72 h, as indicated by comparisons with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group. There were no significant differences for any of the comparisons among the Control-Veh-3XTrained, 5XTrained-5aza, and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups for the tests after 24 h. Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh, 5XTrained-5aza, and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups with the Control-Veh-3XTrained group at 24 h; and comparison of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained at 48 h and 72 h. Plus signs, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the 5XTrained-5aza and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups at 48 h and 72 h.
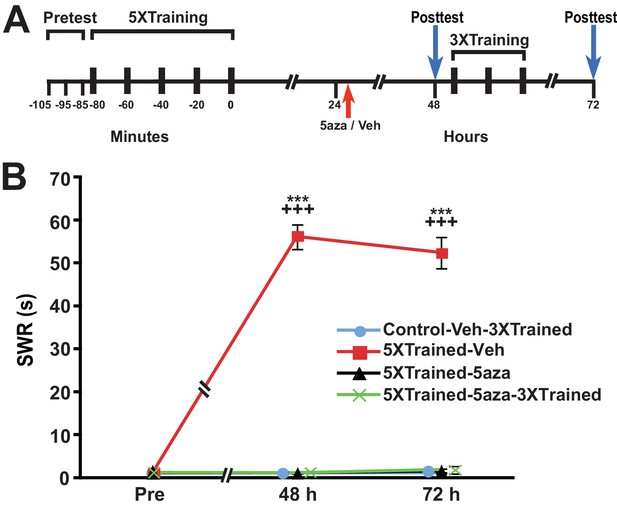
Disruption of established LTS with inhibition of DNMT is not a reconsolidation-related phenomenon.
(A) Experimental protocol. The times at which the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections occurred are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The intrahemocoelic injection of either drug or vehicle is indicated by the red arrow. The animals did not receive a 24 h test prior to the drug/vehicle injection. After the 48-h posttest, animals in the Control-Veh-3XTrained and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups received 3 bouts of sensitization training (3X training). (B) 5-aza injection abolished established LTS in the absence of a posttest at 24 h. Four experimental groups were included: Control-Veh-3XTrained group (n = 7), 5XTrained-Veh group (n = 7), 5XTrained-5aza group (n = 7), and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained group (n = 8). A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that there was a significant group x time interaction (F[6,50] = 105.8, p < 0.0001). Subsequent planned one-way ANOVAs showed that the overall differences among the four groups at both 48 h and 72 h were highly significant (48 h, F[3,25] = 385.4, p < 0.0001;and 72 h, F[3,25] = 183.3, p < 0.0001). SNK posthoc tests revealed that the SWR in the 5XTrained-Veh group was significantly sensitized at both 48 h (mean = 56.1 ± 2.9 s) and 72 h (mean = 52.4 ± 3.7 s) compared with that in the Control-Veh-3XTrained group (p < 0.001 for each comparison). Furthermore, the mean duration of the SWR in the 5XTrained-Veh group was significantly longer than that in the 5XTrained-5aza (1.1 ± 0.1 s at 48 h, p < 0.001; and 1.6 ± 0.6 s at 72 h, p < 0.001) and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained (1.1 ± 0.1 s at 48 h, p < 0.001; and 1.9 ± 0.9 s at 72 h, p < 0.001) groups. The Control-Veh-3XTrained, 5XTrained-5aza, and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups did not differ significantly at either 48 h or 72 h. Thus, the erasure of established LTS by inhibition of DNMT (Figure 6) did not require elicitation of the SWR immediately preceding the drug injection. Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh-3XTrained, 5XTrained-5aza, and 5XTrained-5aza-3XTrained groups at 48 h and 72 h.
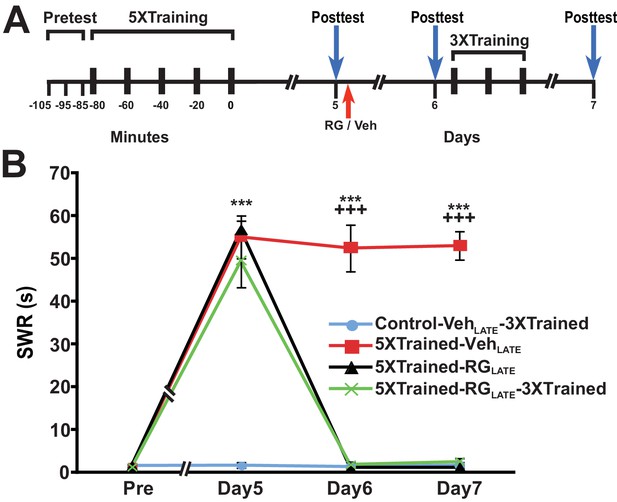
RG108 treatment 5 days after training abolishes LTS in Aplysia.
(A) Experimental protocol. The occurrences of the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The red arrow indicates the time of the intrahemocoelic injection of RG108 or vehicle. After the day six posttest, animals in some groups received partial sensitization training (3 bouts of tail shocks). (B) RG108 injection at day five after training (LATE treatment) erased LTS. There were four experimental groups: Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group (n = 6), 5XTrained-VehLATE group (n = 5), 5XTrained-RGLATE group (n = 6), and 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained group (n = 6). A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that there was a significant group x time interaction (F[9,57] = 66.3, p < 0.0001). Subsequent planned comparisons showed that the overall differences among the four groups on days 5, 6 and 7 were highly significant (day 5, F[3,19] = 43.7, p < 0.0001; day 6, F[3,19] = 105.1, p < 0.0001; and day 7, F[3,19] = 252.5, p < 0.0001). There was significant sensitization at day five prior to RG108/vehicle injection in the 5XTrained-VehLATE (mean duration of the SWR = 55.0 ± 5.0 s), 5XTrained-RGLATE (mean duration of the SWR = 56.7 ± 2.1 s), and 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained (mean duration of the SWR = 49.3 ± 6.1 s) groups compared with the Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group (mean duration of the SWR = 1.7 ± 0.7 s) (p < 0.001 for each comparison). The 5XTrained-VehLATE group also exhibited robust sensitization on day 6 (mean duration of the SWR = 52.4 ± 5.5 s) and 7 (mean duration of the SWR = 53.0 ± 3.3 s) compared with the Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group. Sensitization was absent in the 5XTrained-RGLATE group on day 6 and 7; thus, there was no spontaneous recovery of LTS during the 48-h period after the application of RG108. Three bouts of training shortly after the day six posttest did not restore LTS in the 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained group the next day. In particular, the mean duration of the SWR in the 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained group (2.5 ± 0.8 s) on day 7 was not significantly different from that in the Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group, and was significantly shorter than that in the 5XTrained-VehLATE group (p < 0.001). Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-VehLATE, 5XTrained-RGLATE, and 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained groups with the Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group on day 5; and comparison of the 5XTrained-VehLATE group with the Control-VehLATE-3XTrained group on days 6 and 7. Plus signs, comparisons of the 5XTrained-VehLATE group with the 5XTrained-RGLATE and 5XTrained-RGLATE-3XTrained groups on days 6 and 7.
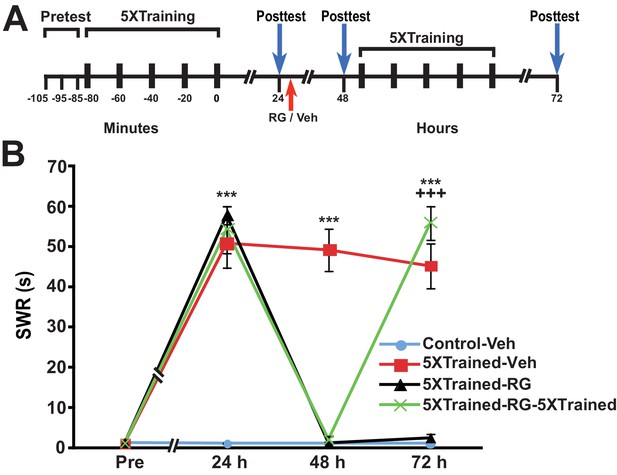
Animals can relearn following elimination of LTS by DNMT inhibition.
(A) Experimental protocol. The times at which the pretests, training, posttests, and drug/vehicle injections occurred are shown relative to the end of the last training session. The time of the intrahemocoelic injection of either RG108 or vehicle is indicated by the red arrow. After the 48-h posttest, animals in the 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained group received a second round of full sensitization training (five bouts of electrical tail shocks). (B) Sensitization retraining produced LTS in animals following erasure of LTM by RG108. There were four experimental groups: Control-Veh group (n = 6), 5XTrained-Veh group (n = 6), 5XTrained-RG group (n = 4), and 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained group (n = 6). A repeated-measures ANOVA indicated that the group x time interaction was significant (F[9,54] = 61.4, p < 0.0001). Subsequent one-way ANOVAs indicated that the overall differences among the four groups at 24 h, 48 h and 72 h were highly significant (24 h, F[3,18] = 33.3, p < 0.0001; 48 h, F[3,18] = 70.7, p < 0.0001; and 72 h, F[3,18] = 54.9, p < 0.0001). SNK posthoc tests performed on the 24-h data revealed that the initial training produced significant sensitization in the 5XTrained-Veh group (mean duration of the SWR = 50.8 ± 6.1 s), 5XTrained-RG group (mean duration of the SWR = 57.8 ± 2.3 s), and 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained group (mean duration of the SWR = 54.2 ± 5.8 s) compared with Control-Veh group (mean duration of the SWR = 1.2 ± 0.2 s; p < 0.001 for each comparison). The SWR of 5XTrained-Veh group also exhibited sensitization at 48 h (mean duration = 49.2 ± 5.2 s) and 72 h (mean duration = 45.2 ± 5.6 s) compared with the Control-Veh group (48 h, mean duration = 1.2 ± 0.2 s, p < 0.001; and 72 h, mean duration = 1.2 ± 0.2 s, p < 0.001). Sensitization memory was significantly disrupted at 48 h in both the 5XTrained-RG (mean SWR = 1.3 ± 0.3 s) and 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained (mean SWR = 2.2 ± 0.7 s) groups by the RG108 injection immediately after the 24-h posttest (p > 0.05 for the comparisons with the Control-Veh group). Retraining after the 48-h posttest reestablished full LTM. The mean duration of the SWR in the 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained group at 72 h (55.8 ± 4.2 s) was significantly greater than that for the Control-Veh group (mean duration = 1.2 ± 0.2 s, p < 0.001), as well as for the 5XTrained-RG group at 72 h (2.5 ± 1.0 s, p < 0.001). Asterisks, comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh, 5XTrained-RG, and 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained groups with the Control-Veh group at 24 h; comparisons of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh, 5XTrained-RG, and 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained groups at 48 h; and comparison of the 5XTrained-Veh group with the Control-Veh and 5XTrained-RG groups at 72 h. Plus signs, comparison of the 5XTrained-RG-5XTrained group with the 5XTrained-RG group at 72 h.





