A team of heterochromatin factors collaborates with small RNA pathways to combat repetitive elements and germline stress
Figures
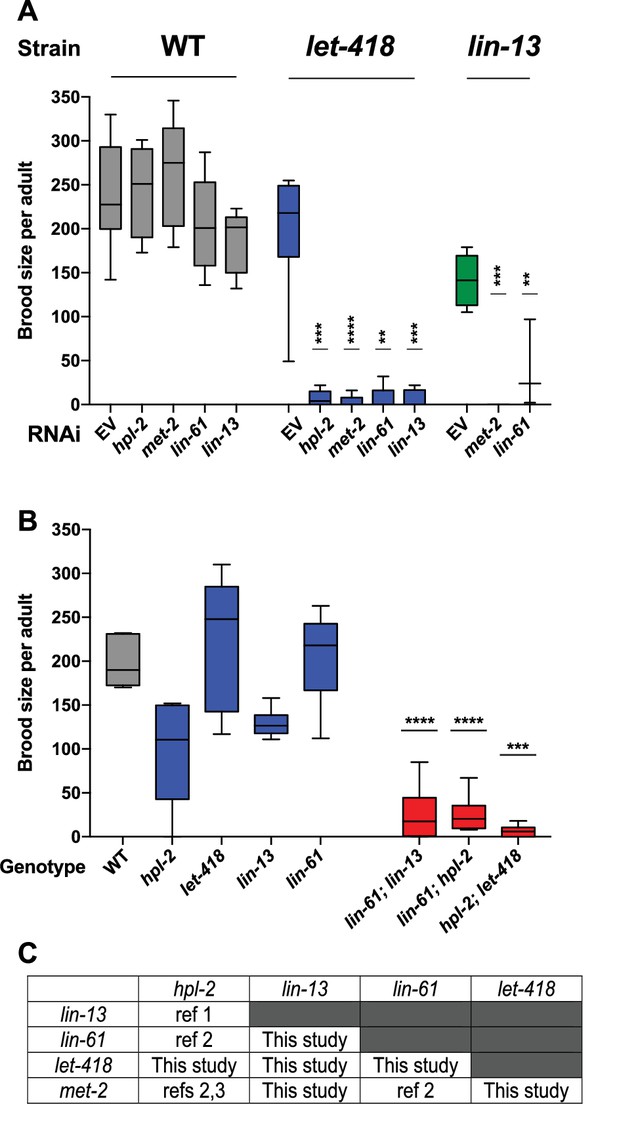
Heterochromatin proteins have redundant roles in fertility.
(A) Genetic interactions in fertility assayed using RNAi. Indicated RNAi of wild-type, let-418(n3536), or lin-13(n770) was conducted by feeding at 20°C as described in the methods. Results are a combination of two independent experiments with the progeny of 3–8 total broods counted for each strain/RNAi combination. A one-sided t-test was used to determine whether the mutant/RNAi combination had a lower brood size than expected under a multiplicative model of interaction when compared to the mutant grown on empty vector RNAi and the individual RNAi knockdowns in wild-type animals. Brood size is significantly lower than expected for all RNAi/mutant combinations at p<0.05. (B) Indicated double mutants were constructed and their brood sizes compared to that of the individual signal mutants raised at 20°C. Statistical testing was as in (A), with brood sizes of the three double mutants significantly lower than expected at p<0.05 in a one-sided t-test. (C) All pairs of hpl-2, lin-13, lin-61, let-418, and met-2 show genetic interactions in fertility, as determined in this study or previous studies. ref 1. Coustam et al, Dev Biol. 2006. ref 2. Koester-Eiserfunke and Fischle, PLoS Genet. 2011. ref 3. Simonet et al, Dev Biol. 2007. Supplementary file 1 shows previously reported sterility phenotypes. Figure 1—figure supplement 1 shows examples and quantification of abnormal oogenesis in heterochromatin mutants.
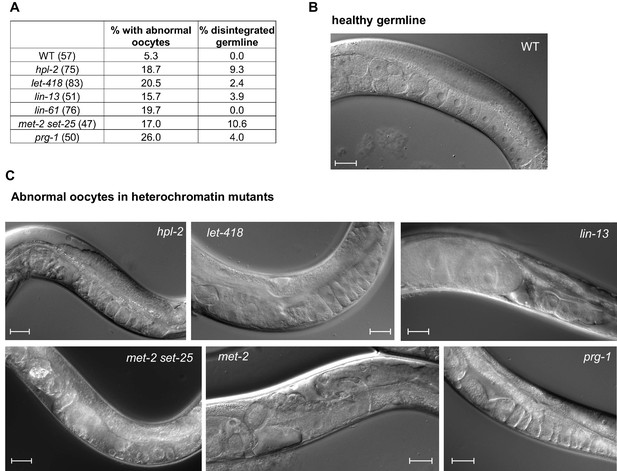
Heterochromatin mutants display abnormal oogenesis.
(A) Strains of the indicated genotype were shifted to 25°C at the L4 stage and imaged by Nomarksi microscopy 48 hr later. Oocyte quality was determined and deemed ‘abnormal’ when oocytes appeared small, round and gapped, showing the appearance of a curdled cytoplasm, or when they were unaligned and disorganized. Numbers in brackets denote the total number of germlines scored. Disintegrated germline refers to the absence of oocytes and an apparent disintegration of (most of the) gonad arm. Representative images of several of the mutants are shown. Scale bar is 33 µm.
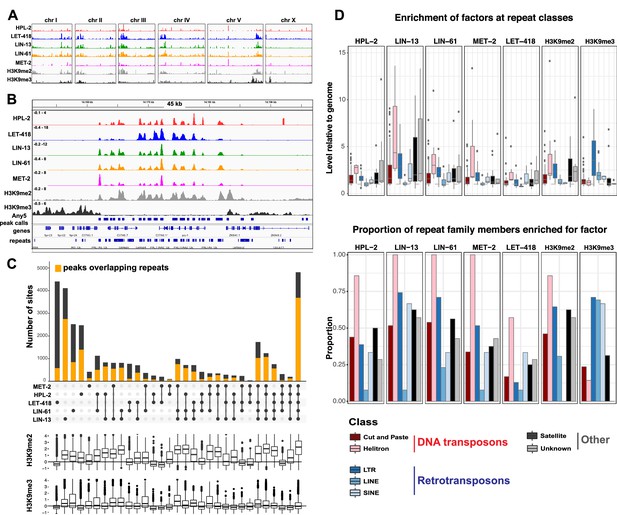
HPL-2, LET-418, LIN-13, LIN-61, and MET-2 show extensive co-binding and are enriched at repetitive elements.
(A) Distribution of the indicated proteins and histone modifications over each C. elegans chromosome. z-scored ChIP-seq tracks are shown for HPL-2 (red), LET-418 (blue), LIN-13 (green), LIN-61 (orange), MET-2 (pink), H3K9me2 (grey) and H3K9me3 (black) on each chromosome, demonstrating enrichment over the autosomal arms. Figure 2—figure supplement 1A shows distributions of peak locations in different chromosome regions. (B) IGV browser screenshot showing similar patterns of the heterochromatin factors and H3K9me2 methylation over a 45 kb region containing multiple repeat elements. z-scored ChIP-seq tracks are as in (A). Any5 peak calls denote combined peak calls for any of the five proteins; repeats are from Dfam2.0 (Hubley et al., 2016). Figure 2—figure supplement 1B shows correlations in signal between all datasets. (C) UpSet plot of the association of heterochromatin factors with the 33,301 Any5 peak calls. Dots indicate peak class is bound by the factor. Bars show total number of peaks per class, the orange portion denoting overlap with repeat elements. Below the bar chart relative enrichments for H3K9me2 and H3K9me3 are shown. The peaks that overlap all five factors constitute the largest class (n = 4810). Figure 2—figure supplement 1 gives total peak numbers per factor, number of peaks overlapping repeats, and number of repeats bound by each factor. Figure 2—source data 1 gives peak calls. (D) Associations of factors and repeat classes. Upper panel: levels of indicated protein or histone modification on families within indicated Dfam 2.0 repeat classes relative to the genome average. Bottom panel: Proportion of families within each repeat class significantly enriched for indicated factor or histone modification. Criteria for enrichment are >1.5 fold mean enrichment of family relative to genome, FDR < 0.1, considering families with at least 10 members. Number of families with 10 or more members within each class are: Cut and paste (n = 89), Helitron (n = 7), LTR (n = 31), LINE (n = 13), SINE (n = 3), Satellite (n = 16), Unknown (n = 7). Figure 2—source data 2 gives enrichment scores for repeat family factor binding.
-
Figure 2—source data 1
Peak calls.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.005
-
Figure 2—source data 2
Enrichment of factors at repeat families.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.006
-
Figure 2—source data 3
Alignment Statistics for ChIP and RNA sequencing.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.007
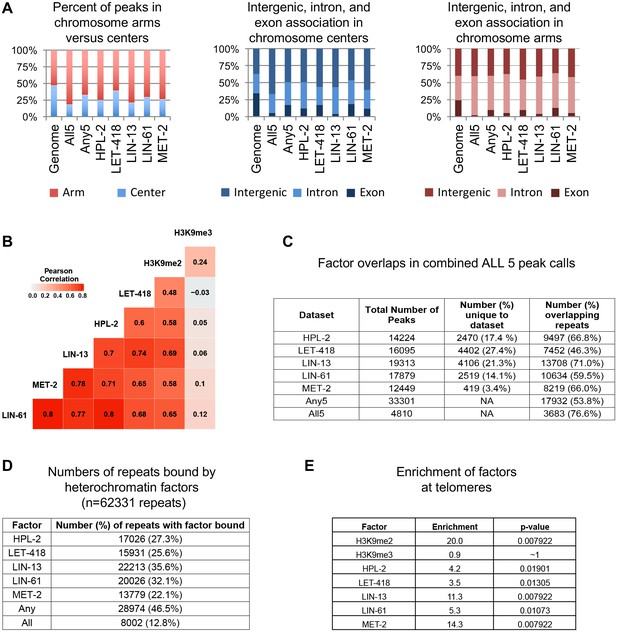
Correlation of HPL-2, LET-418, LIN-13, LIN-61, and MET-2 ChIP-seq tracks and enrichment on chromosome arms, repetitive elements, and telomeres.
(A) Distribution of HPL-2, LET-418, LIN-13, LIN-61, MET-2, All5, or Any5 ChIP-seq peaks between chromosome arms and centers (left) and between genes (introns and exons) and intergenic regions on the centers (middle) and arms (right). (B) Pearson correlation coefficients for ChIP-seq track combined replicates in 100 bp windows. (C) Number of peaks for individual data sets within the 33301 Any5 combined peak calls, the numbers unique to each dataset and the numbers of peaks overlapping repetitive elements. (D) Numbers of Dfam 2.0 repetitive elements (n = 62331) that have factors bound based on IDR peak calls (see Methods). (E) Enrichment scores for H3K9 methylation and binding of factors at telomeres.
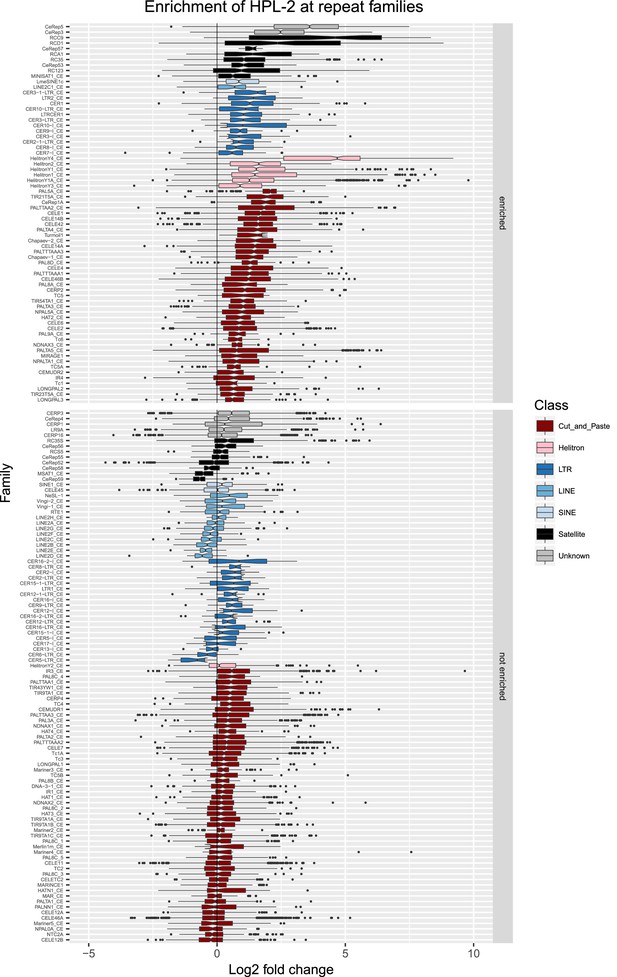
Enrichment of HPL-2 at repeat families.
Boxplots show HPL-2 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
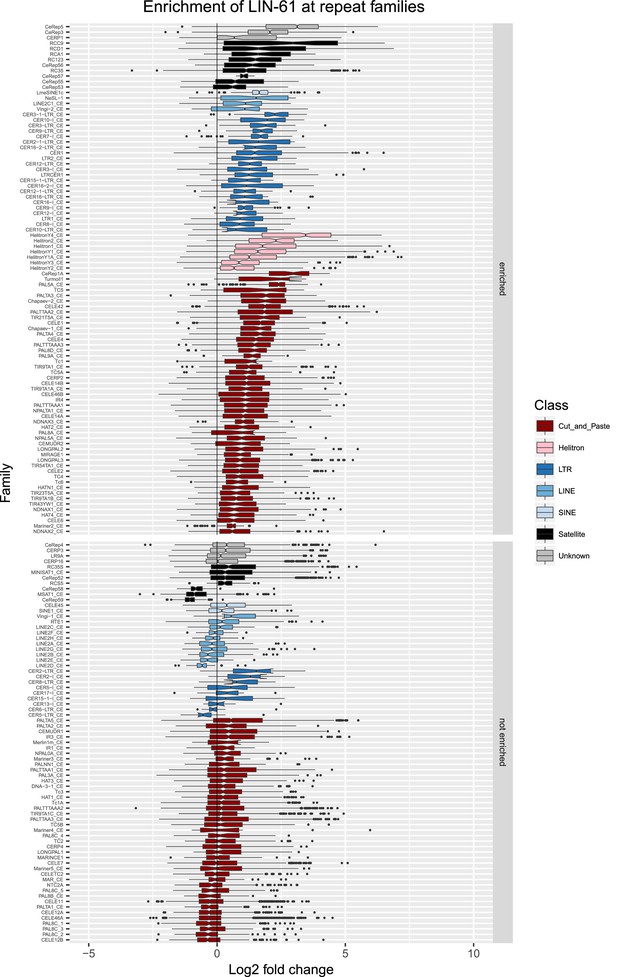
Enrichment of LIN-61 at repeat families.
Boxplots show LIN-61 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
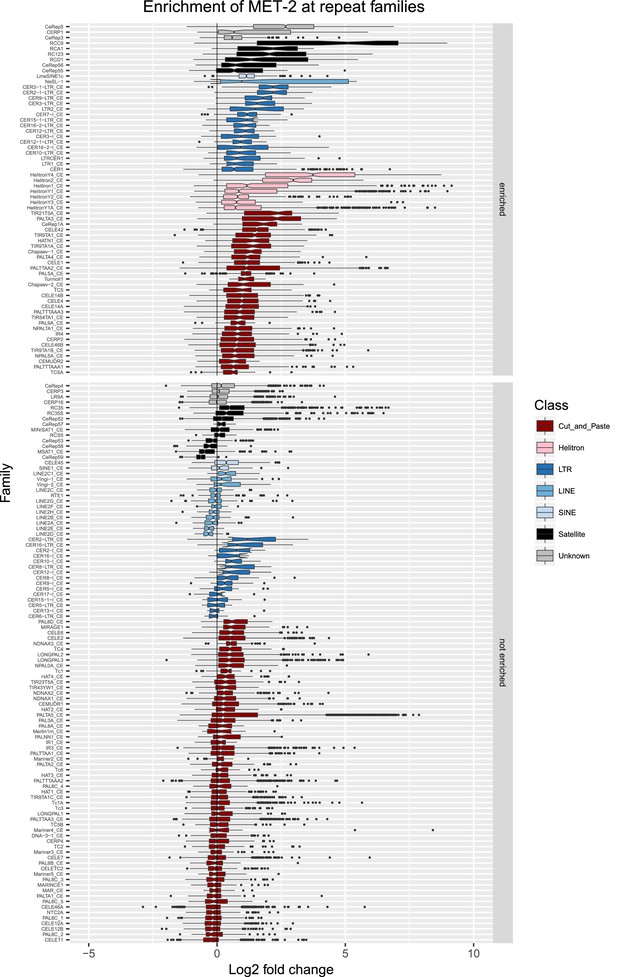
Enrichment of MET-2 at repeat families.
Boxplots show MET-2 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
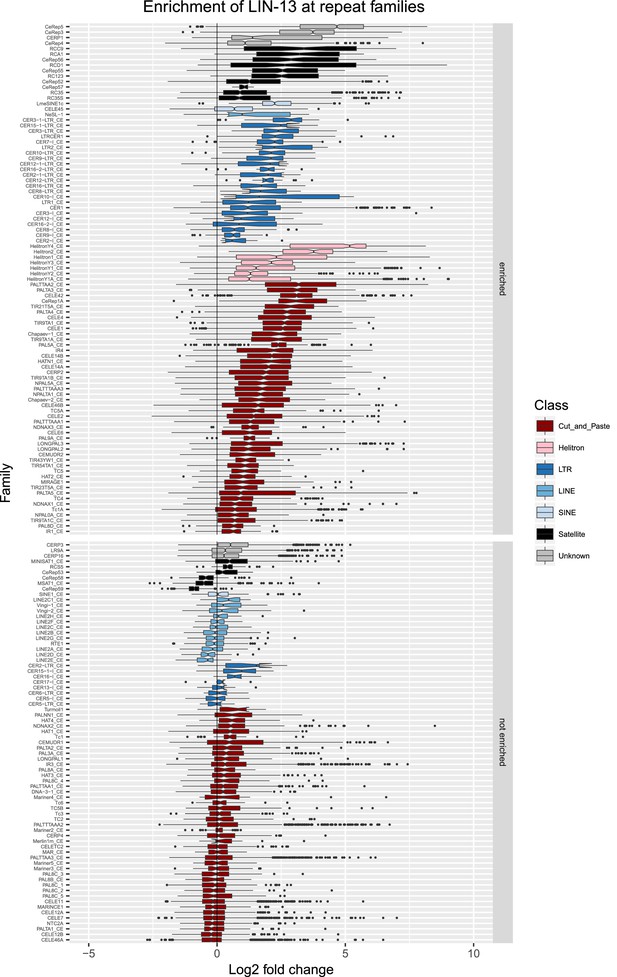
Enrichment of LIN-13 at repeat families.
Boxplots show LIN-13 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
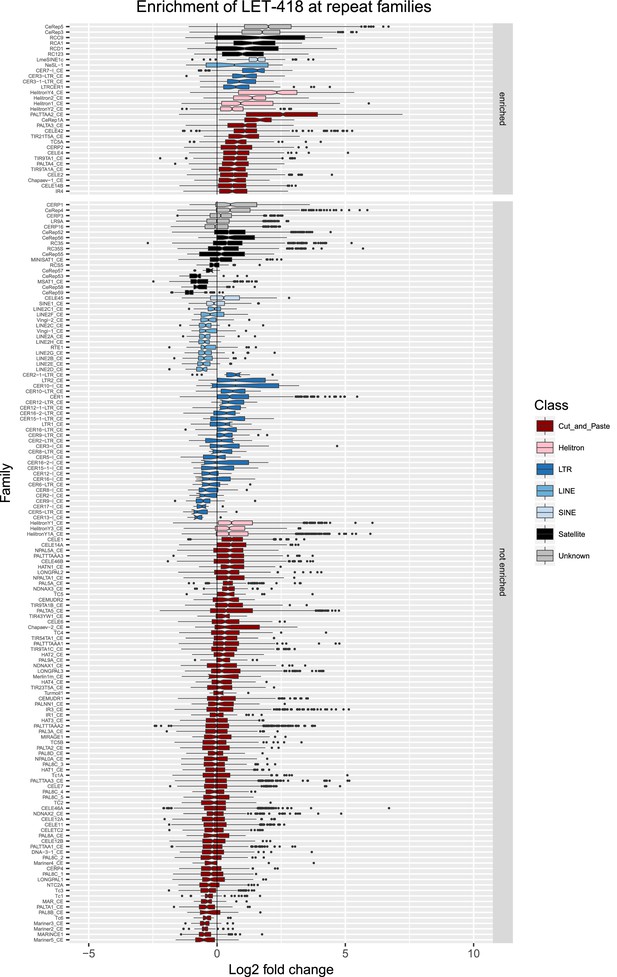
Enrichment of LET-418 at repeat families.
Boxplots show LET-418 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
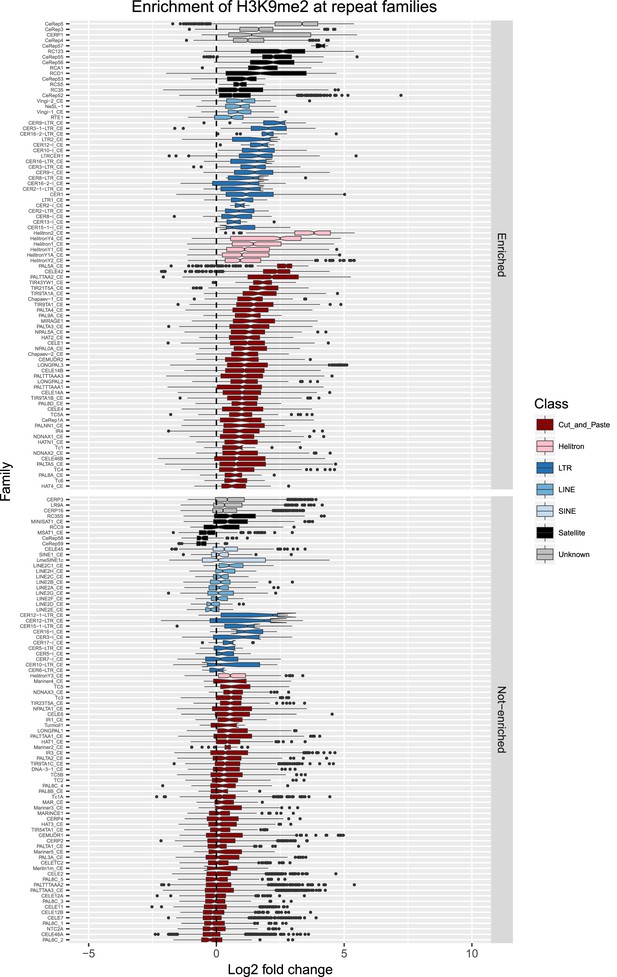
Enrichment of H3K9me2 at repeat families.
Boxplots show H3K9me2 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
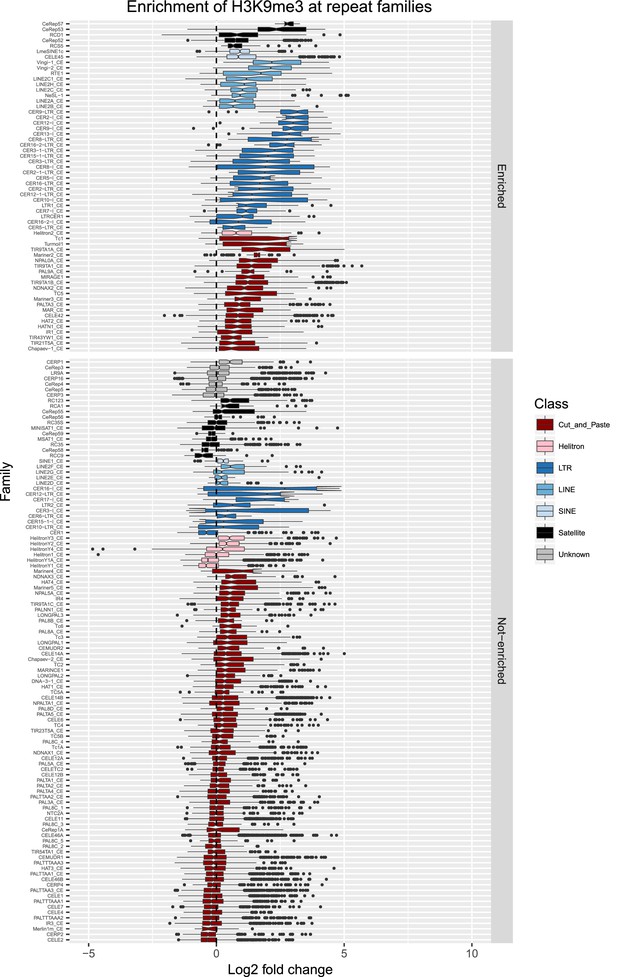
Enrichment of H3K9me3 at repeat families.
Boxplots show H3K9me3 levels measured as log2 fold change relative to the genome median for each repeat family with at least 10 individual repeat elements; boxplots are colored by repeat class. For each repeat family, significance of enrichment relative to the genome median was assessed by a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test. Repeat families with FDR<0.1 and a median fold change greater than 1.5 are labelled as enriched.
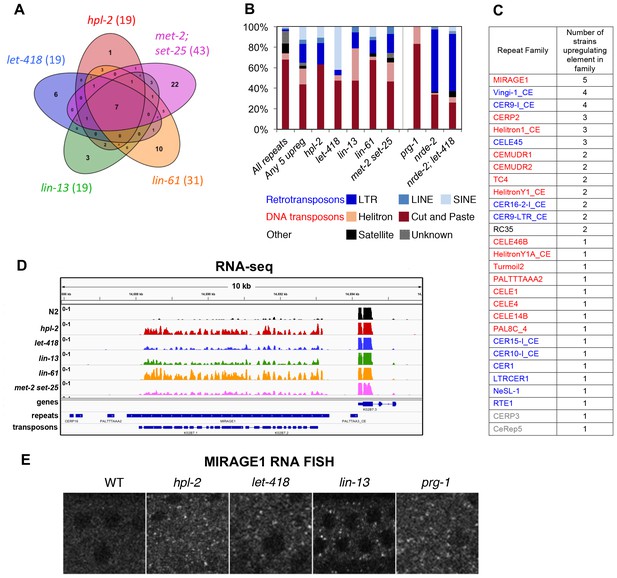
Repetitive elements are upregulated in hpl-2, let-418, lin-13, lin-61, met-2 set-25, prg-1, nrde-2, and nrde-2; let-418 mutants.
(A) Venn diagram of elements upregulated in hpl-2, let-418, lin-13, lin-61, and met-2 set-25 mutants. The seven elements upregulated in all five strains are MIRAGE1 elements. (B) Distribution of Dfam 2.0 repeat classes upregulated in each strain. (C) Repeat families with members upregulated in at least one of hpl-2, let-418, lin-13, lin-61, or met-2 set-25 mutant strains. (D) IGV browser screenshot of a MIRAGE1 element that is upregulated in all mutant strains. Tracks are reads per million of two combined replicates. Figure 3—figure supplement 1 gives further examples of elements upregulated in different strains. (E) Single molecule RNA-FISH signals of MIRAGE one element RNA in the adult germ line (white dots). Signal is not detectable in wild-type but is abundant in the indicated mutant backgrounds. Figure 3—figure supplement 3 shows additional images of MIRAGE1 and sqv-1 control RNA FISH in germline and somatic tissues. Figure 3—figure supplement 2 shows enrichment of heterochromatin factors, H3K9me2, and H3K9me3 on regulated genes and repeats.
-
Figure 3—source data 1
Analysis of repeats.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.017
-
Figure 3—source data 2
Repeats upregulated in any mutant strain.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.018
-
Figure 3—source data 3
Analysis of genes.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.019
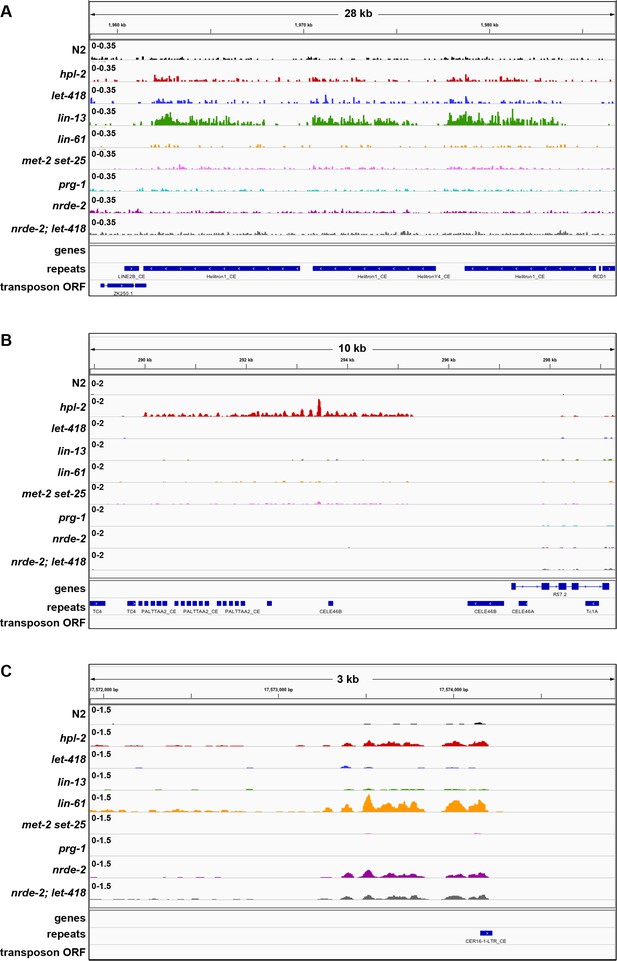
Examples of unique and co-regulated repeat elements in various heterochromatin mutants.
IGV screenshots of repeat elements upregulated in a subset of heterochromatin mutants. (A) HELITRON1 element only upregulated in lin-13 mutants. (B) PALTTAA2 and CELE46B elements only upregulated in hpl-2 mutants. (C) CER16 LTR element upregulated in hpl-2, lin-61, nrde-2 and nrde-2; let-418 mutants. Signal tracks are RPM normalized. Additional tracks show genes, Dfam2.0 repeats, and transposon ORFs.
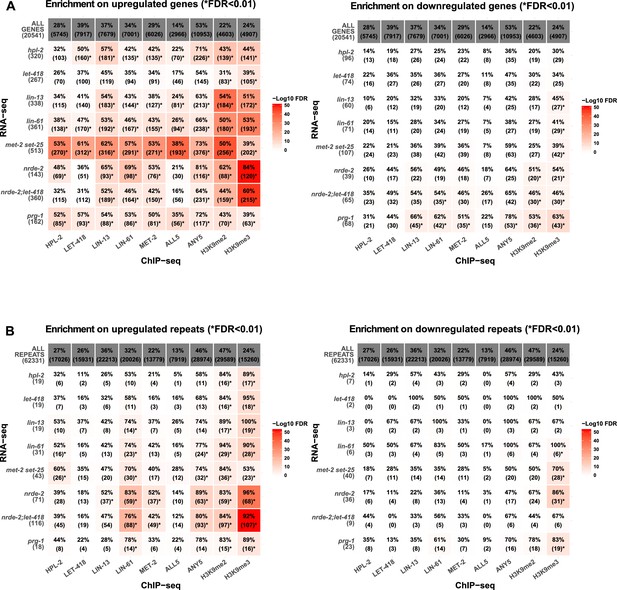
Heterochromatin factors and H3K9 methylation show enriched association with upregulated genes and repeats.
(A) Percent overlap of heterochromatin factor peaks or >1.5 fold enrichment for H3K9me2 or H3K9me3 on upregulated (left) or downregulated (right) genes (−500 bp to gene end). Parentheses give number of genes with overlap, star indicates FDR < 0.01. (B) Enrichment of factors over upregulated repeats in each of the mutant strains.
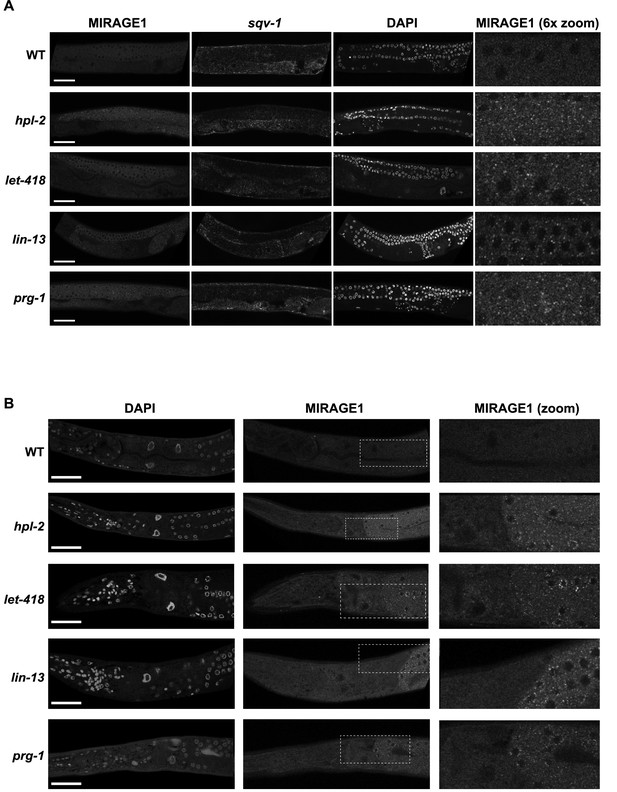
MIRAGE1 RNA is upregulated in the germ lines of hpl-2, lin-13, let-418, and prg-1 mutants.
(A) Single molecule RNA-FISH signals of MIRAGE 1 RNA in the adult germ line (left panels; zoomed in on the right). Middle panels show sqv-1 (positive control) RNA-FISH and DAPI to counterstain nuclei. (B) Single molecule RNA-FISH signals of MIRAGE 1 RNA, showing both germline and somatic tissues. MIRAGE1 (middle and indicated boxes zoomed in on the right) is increased in mutant germlines but remains low in the soma. Left, DAPI counterstain. Scale bar represents 30 µm.
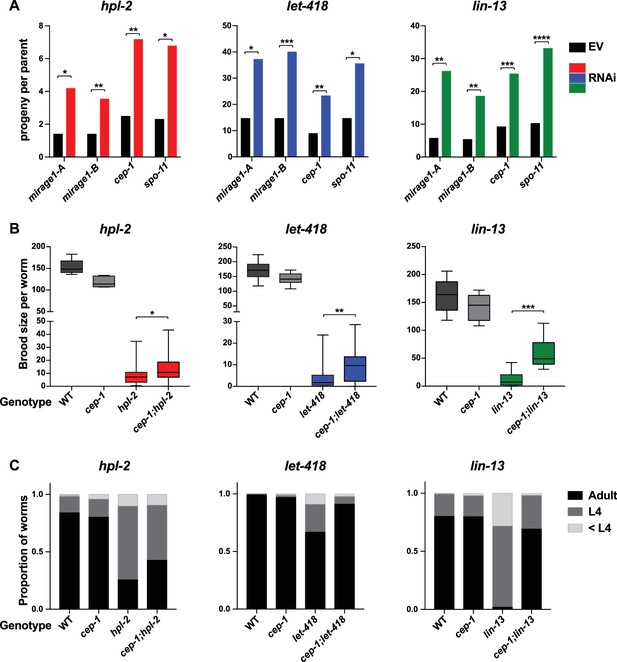
Phenotypic suppression of hpl-2, let-418 and lin-13 by inhibition of MIRAGE1, cep-1/p53, or spo-11.
(A) RNAi of MIRAGE1, cep-1/p53 or spo-11 partially suppresses sterility of hpl-2, let-418, and lin-13. Average number of progeny per worm for control empty vector RNAi (EV) or the indicated RNAi treatments in hpl-2(tm1489), let-418(n3536), or lin-13(n770) (averages of 5–11 experiments). Experiments were done under conditions where the mutant strain was nearly sterile to detect an increase in fertility (see Materials and methods). Control progeny numbers vary by experiment, but were always paired with experimental RNAi. Stars indicate statistical significance assessed using paired t-tests, comparing experimental to control RNAi (p<0.05, one star; p<0.01, two stars; p<0.001, three stars). Two sets of RNAi clones were used to target MIRAGE1 elements (termed mirage-A and mirage-B). RNAi clones used are given in the methods. (B) Mutation of cep-1/p53 partially suppresses sterility of hpl-2, let-418, and lin-13 mutants at 25°C. Statistical significance was assessed using single sided t-tests, asking if cep-1; hpl-2, cep-1; let-418, and cep-1; lin-13 double mutants had larger broods than the corresponding heterochromatin single mutants. See methods for growth conditions. (C) Loss of cep-1 partially rescues growth delay defect of heterochromatin mutants at 25°C. Developmental stage of worms grown from L1 at 25C for approximately 48 hr was assessed (adult, L4, younger than L4). A representative experiment out of three replicates is shown, assaying between 95 and 213 worms in each. See methods for growth conditions.
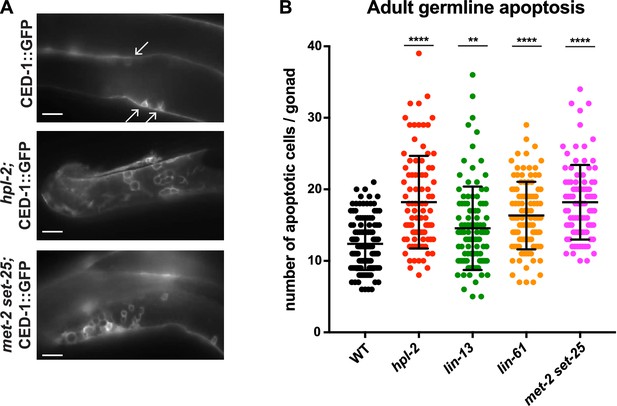
Heterochromatin mutants have increased germline apoptosis.
CED-1::GFP (bcIs39 [Plim-7::ced-1::gfp]), expressed in gonad sheath cells, marks engulfed apoptotic cells in the pachytene region of the adult gonad. (A) CED-1::GFP images for wild type, hpl-2, and met-2 set-25 mutant gonads. Arrows point to engulfed apoptotic cells; scale bar = 16 um. (B) Number of apoptotic cells per gonad arm for wild-type (bcIs39), hpl-2(tm1489); bcIs39, lin-13(n770); bcIs39, and met-2(n4256) set-25(n5021); bcIs39. Shown are the combined data points of at least three independent replicates; each dot represents an individual gonad arm count. Bars denote mean and SD. Mann-whitney non-parametric tests were performed on mutant versus control. (p-values for hpl-2, lin-61, met-2 set-25 are <0.0001; p-value for lin-13 is 0.009). Strains were cultured at 20°C and scored 48 hr after the L4 stage. Figure 5—figure supplement 1 shows increased sensitivity of hpl-2 to IR-induced DNA damage.
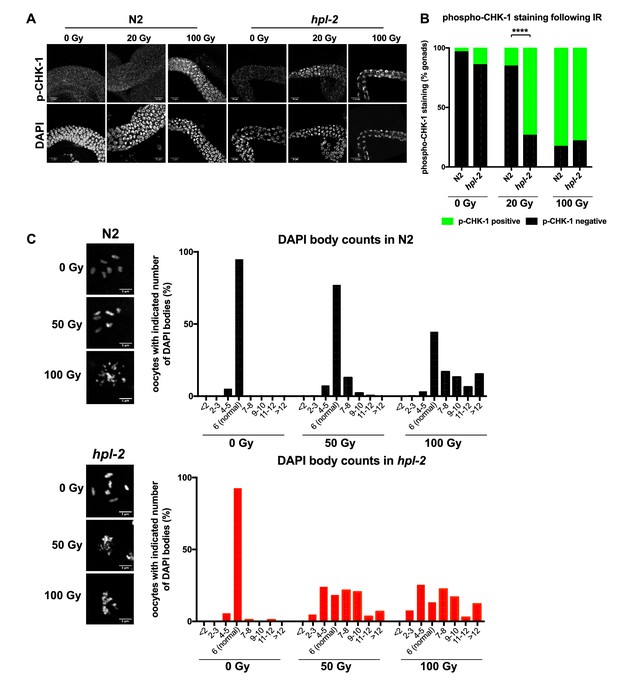
hpl-2 mutants are hypersensitive to ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage.
(A) Phospho-CHK-1 staining of adult germ lines 1 hr post IR treatment. Bars are 10 µm. (B) Quantification of phospho-CHK-1 staining. hpl-2 mutants showed significantly more phospho-CHK-1 positive gonads than wild-type at an intermediate dose of 20 Gy. Strains were grown at 25°C. (C) Images and counts of oocyte chromosomes and fragments following IR. N2 and hpl-2(tm1489) were grown at 20°C, irradiated at 0, 50, and 100 Gy at the L4 stage, and stained with DAPI after 24 hr. Left, representative photographs of N2 and hpl-2 oocytes. Right, counts of DAPI stained fragments in oocytes at the indicated dose of IR. The majority of non-irradiated N2 and hpl-2 oocytes have six distinct DAPI bodies, representing the six bivalent chromosomes. hpl-2 mutants show more fragmentation of oocyte chromosomes at 50 and 100 Gy, indicating a defect in repair of exogenous DNA damage. Bars are 5 µm. A minimum of 88 oocytes were scored over two to three independent experiments.
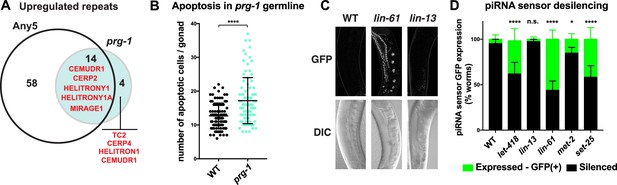
Heterochromatin factors interact with the piRNA pathway.
(A) Venn diagram showing extent of overlap between repeats upregulated in prg-1 mutants and repeats upregulated in any of the five heterochromatin factor mutant strains (hpl-2, let-418, lin-13, lin-61, or met-2 set-25). Listed in the Venn are the numbers of repeats and repeat families common or unique to prg-1. (B) prg-1 mutant germ lines show increased germ cell death. Shown are the number of apoptotic cells per gonad arm for bcIs39 (CED-1::GFP) and prg-1; bcIs39 (CED-1::GFP). Each dot represents an individual gonad arm count. Bars denote mean and SD. A minimum of 25 gonads were scored per experiment and shown are the combined datapoints of at least three independent replicates. Mann-whitney non-parametric tests were performed on mutant versus control (p-value<0.0001). Strains were cultured at 20°C until L4 stage, then shifted to 25°C for 48 hr before scoring. (C, D) Heterochromatin mutants desilence a piRNA sensor. piRNA sensor expression (mjIs144 [mex-5p::HIS-58::GFP::piRNA(21UR-1)::tbb-2–3’UTR]) was quantified in one day old wild-type and heterochromatin mutants cultured at 20°C. (C) Representative GFP and DIC microscope images of adult germlines in which the reporter is silent (WT, lin-13) or expressed (lin-61). (D) Quantification of piRNA sensor expression in wild type and heterochromatin mutants. Shown are the means and standard error of the percentage of worms which at least weakly desilenced the GFP reporter in oocytes and pachytene regions. A minimum of 100 worms for each strain was assessed over four independent experiments. Fishers exact tests were performed on the combined datapoints to address significance, with let-418 (p-value<0.0001), lin-61 (p-value<0.0001) and set-25 (p-value<0.0001) all displaying increased frequency of expression of the piRNA sensor reporter, while sensor expression in lin-13 is not significantly different from wild type (p-value 0.4419). met-2 mutants weakly desilence the sensor in a small subset of adults scored (p-value 0.0215).
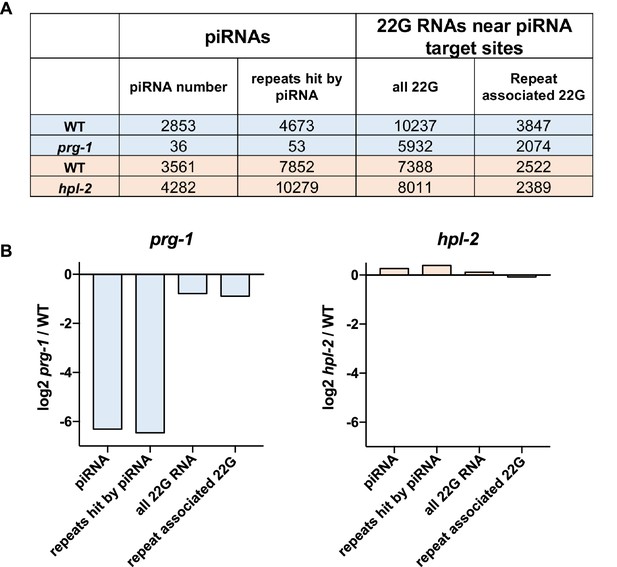
Quantification of piRNAs and dependent 22G RNAs in prg-1 and hpl-2 mutants.
(A) Unique piRNAs, repeat elements targeted by a piRNA, number of unique 22G RNAs mapping near piRNA target sites, and number of repeat elements hit by a piRNA-associated 22G RNA. The number in each class found in 530039 unique small RNA positions subsampled from each dataset (prg-1, hpl-2, and matched wild-types) is shown. (B) log2 ratios of the relative change in abundance of the indicated classes of small RNA or repeats in mutant strains compared to wild-type. Datasets used and the procedure for calculating piRNA and dependent 22G RNA number is given in the Methods.
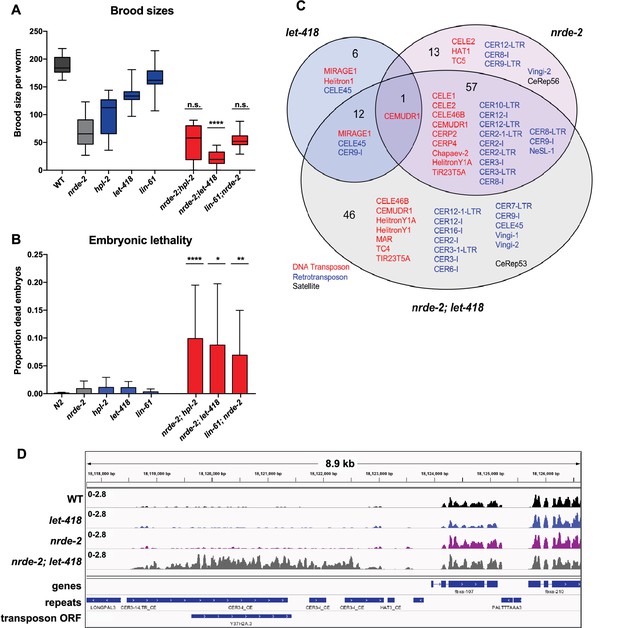
nrde-2 and let-418 show functional redundancy.
(A) nrde-2 and let-418 mutants show genetic interaction in fertility. Brood sizes of nrde-2; hpl-2, nrde-2; let-418, and nrde-2; lin-61 double mutants were compared to those of single mutants. Synchronized single or double mutant strains of the indicated genotype were grown at 15°C until the L3 stage and then transferred to 25°C, and total progeny including dead embryos determined for 12–24 mothers across two independent experiments. A single-sided Mann-Whitney U test was used to determine whether the double mutant had a lower brood size than expected under a multiplicative model of interaction when compared to the individual single mutants. Brood size is significantly lower than expected for nrde-2; let-418 (p=9.21E-11) but not lin-61; nrde-2 (p=0.20) or nrde-2; hpl-2 (p=98). (B) nrde-2; hpl-2, nrde-2;let-418 and lin-61;nrde-2 double mutants show increased proportion of dead embryos within their broods compared to single mutants. Total number of dead embryos was determined as a proportion relative to their total brood size for the experiment in (A). Mann-Whitney U tests were performed to compare the proportion of unhatched eggs in double mutants relative to nrde-2 single mutants, and were all found to be significant at p<0.05. (C) Repeat families with members upregulated in let-418, nrde-2, and nrde-2; let-418 young adult worms. Figure 7—figure supplement 1A compares repeat families upregulated in nrde-2, prg-1, or any of the five heterochromatin mutants (D) Example of repeats upregulated in nrde-2; let-418, but not the single mutants. Tracks are RNA-seq reads per million of two combined replicates. Figure 7—figure supplement 1B shows lack of MIRAGE1 expression in the nrde-2 mutant background.
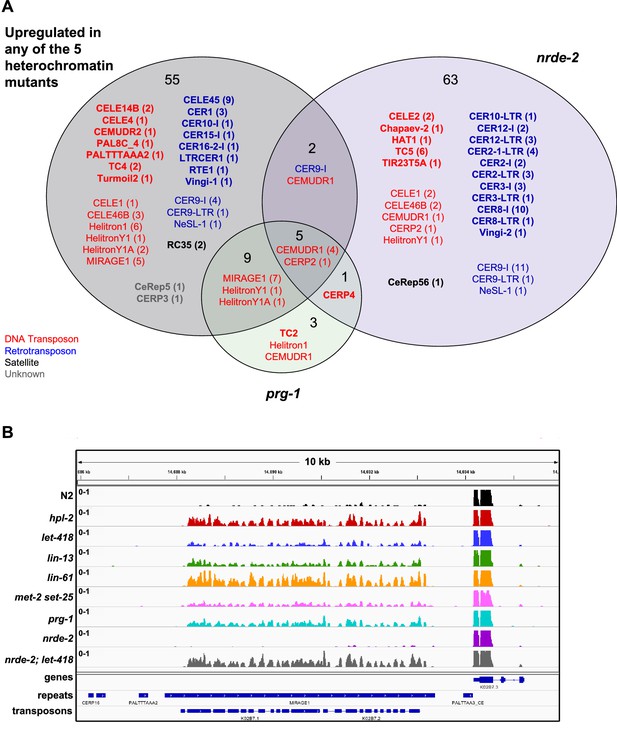
Overlap of nrde-2, prg-1, and heterochromatin targets.
(A) Repeat families with members upregulated in nrde-2, prg-1, and any of the five heterochromatin mutants (let-418, hpl-2, lin-13, lin-61, and met-2 set-25). Families in bold are specific to a particular overlap. (B) RNA-seq tracks showing MIRAGE element upregulated in heterochromatin factor and prg-1 mutants but not in nrde-2 mutants.
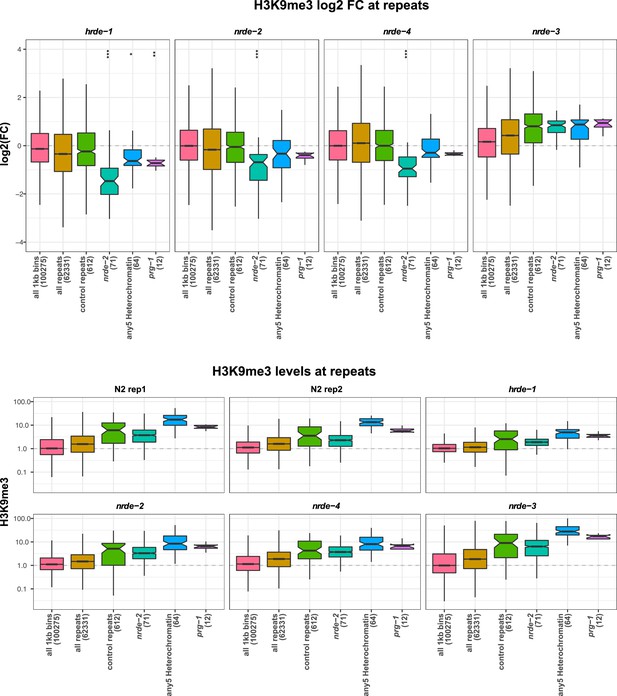
H3K9me3 levels on repeats in nrde mutants.
(Top) H3K9me3 log2FC of average signal at indicated regions in hrde-1, nrde-2, nrde-4, and nrde-3 mutants relative to wild-type. Control repeats have > 1.5 fold average signal in wild-type relative to genome average, and no enrichment for any heterochromatin factor. nrde-2, all repeats upregulated in nrde-2 mutants; any5 Heterochromatin, repeats upregulated in any of the five heterochromatin mutant strains, but not in nrde-2 mutants; prg-1, repeats upregulated in prg-1 mutants but not in nrde-2 mutants. Parentheses show number of elements in each set. A reduction of H3K9me3 at repeat sets of interest was assessed by comparing to all repeats using a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test: one star, p<0.1, two stars, p<0.05; three stars, p<0.001. (Bottom) H3K9me3 levels relative to genome average at indicated regions in each dataset.
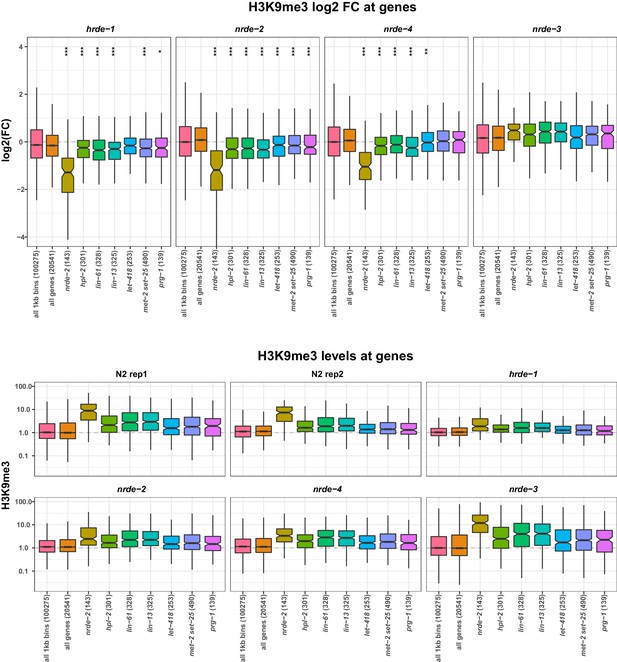
H3K9me3 levels on genes in nrde mutants.
(Top) H3K9me3 log2FC of average signal at indicated regions in hrde-1, nrde-2, nrde-4, and nrde-3 mutants relative to wild-type. nrde-2, genes upregulated in nrde-2 mutants. For each of the other strains, gene sets are those upregulated in the indicated mutant but not upregulated in nrde-2 mutants. Parentheses show number of genes in each set. A reduction of H3K9me3 at gene sets of interest was assessed by comparing to all genes using a single-sided Mann-Whitney U test: one star, p<0.1, two stars, p<0.05; three stars, p<0.001. (Bottom) H3K9me3 levels relative to genome average at indicated regions in each dataset.
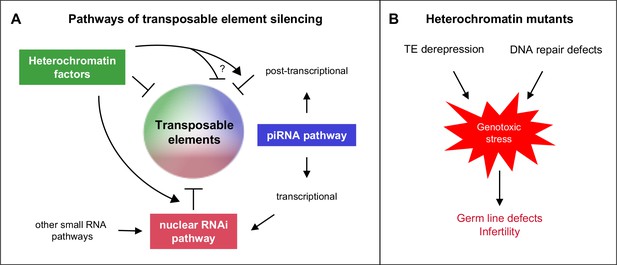
Heterochromatin proteins collaborate with small RNAi pathways to maintain fertility.
(A) Pathways of transposable element silencing in C. elegans. Heterochromatin factors participate in repetitive element silencing together with the piRNA and nuclear RNAi pathways, as well as targeting elements independently of these pathways. (B) Derepression of transposable elements and defects in DNA repair likely generate genotoxic stress that leads to germ line defects and infertility in heterochromatin factor mutants.

Quantification of piRNA sensor expression in wild type and heterochromatin mutants hpl-2, let-418 and lin-61.
Animals were fed on indicated RNAi bacteria from L1 at 20°C and scored as 1 day old adults, similar to Figure 6D. A minimum of 15 worms were scored over 2 independent experiments. None of the RNAi treatments resilenced the sensor.
Additional files
-
Supplementary file 1
LET-418, LIN-13, HPL-2, LIN-61, and MET-2 are required for normal fertility.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.033
-
Supplementary file 2
Strains used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.034
-
Supplementary file 3
Antibodies used in this study.
- https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21666.035





