Mechanism of allosteric regulation of β2-adrenergic receptor by cholesterol
Figures
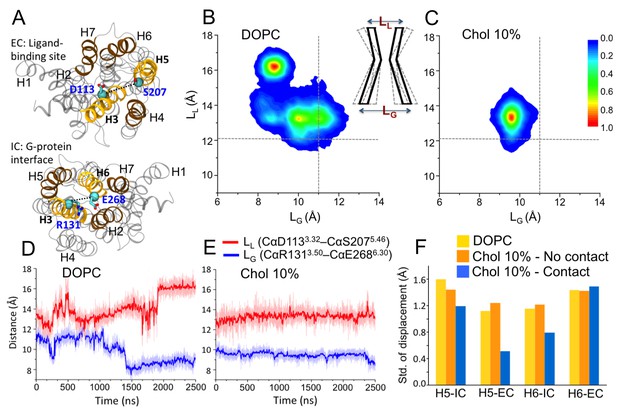
Conformational dynamics of β2AR.
(A) The distances between the Cα atoms of D1133.32–S2075.46 (distance defined as LL) and R1313.50–E2686.30 (LG) pairs used to measure the fluctuations at the ligand and G-protein binding sites, respectively. (B–C) The conformational distributions of β2AR in membranes with 0 and 10 mol% cholesterol (Chol) as a function of LL and LG. The gray dotted lines represent the corresponding LL and LG values in the inactive crystal structure of β2AR (Hanson et al., 2008). The cartoon diagram shows the fluctuations of LL and LG at the ligand and G-protein binding sites of the receptor, respectively. (D–E) The time evolution of LL (light red) and LG (light blue) in systems with 0 and 10 mol% cholesterol. Corresponding 50-point running averages are shown in dark colors. (F) Standard deviation for the distribution of the distance between the intracellular (IC) (or extracellular (EC)) end of H5 and its average position, and its dependence on whether the given end of H5 is in contact with cholesterol or not; similarly for H6.
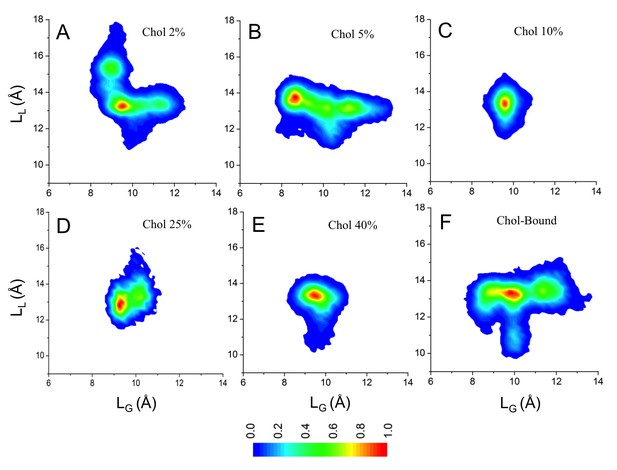
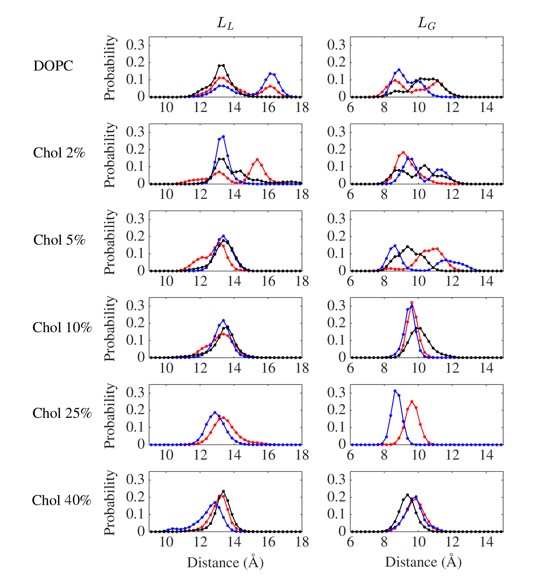
Conformational distributions of β2AR in lipid bilayers with various cholesterol (Chol) concentrations.
In panels (A–F) the distributions are plotted as a function of LL (distance between the Cα atoms of D1133.32 and S2075.46) at the ligand binding site and LG (distance between the Cα atoms of R1313.50 and E2686.30) at the G protein-binding site. (A–E) Starting from situations where no cholesterol molecules were initially bound to β2AR, distributions are plotted over all independent trajectories of a given system, where the equilibration time (the first 100 ns) was discarded from the analysis. (F) β2AR conformational distribution in control simulations, where cholesterol molecules were initially bound at the eight interaction sites of β2AR predicted by our simulations, but no further cholesterol was in the membrane (total (average) cholesterol concentration 1.9 mol%). Here, there is reason to keep in mind the rapid migration of cholesterols away from the receptor surface when the cholesterol concentration is low (see main text and Figure 5), implying that panel (F) corresponds to cholesterol-rich conditions in the vicinity of the receptor at very short times but to cholesterol-poor conditions at long times.
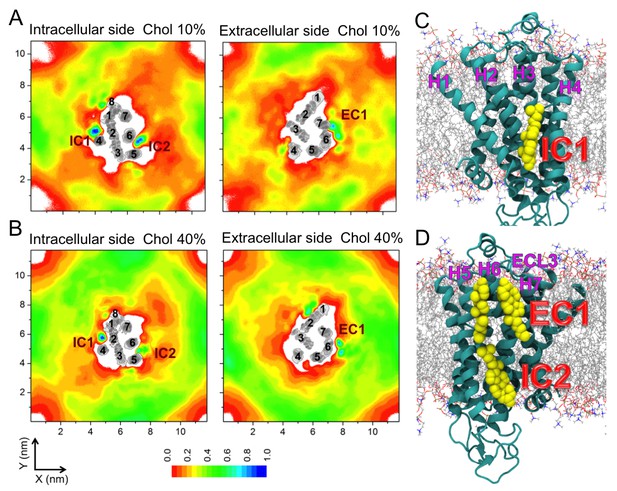
Cholesterol interaction sites on β2AR.
(A–B) 2D number densities of cholesterol (Chol) around β2AR. The data are averaged over all independent trajectories for a given cholesterol concentration (Table 1) and normalized with respect to the maximum density for that particular cholesterol concentration. The intracellular (IC) and extracellular (EC) bilayer leaflets are depicted separately. The major cholesterol interaction sites (IC1, IC2 and EC1) are marked in the density plots. The IC and EC sides of the transmembrane regions (H1–H7) of β2AR are shown in gray scale (the darker the color, the higher is the number density) and numbered accordingly. (C–D) Cartoon representation of three main cholesterol interaction sites in β2AR. IC1 (H1–H4) and IC2 (H5–H6) are located on the intracellular side, and EC1 comprised of two closely placed cholesterols between H5-H6 and H6-ECL3-H7 is located on the extracellular side of β2AR.
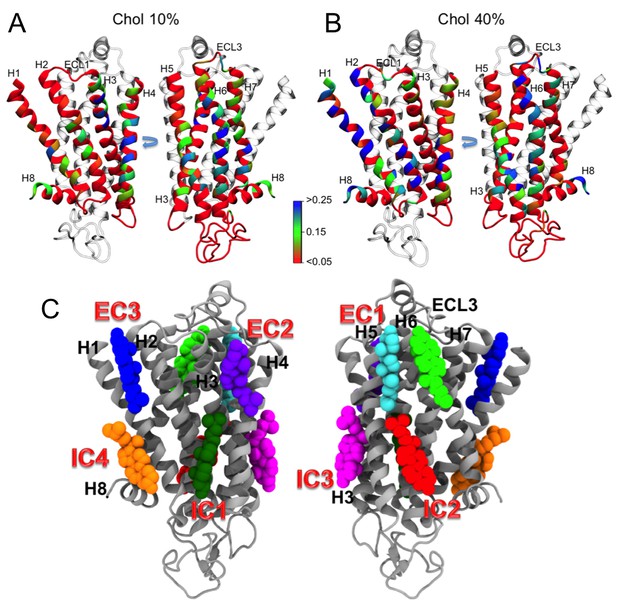
Residues of β2AR involved in cholesterol binding, and cholesterol interaction sites on β2AR.
Panels (A–B) (top): Cholesterol occupancy time per residue of β2AR described in terms of the normalized time fraction, where a value of one stands for a contact throughout the simulation trajectory and zero means no contact. Results are given for (A) 10 and (B) 40 mol% of cholesterol. The residues of β2AR are defined to be in contact with cholesterol when any non-hydrogen atom of the residue is within ≤0.5 nm of any heavy atom of cholesterol. The data show that there are several hot spots (blue) as cholesterol binding sites. These plots were averaged from all independent simulations for a given cholesterol concentration, where the equilibration time (the first 100 ns of the simulation) was disregarded from the analysis. Panels (C) (bottom): Interaction sites as obtained from our simulations, are shown from two perspectives around the protein. EC and IC stand for extracellular and intracellular, respectively. Interaction sites at the intracellular (IC) side: IC1 (dark green) between helices (H) 1–4, IC2 (red) between H5 and H6, IC3 (magenta) between H3 and H5, and IC4 (orange) between H1 and H8. Interaction sites at the extracellular (EC) side: EC1 comprised of two closely placed cholesterol molecules between H5 and H6 (cyan) and in space surrounded by H6-ECL3-H7 (green), EC2 (purple) between H3 and H4, and EC3 (blue) between H1-H2-ECL1 (where ECL stands for the extracellular loop).
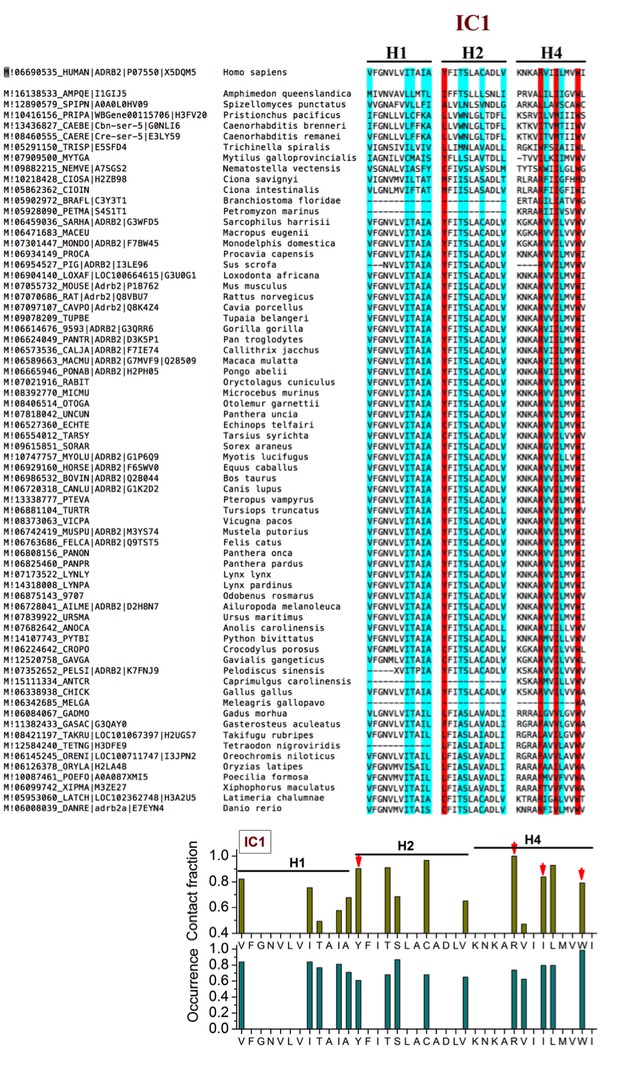
Sequence alignment of β2AR orthologues around the cholesterol-binding site IC1.
The residues that play a major role (contact fraction ≥ 0.4, where one stands for maximum contact and zero for no contact) in cholesterol binding are highlighted. Here for IC1, the residues in the cholesterol consensus motif are highlighted in red. Following sequence alignment, shown are the contact fraction per residue (tan bars) and its occurrence in the set of sequences (cyan bars) [one stands for 100% and zero for no occurrence]. The occurrence represents the extent a particular residue is conserved.
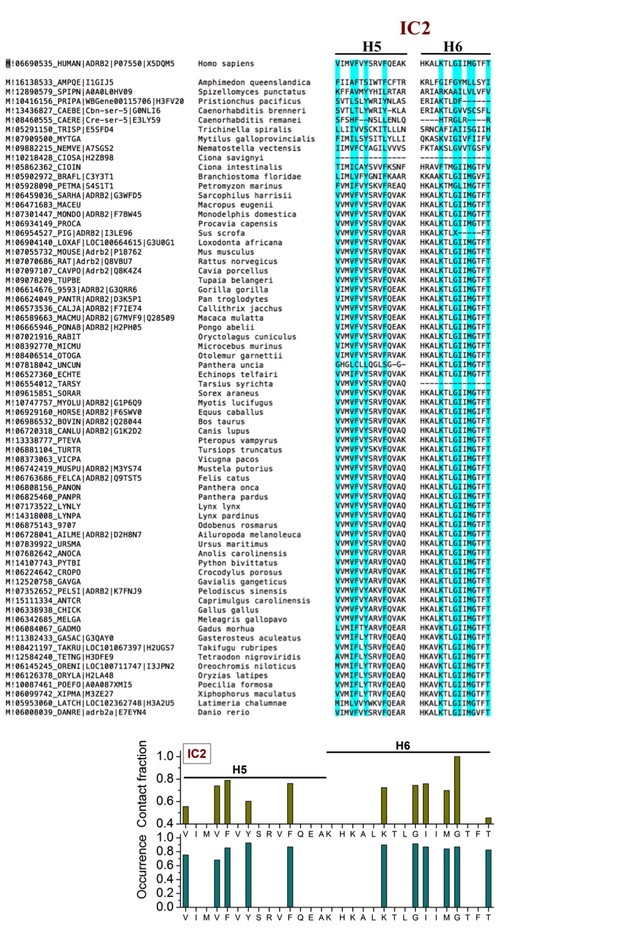
Sequence alignment of β2AR orthologues around the cholesterol-binding site IC2.
The residues that play a major role (contact fraction ≥ 0.4, where one stands for maximum contact and zero for no contact) in cholesterol binding are highlighted. Following sequence alignment, shown are the contact fraction per residue (tan bars) and its occurrence in the set of sequences (cyan bars) [one stands for 100% and zero for no occurrence]. The occurrence represents the extent a particular residue is conserved.
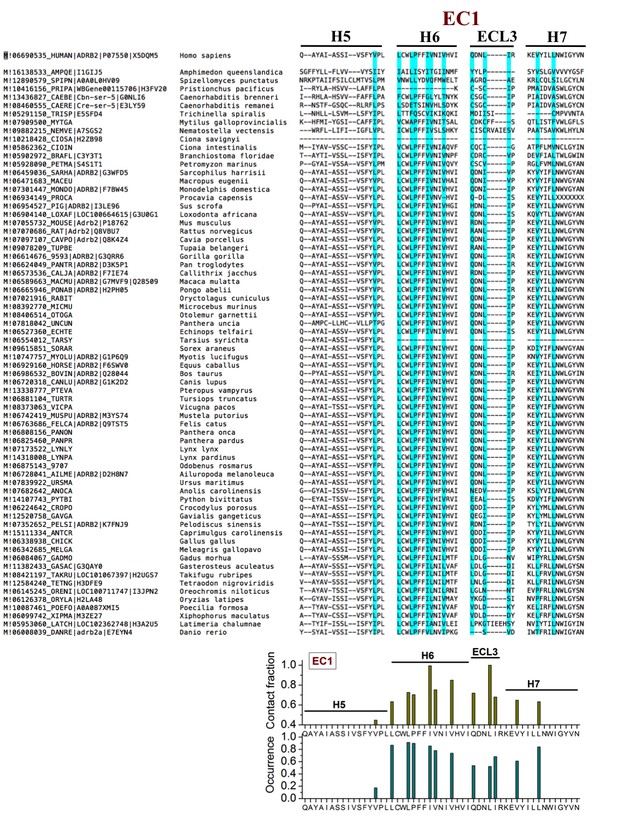
Sequence alignment of β2AR orthologues around the cholesterol-binding site EC1.
The residues that play a major role (contact fraction ≥ 0.4, where one stands for maximum contact and zero for no contact) in cholesterol binding are highlighted. Following sequence alignment, shown are the contact fraction per residue (tan bars) and its occurrence in the set of sequences (cyan bars) [one stands for 100% and zero for no occurrence]. The occurrence represents the extent a particular residue is conserved.
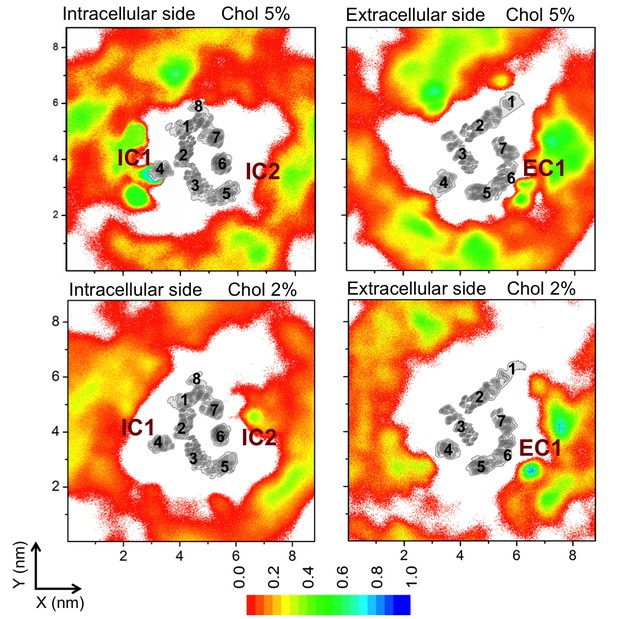
Cholesterol density around the receptor at low cholesterol concentrations.
Two-dimensional (2D) averaged and normalized number densities of cholesterol around β2AR shown at low cholesterol concentrations (2 and 5 mol%). The intracellular and extracellular leaflets are depicted separately. The intracellular and extracellular sides of the transmembrane regions of β2AR are shown in gray scale (the darker the color, the higher is the number density), and they are numbered accordingly to show the locations of the individual helices (H1–H7).
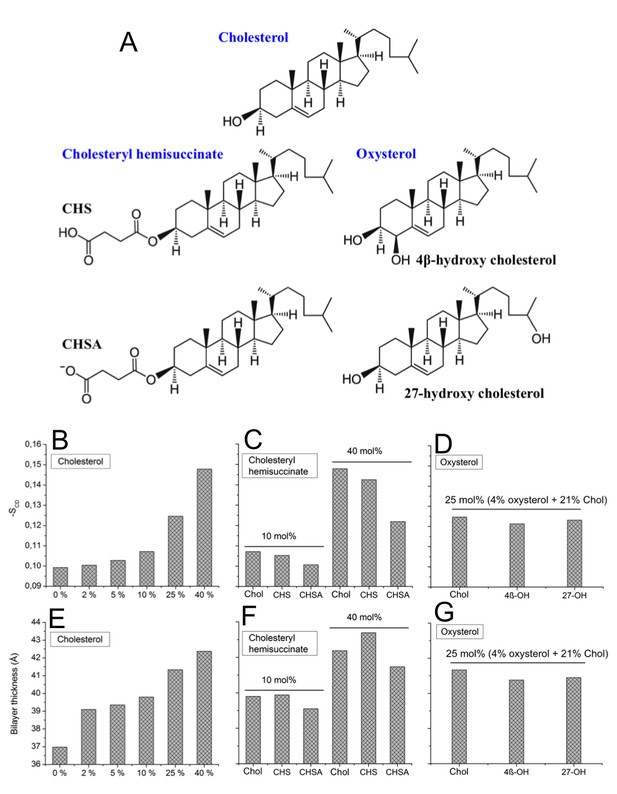
Structure of cholesterol analogues and properties of sterol-containing bilayers.
(A) The different cholesterol analogues used in the current study. (B–D) Average lipid chain order parameter SCD of DOPC bilayers with different concentrations of cholesterol or cholesterol-analogues. (E–G) Average bilayer thickness in DOPC bilayers with different concentrations of cholesterol or cholesterol-analogues. Error bars for order parameter and thickness are less than 0.02 and 0.005 Å, respectively.
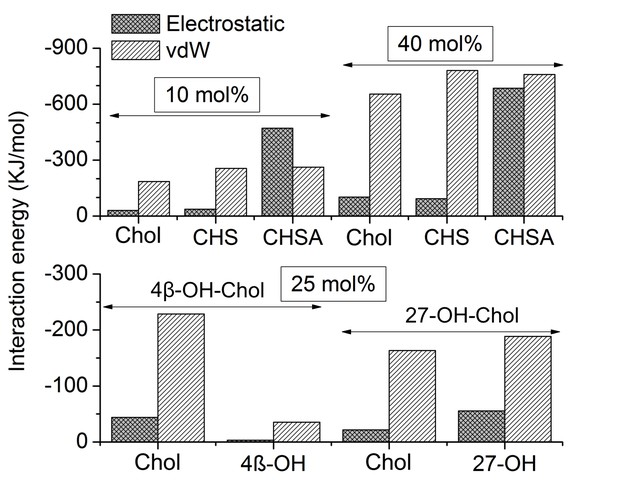
Interactions of cholesterol and cholesterol-like molecules with β2AR.
The average interaction energies for van der Waals (vdW) and electrostatic interactions are determined separately. Error bars are in the range of 0.1–1 kJ/mol. The lower panel represents the oxysterol-containing systems, where a fraction of cholesterol is replaced by 4β-OH-Chol and 27-OH-Chol, respectively, resulting in bilayers with 4 mol% oxysterol and 21 mol% cholesterol.
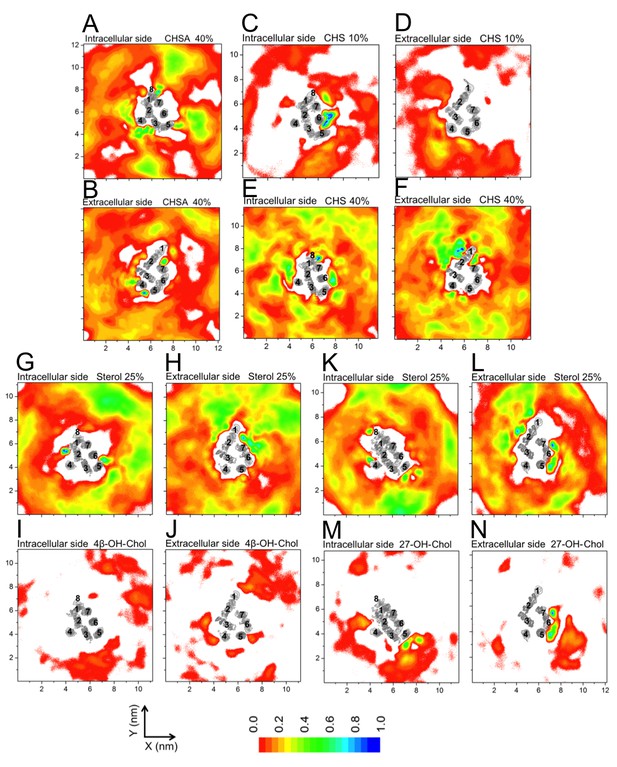
Densities of sterols around β2AR.
Normalized 2D average number densities around β2AR: (A–B) CHSA (the deprotonated form of cholesteryl hemisuccinate (CHS)); (C–F) CHS. Densities of sterols in mixed sterol-containing bilayers with other molecules: (G–H) 4β-hydroxy-Chol (4β-OH-Chol); (K–L) 27-hydroxy-Chol (27-OH-Chol). The densities of 4β-OH-Chol and 27-OH-Chol are shown separately: (I–J) 4β-OH-Chol; (M–N) 27-OH-Chol. For descriptions of models, see Table 1. For each system, the intracellular and extracellular bilayer leaflets are depicted separately. The intracellular and extracellular sides of β2AR transmembrane regions (H1–H7) are shown in gray scale (the darker the color, the higher the number density) and numbered accordingly.
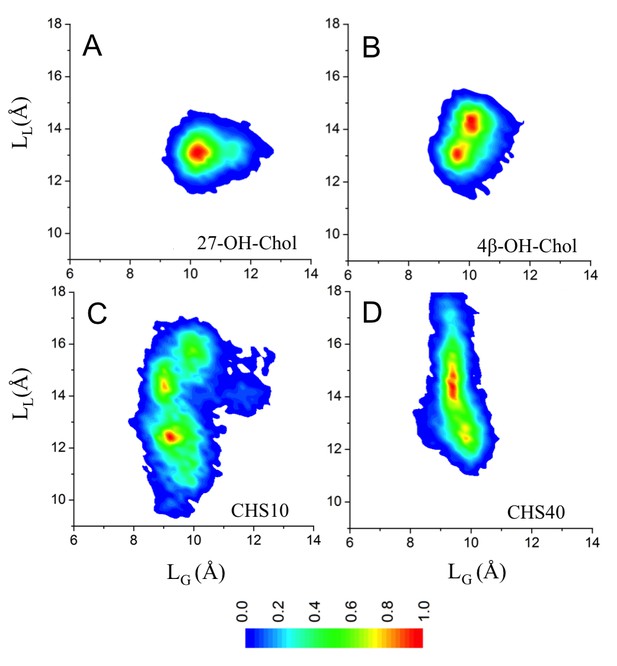
Conformational distributions of β2AR in lipid bilayers with different cholesterol analogues.
(A–B) Oxysterol-containing systems having 4 mol% of oxysterol (27-OH-Chol or 4β-OH-Chol) and 21% cholesterol. (C–D) DOPC bilayer with 10 mol% and 40 mol% of CHS. Conformational distributions are calculated over all independent trajectories of a given system, where the equilibration time (100 ns) is disregarded from the analysis. The CαD1133.32–CαS2075.46 (defined as LL) and CαR1313.50–CαE2686.30 (LG) distances represent the fluctuations in the ligand and the G protein-binding sites, respectively.
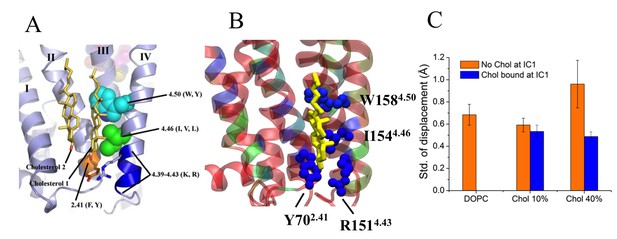
IC1 interaction site.
Specific cholesterol binding site in β2AR with the cholesterol consensus motif displayed with side chain positions of the conserved amino acid residues, as found in (A) the crystal structure (ref. 17) and (B) during our simulation. In the simulation snapshot, residues are colored according to their strength of interaction with cholesterol (red represents the weakest and blue represents the strongest interaction). (C) As to the time-dependent distance between H4 and its average position, as the H4 helix fluctuates around its average location, shown here are results for the standard deviation of the distance fluctuations. Data are given for cases, where IC1 is occupied (blue) or unoccupied (orange) by cholesterol.
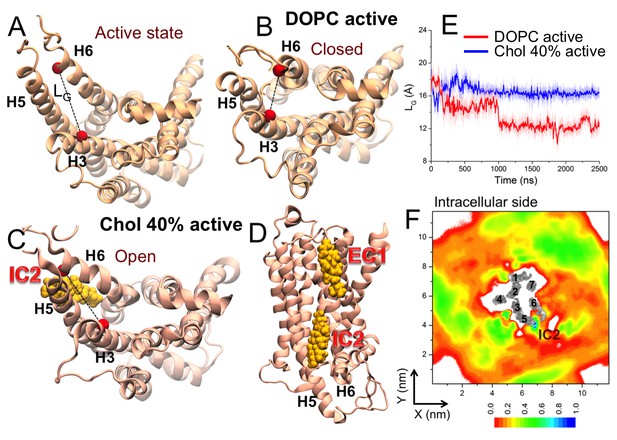
Effect of cholesterol on the active conformation of β2AR.
Cytosolic view of β2AR (A) in the beginning of a simulation (active state) as well as in representative simulation snapshots in (B) a DOPC bilayer and (C) in the presence of 40 mol% cholesterol. The dotted line represents the distance between the Cα atoms of R1313.50–E2686.30 (defined as LG), used to measure the fluctuation at the G protein-binding site. (D) Simulation snapshot (in the presence of 40 mol% cholesterol) showing cholesterol binding at the interaction sites of β2AR. (E) The time evolution of LG in systems with 0 (light red) and 40 mol% cholesterol (light blue). Corresponding 50-point running averages are shown in dark colors (red, blue). (F) 2D number densities of cholesterol around β2AR (cytosolic view). The individual transmembrane helixes of β2AR are numbered and shown in gray scale (as in Figure 2A,B).
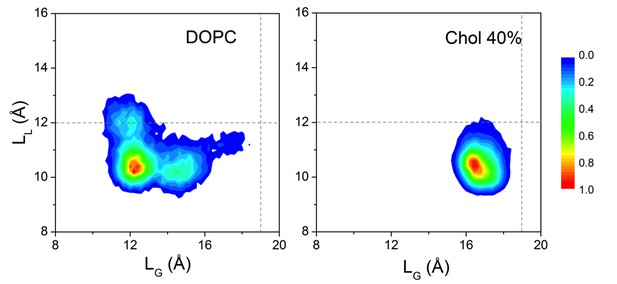
Conformational distribution of β2AR starting from the active state.
The conformational distributions of β2AR in (left) a DOPC bilayer and (right) a DOPC bilayer with 40 mol% cholesterol (Chol) as a function of LL and LG. The gray dotted lines represent the corresponding LL and LG values in the initial active crystal structure of β2AR. The distribution is averaged over the different replicas of each system.
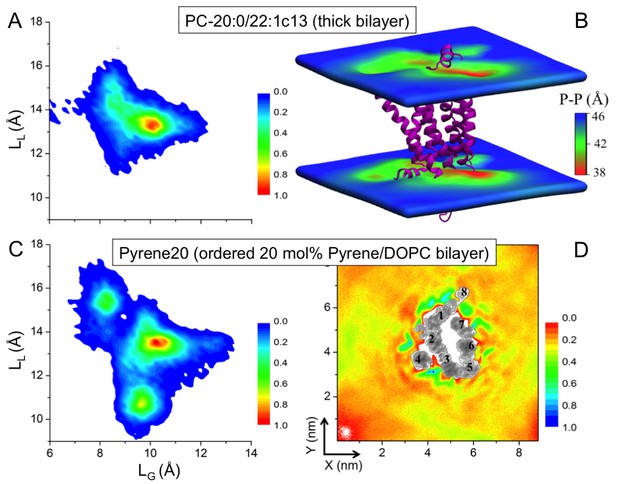
Impact of membrane-mediated effects on the β2AR conformation.
The conformational distribution of β2AR in bilayers composed of (A) long-chain PC-20:0/22:1 c13 lipids and (C) DOPC with 20 mol% pyrene (Pyrene20). (B) 3D-distribution of bilayer thickness in the thicker PC-20:0/22:1 c13 membrane. The receptor is shown as a purple cartoon. (D) 2D number density of pyrene around β2AR.
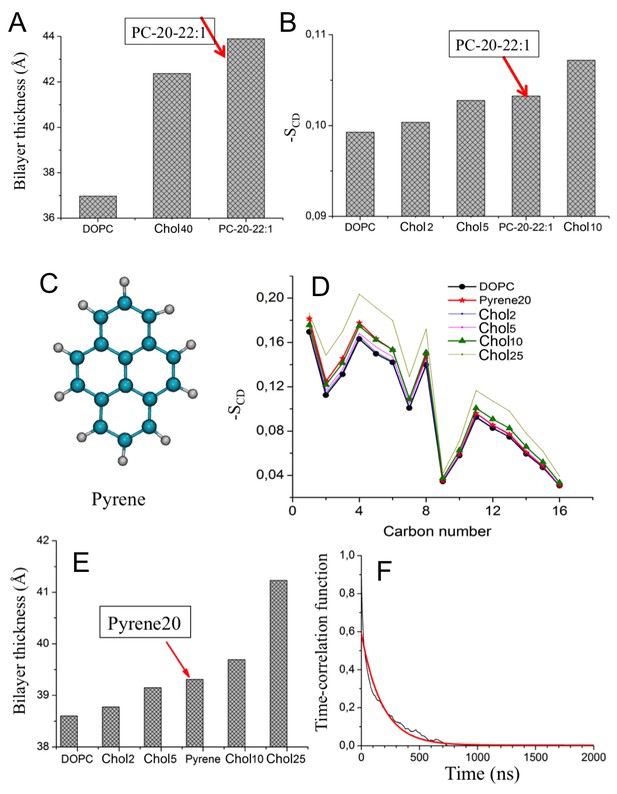
Properties of thick and/or ordered cholesterol-free bilayers.
(A–B) Long-chain PC bilayer properties compared to those of cholesterol-rich and DOPC systems. (A) The average bilayer thickness in several different bilayer systems (see Table 1). (B) The average lipid chain order parameter of a bilayer composed of long-chain PC-20:0/22:1 c13 lipids. Error bars for thickness and order parameter are less than 0.005 Å and 0.02, respectively. Panels (C–F) show results of pyrene-containing bilayer systems. (C) The structure of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon compound pyrene. Bilayer properties of the pyrene-containing membrane: (D) lipid chain order parameter and (E) the average bilayer thickness, in comparison with other cholesterol-containing bilayers. Error bars for thickness are less than 0.005 Å. (F) The probability of finding pyrene at the β2AR surface. The corresponding fit based on exponential decay is shown in red.
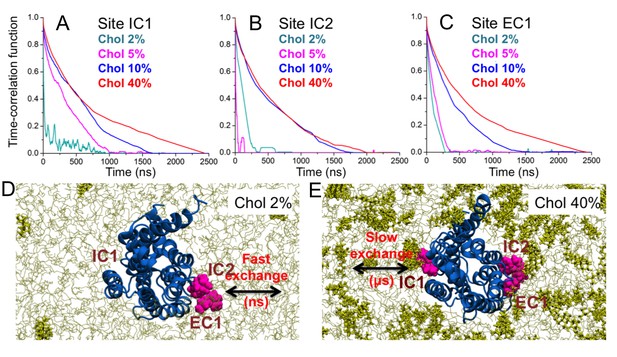
Binding time of cholesterol.
(A–C) Time-correlation function of cholesterol (Chol) at the three major interaction sites (IC1, IC2, EC1) on the β2AR surface. Initially cholesterol is bound to the site (distance ≤ 0.5 nm) and the correlation function describes the probability that cholesterol remains bound to the given site for increasing time. Data are shown for DOPC-cholesterol membranes with 2, 5, 10, and 40 mol% of cholesterol. (D–E) Schematic representation showing the transition from fast to slow exchange as cholesterol concentration increases from 2 to 40 mol%. Color code: β2AR (blue), DOPC (thin grey lines), cholesterol molecules bound to the interaction sites (purple), and other cholesterol molecules not bound to the receptor (yellow sticks).
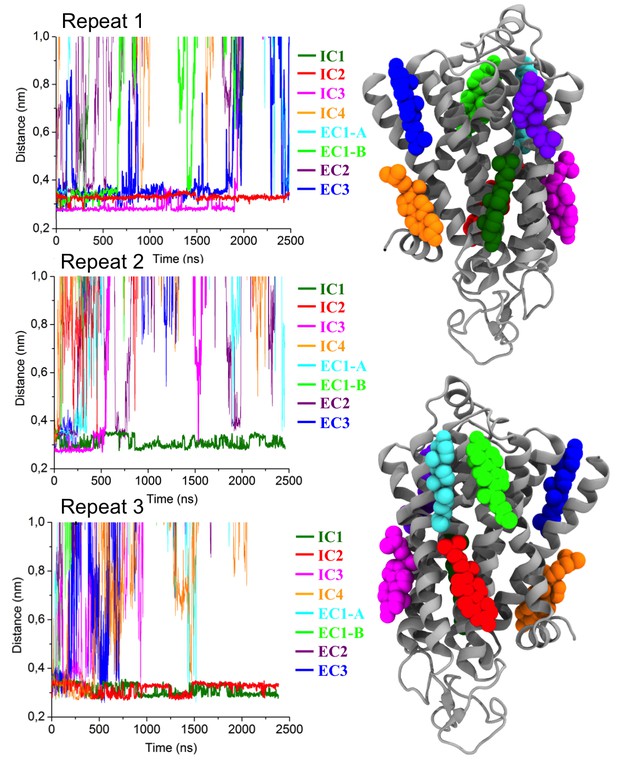
Interaction of cholesterol with β2AR.
Time development for the distances of cholesterol molecules from the β2AR surface, where these cholesterol molecules were initially bound at the eight binding sites identified in this study (cholesterol-bound, see Table 1; Figure 2—figure supplement 1). Here, EC1-A and EC1-B stand for the two cholesterol molecules in the EC1 binding site. The rest of the membrane was initially cholesterol-free. Shown here are the data based on the three independent repeats.
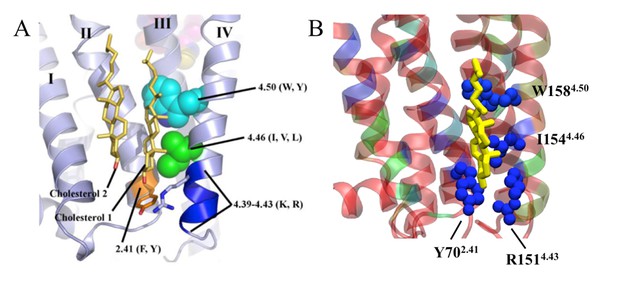
Specific cholesterol binding site in β2AR with CCM displayed with side chain positions of conserved amino acid residues, as found in (A) the crystal structure (1) and (B) during our simulation.
In the simulation snapshot, residues are colored according to their strength of interaction with cholesterol (red represents the weakest and blue represents the strongest interaction).
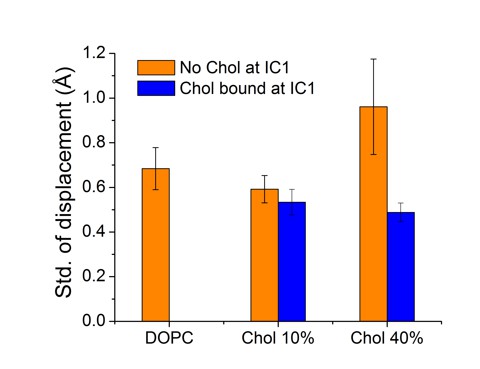
For the time-dependent distance betweenH4 and its average position, as the H4 helix fluctuates around its average location, shown here are results for the standard deviation of the distance fluctuations.
Data are given for cases, where IC1 is occupied (blue) or unoccupied (orange) by cholesterol.
Distributions of LL and LG distances from individual trajectories (shown in different colors) for various cholesterol concentrations.
https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18432.028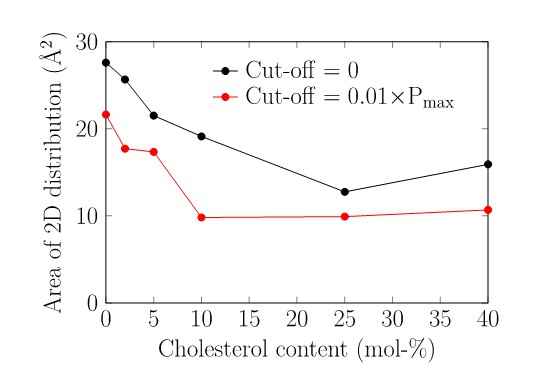
Area in the 2D histogram visited by the receptor conformations.
The bin edge length was set to 0.1 Å in both dimensions.
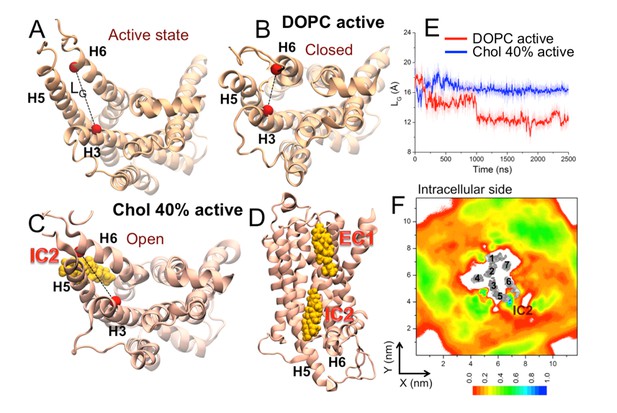
Cytosolic view of β2AR (A) in the beginning of simulation (active state) as well as in representative simulation snapshots in (B) a DOPC bilayer and (C) in the presence of 40 mol% cholesterol.
The dotted line represents the distance between the Cα atoms of R1313.50–E2686.30 (defined as LG) used to measure the fluctuation at the G protein binding site. (D) Simulation snapshot (in the presence of 40 mol% cholesterol) showing cholesterol binding at the interaction sites of β2AR. (E) The time evolution of LG in systems with 0 (light red) and 40 mol% cholesterol (light blue). Corresponding 50-point running averages are shown in dark colors. (F) 2D number densities of cholesterol (Chol) around β2AR (cytosolic view). The transmembrane regions of β2AR are shown in gray scale (the darker the color, the higher is the number density), and they are numbered accordingly to show the locations of the individual helices (H1-H7).
Videos
Spontaneous binding/unbinding of cholesterol at the three main cholesterol interaction sites of β2AR during a 2.5-μs simulation with 10 mol% of cholesterol.
Cholesterols interacting at the cholesterol-binding sites are highlighted (yellow at IC1; green at IC2; and blue and red at EC1). Other cholesterols are shown in gray. For clarity, other lipids in a membrane are not shown.
Spontaneous binding/unbinding of cholesterol at the three main cholesterol interaction sites of β2AR during a 2.5-μs simulation with 40 mol% of cholesterol.
Cholesterols interacting at the cholesterol-binding interaction sites are highlighted (yellow and green at IC1; red, blue and orange at IC2; and pink, purple and cyan at EC1). Other cholesterols are shown in gray. For clarity, other lipids in a membrane are not shown.
Tables
Descriptions of systems simulated: β2AR in bilayers with varying lipid compositions. ‘Chol’ stands for cholesterol.
Systems* | Initial lipid arrangement around β2AR | Lipids | Sterol mol % | No. of repeats† | Time (μs)‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
DOPC | Random | DOPC | 0 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
DOPC-active | Random | DOPC | 0 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
C H O L | Chol2 | Random | DOPC + Chol | 2 | 3 | 3×2.5 | R A N D O M |
Chol5 | Random | DOPC + Chol | 5 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
Chol10 | Random | DOPC + Chol | 10 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
Chol25 | Random | DOPC + Chol | 25 | 2 | 2×2 | ||
Chol40 | Random | DOPC + Chol | 40 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
Chol40-active | Random | DOPC + Chol | 40 | 3 | 3×2.5 | ||
C H S | CHS10 | Random | DOPC + CHS | 10 | 2 | 2×2 | |
CHS40 | Random | DOPC + CHS | 40 | 2 | 2×2 | ||
CHSA10 [A for anionic] | Random | DOPC + CHSA | 10 | 1 | 2 | ||
CHSA40 | Random | DOPC + CHSA | 40 | 1 | 2 | ||
O X Y S T E R O L | 27-OH-Chol | Random [16 mol % Chol was randomly replaced by 27-OH-Chol] | DOPC + Chol + 27-OH-Chol | 25 (4 mol% 27-OH-Chol + 21 mol% Chol) | 3 | 2 + 1 + 1 | |
4β-Chol | Random [16 mol% Chol was randomly replaced by 4β-OH-Chol] | DOPC + Chol + 4β-OH-Chol | 25 (4 mol% 4β-OH-Chol + 21 mol% Chol) | 3 | 1 + 1 + 1 | ||
Chol-Bound§ | 8 cholesterols bound at sites predicted by simulations | DOPC + Chol | 1.9 | 3 | 3×2.5 | B O U N D | |
Chol-IC1 | 2 Chol bound at IC1 | DOPC + Chol | <1 | 2 | 2×2 | ||
CHS-IC1 | 2 CHS bound at IC1 | DOPC + CHS | <1 | 1 | 2 | ||
CHSA-IC1 | 2 CHSA bound at IC1 | DOPC + CHSA | <1 | 1 | 2 | ||
PC-20:0–22:1 c13 [Double bond at carbon 13] | Random | PC-20:0–22:1 c13 | 0 | 3 | 3×1.5 | ||
Pyrene20 | Random | DOPC + 20 mol% pyrene | 0 | 3 | 3×1.5 |
-
*In the DOPC-active and Chol40-active systems, we used the active-state conformation of the receptor as the starting structure; for all the other systems, we used the inactive conformation.
-
†For systems with no sterols initially bound to β2AR, i.e., the systems which started with a random distribution of lipids, a number of different repeat simulations for each lipid composition were performed with different initial lipid arrangements around the receptor. For systems with sterols initially bound to β2AR (seed and BOUND), different replicas were generated with different starting velocities.
-
‡Listed are the simulation times of production simulations; the equilibration time of the systems (100 ns) is not included.
-
§In the Chol-Bound system, eight cholesterol molecules were initially (at time zero of the simulation) bound at eight binding sites predicted by the present simulations, while the rest of the system had no cholesterol at all.
Interactions* of sterols at the three high-affinity cholesterol-binding sites.
Cholesterol/Cholesterol analogue | High-affinity cholesterol interaction sites | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
IC1 | IC2 | EC1 | ||||
vdW interaction energy (kJ/mol) | No. of contacts | vdW interaction energy (kJ/mol) | No. of contacts | vdW interaction energy (kJ/mol) | No. of contacts | |
Cholesterol† | −138.04 ± 0.20 | 141.02 ± 0.22 | −95.06 ± 0.12 | 90.65 ± 0.16 | −129.51 ± 0.29 | 104.38 ± 0.28 |
CHS | −29.63 ± 0.14 | 28.78 ± 0.16 | −98.75 ± 0.11 | 96.30 ± 0.16 | - | - |
27-OH-Chol | −32.17 ± 0.30 | 34.95 ± 0.33 | −22.69 ± 0.23 | 28.41 ± 0.28 | −132.85 ± 0.27 | 120.20 ± 0.30 |
4β-OH-Chol | - | - | - | - | −41.80 ± 0.48 | 33.41 ± 0.42 |
-
* Shown are the total van der Waals (vdW) interaction energy and the number of contacts between cholesterol and β2AR, when cholesterol is in the IC1, IC2, or EC1 binding site (and similarly for the cholesterol analogues).
-
† Calculations are based on systems having ≥10 mol% cholesterol. Shown here are the average values over different trajectories.





